Abstract
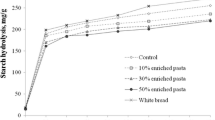
The underutilized millets and legumes (proso millet, little millet, soaked and germinated faba beans) were mixed in different combinations to develop ready to eat porridge. Physiochemical and functional properties such as color, water absorption index (WAI), water solubility index (WSI), pasting properties, microstructure and in vitro starch digestibility of formulated porridge mix were evaluated. The porridge mix formulations exhibited a considerable amount of proteins (17.97–22.17 g/100 g) and carbohydrates (70.24–72.25 g/100 g). WAI and WSI of the different porridge formulations (P1-P6) ranged from 3.07 to 3.34 g/g and 10.37 to 25.81 g/100 g/100 g, respectively. The in vitro starch digestibility of formulation P5 (little millet, proso millet and soaked faba bean) was significantly higher (67.70%) compared to other formulations. This study concluded that nutritional, functional values as well as the digestibility of porridge mixes were improved after incorporation of soaked faba beans. The ready to eat porridge mix based on underutilized legumes and millets can serve as source of macro and micronutrients for all age groups.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WAI:
-
Water absorption index
- WSI:
-
Water solubility index
- WAC:
-
Water absorption capacity
- TPC:
-
Total phenolic content
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- IVSD:
-
In vitro Starch digestibility
References
Anitha S, Govindaraj M, Kane-Potaka J (2020) Balanced amino acid and higher micronutrients in millets complements legumes for improved human dietary nutrition. Cereal Chem 97(1):74–84
Annor GA, Tyl C, Marcone M, Ragaee S, Marti A (2017) Why do millets have slower starch and protein digestibility than other cereals? Trends Food Sci Technol 66:73–83
Apea-Bah FB, Minnaar A, Bester MJ, Duodu KG (2016) Sorghum–cowpea composite porridge as a functional food, Part II: Antioxidant properties as affected by simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem 197:307–315
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (2005) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Analytical Chemists. Association of Official Analytical Chemists
Cheng W, Gao L, Wu D, Gao C, Meng L, Feng X, Tang X (2020) Effect of improved extrusion cooking technology on structure, physiochemical and nutritional characteristics of physically modified buckwheat flour: Its potential use as food ingredients. LWT-Food Sci Technol 133:109872
Collado E, Klug TV, Martínez-Hernández GB, Artés-Hernández F, Martínez-Sánchez A, Aguayo E, Gómez PA (2019) Nutritional and quality changes of minimally processed faba (Vicia faba L.) beans during storage: Effects of domestic microwaving. Postharvest Biol Technol 151:10–18
Devisetti R, Yadahally SN, Bhattacharya S (2014) Nutrients and antinutrients in foxtail and proso millet milled fractions: Evaluation of their flour functionality. LWT-Food Sci Technol 59(2):889–895
Embaby HES (2010) Effect of soaking, dehulling, and cooking methods on certain antinutrients and in vitro protein digestibility of bitter and sweet lupin seeds. Food Sci Biotechnol 19(4):1055–1062
Handa V, Kumar V, Panghal A, Suri S, Kaur J (2017) Effect of soaking and germination on physicochemical and functional attributes of horsegram flour. J Food Sci Technol 54(13):4229–4239
Hoffman JR, Falvo MJ (2004) Protein-what is best? J Sports Sci Med 3:118–130
**g QI, Yingguo LYU, Yuanhui WANG, Jie CHEN, Panfeng HOU (2018) Formula and quality study of multigrain noodles. Grain Oil Sci Technol 1(4):157–162
Kumar KA, Sharma GK, Khan MA, Semwal AD (2016) A study on functional, pasting and micro-structural characteristics of multigrain mixes for biscuits. J Food Meas Charac 10(2):274–282
Kumar SR, Sadiq MB, Anal AK (2020) Comparative study of physicochemical and functional properties of pan and microwave cooked underutilized millets (proso and little). LWT-Food Sci Technol 128:109465
Kumar SR, Sadiq MB, Anal AK (2021) Comparative study of physicochemical and functional properties of soaked, germinated and pressure cooked Faba bean. J Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05010-x
Mandge HM, Sharma S, Dar BN (2014) Instant multigrain porridge: effect of cooking treatment on physicochemical and functional properties. J Food Sci Technol 51(1):97–103
Mariotti F, Gardner CD (2019) Dietary protein and amino acids in vegetarian diets—A review. Nutrients 11(11):2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112661
Medhe S, Jain S, Anal AK (2019) Effects of sprouting and cooking processes on physicochemical and functional properties of moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia) seed and flour. J Food Sci Technol 56(4):2115–2125
Momanyi D, Owino W, Makokha A (2020) Formulation, nutritional and sensory evaluation of baobab based ready-to-eat sorghum and cowpea blend snack bars. Sci Afr 7:e00215
Multari S, Stewart D, Russell WR (2015) Potential of fava bean as future protein supply to partially replace meat intake in the human diet. Compr Rev Sci F 14(5):511–522
Negi A, Boora P, Khetarpaul N (2001) Starch and protein digestibility of newly released moth bean cultivars: effect of soaking, dehulling, germination and pressure cooking. Food Nahrung 45(4):251–254
Niu M, Hou GG, Kindelspire J, Krishnan P, Zhao S (2017) Microstructural, textural, and sensory properties of whole-wheat noodle modified by enzymes and emulsifiers. Food Chem 223:16–24
Park IM, Ibáñez AM, Zhong F, Shoemaker CF (2007) Gelatinization and pasting properties of waxy and non-waxy rice starches. Starch-Stärke 59(8):388–396
Pradeep PM, Dharmaraj U, Rao BS, Senthil A, Vijayalakshmi NS, Malleshi NG, Singh V (2014) Formulation and nutritional evaluation of multigrain ready-to-eat snack mix from minor cereals. J Food Sci Technol 51(12):3812–3820
Rathod RP, Annapure US (2017) Physicochemical properties, protein and starch digestibility of lentil based noodle prepared by using extrusion processing. LWT-Food Sci Technol 80:121–130
Sadiq MB, Hanpithakpong W, Tarning J, Anal AK (2015) Screening of phytochemicals and in vitro evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of leaves, pods and bark extracts of Acacia nilotica (L.) Del. Ind Crops Prod 77:873–882
Saleh HM, Hassan AA, Mansour EH, Fahmy HA, El-Bedawey AEFA (2019) Melatonin, phenolics content and antioxidant activity of germinated selected legumes and their fractions. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 18(3):294–301
Samaei SP, Ghorbani M, Tagliazucchi D, Martini S, Gotti R, Themelis T, Tesini F, Gianotti A, Toschi TG, Babini E (2020) Functional, nutritional, antioxidant, sensory properties and comparative peptidomic profile of faba bean (Vicia faba, L.) seed protein hydrolysates and fortified apple juice. Food Chem 330:127120
Shrestha S, Sadiq MB, Anal AK (2018) Culled banana resistant starch-soy protein isolate conjugate based emulsion enriched with astaxanthin to enhance its stability. Int J Biol Macromol 120:449–459
Srikaeo K, Furst JE, Hosken RW, Ashton JF (2005) Physical properties of cooked wheat grains as affected by cooking temperature and duration. Int J Food Prop 8(3):469–479
Vilakati N, MacIntyre U, Oelofse A, Taylor JR (2015) Influence of micronization (infrared treatment) on the protein and functional quality of a ready-to-eat sorghum-cowpea African porridge for young child-feeding. LWT-Food Sci Technol 63(2):1191–1198
Wani IA, Hamid H, Hamdani AM, Gani A, Ashwar BA (2017) Physico-chemical, rheological and antioxidant properties of sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) as affected by pan and microwave roasting. J Advan Res 8(4):399–405
Xu E, Wu Z, Pan X, Long J, Wang F, Xu X, Jiao A (2016) Effect of enzymatic (thermostable α-amylase) treatment on the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of extruded rice incorporated with soybean flour. Food Chem 197:114–123
Yang Q, Zhang P, Qu Y, Gao X, Liang J, Yang P, Feng B (2018) Comparison of physicochemical properties and cooking edibility of waxy and non-waxy proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). Food Chemi 257:271–278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. SRK performed all the experiments and compiled the data. GS assisted in performing some experiments. Dr. AKA supervised the project and helped in writing manuscript. Dr. MBS helped in experimental design, data analysis and manuscript drafting.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data availability
Data available on request from authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S.R., Sadiq, M.B., Singh, G. et al. Formulation of nutritional and ready to mix gluten-free porridge from proso millet (Panicum miliaceum) little millet (Panicum sumatrense) and legume faba bean (Vicia faba). J Food Sci Technol 59, 2821–2829 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05305-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05305-z