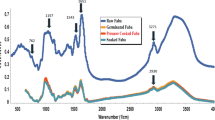
Abstract
Selected moth beans (Vigna aconitifolia) were subjected to different processes such as sprouting and cooking. Their respective flours were prepared and evaluated for their physicochemical and functional characteristics. From our study, it was observed that the ash content of raw moth bean flour was considerably higher in comparison to the sprouted and cooked moth bean flour. On the other hand, the crude lipid and fiber content of sprouted moth bean flour were remarkably higher compared to raw and cooked moth bean flour, respectively. The raw moth bean flour exhibited considerably better emulsifying activity compared to the sprouted moth bean flour. Sprouted bean flour was showing higher emulsion stability than the raw bean flours and the cooked bean flour reported zero emulsion stability. The value of foaming stability was not significantly different among raw and sprouted moth bean, but it was significantly low in cooked moth bean flour. Raw moth bean flour was found to exhibit higher gelation concentration than the sprouted and cooked flours. This study highlights the variations observed in the physicochemical and pasting characteristics of moth bean seeds (raw, sprouted and cooked) and their respective flours.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajibola CF, Malomo SA, Fagbemi TN, Aluko RE (2016) Polypeptide composition and functional properties of African yam bean seed (Sphenostylis stenocarpa) albumin, globulin and protein concentrate. Food Hydrocoll 56:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.12.013
AOAC (2000) Official method of analysis of AOAC international. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg
Benítez V, Cantera S, Aguilera Y, Mollá E, Esteban RM, Díaz MF, Martín-Cabrejas MA (2013) Impact of germination on starch, dietary fiber and physicochemical properties in non-conventional legumes. Food Res Int 50:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.09.044
Boye J, Zare F, Pletch A (2010) Pulse proteins: processing, characterization, functional properties and applications in food and feed. Food Res Int 43:414–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2009.09.003
Deshpande S, Campbell C (1992) Genotype variation in BOAA, condensed tannins, phenolics and enzyme inhibitors of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus). Can J Plant Sci 72:1037–1047. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps92-130
Dhaliwal Y, Aggarwal R (1999) Composition of fat in soybeans as affected by duration of germination and drying temperature. J Food Sci Technol 36:266–267
Dueñas M, Martínez-Villaluenga C, Limón RI, Peñas E, Frias J (2015) Effect of germination and elicitation on phenolic composition and bioactivity of kidney beans. Food Res Int 70:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.018
Elkhalifa AEO, Bernhardt R (2010) Influence of grain germination on functional properties of sorghum flour. Food Chem 121:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.12.041
Flores-Farías R, Martínez-Bustos F, Salinas-Moreno Y, Chang YK, Hernandez JG, Ríos E (2000) Physicochemical and rheological characteristics of commercial nixtamalised Mexican maize flours for tortillas. J Sci Food Agric 80:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0010(20000501)80:6%3c657:aid-jsfa576%3e3.0.co;2-j
Ghavidel RA, Prakash J (2006) Effect of germination and dehulling on functional properties of legume flours. J Sci Food Agric 86:1189–1195. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2460
Ghavidel RA, Prakash J (2007) The impact of germination and dehulling on nutrients, antinutrients, in vitro iron and calcium bioavailability and in vitro starch and protein digestibility of some legume seeds. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:1292–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2006.08.002
Ghumman A, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Impact of germination on flour, protein and starch characteristics of lentil (Lens culinari) and horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum L.) lines. LWT Food Sci Technol 65:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.075
Gupta N, Shrivastava N, Singh PK, Bhagyawant SS (2016) Phytochemical evaluation of moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia L.) seeds and their divergence. Biochem Res Int 2016:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3136043
Hamid S, Muzaffar S, Wani IA, Masoodi FA, Bhat MM (2016) Physical and cooking characteristics of two cowpea cultivars grown in temperate Indian climate. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 15:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2014.08.002
Han JJ, Janz JA, Gerlat M (2010) Development of gluten-free cracker snacks using pulse flours and fractions. Food Res Int 43:627–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2009.07.015
Henshaw FO, McWatters KH, Akingbala JO, Chinnan MS (2003) Thermal properties of cowpea flour: a study by differential scanning calorimetry. Food/Nahrung 47:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/food.200390038
Jain AK, Kumar S, Panwar J (2009) Antinutritional factors and their detoxification in pulses—a review. Agric Rev 30:64–70
Kaur S, Singh N, Sodhi NS, Rana JC (2009) Diversity in properties of seed and flour of kidney bean germplasm. Food Chem 117:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.002
Khatoon N, Prakash J (2006) Nutrient retention in microwave cooked germinated legumes. Food Chem 97:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.03.007
Martín-Cabrejas MA, Díaz MF, Aguilera Y, Benítez V, Mollá E, Esteban RM (2008) Influence of germination on the soluble carbohydrates and dietary fibre fractions in non-conventional legumes. Food Chem 107:1045–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.020
Martín-Cabrejas MA, Aguilera Y, Pedrosa MM, Cuadrado C, Hernández T, Díaz S, Esteban RM (2009) The impact of dehydration process on antinutrients and protein digestibility of some legume flours. Food Chem 114:1063–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.10.070
Megat Rusydi M, Noraliza C, Azrina A, Zulkhairi A (2011) Nutritional changes in germinated legumes and rice varieties. Int Food Res J 18:703–713
Nasrin TAA, Noomhorm A, Anal AK (2015) Physico-chemical characterization of culled plantain pulp starch, peel starch, and flour. Int J Food Prop 18:165–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2013.828747
Neto VQ, Narain N, Silva J, Bora P (2001) Functional properties of raw and heat processed cashew nut (Anacardium occidentale, L.) kernel protein isolates. Food/Nahrung 45:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3803(20010801)45:4%3c258:aid-food258%3e3.0.co;2-3
Ohtsubo K, Suzuki K, Yasui Y, Kasumi T (2005) Bio-functional components in the processed pre-germinated brown rice by a twin-screw extruder. J Food Compos Anal 18:303–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2004.10.003
Reyes-Bastidas M, Reyes-Fernández E, López-Cervantes J, Milán-Carrillo J, Loarca-Piña G, Reyes-Moreno C (2010) Physicochemical, nutritional and antioxidant properties of tempeh flour from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Sci Technol Int 16:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1177/1082013210367559
Romano A, Giosafatto C, Masi P, Mariniello L (2015) Impact of dehulling on the physico-chemical properties and in vitro protein digestion of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Funct 6:1345–1351
Rui X, Boye JI, Ribereau S, Simpson BK, Prasher SO (2011) Comparative study of the composition and thermal properties of protein isolates prepared from nine Phaseolus vulgaris legume varieties. Food Res Int 44:2497–2504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.01.008
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Seena S, Sridhar K (2005) Physicochemical, functional and cooking properties of under explored legumes, Canavalia of the southwest coast of India. Food Res Int 38:803–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2005.02.007
Sharma S, Singh N, Virdi AS, Rana JC (2015) Himalayan kidney bean germplasm: grain-flour characteristics, structural-functional properties and in vitro digestibility of starches. Food Res Int 77:498–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.08.030
Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A, Rana JC (2015) Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll 43:679–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.07.024
Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2005) Nutritional and antinutritional composition, in vitro amino acid availability, starch digestibility and predicted glycemic index of differentially processed mucuna beans (Mucuna pruriens var. utilis): an under-utilised legume. Food Chem 91:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.02.044
Siddiq M, Ravi R, Harte J, Dolan K (2010) Physical and functional characteristics of selected dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flours. LWT Food Sci Technol 43:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2009.07.009
Singh N, Kaur M, Sandhu KS, Sodhi NS (2004) Physicochemical, cooking and textural characteristics of some Indian black gram (Phaseolus mungo L.) varieties. J Sci Food Agric 84:977–982. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.1744
Świeca M, Gawlik-Dziki U, Kowalczyk D, Złotek U (2012) Impact of germination time and type of illumination on the antioxidant compounds and antioxidant capacity of Lens culinaris sprouts. Sci Hort 140:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.04.005
Tharanathan R, Mahadevamma S (2003) Grain legumes-a boon to human nutrition. Trends Food Sci Technol 14:507–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2003.07.002
Wang N, Hatcher DW, Gawalko EJ (2008) Effect of variety and processing on nutrients and certain anti-nutrients in field peas (Pisum sativum). Food Chem 111:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.03.047
Wang N, Hatcher D, Toews R, Gawalko E (2009) Influence of cooking and dehulling on nutritional composition of several varieties of lentils (Lens culinaris). LWT Food Sci Technol 42:842–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2008.10.007
Wani IA, Sogi DS, Gill BS (2013) Physicochemical and functional properties of flours from three Black gram (Phaseolus mungo L.) cultivars. Int J Food Sci Technol 48:771–777. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12025
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledged scholarship donor Social Justice and Special Assistance Department, Government of Maharashtra, India and Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand to conduct this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medhe, S., Jain, S. & Anal, A.K. Effects of sprouting and cooking processes on physicochemical and functional properties of moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia) seed and flour. J Food Sci Technol 56, 2115–2125 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03692-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03692-y