Abstract
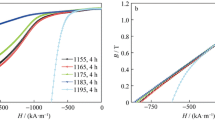
Sm(CobalFe0.245Cu0.07Zr0.02)7.8 (at%) sintered magnets with high remanence (Br ~1.15 T) were prepared using a traditional powder metallurgy method. Tunable magnetic properties, especially intrinsic coercivity (H cj), were obtained through adjusting isothermal procedure parameters. H cj of the magnets increases from 305 to 752 kA · m−1 with isothermal annealing time increasing from 3 to 20 h, while B r of the magnets almost keeps constant. From the bright field transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images, it is found that: (1) there is dispersed precipitated phase with very small size in the magnet annealed for 3 h, while the magnets annealed for 20 h have distinct and intact cellular structure; (2) the number density of Z-phase in magnet annealed for 20 h is bigger than that for 3 h. Besides, the finer microstructures were studied with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo Y, Yu DB, Li HW, Zhuang WD, Li KS, Yan WL. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of SmFe(9-x)Cox alloys. Rare Met. 2014;33(1):54.
Pragnell WM, Evans HE, Williams AJ. Oxidation protection of Sm2Co17-based alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2012;517:92.
Fang YK, Chang HW, Guo ZH, Liu T, Li XM, Li W, Chang WC, Han BS. Magnetic microstructures of phase-separated Sm–Co 2:17-type sintered magnets. J Alloy Compd. 2008;462:376.
Rabenberg L, Mishra RK, Thomas G. Microstructures of precipitation-hardened SmCo permanent magnets. J Appl Phys. 1982;53(3):2389.
Kronmüller H, Goll D. Micromagnetic analysis of pinning-hardened nanostructured, nanocrystalline Sm2Co17 based alloys. Scripta Mater. 2002;47(8):545.
Kronmüller H, Goll D. Analysis of the temperature dependence of the coercive field of Sm2Co17 based magnets. Scripta Mater. 2003;48(7):833.
Goll D, Stadelmaier HH, Kronmüller H. Samarium–cobalt 2:17 magnets: analysis of the coercive field of Sm2(CoFeCuZr)17 high-temperature permanent magnets. Scripta Mater. 2010;63(2):243.
Stadelmaier HH, Kronmüller H, Goll D. Samarium–cobalt 2:17 magnets: identifying Smn+1Co5n-1 phases stabilized by Zr. Scripta Mater. 2010;63:843.
Paul DI. Extended theory of the coercive force due to domain wall pinning. J Appl Phys. 1982;53(3):2362.
Gopalan R, Hono K, Yan A, Gutfleisch O. Direct evidence for Cu concentration variation and its correlation to coercivity in Sm(Co0.74Fe0.1Cu0.12Zr.04)7.4 ribbons. Scripta Mater. 2009;60(9):764.
Livingston JD, Martin DL. Microstructure of aged (Co, Cu, Fe)7Sm magnets. J Appl Phys. 1977;48(3):1350.
Zhaohui Guo, Wei Pan, Wei Li. Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)z sintered magnets with a maximum operating temperature of 500 °C. J Magn Magn Mater. 2006;303:e396.
Goll D, Kronmüller H, Stadelmaier HH. Micromagnetism and the microstructure of high temperature permanent magnets. J Appl Phys. 2004;96(11):6534.
**ong XY, Ohkubo T, Koyama T, Ohashi K, Tawara Y, Hono K. The microstructure of sintered Sm(Co0.72Fe0.20Cu0.055Zr0.025)7.5 permanent magnet studied by atom probe. Acta Mater. 2004;52:737.
Feng HB, Chen HS, Guo ZH, Yu RH, Li W. Twinning structure in Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)z permanent magnet. Intermetallics. 2010;18:1067.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB643701) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51171048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Zhu, MG., Fang, YK. et al. Microstructures and coercivity mechanism of 2:17-type Sm-Co magnets with high remanence. Rare Met. 41, 1353–1356 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0513-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0513-6