Abstract
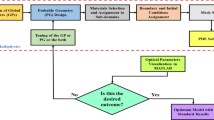
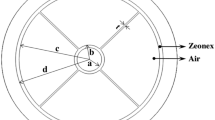
The present study reports a design procedure and numerical investigation of a photonic crystal fiber biosensor. The proposed sensor is consisting of irregular arranged rectangular holes. The core area has been arranged of a single rectangle for sensing the cancer cells and normal cells in the frequency range 1.0–2.5 THz. Zeonex has been utilized as a fiber material. The model has been organized and computationally investigated employing software based on the finite element method. The modeling of the designed sensor authenticates its capability in identifying cancer cells. An absorbing layer: perfectly matched layer has been used for calculating optical characteristics. It has been observed that the designed PCF sensor gives a high relative sensitivity of 81.38% for cancer cells and 65.83% for normal cells, respectively. Reduced confinement loss as 5.828 × 10−25 cm−1 has been achieved. Also, the effective area 2.549 × 10−8 µm2, birefringence 4.709 × 10−4, propagation constant 1.01961 × 10−24 and effective refractive index as 1.475 × 10−18 have been investigated. The present manufacturing technique is appropriate for the designing of proposed PCF sensor.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
S. Suresh, Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Biomater 3, 413–438 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2007.04.002
M.J.B.M. Leon, M.A. Kabir, Design of a liquid sensing photonic crystal fiber with high sensitivity, bireferingence & low confinement loss. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 28, 100335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2020.100335
A. Habib, A.N.Z. Rashed, H.M. El-Hageen, A.M. Alatwi, Extremely sensitive photonic crystal fiber-based cancer cell detector in the terahertz regime. Plasmonics 16, 1297–1306 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01409-6
E.T.H. Fontham, A.M.D. Wolf, T.R. Church et al., Cervical cancer screening for individuals at average risk: 2020 guideline update from the American cancer society. CA Cancer J Clin 70, 321–346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21628
G.E. Dressing, P. Thomas, Identification of membrane progestin receptors in human breast cancer cell lines and biopsies and their potential involvement in breast cancer. Steroids 72, 111–116 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2006.10.006
K. Tajima, Y. Obata, H. Tamaki et al., Expression of cancer/testis (CT) antigens in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 42, 23–33 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5002(03)00244-7
K. Glunde, Z.M. Bhujwalla, Metabolic tumor imaging using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Semin Oncol 38, 26–41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.11.001
L.P. Shivangani, P.K. Singh et al., Design and modeling of reconfigurable surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensor using Al2O3, nickel, and heterostructure BlueP/WSe2 nanofilms. J Opt (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00973-2
A. Umar, P. Lohia, S. Singh et al., Graphene and nickel nanomaterials based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor: a theoretical study. J Nanoelectron Optoelectron 17, 1215–1218 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1166/jno.2022.3320
Bulbul A.A.M., Jibon R.H., Awal M.A., et al., Toxic Chemicals Detection using Photonic Crystal Fiber in THz Regime. 2020 11th Int Conf Comput Commun Netw Technol ICCCNT 2020 2–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCNT49239.2020.9225544
S. Singh, P.K. Singh, A. Umar et al., 2D nanomaterial-based surface plasmon resonance sensors for biosensing applications. Micromachines 11, 1–28 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11080779
J. El Haddad, B. Bousquet, L. Canioni, P. Mounaix, Review in terahertz spectral analysis. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 44, 98–105 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.11.009
Rana S., Islam S., Sultana J., et al. A highly birefringent slotted-core THz fiber. Proc 9th Int Conf Electr Comput Eng ICECE 2016 226–229. (2017) https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECE.2016.7853897
K. Ahmed, F. Ahmed, S. Roy et al., refractive index-based blood components sensing in terahertz spectrum. IEEE Sens J 19, 3368–3375 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2895166
S. Olyaee, A. Naraghi, V. Ahmadi, High sensitivity evanescent-field gas sensor based on modified photonic crystal fiber for gas condensate and air pollution monitoring. Optik (Stuttg) 125, 596–600 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.07.047
M.S. Islam, K.M. Samaun Reza, M.R. Islam, Topas based high birefringent and low loss single mode hybrid-core porous fiber for broadband application. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 56, 399–404 (2018)
T. Zhao, S. Lou, X. Wang et al., Simultaneous measurement of curvature, strain and temperature using a twin-core photonic crystal fiber-based sensor. Sensors (Switzerland) (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072145
A. Umar, S. Singh, S. Yadav et al., Numerical study of surface plasmon resonance biosensor using aluminium oxide and bismuth telluride nanomaterials for skin cancer cell detection. J Nanoelectron Optoelectron 17, 1655–1658 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1166/jno.2022.3358
M. Aliee, M.H. Mozaffari, H. Saghaei, Dispersion-flattened photonic quasicrystal optofluidic fiber for telecom C band operation. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.photonics.2020.100797
M.S. Islam, C.M.B. Cordeiro, J. Sultana et al., A Hi-Bi ultra-sensitive surface plasmon resonance fiber sensor. IEEE Access 7, 79085–79094 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2922663
M.R. Islam, M.F. Kabir, K.M.A. Talha, M.S. Arefin, Highly birefringent honeycomb cladding terahertz fiber for polarization-maintaining applications. Opt Eng 59, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.oe.59.1.016113
T. Yasui, Y. Namihira, M.A. Hossain et al., High numerical aperture square lattice structure photonic crystal fiber for optical coherence tomography. Int Conf Adv Technol Commun (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ATC.2013.6698113
E. Coscelli, R. Dauliat, F. Poli et al., Analysis of the modal content into large-mode-area photonic crystal fibers under heat load. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 22, 323–330 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2015.2479156
M. Moshiur Rahman, F. Akter Mou, M. Imamul Hassan Bhuiyan, M. Rakibul Islam, Design and characterization of a circular sectored core cladding structured photonic crystal fiber with ultra-low EML and flattened dispersion in the THz regime. Opt Fiber Technol 55, 102158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2020.102158
S.M. Salimullah, M. Faisal, Ultra-wideband and coherent supercontinuum generation (near and mid-infrared) in dispersion flattened ZnGeP2 photonic crystal fiber. Alexandria Eng J 70, 289–300 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2023.03.002
M.S. Islam, J. Sultana, M. Faisal et al., A modified hexagonal photonic crystal fiber for terahertz applications. Opt Mater (Amst) 79, 336–339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.03.054
X. Kong, X. Li, X. Jiang, B. Tang, An ultra large negative dispersion regular octagonal PCF with liquid infiltration AOPC 2015. Adv Laser Technol Appl 9671, 96711G (2015). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2200942
M. Mayilamu, J.Q. Yao, Y. Lu, Y.P. Miao, Highly nonlinear and birefringent photonic crystal fiber at 1.55 μm. Guangxue **gmi Gongcheng/Optics Precis Eng 22, 588–596 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3788/OPE.20142203.0588
J. Wu, S. Li, X. **g et al., Elliptical photonic crystal fiber polarization filter combined with surface plasmon resonance. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 30, 1368–1371 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2018.2845459
V. Devika, M.S.M. Rajan, Hexagonal PCF of honeycomb lattice with high birefringence and high nonlinearity. Int J Mod Phys B 34, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979220500940
Hu D.J.J., Xu Z., Ertman S., et al. Two core photonic crystal fiber with hybrid guiding Mechanisms. 2017 Conf Lasers Electro-Optics Pacific Rim, CLEO-PR 2017 2017-Janua:1–3. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CLEOPR.2017.8118922
S. Uddin, D.K. Singh, A solid silica core based non-linear hybrid PCF with low confinement loss. Optik (Stuttg) 127, 10399–10411 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.08.043
C. Markos, I. Kubat, O. Bang, Hybrid polymer photonic crystal fiber with integrated chalcogenide glass nanofilms. Sci Rep (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06057
M.S. Islam, J. Sultana, A. Dinovitser et al., Zeonex-based asymmetrical terahertz photonic crystal fiber for multichannel communication and polarization maintaining applications. Appl Opt 57, 666 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.57.000666
M. Goto, A. Quema, H. Takahashi et al., Teflon photonic crystal fiber as Terahertz Waveguide. Japanese J Appl Physics Part 2 Lett. 43, 2–5 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.43.l317
M. Islam, J. Rahman, M. Islam, Topas based low loss and dispersion flatten decagonal porous core photonic crystal fiber for terahertz communication. Int. J. Microw. Opt. Technol 14, 62 (2019)
M. Klimczak, B. Siwicki, A. Heidt, R. Buczyński, Coherent supercontinuum generation in soft glass photonic crystal fibers. Photonics Res 5, 710 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/prj.5.000710
A.M.R. Pinto, M. Lopez-Amo, Photonic crystal fibers for sensing applications. J Sensors (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/598178
S.H. Kassani, R. Khazaeinezhad, Y. Jung et al., Suspended ring-core photonic crystal fiber gas sensor with high sensitivity and fast response. IEEE Photonics J 7, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2015.2396121
M.S. Islam, J. Sultana, A. Dinovitser et al., Sensing of toxic chemicals using polarized photonic crystal fiber in the terahertz regime. Opt Commun 426, 341–347 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2018.05.030
S. Singh, A.K. Sharma, P. Lohia et al., Ferric oxide and heterostructure BlueP/MoSe2 nanostructure based SPR sensor using magnetic material nickel for sensitivity enhancements. Nanomaterials 12, 107126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2021.107126
A.M.F. Shivangani, Y. Al-Hadeethi et al., Numerical study to enhance the sensitivity of a surface plasmon resonance sensor with BlueP/WS2-Covered Al2 O3-Nickel Nanofilms. Nanomaterials (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132205
Islam M.S., Sultana J., Dinovitser A., et al. A novel Zeonex based photonic sensor for alcohol detection in beverages. 2nd IEEE Int Conf Telecommun Photonics, ICTP 2017 2017-Decem:114–118. (2018) https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTP.2017.8285905
P. Sharan, S.M. Bharadwaj, F.D. Gudagunti, P. Deshmukh, Design and modelling of photonic sensor for cancer cell detection. 2014 Int Conf IMpact E-Technology US. IMPETUS 2014, 20–24 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/IMPETUS.2014.6775872
Sharma P., Sharan P., Deshmukh P. A photonic crystal sensor for analysis and detection of cancer cells. 2015 Int Conf Pervasive Comput Adv Commun Technol Appl Soc ICPC 2015 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1109/PERVASIVE.2015.7087208
N.R. Ramanujam, I.S. Amiri, S.A. Taya et al., Enhanced sensitivity of cancer cell using one dimensional nano composite material coated photonic crystal. Microsyst Technol 25, 189–196 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3947-6
V. Shirmohammadli, N. Manavizadeh, Numerical modeling of cell trajectory inside a dielectrophoresis microdevice designed for breast cancer cell screening. IEEE Sens J 18, 8215–8222 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2865699
M.A. Mollah, M. Yousufali, I.M. Ankan et al., Twin core photonic crystal fiber refractive index sensor for early detection of blood cancer. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 29, 100344 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2020.100344
M.A. Jabin, K. Ahmed, M.J. Rana et al., Surface plasmon resonance based titanium coated biosensor for cancer cell detection. IEEE Photonics J (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2019.2924825
M.A. Jabin, Y. Luo, G.D. Peng et al., Design and fabrication of amoeba faced photonic crystal fiber for biosensing application. Sensors Actuators, A Phys 313, 112204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112204
M.S. Islam, J. Sultana, J. Atai et al., Ultra low-loss hybrid core porous fiber for broadband applications. Appl Opt 56, 1232 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.56.001232
J.D. Shephard, W.N. MacPherson, R.R.J. Maier et al., Single-mode mid-IR guidance in a hollow-core photonic crystal fiber. Opt Express 13, 7139 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1364/opex.13.007139
R.H. Jibon, M.E. Rahaman, M.A. Alahe, Detection of primary chemical analytes in the THz regime with photonic crystal fiber. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 33, 100427 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100427
T. Photonic, C. Fiber, An Ultra-Wideband Single-Polarization-Single-Mode. 21–22 (2020)
M.M.A. Eid, A.N.Z. Rashed, A.A.M. Bulbul, E. Podder, Mono-rectangular core photonic crystal fiber (MRC-PCF) for skin and blood cancer detection. Plasmonics 16, 717–727 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01334-0
S. Yadav, S. Singh, P. Lohia et al., Delineation of profoundly birefringent nonlinear photonic crystal fiber in terahertz frequency regime. J Opt Commun (2022). https://doi.org/10.1515/joc-2022-0143
N.K.B. Suthar, Advances in Photonic crystals and Devices (2019)
V.S. Chaudhary, D. Kumar, B.P. Pandey, S. Kumar, Advances in photonic crystal fiber-based sensor for detection of physical and biochemical parameters- a review. IEEE Sens J 23, 1012–1023 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3222969
S. Singh, A.K. Sharma, P. Lohia et al., Design and modelling of high-performance surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensor using batio3, mxene and nickel hybrid nanostructure. Plasmonics 17, 2049–2062 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01692-x
Acknowledgements
The author is very grateful to Dr. Vijay Shanker Choudhary, Galgotias University and Dr. Sachin Singh, IAAM Sweden for their valuable support.
Funding
No external funding support is received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SY: original manuscript writing, methodology, software analysis, conceptualization while DKD and PL: reviewing, editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
This is a theoretical analysis, so no ethical authorization is required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S., Lohia, P. & Dwivedi, D.K. Eminently sensitive mono-rectangular photonic crystal fiber-based sensor for cancer cell detection in THz regime. J Opt 53, 528–537 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01191-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01191-0