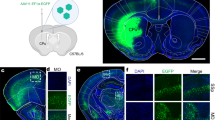
Abstract
Retrograde adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are capable of infecting the axons of projection neurons and serve as a powerful tool for the anatomical and functional characterization of neural networks. However, few retrograde AAV capsids have been shown to offer access to cortical projection neurons across different species and enable the manipulation of neural function in non-human primates (NHPs). Here, we report the development of a novel retrograde AAV capsid, AAV-DJ8R, which efficiently labeled cortical projection neurons after local administration into the striatum of mice and macaques. In addition, intrastriatally injected AAV-DJ8R mediated opsin expression in the mouse motor cortex and induced robust behavioral alterations. Moreover, AAV-DJ8R markedly increased motor cortical neuron firing upon optogenetic light stimulation after viral delivery into the macaque putamen. These data demonstrate the usefulness of AAV-DJ8R as an efficient retrograde tracer for cortical projection neurons in rodents and NHPs and indicate its suitability for use in conducting functional interrogations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Liu Q, Wu Y, Wang H, Jia F, Xu F. Viral tools for neural circuit tracing. Neurosci Bull 2022, 38: 1508–1518.
Kandel E, Schwartz J, Jessell T, Siegelbaum S, Hudspeth A. Principles of Neural Science, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill Professional, New York, 2012, 1760.
Wickersham IR, Lyon DC, Barnard RJO, Mori T, Finke S, Conzelmann KK. Monosynaptic restriction of transsynaptic tracing from single, genetically targeted neurons. Neuron 2007, 53: 639–647.
Lo L, Anderson DJ. A cre-dependent, anterograde transsynaptic viral tracer for map** output pathways of genetically marked neurons. Neuron 2011, 72: 938–950.
Kondoh K, Lu Z, Ye X, Olson DP, Lowell BB, Buck LB. A specific area of olfactory cortex involved in stress hormone responses to predator odours. Nature 2016, 532: 103–106.
Schwarz LA, Miyamichi K, Gao XJ, Beier KT, Weissbourd B, DeLoach KE, et al. Viral-genetic tracing of the input-output organization of a central noradrenaline circuit. Nature 2015, 524: 88–92.
Qiu L, Zhang B, Gao Z. Lighting up neural circuits by viral tracing. Neurosci Bull 2022, 38: 1383–1396.
Haery L, Deverman BE, Matho KS, Cetin A, Woodard K, Cepko C, et al. Adeno-associated virus technologies and methods for targeted neuronal manipulation. Front Neuroanat 2019, 13: 93.
Rabinowitz JE, Samulski RJ. Building a better vector: The manipulation of AAV virions. Virology 2000, 278: 301–308.
Hudry E, Vandenberghe LH. Therapeutic AAV gene transfer to the nervous system: A clinical reality. Neuron 2019, 101: 839–862.
Tervo DG, Hwang BY, Viswanathan S, Gaj T, Lavzin M, Ritola KD, et al. A designer AAV variant permits efficient retrograde access to projection neurons. Neuron 2016, 92: 372–382.
Tordo J, O’Leary C, Antunes ASLM, Palomar N, Aldrin-Kirk P, Basche M, et al. A novel adeno-associated virus capsid with enhanced neurotropism corrects a lysosomal transmembrane enzyme deficiency. Brain 2018, 141: 2014–2031.
Davidsson M, Wang G, Aldrin-Kirk P, Cardoso T, Nolbrant S, Hartnor M, et al. A systematic capsid evolution approach performed in vivo for the design of AAV vectors with tailored properties and tropism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116: 27053–27062.
Jennings CG, Landman R, Zhou Y, Sharma J, Hyman J, Movshon JA, et al. Opportunities and challenges in modeling human brain disorders in transgenic Primates. Nat Neurosci 2016, 19: 1123–1130.
Luo L, Callaway EM, Svoboda K. Genetic dissection of neural circuits: A decade of progress. Neuron 2018, 98: 256–281.
Zeng H, Sanes JR. Neuronal cell-type classification: Challenges, opportunities and the path forward. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017, 18: 530–546.
Weiss AR, Liguore WA, Domire JS, Button D, McBride JL. Intra-striatal AAV2.retro administration leads to extensive retrograde transport in the rhesus macaque brain: Implications for disease modeling and therapeutic development. Sci Rep 2020, 10: 6970.
Cushnie AK, El-Nahal HG, Bohlen MO, May PJ, Basso MA, Grimaldi P, et al. Using rAAV2-retro in rhesus macaques: Promise and caveats for circuit manipulation. J Neurosci Methods 2020, 345: 108859.
Albaugh DL, Smith Y, Galvan A. Comparative analyses of transgene expression patterns after intra-striatal injections of rAAV2-retro in rats and rhesus monkeys: A light and electron microscopic study. Eur J Neurosci 2020, 52: 4824–4839.
Bohlen MO, McCown TJ, Powell SK, El-Nahal HG, Daw T, Basso MA, et al. Adeno-associated virus capsid-promoter interactions in the brain translate from rat to the nonhuman primate. Hum Gene Ther 2020, 31: 1155–1168.
Grimm D, Lee JS, Wang L, Desai T, Akache B, Storm TA, et al. In vitro and in vivo gene therapy vector evolution via multispecies interbreeding and retargeting of adeno-associated viruses. J Virol 2008, 82: 5887–5911.
Zhang Z, Shan L, Wang Y, Li W, Jiang M, Liang F, et al. Primate preoptic neurons drive hypothermia and cold defense. Innovation (Camb) 2023, 4: 100358.
Shan L, Yuan L, Zhang B, Ma J, Xu X, Gu F, et al. Neural integration of audiovisual sensory inputs in macaque amygdala and adjacent regions. Neurosci Bull 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01043-8.
Franklin K, Paxinos G. The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 3rd edition ed: Elsevier Inc., 2008.
Kravitz AV, Freeze BS, Parker PRL, Kay K, Thwin MT, Deisseroth K, et al. Regulation of parkinsonian motor behaviours by optogenetic control of basal Ganglia circuitry. Nature 2010, 466: 622–626.
Dai J, Brooks DI, Sheinberg DL. Optogenetic and electrical microstimulation systematically bias visuospatial choice in Primates. Curr Biol 2014, 24: 63–69.
Magno LAV, Tenza-Ferrer H, Collodetti M, Aguiar MFG, Rodrigues APC, da Silva RS, et al. Optogenetic stimulation of the M2 cortex reverts motor dysfunction in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 2019, 39: 3234–3248.
Gong X, Mendoza-Halliday D, Ting JT, Kaiser T, Sun X, Bastos AM, et al. An ultra-sensitive step-function opsin for minimally invasive optogenetic stimulation in mice and macaques. Neuron 2020, 107(38–51): e8.
Bartlett JS, Wilcher R, Samulski RJ. Infectious entry pathway of adeno-associated virus and adeno-associated virus vectors. J Virol 2000, 74: 2777–2785.
Pillay S, Meyer NL, Puschnik AS, Davulcu O, Diep J, Ishikawa Y, et al. An essential receptor for adeno-associated virus infection. Nature 2016, 530: 108–112.
Harris JA, Mihalas S, Hirokawa KE, Whitesell JD, Choi H, Bernard A, et al. Hierarchical organization of cortical and thalamic connectivity. Nature 2019, 575: 195–202.
Tasic B, Menon V, Nguyen TN, Kim TK, Jarsky T, Yao Z, et al. Adult mouse cortical cell taxonomy revealed by single cell transcriptomics. Nat Neurosci 2016, 19: 335–346.
Kim EJ, Juavinett AL, Kyubwa EM, Jacobs MW, Callaway EM. Three types of cortical layer 5 neurons that differ in brain-wide connectivity and function. Neuron 2015, 88: 1253–1267.
Peng H, **e P, Liu L, Kuang X, Wang Y, Qu L, et al. Morphological diversity of single neurons in molecularly defined cell types. Nature 2021, 598: 174–181.
Wang J, Sun P, Lv X, ** S, Li A, Kuang J, et al. Divergent projection patterns revealed by reconstruction of individual neurons in orbitofrontal cortex. Neurosci Bull 2021, 37: 461–477.
He M, Huang ZJ. Genetic approaches to access cell types in mammalian nervous systems. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2018, 50: 109–118.
Feng G, Mellor RH, Bernstein M, Keller-Peck C, Nguyen QT, Wallace M, et al. Imaging neuronal subsets in transgenic mice expressing multiple spectral variants of GFP. Neuron 2000, 28: 41–51.
Denman DJ, Contreras D. Complex effects on in vivo visual responses by specific projections from mouse cortical layer 6 to dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus. J Neurosci 2015, 35: 9265–9280.
Deng C, Yuan H, Dai J. Behavioral manipulation by optogenetics in the nonhuman primate. Neuroscientist 2018, 24: 526–539.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Lu laboratory for helpful discussions and comments. This work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2019YFA0903803 and 2018YFA0801404), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871090, 32000730, 81961128019, and 81901397), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (JCYJ20190809171003698, JCYJ202103243001018, JCYJ20180507182505475, and JCYJ20180504165804015), Shenzhen Technological Research Center for Primate Translational Medicine (F-2021-Z99-504979), Youth Innovation Promotion Association (CAS 2017120), Chinese Academy of Sciences International Partnership Program (172644KYSB20170004), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M653115.), CAS Key Laboratory of Brain Connectome and Manipulation (2019DP173024), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Brain Connectome and Behavior (2017B030301017), and International Science and Technology Cooperation Base of Guangdong Province (2019A050505008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y.C., J.W., J. Liu, J. Lin, J.D., and Z.L. are co-inventors on a patent that is being filed for this technology.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wang, J., Liu, J. et al. A Novel Retrograde AAV Variant for Functional Manipulation of Cortical Projection Neurons in Mice and Monkeys. Neurosci. Bull. 40, 90–102 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01091-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-023-01091-0