Abstract
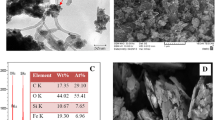
The electrocatalytic oxidation of contraflam was investigated in alkaline solution on nickel and nickel–copper alloy modified glassy carbon electrodes (GC/Ni and GC/NiCu). We prepared these electrodes by galvanostatic deposition and the surface morphologies and compositions of electrodes were determined by energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometric methods were employed to characterize the oxidation process and its kinetics. Voltammetric studies exhibit one pair of well-defined redox peaks, which is ascribed to the redox process of the nickel and followed by the greatly enhanced current response of the anodic peak in the presence of contraflam and a decrease in the corresponding cathodic current peak. This indicates that the immobilized redox mediator on the electrode surface was oxidized contraflam via an electrocatalytic mechanism. The catalytic currents increased linearly with the concentration of contraflam in the range of 0.25–1.5 mmol/L. The anodic peak currents were linearly proportional to the square root of scan rate. This behaviour is the characteristic of a diffusion-controlled process. The determination of contraflam in capsules is applied satisfactorily by modified electrode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
REMINGTON J P, TROY D B, BERINGER P. Remington: The science and practice of pharmacy [M]. New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006.
BRAYFIELD A. Martindale: The complete drug reference [M]. New York: Pharmaceutical Press, 2014.
SHAH D A, RANA J P, BALDANIA S L, CHHALDTIYA U K, BHATT K K. High-performance thin-layer chromatographic method for the estimation of paracetamol, dicyclomine hydrochloride, and mefenamic acid in combined tablet dosage form [J]. JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography-Modern TLC, 2014, 27: 52–57.
AL-ABACHI M Q, HADI H. Simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of mefenamic acid in pharmaceutical preparations [J]. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 69: 769–776.
BEIRAGHI A, POURGHAZI K, AMOLI-DIVA M, RAZMARA A. Magnetic solid phase extraction of mefenamic acid from biological samples based on the formation of mixed hemimicelle aggregates on Fe3O4 nanoparticles prior to its HPLC-UV detection [J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2014, 945: 46–52.
ZISIMOPOULOS E G, TSOGAS G Z, GIOKAS D L, KAPAKOGLOU N I, VLESSIDIS A G. Indirect chemiluminescence-based detection of mefenamic acid in pharmaceutical formulations by flow injection analysis and effect of gold nanocatalysts [J]. Talanta, 2009, 79: 893–899.
PEREZ-RUIZ T, MARTINZ-LOZANO C, SANZ A, BRAVO E. Determination of flufenamic, meclofenamic and mefenamic acids by capillary electrophoresis using β-cyclodextrin [J]. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 1998, 708: 249–256.
MOREIRA A P L, MARTINI M, CARVALHO L M. Capillary electrophoretic methods for the screening and determination of pharmacologic adulterants in herbal-based pharmaceutical formulations [J]. Electrophoresis, 2014, 35: 3212–3230.
SONG J F, GUO W, KANG X F, HU Y H. Investigation and application of polarographic catalytic wave of oxygen reduction caused by mefenamic acid [J]. Sci China B, 1993, 36: 906–911.
BLANCO-LOPEZ M C, LOBO-CASTANON M J, MIRANDAORDIERES A J, TUÑÓN-BLANCO P. Voltammetric response of diclofenac-molecularly imprinted film modified carbon electrodes [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2003, 377: 257–261.
AHMADI M, MADRAKIAN T, AFKHAMI A. Molecularly imprinted polymer coated magnetite nanoparticles as an efficient mefenamic acid resonance light scattering nanosensor [J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2014, 852: 250–256.
MOGHADDAM A B, MOHAMMADI A, MOHAMMADI S. Electroanalysis of mefenamic acid in pharmaceutical formulation and spiked biological fluids on modified carbon nanotube electrode [J]. Pharmaceut Anal Acta, 2012, 3: 6–10.
RIYANTO A, ANSHORI A. Electroanalysis of mefenamic acid using platinum powder composite microelectrode (PPCM) [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2014, 6: 159–169.
DOU Z, CUI L, HE X. Electrochimical determination of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine by poly(xylitol) modified glassy carbon electrode [J]. J Cent South Univ T, 2014, 21(3): 870–876.
MOHAMMADI A, MOGHADDAM A B, ALIKHANI E, EILKHANIZHDEH K, MOZAFFARI S. Electrochemical quantification of fluoxetine in pharmaceutical formulation using carbon nanoparticles [J]. Micro Nano Lett, IET, 2013, 8: 853–857.
MOGHADDAM A B, MOHAMMADI A, MOHAMMADI S, RAYEJI D, DINARVAND R, BAGAI M, WALKER R B. The determination of acetaminophen using a carbon nanotube: Graphite-based electrode [J]. Microchim Acta, 2010, 171: 377–384.
GHORBANI-BIDKORBEH F, SHAHROKHIAN S, MOHAMMADI A, DINARVAND R. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of tramadol and acetaminophen using carbon nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode [J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55: 2752–2759.
SHAHROKHIAN S, GHORBANI-BIDKORBEH F, MOHAMMADI A, DINARVAND R. Electrochemical determinations of 6-mercaptopurine on the surface of a carbon nanotube-paste electrode modified with a cobalt salophen complex [J]. J Solid State Electrochem, 2012, 16: 1643–1650.
NAEEMY A, MOHAMMADI A, BAKHTIARI H, ASHOURI N, WALKER R B. Electro- oxidation of acetaminophen on nickel/poly (O-aminophenol)/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite modified graphite electrode [J]. Micro Nano Lett, IET, 2014, 9: 691–696.
MOHAMMADI A, MOGHADDAM A B, BADRAGHI J. Direct electron transfer of ferritin on electrodeposited nickel oxide cubic nanoparticles [J]. Anal Methods, 2012, 4: 1024–1028.
MOHAMMADI A, MOGHADDAM A B, KAZEMZAD M, DINARVAND R, BADRAGHI J. Synthesis of nickel oxides nanoparticles on glassy carbon as an electron transfer facilitator for horseradish peroxidase: Direct electron transfer and H2O2 determination [J]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2009, 29: 1752–1758.
EHSANI A, MAHJANI M G, JAFARIAN M, NAEEMY A. Influence of ionic surfactant on physio-electrochemical properties and fractal dimension of poly ortho aminophenol film [J]. Prog Org Coat., 2010, 69: 510–516.
EHSANI A, MAHJANI M G, JAFARIAN M, NAEEMY A. Electrosynthesis of polypyrrole composite film and electrocatalytic oxidation of ethanol [J]. Electrochim Acta, 2012, 71: 128–133.
FEIZBAKHSH A, EHSANI A, NAEEMY A. Electrocatalytic oxidation of paracetamol on Ni and NiCu alloy modified glassy carbon electrode [J]. J Chinese Chem Soc, 2012, 59: 1086–1093.
KHULBE K, MANN R, MANOOGIAN A. Behavior of nickel-copper alloy in hydrogenation, orthohydrogen-parahydrogen conversion and H2-D2 exchange reaction [J]. Chem Rev, 1980, 80: 417–428.
BRIGGS G, SNODIN P. Ageing and the diffusion process at the nickel hydroxide electrode [J]. Electrochim Acta, 1982, 27: 565–572.
HAHN F, BEDEN B, CROISSANT M, LAMY C. In situ UV visible reflectance spectroscopic investigation of the nickel electrodealkaline solution interface [J]. Electrochim Acta, 1986, 31: 335–342.
DESILVESTRO J, CORRIGAN D A, WEAVER M J. Characterization of redox states of nickel hydroxide film electrodes by in situ surface Raman spectroscopy [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1988, 135: 885–892.
CHEN S, BROWN L, LEVENDORF M, CAI W JU S Y, EDGEWORTH J, LI X, MAGNUSON C W, VELAMAKANNI A, PINER R D. Oxidation resistance of graphene-coated Cu and Cu/Ni alloy [J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5: 1321–1327.
LUO P, PRABHU S V, BALDWIN R P. Constant potential amperometric detection at a copper-based electrode: Electrode formation and operation [J]. Anal Chem, 1990, 62: 752–755.
CHEN J, BRADHURST D, DOU S. Nickel hydroxide as an active material for the positive electrode in rechargeable alkaline batteries [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1999, 146: 3606–3612.
SINGH D. Characteristics and Effects of γ-NiOOH on cell performance and a method to quantify it in nickel electrodes [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1998, 145: 116–120.
LUO P F, KUWANA T, PAUL D K. Electrochemical and XPS study of the nickel-titanium electrode surface [J]. Anal Chem, 1996, 68: 3330–3337.
BARD A J, FAULKNER L R. Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and applications [M]. Vol. 2. New York: Wiley, 1980.
HELI H, JABBARI A, MAJDI S, MAHJOUB M, MOOSAVIMOVAHEDI A, SHEIBANI S. Electrooxidation and determination of some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on nanoparticles of Ni–curcumin-complex-modified electrode [J]. J Solid State Electrochem, 2009, 13: 1951–1958.
MILLER J C, MILLER J N. Statistics for analytical chemistry [M]. 4th ed. New York: Ellis-Harwood, 1994.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge financial assistance from Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N., Ali, M., Ali, E. et al. Electrocatalytic behaviour of Ni and NiCu alloy modified glassy carbon electrode in electro-oxidation of contraflam. J. Cent. South Univ. 24, 1703–1712 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3577-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3577-7