Abstract
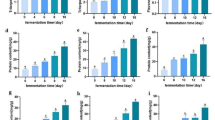
Barley grains from different cultivars were fermented with a fungal strain Aspergillus awamorinakazawa using solid state fermentation technique and enhancement of bioactive properties were studied. The bioactive properties studied were total phenolic content (TPC), antioxidant activity (AOA), ABTS scavenging capacity (ABTS+), total flavonoids content (TFC), and metal chelating activity (MCA). For control samples TPC, AOA, TFC, and MCA was found the highest for cv.BH-885 whereas ABTS+ was the highest for cv.BH-932. It was found that fermentation resulted in significant increase in bioactive properties till 5th day and thereafter they decreased. On 5th day of fermentation, the TPC, TFC and ABTS were observed the highest for cv.BH-885 whereas AOA and MCA were the highest for cv.PL-172 and cv.BH-902. Paired t-test values were calculated to study the effect of duration in terms of the number of days of fermentation (0 day compared with 2–6 days). Comparison revealed significant differences in t-values for various bioactive properties studied. Significant correlations were observed among different bioactive properties. TPC and AOA of flours were highly positively correlated (r = 0.988, p < 0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Frias, M.L. Miranda, R. Doblado, C. R, Vidal-Valverde, Effect of germination and fermentation on the antioxidant vitamin content and antioxidant capacity of Lupinus albus L. var. Multolupa. Food Chem. 92, 211–220 (2005)
S. Martins, S.I. Mussatto, G. Martinez-Avila, J. Montanez-Saenz, C.N. Aguilar, J.A. Teixeira, Bioactive phenolic compounds: production and extraction by solid substrate fermentation. A review. Biotech. Adv. 29, 365–373 (2011)
M.J.R. Nout, J.L. Kiers, Tempe fermentation, innovation and functionality, Update into the third millennium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98, 789–805 (2005)
K.R. Babu, T. Satyanarayana, α-Amylase production by thermophilic Bacillus coagulans in solid state fermentation. Process Biochem. 30, 305–309 (1995)
C.N. Aguilar, A. Aguilera-Carbo, A. Robledo, J. Ventura, R. Belmares, D. Martinez, Production of antioxidants nutraceuticals by solid-state cultures of pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel and creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) leaves. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 46, 218–222 (2008)
P.S. nee’ Nigam, in Biotechnology for Agro-industrial Residues Utilization, ed. by P.S. nee’ Nigam, A. Pandey. Production of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites, (Springer, Dordrecht, 2009), p. 129–145
K.S. Sandhu, S. Punia, M. Kaur, Effect of duration of solid state fermentation by Aspergillus awamorinakazawa on antioxidant properties of wheat cultivars. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 71, 323–328 (2016)
T.B. Dey, R.C. Kuhad, Enhanced production and extraction of phenolic compounds from wheat by solid-state fermentation with Rhizopus oryzae RCK2012. Biotechnol. Rep. 4, 120–127 (2014)
A. Gibreel, J.R. Sandercock, J. Lan, L.A. Goonewardene, R.T. Zijlstra, J.M. Curtis, D.C. Bressler, Fermentation of barley by using Saccharomyces cerevisiae: examination of barley as a feedstock for bioethanol production and value-added products. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 1363–1372 (2009)
R.K. Salar, S.S. Purewal, M.S. Bhatti, Optimization of extraction conditions and enhancement of phenolic content and antioxidant activity of pearl millet fermented with Aspergillus awamori MTCC-548. Resour Eff. Technol. 2, 148–157 (2016)
T. Bhanja, S. Rout, R. Banerjee, B.C. Bhattacharyya, Studies on the performance of a new bioreactor for improving antioxidant potential of rice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 41, 1459–1465 (2008)
C. Lin, Y. Wei, C. Chou, Enhanced antioxidative activity of soybean koji prepared with various filamentous fungi. Food Microbiol. 23, 628–633 (2006)
S. Cai, O. Wang, W. Wu, S. Zhu, F. Zhou, B. Ji, F. Gao, D. Zhang, J. Liu, Q. Cheng, Comparative study of the effects of solid-state fermentation with three filamentous fungi on the total phenolics content (TPC), flavonoids, and antioxidant activities of subfractions from oats (Avena sativa L.). J Agric. Food Chem. 60, 507–513 (2012)
P. McCue, K. Shetty, Role of carbohydrate-cleaving enzymes in phenolic antioxidant mobilization from whole soybean fermented with Rhizopus oligosporus. Food Biotechnol. 17, 27–37 (2003)
D. Hunaefi, D.N. Akumo, I. Smetansk, Effect of fermentation on antioxidant properties of red cabbages. Food Biotechnol. 27, 66–85 (2013)
R.L. Heiniö, K. Katina, A. Wilhelmson, O. Myllymäki, T. Rajamäki, K. Latva-Kala, Relationship between sensory perception and flavor active volatile compounds of germinated, sourdough fermented and native rye following the extrusion process. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 36, 533–545 (2003)
K. Katina, R. A, Laitila, Juvonen, K.H. Liukkonen, S. Kariluoto, V. V. Piironen, Bran fermentation as a means to enhance technological properties and bioactivity of rye. Food Microbiol 24, 175–186 (2007)
J.A. Delcour, X. Rouau, C.M. Courtin, K. Poutanen, R. Ranieri, Technologies for enhanced exploitation of the health-promoting potential of cereals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 25, 78–86 (2012)
T. Madhujith, M. Izydorczyk, F. Shahidi, Antioxidant activity of pearled barley fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 3283–3289 (2006)
T.M. Đorđevic, S.S. Šiler-Marinković, S.I. Dimitrijević-Branković, Effect of fermentation on antioxidant properties of some cereals and pseudo cereals. Food Chem. 119, 957–963 (2010)
L. Gao, S. Wang, B.D. Oomah, G. Mazza, in Wheat Quality Elu-cidation, ed. by P. Ng, C.W. Wrigley. Wheat Quality: Antioxidant Activity of Wheat Millstreams, (AACC International, St Paul, 2002), p. 219–233
J. Zhishen, T. Mengcheng, W. Jianming, The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging efects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 64, 555–559 (1999)
W. Brand-Williams, M.E. Cuvelier, C. Berset, Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 28, 25–30 (1995)
T.C.P. Danis, V.M.C. Madeira, M.L.M. Almeida, Action of phenolic derivates (acetaminophane, salycilate, and 5-aminosalycilate) as inhibitors of membrane lipid peroxidation and as peroxyl radical scavengers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 315, 161–169 (1994)
R. Re, N. Pellegrini, A. Proteggente, A. Pannala, M. Yang, C. Rice-Evans, Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26, 1231–1237 (1999)
B.A. Snyder, R.J. Nicholson, Synthesis of phytoalexins in sorghum as a site-specific response to fungal ingress. Science 248, 1637–1639 (1990)
P. Sharma, H.S. Gujral, Antioxidant and polyphenol oxidase activity of germinated barley and its milling fractions. Food Chem. 120, 673–678 (2010)
T. Bhanja, R. A, Kumari, Banerjee, Enrichment of phenolics and free radical scavenging property of wheat koji prepared with two filamentous fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 2861–2866 (2009)
R. Robbins, in Citrus Nutrition and Quality, ed. by S. Nagy, J. Attaway. Medical and Nutritional Aspects of Citrus Bioflavonoids, (American Chemical Society, Washington DC, 1980)
I.H. Lee, Y.H. Hung, C.C. Chou, Solid-state fermentation with fungi to enhance the antioxidative activity, total phenolic and anthocyanin contents of black bean. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 121, 150–156 (2008)
J. Loponen, M. Mikola, K. Katina, T. Sontag-Strohm, H. Salovaara, Degradation of HMW glutenins during wheat sourdough fermentations. Cereal Chem. 81, 87–93 (2004)
B. Bartolomé, C. Gomez-Cordovés, Barley spent grain: release of hydroxycinnamic acids (ferulic and p-coumaric acids) by commercial enzyme preparations. J. Sci. Food Agric. 79, 435–439 (1999)
T.K. Bhat, B. Singh, O.P. Sharma, Microbial degradation of tannins: a current perspective. Biodegradation 9, 343–357 (1998)
C.Y. Wang, S.J. Wu, Y.T. Shyu, Antioxidant properties of certain cereals as affected by food-grade bacteria fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 117, 449–456 (2014)
J.P.E. Spencer, M.M.A.E. Mohsen, C. Rice-Evans, Cellular uptake and metabolism of flavonoids and their metabolites: Implications for their bioactivity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 423, 148–161 (2004)
C.H. Liang, J.L. Syu, J.L. Mau, Antioxidant properties of solid-state fermented adlay and rice by Phellinus linteus. Food Chem. 116, 841–845 (2009)
Y. Bhatia, S. Mishra, V.S. Bisaria, Microbial β-glucosidases: cloning, properties, and applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol 22, 375–407 (2002)
T. Yamaguchi, H. Takamura, T. Matoba, J. Terao, HPLC method for evaluation of the free radical-scavenging activity of foods by using 1,1-diphenyl- 2-picrylhydrazyl. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 62, 1201–1204 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandhu, K.S., Punia, S. Enhancement of bioactive compounds in barley cultivars by solid substrate fermentation. Food Measure 11, 1355–1361 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9513-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9513-6