Abstract
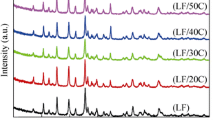
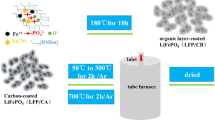
Pristine LiFePO4 (LFP) and carbon-coated LiFePO4 (LFP/C) are synthesized by sol-gel process using citric acid as a carbon precursor. LFP/C is prepared with three different stoichiometric ratios of metal ions and citric acid, namely 1:0.5, 1:1, and 1:2. Prepared LFP and LFP/C powder samples are characterized by X-ray diffractometer, field emission scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, and Raman spectrophotometer. Electrochemical performances of pristine and carbon-coated LFP are investigated by charge-discharge and cyclic voltammetry technique. The results show that LFP/C (1:1) with an optimum thickness of 4.2 nm and higher graphitic carbon coating has the highest discharge capacity of 148.2 mA h g−1 at 0.1 C rate and 113.1 mA h g−1 at a high rate of 5 C among all four samples prepared. The sample LFP/C (1:1) shows 96% capacity retention after 300 cycles at 1 C rate. The decrease in discharge capacity (141.4and 105.9 mA h g−1 at 0.1 and 5 C, respectively) is observed for the sample LFP/C (1:2). Whereas, pristine LFP shows the lowest discharge capacity of 111.1 mA h g−1 at 0.1 C and capacity was decreased very fast and work only up to 147 cycles. Moreover, cyclic voltammetry has also revealed the lowest polarization of 0.19 V for LFP/C (1:1) and the highest 0.4 V for pristine LFP.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang K, Sun J, Yu X, Li H, Huang X (2009) Electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 thin films with different morphology and crystallinity. Electrochim Acta 54(26):6565–6569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.06.030
Julien CM, Mauger A, Zaghib K, Groult H (2014) Comparative issues of cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. inorganics 2(1):132–154. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics2010132
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 144(4):1188–1193. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1837571
Ellis BL, Lee KT, Nazar LF (2010) Positive electrode materials for Li-ion and Li-batteries. Chem Mater 22(3):691–714. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm902696j
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414(6861):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104644
Prosini PP, Lisi M, Zane D, Pasquali M (2002) Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4. Solid State Ionics 148(1-2):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00134-0
Amin R, Balaya P, Maier J (2007) Anisotropy of electronic and ionic transport in LiFePO4 single crystals. Electrochemi Solid-State Lett 10(1):A13–A16. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2388240
Delmas C, Maccario M, Croguennec L, Cras FL, Weill F (2008) Lithium deintercalation in LiFePO4 nanoparticles via a domino-cascade model. Nature Mater 7(8):665–671. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2230
Hsu F, Tsay SY, Hwang BJ (2004) Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized LiFePO4 cathode materials prepared by a citric acid-based sol–gel route. J Mater Chem 14(17):2690–2695. https://doi.org/10.1039/B406774F
Huang HY, Goodenough JB (2008) High-rate LiFePO4 lithium rechargeable battery promoted by electrochemically active polymers. Chem Mater 20(23):7237–7241. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm8012304
Dominko R, Bele M, Gaberscek M, Remskar M, Hanzel D, Pejovnik S, Jamnik J (2005) Impact of the carbon coating thickness on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C composites. J Electrochem Soc 152(3):A607–A610. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1860492
Chunga SY, Chiang YM (2003) Microscale measurements of the electrical conductivity of doped LiFePO4. Electrochemi. and Solid-State Lett. 6 A278-A281
Herle PS, Ellis B, Coombs N, Nazar LF (2004) Nano-network electronic conduction in iron and nickel olivine phosphates. Nature Mater 3(3):147–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1063
Wang P, Zhang G, Li Z, Sheng W, Zhang Y, Gu J, Zheng X, Cao FF (2016) Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4@N-doped carbon nanocomposites using polybenzoxazine as nitrogen and carbon sources. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(40):26908–26915. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10594
Wang P, Zhang G, Cheng J, You Y, Li YK, Ding C, Gu JJ, Zheng XS, Zhang CF, Cao FF (2017) Facile synthesis of carbon-coated spinel Li4Ti5O12/rutile-TiO2 composites as an improved anode material in full lithium-ion batteries with LiFePO4@N-doped carbon cathode. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(7):6138–6143. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b15982
Wang J, Xueliang S (2015) Olivine LiFePO4: the remaining challenges for future energy storage. Energy Environ Sci 8(4):1110–1138. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EE04016C
Parrish G, (1999) Carburizing: microstructures and properties, ASM International, USA, 1999
Zhang D, Yu X, Wang Y, Cai R, Shao Z, Liao XZ, Ma ZF (2009) Ball milling-assisted synthesis and electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C for lithium-ion battery adopting citric acid as carbon precursor. J Electrochem Soc 156(10):A802–A808. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3183880
Fey GTK, Lu TL, Wu FY, Li WH (2008) Carboxylic acid-assisted solid-state synthesis of LiFePO4/C composites and their electrochemical properties as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochemi 12:825–833
Wong HC, Carey JR, Chen JS (2010) Physical and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C composite cathode prepared from aromatic diketone-containing precursors. Int J Electrochem Sci 5:1090–1102
Park KS, Schougaard SB, Goodenough JB (2007) Conducting-polymer/iron-redox-couple composite cathodes for lithium secondary batteries. Adv Mater 19(6):848–851. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200600369
Toprakci O, Toprakci HAK, Ji L, Xu G, Lin Z, Zhang X (2012) Carbon nanotube-loaded electrospun LiFePO4/carbon composite nanofibers as stable and binder-free cathodes for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(3):1273–1280. https://doi.org/10.1021/am201527r
Dhindsa KS, Mandal BP, Bazzi K, Lin MW, Nazri M, Nazri GA, Naik VM, Garg VK, Oliveira AC, Vaishnava P, Naik R, Zhou ZX (2013) Enhanced electrochemical performance of graphene modified LiFePO4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 253:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2013.08.030
Zaghib K, Shim J, Guerfi A, Charest P, Striebel KA (2005) Effect of carbon source as additives in LiFePO4 as positive electrode for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8(4):A207–A210. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1865652
Zhang SS, Allen JL, Xua K, Jow TR (2005) Optimization of reaction condition for solid-statesynthesis of LiFePO4-C composite cathodes. J Power Sources 147(1–2):234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.01.004
Wilcox JD, Doeff MM, Marcinek M, Kostecki R (2007) Factors influencing the quality of carbon coatings on LiFePO4. J Electrochemi Soc 154(5):A389–A395. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2667591
Doeff MM, Wilcox JD, Yu R (2008) Impact of carbon structure and morphology on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C composites. J Solid State Electrochem 12(7–8):995–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-007-0419-9
Belharouak I, Johnson C, Amine K (2005) Synthesis and electrochemical analysis of vapor-deposited carbon-coated LiFePO4. Electrochemi Communi 7(10):983–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2005.06.019
Hwang BJ, Santhanamand R, Liu DG (2001) Characterization of nanoparticles of LiMn2O4 synthesized by citric acid sol-gel method. J Power Sources 97:441–446
Dou J, Kang X, Wumaier T, Hua N, Han Y, Xu G (2012) Oxalic acid-assisted preparation of LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 16(5):1925–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1585-3
Chung SY, Bloking JT, Chiang YM (2002) Electronically conductive phospho-olivines as lithium storage electrodes. Nat Mater 1(2):123–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat732
Wang LN, Zhan XC, Zhang ZG, Zhang KL (2008) A soft chemistry synthesis routine for LiFePO4-C using a novel carbon source. J Alloys Compds 456(1–2):461–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.02.103
Wang D, Cao L, Huang J, Wu J (2013) Effects of different chelating agents on the composition, morphology and electrochemical properties of LiV3O8 crystallites synthesized via sol–gel method. Ceram Int 39(4):3759–3764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.214
Mi CH, Zhao XB, Cao GS, JP T (2005) In situ synthesis and properties of carbon-coated LiFePO4 as Li-ion battery cathodes. J Electrochem Soc 152(3):A483–A487. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1852438
Prosini PP, Zane D, Pasquali M (2001) Improved electrochemical performance of a LiFePO4-based composite cathode. Electrochim Acta 46(23):3517–3523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(01)00631-4
Huang H, Yin SC, Nazar LF (2001) Approaching theoretical capacity of LiFePO4 at room temperature at high rates. Electrochemi Solid-State Lett 4(10):A170–A172. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1396695
Chang YC, Peng CT, Hung IH (2014) Effects of particle size and carbon coating on electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C prepared by hydrothermal method. J Mater Sci 49(20):6907–6916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8395-9
Cho YD, Fey GTK, Kao HM (2009) The effect of carbon coating thickness on the capacity of LiFePO4/C composite cathodes. J Power Sources 189(1):256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.09.053
Doeff MM, Hu Y, McLarnon F, Kostecki R (2003) Effect of surface carbon structure on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4. Electrochemi Solid State Lett 6(10):A207–A209. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1601372
Schwan J, Ulrich S, Bathori V, Erhardt H, Silva SRP (1996) Raman spectroscopy on amorphous carbon films. J Applied Physics 80: 440–447, 1, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.362745
Julien CM, Zaghib K, Mauger A, Massot M, Ait-Salah A, Selmane M, Gendron F (2006) Characterization of the carbon coating onto LiFePO4 particles used in lithium batteries. J Appl Phys 100: 063511–063517, 6, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2337556
Michel A, Goodenough JB, Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Masquelier C (2003) Cathode materials for secondary (rechargeable) lithium batteries. US Pat 6514640
Okada S, Sawa S, Egashira M, Yamaki J, Tabuchi M, Kageyama H, Konishi T, Yoshino A (2001) Cathode properties of phoshpho-olivine LiMPO4 for lithium secondary battery. J Power Sources 97–98:430–432
Gao F, Tang Z (2008) Kinetic behavior of LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 53(15):5071–5075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.10.069
Liu H, Li C, Zhang HP, Fu LJ, Wu YP, Wu HQJ (2006) Kinetic study on LiFePO4/C nano composites synthesized by solid state technique. J Power Sources 159(1):717–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.10.098
Shin HC, Cho WI, Jang H (2006) Electrochemical properties of the carbon-coated LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion secondary batteries. J Power Sources 159(2):1383–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.12.043
YB X, YJ L, Yan L, Yang ZY, Yang RD (2006) Synthesis and effect of forming Fe2P phase on the physics and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C materials. J Power Sources 160:570–576
Liu HW, Tang DG (2008) The low cost synthesis of nanoparticles LiFePO4/C composite for lithium rechargeable batteries. Solid State Ionics 179(33-34):1897–1901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2008.05.005
Shin HC, Chob WI, Jang H (2006) Electrochemical properties of carbon-coated LiFePO4 cathode using graphite, carbon black, and acetylene black. Electrochimi Acta 52(4):1472–1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2006.01.078
Fey GTK, Chena YG, Kaob HM (2009) Electrochemical properties of LiFePO4 prepared via ball-milling. J Power Sources 189(1):169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.10.016
Lu CZ, Fey GTK, Kao HM (2009) Study of LiFePO4 cathode materials coated with high surface area carbon. J Power Sources 189:155–162
Zhao B, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Tao H, Zhong M, Jiao Z (2009) Morphology and electrical properties of carbon coated LiFePO4 cathode materials. J Power Sources 189(1):462–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.12.069
Xu Z, Xu L, Lai Q, Ji X (2007) Microemulsion synthesis of LiFePO4/C and its electrochemical properties as cathode materials for lithium-ion cells. Mater Chemistry Physics 105:80–85
Wang L, Liang GC, XQ O, Zhi XK, Zhang JP, Cui JY (2009) Effect of synthesis temperature on the properties of LiFePO4/C composites prepared by carbothermal reduction. J Power Sources 189(1):423–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.07.032
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India (Grant No. 03/1318/14/EMR-II) for its financial support. The authors would also like to acknowledge Dr. Soumya Shankar Ghosh (Postdoctoral Fellow in our department) for his technical support and suitable discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, H., Sil, A. Effect of carbon coating on electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathode material for Li-ion battery. Ionics 24, 2543–2553 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2423-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2423-0