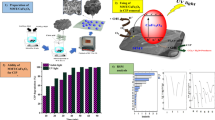
Abstract
The present study was designed to synthesize and characterize calcium oxide nanoparticles (using mangrove oyster shell as a precursor) and apply the synthesized nanoparticles as a photocatalyst to degrade procaine penicillin in an aqueous solution. The photocatalyst exhibited an average band gap of 4.42 eV, showed a maximum wavelength of absorbance in the UV region (i.e., 280 nm), and is a microporous nanoparticle with a particle diameter of 50 nm. The photocatalyzed degradation of the drug was conducted under natural sunlight, and the influence of parameters such as the period of contact, catalyst load, pH, initial drug concentration, and ionic strength was investigated concerning the degradation profile. The results obtained from response surface analysis indicated that an optimum degradation efficiency of about 93% can be obtained at a concentration, pH, and catalyst dosage of 0.125 M, 2, and 0.20 g respectively, at 0.902 desirabilities. The Langmuir–Hinshelwood, modified Freundlich, parabolic diffusion, pseudo-first-/second-order, and zero-, first-, and second-order kinetic parameters were tested to ascertain the best model that best described the experimental data. Consequently, the Langmuir–Hinshelwood, modified Freundlich, and pseudo-second-order models were accepted based on the minimum error and higher R2 values. Based on the Langmuir–Hinshelwood rate constants for adsorption and photodegradation as well as the evaluated valence bond potential, the degradation of the drug first proceeded through the mechanism of adsorption and followed by the oxidation of the drug by superoxide (generated from the interaction of electrons that generated by through the absorption of UV radiation). The quantum chemical calculation gave evidence that pointed towards the establishment of strong agreement with experimental data and also showed that the carboxyl functional group in the drug is the target site for adsorption and subsequent degradation.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alİcanoglu P, Sponza DT (2017) Removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotic with nano graphene oxide magnetite composite: comparison of adsorption and photooxidation processes. Desalin Water Treat 63:293–307
Ahmad I, Ahmad S, Anwar Z, Ali Sheraz MA and Sikorski M (2016). Photostability and photostabilization of drugs and drug products. Int J Photoenergy.https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8135608
Ajenifuja E, Ajao JA, Ajayi EOB (2017) Equilibrium adsorption isotherm studies of Cu (II) and Co (II) in high concentration aqueous solutions on Ag-TiO2-modified kaolinite ceramic adsorbents. Appl Water Sci 7:2279–2286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0403-6
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Alothman ZA, Badiah AY (2018) Kinetics, thermodynamics, and modeling of amido black dye photodegradation in water using Co/TiO2 nanoparticles. Photochem Photobiol 94:935–941 7
Ali I, Al Othman ZA, Al-Mohaimeed AM, Alwarthan A (2019) Modeling of fenuron pesticide adsorption on CNTs for mechanistic insight and removal in water. Environ Res. 170:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.066
Al-Khateeb LA, Hakami W, Abdel Salam M (2017) Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from water using high surface area nanographene: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 24(1):733–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.06.068
Alothman ZA, Bahkali AH, Khiyami MA, Alfadul SM, Wabaidur SM, Alam M, Alfarhan BZ (2020) Low cost biosorbents from fungi for heavy metals removal from wastewater. Sep Sci Technol 55(10):1766–1775. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1608242
Ameh PO, Odiongenyi AO, Eddy NO (2012) Joint effect of Anogessiusleocarpus gum (AL gum) exudate and halide ions on the corrosion of mild steel in 0.1 M HCl. Portugaliae Electrochim Acta 30(4):235–24
Anantharaman A, Ramalakshmi S, George M (2016) Green synthesis of calcium oxide nanoparticles and its applications. Int J Eng Res Appl 6(10):27–31
Anku WW, Kiarii EM, Sharma R, Joshi GM, Shukla SK, Govender PP (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals using graphene based materials. In: Naushad M (ed) A new generation material graphene: applications in water technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75484-0_7
Arbpour N, Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A (2016) Photodegradation of cotrimaxazole by clinoptilolite-supported nickel oxide. Process Saf Environ Prot 102(2):431–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.04.025
Ayoub H, Kassir M, Raad M, Bazzi H, Hijazi A (2017) Effect of drug structure on the photodegradation kinetic using TiO2 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Chem Eng 5:31–45. https://doi.org/10.4236/msce.2017.56004
Azeez SO, Saheed IO, Adekola FA, Salu SS (2022) Preparation of TiO2 activated kaolinite composite for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine buedrug. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop 36(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.4314/bcse.v36i1.2
Azhar A, Yamauchi Y, Allah AE, Alothman ZA, Badjah AY, Naushad M, Habila M, Wabaidur S, Wang J, Zakaria MB (2019) Nanoporous iron oxide/carbon composites through in-situ deposition of Prussian blue nanoparticles on graphene oxide nanosheets and subsequent thermal treatment for supercapacitor applications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 9(5):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050776
Begum S, Narwade VN, Halge DI, Jejurikar SM, Dadge JW, Muduli S, Mahabole MP, Bogle KA (2020) Remarkable photocatalytic degradation of Remazol Brilliant Blue R drug using bio-photocatalyst ‘nano-hydroxyapatite. Mater Res Express 7(4):025013. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6f3b
Bhangare D, Rajput N, Jadav T, Sagu AK, Tekade RK and Sengupta P (2022). Systematic strategies for degradation kinetic study of pharmaceuticals: an issue of utmost importance concerning current stability analysis practices. J Anal Sci Technol 13(7):. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-022-00317-6.
Bhavya C, Mathadevan KM, Madhusudhana N (2016) Synthesis of calcium oxide nanoparticles and its mortality study on fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 10(12):55–60
Bokuniaeva, A. O. and Vorokh, A. S. (2019). The estimation of particle size using the Debye equation and the Scherrer formula for polyphasic TiO2 powder. J Physics: Conf Series 1410. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1410/1/012057.
Bownik A, Ślaska B, Bochra J, Gumieniak K, Gałek K (2019) Procaine penicillin alters swimming behaviour and physiological parameters of Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(18):18662–18673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05255-2
Butt AR, Ejaz S, Baron JC, Ikram M, Ali S (2015) CaO nanoparticles as a potential drug delivery agent for biomedical applications. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 10(3):799–809
Chavoshan S, Khodadadi M, Nasseh N (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of penicillin G from simulated wastewater using the UV ZnO process: isotherm and kinetic study. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18(1):107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00442-7
Eddy NO (2010) Theoretical study on some amino acids and their potential activity as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in HCl. Mol Simul 35(5):354–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927020903483270
Eddy NO, Essien NB (2017) Computational chemistry study of the toxicity of some m-tolyl acetate derivatives insecticides and molecular design of structurally related products. In Silico Pharmacol 5(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-017-0036-y
Eddy NO, Ita BI (2011) Theoretical and experimental studies on the inhibition potentials of aromatic oxaldehydes for the corrosion of mild steel in 0.1 M HCl. J Mol Model 17:633–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0749
Eddy NO, Odoemelam SA, Ibiam E (2010a) Ethanol extract of Occimiumgratissimum as a green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in H2SO4. Green Chem Lett Rev 3(3):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518251003636428
Eddy NO, Ebenso EE, Ibok UJ (2010b) Adsorption, synergistic inhibitive effect and quantum chemical studies on ampicillin and halides for the corrosion of mild Steel. J Appl Electrochem 40:445–456
Eddy NO, Garg R (2021) CaO nanoparticles, synthesis and application in water purification. Chapter 11. In: Garg R, Eddy NO (eds) Handbook of research on green synthesis and applications of nanomaterials. Global Publisher. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-8936-6.
Eddy NO, Garg R, Garg R, Aikoye A and Ita BI (2022). Waste to resource recovery: mesoporous adsorbent from orange peel for the removal of trypan blue drug from aqueous solution. Biomass Convers Biorefinery.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02571-5
Eddy NO (2020). Theoretical chemistry study on the toxicity of some polychlorobiphenyl (PCB) compounds using molecular descriptors. Sci Afr 10:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00587
Ezeibe AU, Achilike JB, Nieonu EC, Atuegbu OM (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using magnetic iron oxide. Int J Sci Eng Res 10(6):1445–1448
Gandhi N, Shruthi Y, Sirisha G, Anusha CR (2021) Facile and eco-friendly method for synthesis of calcium oxide CaO nanoparticles and its potential application in agriculture. Haya Saudi J Life Sci 6(5):89–103. https://doi.org/10.36348/sjls.2021.v06i05.003
Gedda G, Pandev S, Lin Y and Wu H (2015). Antimicrobial effect of calcium oxide nanoplates fabricated from shrimp shells. Green Chem.https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc00615e
González-González RB, Sharma P, Singh SP, Américo-Pinheiro JHP, Parra-Saldívar R, Bilal M and Iqbal HMN (2022). Persistence, environmental hazards, and mitigation of pharmaceutically active residual contaminants from water matrices Sci Total Environ 821:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153329.
Gowthami R, Keerthana G (2020) Synthesis, characterisation and antibacterial activities of calcium oxide nanoparticles by precipitation method. Nanoscale Rep 3(2):27–31 https://www.nanoscalereports.com/index.php/nr/article/view/51
Habte L, Shiferaw N, Mulatu D, Thenepalli T, Chilakala R, Ahn JW (2019) Synthesis of nano-calcium oxide from waste eggshell by sol gel method Lulit. Sustainability 11:3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113196
Hamestera MRR, Balzera PS, Beckerb D (2012) Characterization of calcium carbonate obtained from oyster and mussel shells and incorporation in polypropylene. Mater Res 15(2):204–208. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392012005000014
Ismail AM, Nasr R (2021) Structural characterization of PVDF/PVA polymer blend film doped with different concentration of NiO NPs for photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye under visible light. Appl Polymer Sci 139(13):51847. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.51847
Jalu RG, Chamada TA and Kasirajan R (2021). Calcium oxide nanoparticles synthesis from hen eggshells for removal of lead (Pb(II)) from aqueous solution. Environ Challenges 4:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100193.
Jimenez-Relinque E, Lee SF, Plaza L, Castellote M (2022) Synergetic adsorption–photocatalysis process for water treatment using TiO2 supported on waste stainless steel slag. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:39712–39722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18728-8
Khan MA, Alqadami AA, Wabaidur SM, Siddiqui MR, Jeon B, Alshareef SA, Alothman ZA and Hamedelniel AE (2020). Oil industry waste based non-magnetic and magnetic hydrochar to sequester potentially toxic post-transition metal ions from water. J Hazard Mater 400:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123247
Kurnia KA, Rahayu AP, Islami AF, Kusumawati Y, Wenten IG, Rahmah AU, Saepurahman Wellia DV and Saefumillah A (2022). Insight into the adsorption of dyes onto chitin in aqueous solution: an experimental and computational study. Arab J Chem 15(11):. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104293
Kuzminski K, Morawski A, Janus M (2018) Application of modified concrete to remove surfactants from water. E35 Web Conf 59(11):00016. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20185900016
Ledezma-Espinoza A, Challis JK, Roa-Gutierrez F, Sánchez-Kopper A, Castellón E and Wong CS (2021). Photolysis of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug sulindac: elucidation of kinetic behaviour and photodegradation pathways in water. Environ Sci: Processes Impacts. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00167A.
Li Y, Qiao X, Zhang YN, Zhou C, **e H, Chen J (2016) Effects of halide ions on photodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics: formation of halogenated intermediates. Water Res 102:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.054
Li F, Kong Q, Chen P, Liu H, Lv W, Yao K (2017) Effect of halide ions on the photodegradation of ibuprofen in aqueous environments. Chemosphere 166:412–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.108
Mahdi AS, Kamel BAF, Ahmed AS, Dawood KM (2021) Thermodynamic studies for photo degradation of glibinclamide drug. Res J Pharm Technol 14(9):4987–90. https://doi.org/10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00868
Mahmood NQ, Marossy K, Baumli P (2021) Effects of nanocrystalline calcium oxide particles on mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of EPDM rubber. Colloid Polym Sci 299:1669–1682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04888-5
Makula P, Pacia M, Macyk W (2018) How to correctly determine the band gap energy of modified semiconductor photocatalysts based on UV–Vis spectra. J Phys Chem Lett 9(23):6814–6817. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b02892
Mashkour MS, Juda AM, Al-Sultani HA (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of paracetmol and procaine. Int J ChemTech Res 9(11):412–425
Mestre AS, Carvalho AP (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals carbamazepine, diclofenac, and sulfamethoxazole by semiconductor and carbon materials: a review. Molecules 24(20):3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203702
Mohamed A, Salama A, Nasser WS and Uheida A (2018). Photodegradation of ibuprofen, cetirizine, and naproxen by PAN-MWCNT/TiO2–NH2 nanofiber membrane under UV light irradiation. Environ Sci Eur 30 (47):. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-018-0177-6
Nourmoradi H, Daneshfar A, Mazloomi S, Bagheri J, Barati S (2019) Removal of Penicillin G from aqueous solutions by a cationic surfactant modified montmorillonite. Methods X 6:1967–1973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.08.019
Olusegun SJ, Larrea G, Osial M, Jackowska K, Krysinski P (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Tetracycline Case Catal 11:1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11101243
Osuntokun J, Onwudiwe DC, Ebenso EE (2018) Aqueous extract of broccoli mediated synthesis of CaO nanoparticles and its application in the photocatalytic degradation of bromocrescol green. IET Nanobiotechnol 12(7):888–894. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0277
Pavanello A, Fabbri D, Calza P, Battiston D, Miranda MA and Marin L (2021). Photocatalytic degradation of drugs in water mediated by acetylated riboflavin and visible light: a mechanistic study. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biology 221:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112250
Polianciuc SI, Gurzău AE, Kiss B, Stefan MG, Loghin F (2020) Antibiotics in the environment: causes and consequences. Med Pharm Rep 93(3):231–240. https://doi.org/10.15386/mpr-1742
Rastinfard A, Nazarpak MH, Moztarzadeh F (2018) Controlled chemical synthesis of CaO2 particles coated with polyethylene glycol: characterization of crystallite size and oxygen release kinetics. RSC Adv 8:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA08758F
Rizwan M, Durrani AZ, Ahmad T, Ahmad SS and Chaudhry M (2021). Comparative therapeutic efficacy of procaine penicillin, Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract and Cocos nucifera oil against subclinical mastitis. Livestock Sci 251:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2021.104655.
Rytwo G and Zelkind AL (2022). Evaluation of kinetic pseudo-order in the photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin. Catalysts 12(24):. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010024
Sanakousar MF, Vidyasagar CC, Jiménez-Pérez VM, Jayannac BK, Mouneshd AH and Prakash SK (2021). Efficient photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet drug and electrochemical performance of modified MWCNTs/Cd-ZnO nanoparticles with quantum chemical calculations. J Hazard Mater Adv 2:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2021.100004.
Shaban YA (2019) Solar light-induced photodegradation of chrysene in seawater in the presence of carbon-modified n-TiO2 nanoparticles. Arab J Chem 12(5):652–663
Shetty R, Chavan VB, Kulkarni PS, Kulkarni BD, Kamble SP (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals pollutants using N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst: identification of CFX degradation intermediates. Indian Chem Eng 59(3):177–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00194506.2016.1150794
Sosa-Hernández JE, Rodas-Zuluaga LI, López-Pacheco IY, Melchor-Martínez EM, Aghalari Z, Limón DS, Iqbal HMN and Parra-Saldívar R (2021). Sources of antibiotics pollutants in the aquatic environment under SARS-CoV-2 pandemic situation. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 4:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100127.
Sun B, Yang X, Zhao D, Zhang L (2018) First-principles study of adsorption mechanism of NH3 on different ZnO surfaces on organics photocatalytic degradation purpose. Comput Mater Sci 241:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2017.09.013
Sutapa IW, Wahab AW, Taba P and Nafie NL (2018) Synthesis and structural profile analysis of the mgo nanoparticles produced through the sol-gel method followed by annealing process. Orient J Chem 34(2):.https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/340252
Talebi S, Chaibakhsh N, Shoeili ZM (2017) Application of nanoscale ZnS/TiO2 composite for optimized photocatalytic decolorization of a textile drug. J Appl Res Technol 15(4):378–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jart.2017.03.007
Trawiński J, Skibiński R (2017) Studies on photodegradation process of psychotropic drugs: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(2):1152–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7727-5
Uddin MJ, Alam MM, Islam MA, Snigda SR, Das S, Rahman MM, Uddin MN, Morris CA, Gonzalez RD, Diebold U, Dickens TJ, Okoli OI et al (2013) Tailoring the photocatalytic reaction rate of a nanostructured TiO2 matrix using additional gas phase oxygen. Int Nano Lett 3:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-16
Wabaidur SM, Khan MA, Siddiqui MR, Otero M, Jeon B, Alothman ZA and Hakami AAH (2020). Oxygenated functionalities enriched MWCNTs decorated with silica coated spinel ferrite – a nanocomposite for potentially rapid and efficient de-colorization of aquatic environment. J Mol Liq 317:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113916
Wang X, Ryu D, Houtkooper RH, Auwerx J (2015) Antibiotic use and abuse: a threat to mitochondria and chloroplasts with impact on research, health, and environment. BioEssays 37:1045–1053
Wu Y, Liu W, Wang Y, Hu X, He Z, Chen X, Zhao Y (2018) Enhanced removal of antibiotic in wastewater using liquid nitrogen-treated carbon material: material properties and removal mechanisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(12):2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122652
Yang J, Shojaei S, Shojaei S (2022) Removal of drug and dye from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide adsorption studies and chemometrics methods. npj Clean Water 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00148-3
Zandi A, Akbari Seneh R and Chiyaneh R (2022). The impact of clinoptilolite natural zeolite on the photocatalytic properties and performance of BiOI semiconductor in the photodegradation of drug wastewater. J Pet Res. https://doi.org/10.22078/pr.2022.4669.3099
Zhou Y, Zhang X, Zhao Z, Zhang Q, Wang F, Lin Y (2014) Effect of pH on the visible-light induced photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance of hierarchical Bi2WO6 micropores. Superlattices Microstruct 72:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.04.018
Zhou L, Guo X, Lai C and Wang W (2018). Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate. Open Chem 16(1):.https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2018-0108
Zia J, Riaz U (2020) Microwave-assisted degradation of paracetamol drug using polythiophene-sensitized Ag-Ag2O heterogenous photocatalysts derived from plant extract. ACS Omega 5(27):16386–16394. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00405
Funding
The research work that generated this publication was sponsored by the Tertiary Education Trust Fund of Nigeria (TETFUND) through the National Research grant (2020) with Prof. Nnabuk Okon Eddy as the principal investigator (grant number: TRTF/ES/DR&D-CE/NRF2020/SETI/98/VOL.1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception, design, literature review, data collection, and writing the draft. All authors read, edited, and approved the final manuscript.
NnabukOkon Eddy: supervision, conceptualization, resources, data curation, analysis, and writing original draft.
Anduang O. Odiongenyi: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing, review, and editing.
Rajni Garg: conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, writing, review, and editing.
Richard Alexis Ukpe: conceptualization, methodology, validation, resources, writing, review, and editing.
Rishav Garg: conceptualization, visualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing, review, and editing.
Ahmed El Nemr: conceptualization, visualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing, review, and editing.
Comfort Michael Ngwu: conceptualization, visualization, formal analysis, writing, review, and editing.
Imeh Jospeh Okop: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, formal analysis, writing, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All authors approve the ethics and consent to participate in this research.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented to publish this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eddy, N.O., Odiongenyi, A.O., Garg, R. et al. Quantum and experimental investigation of the application of Crassostrea gasar (mangrove oyster) shell–based CaO nanoparticles as adsorbent and photocatalyst for the removal of procaine penicillin from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 64036–64057 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26868-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26868-8