Abstract
Background
Protease S (PrtS) from Photorhabdus laumondii belongs to the group of protealysin-like proteases (PLPs), which are understudied factors thought to play a role in the interaction of bacteria with other organisms. Since P. laumondii is an insect pathogen and a nematode symbiont, the analysis of the biological functions of PLPs using the PrtS model provides novel data on diverse types of interactions between bacteria and hosts.
Methods and results
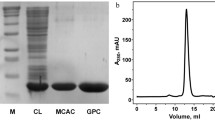
Recombinant PrtS was produced in Escherichia coli. Efficient inhibition of PrtS activity by photorin, a recently discovered emfourin-like protein inhibitor from P. laumondii, was demonstrated. The Galleria mellonella was utilized to examine the insect toxicity of PrtS and the impact of PrtS on hemolymph proteins in vitro. The insect toxicity of PrtS is reduced compared to protease homologues from non-pathogenic bacteria and is likely not essential for the infection process. However, using proteomic analysis, potential PrtS targets have been identified in the hemolymph.
Conclusions
The spectrum of identified proteins indicates that the function of PrtS is to modulate the insect immune response. Further studies of PLPs’ biological role in the PrtS and P. laumondii model must clarify the details of PrtS interaction with the insect immune system during bacterial infection.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Cabral CM, Cherqui A, Pereira A, Simoes N (2004) Purification and characterization of two distinct metalloproteases secreted by the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus sp. strain Az29. Applied and environmental microbiology. 70(7):3831–8. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.7.3831-3838.2004
Demidyuk IV, Gasanov EV, Safina DR, Kostrov SV (2008) Structural organization of precursors of thermolysin-like proteinases. Protein J 27(6):343–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-008-9143-2
Demidyuk IV, Gromova TY, Kostrov SV (2013) Protealysin. In: Rawlings ND, aGS (eds) Handbook of proteolytic enzymes. Academic, Oxford, pp 507–602
Kyostio SR, Cramer CL, Lacy GH (1991) Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora extracellular protease: characterization and nucleotide sequence of the gene. J Bacteriol 173(20):6537–6546. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.20.6537-6546.1991
Feng T, Nyffenegger C, Hojrup P, Vidal-Melgosa S, Yan KP, Fangel JU et al (2014) Characterization of an extensin-modifying metalloprotease: N-terminal processing and substrate cleavage pattern of Pectobacterium carotovorum Prt1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(24):10077–10089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5877-2
Eshwar AK, Wolfrum N, Stephan R, Fanning S, Lehner A (2018) Interaction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and Zpx in Cronobacter turicensis LMG 23827(T) mediated infections in the zebrafish model. Cell Microbiol 20(11):e12888. https://doi.org/10.1111/cmi.12888
Bozhokina E, Kever L, Khaitlina S (2020) The Serratia grimesii outer membrane vesicles-associated grimelysin triggers bacterial invasion of eukaryotic cells. Cell Biol Int 44(11):2275–2283. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11435
Khaitlina S, Bozhokina E, Tsaplina O, Efremova T (2020) Bacterial actin-specific endoproteases Grimelysin and Protealysin as virulence factors contributing to the invasive activities of Serratia. Int J Mol Sci 21(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114025
Tsaplina OA, Efremova TN, Kever LV, Komissarchik YY, Demidyuk IV, Kostrov SV et al (2009) Probing for actinase activity of protealysin. Biochemistry 74(6):648–654. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0006297909060091
Tsaplina O, Efremova T, Demidyuk I, Khaitlina S (2012) Filamentous actin is a substrate for protealysin, a metalloprotease of invasive Serratia proteamaculans. FEBS J 279(2):264–274. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08420.x
Tsaplina O, Demidyuk I, Artamonova T, Khodorkovsky M, Khaitlina S (2020) Cleavage of the outer membrane protein OmpX by protealysin regulates Serratia proteamaculans invasion. FEBS Lett 594(19):3095–3107. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13897
Bozhokina ES, Tsaplina OA, Efremova TN, Kever LV, Demidyuk IV, Kostrov SV et al (2011) Bacterial invasion of eukaryotic cells can be mediated by actin-hydrolysing metalloproteases grimelysin and protealysin. Cell Biol Int 35(2):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1042/CBI20100314
Held KG, LaRock CN, D’Argenio DA, Berg CA, Collins CM (2007) A metalloprotease secreted by the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens induces melanization. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(23):7622–7628. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01000-07
Warshan D, Espinoza JL, Stuart RK, Richter RA, Kim SY, Shapiro N et al (2017) Feathermoss and epiphytic Nostoc cooperate differently: expanding the spectrum of plant-cyanobacteria symbiosis. ISME J 11(12):2821–2833. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.134
Chukhontseva KN, Berdyshev IM, Safina DR, Karaseva MA, Bozin TN, Salnikov VV et al (2021) The protealysin operon encodes emfourin, a prototype of a novel family of protein metalloprotease inhibitors. Int J Biol Macromol 169:583–96.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.170
Tsaplina O, Khaitlina S, Chukhontseva K, Karaseva M, Demidyuk I, Bakhlanova I et al (2022) Protealysin targets the bacterial housekee** proteins FtsZ and RecA. Int J Mol Sci 23(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810787
Clarke DJ (2020) Photorhabdus: a tale of contrasting interactions. Microbiology 166(4):335–348. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000907
Lanois A, Pages S, Bourot S, Canoy AS, Givaudan A, Gaudriault S (2011) Transcriptional analysis of a Photorhabdus sp. variant reveals transcriptional control of phenotypic variation and multifactorial pathogenicity in insects. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(3):1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01696-10
Marokhazi J, Lengyel K, Pekar S, Felfoldi G, Patthy A, Graf L et al (2004) Comparison of proteolytic activities produced by entomopathogenic Photorhabdus bacteria: strain- and phase-dependent heterogeneity in composition and activity of four enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(12):7311–7320. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.12.7311-7320.2004
Berdyshev IM, Svetlova AO, Chukhontseva KN, Karaseva MA, Varizhuk AM, Filatov VV et al (2023) Production and characterization of Photorin, a novel proteinaceous protease inhibitor from the entomopathogenic Bacteria Photorhabdus Laumondii. Biochemistry 88(9):1356–1367. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297923090158
Demidyuk IV, Kalashnikov AE, Gromova TY, Gasanov EV, Safina DR, Zabolotskaya MV et al (2006) Cloning, sequencing, expression, and characterization of protealysin, a novel neutral proteinase from Serratia proteamaculans representing a new group of thermolysin-like proteases with short N-terminal region of precursor. Protein Exp Purif 47(2):551–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2005.12.005
Gasparov VS, Degtiar VG (1994) Protein determination by binding with the dye Coomassie brilliant blue G-250. Biochemistry 59(6):763–777
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Sambrook J, Russell DW, Sambrook J (2006) The condensed protocols from molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Karaseva MA, Chukhontseva KN, Lemeskina IS, Pridatchenko ML, Kostrov SV, Demidyuk IV (2019) An internally quenched fluorescent peptide substrate for Protealysin. Sci Rep 9(1):14352. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50764-2
Berdyshev IM, Karaseva MA, Demidyuk AIV (2022) Assay for protealysin-like protease inhibitor activity. Bio-protocol 12(19). https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.4528
Copeland RA (2023) Enzymes: a practical introduction to structure, mechanism, and Data Analysis. Wiley
Agarwal R, Zakharov S, Hasan SS, Ryan CM, Whitelegge JP, Cramer WA (2014) Structure-function of cyanobacterial outer-membrane protein, Slr1270: homolog of Escherichia coli drug export/colicin import protein, TolC. FEBS Lett 588(21):3793–3801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.08.028
Shevchenko A, Tomas H, Havlis J, Olsen JV, Mann M (2006) In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat Protoc 1(6):2856–2860. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.468
Grunina TM, Demidenko AV, Lyaschuk AM, Poponova MS, Galushkina ZM, Soboleva LA et al (2017) Recombinant human erythropoietin with additional processable protein domains: purification of protein synthesized in Escherichia coli Heterologous expression system. Biochemistry 82(11):1285–1294. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917110062
Martens L, Vandekerckhove J, Gevaert K (2005) DBToolkit: processing protein databases for peptide-centric proteomics. Bioinformatics 21(17):3584–3585. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti588
Pobeguts OV, Ladygina VG, Evsyutina DV, Eremeev AV, Zubov AI, Matyushkina DS et al (2020) Propionate induces virulent properties of Crohn’s disease-associated Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol 11:1460. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01460
Adekoya OA, Sylte I (2009) The thermolysin family (M4) of enzymes: therapeutic and biotechnological potential. Chem Biol Drug Des 73(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00757.x
Roche RS, Voordouw G (1978) The structural and functional roles of metal ions in thermolysin. CRC Crit Reviews Biochem 5(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409237809177138
Ji JL, Han SJ, Zhang RJ, Yu JB, Li YB, Yu XP et al (2022) Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 plays an important role in the development and reproduction of Nilaparvata lugens. Insects 13(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13030303
Jiang H, Vilcinskas A, Kanost MR (2010) Immunity in lepidopteran insects. Adv Exp Med Biol 708:181–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8059-5_10
Wen D, Luo H, Li T, Wu C, Zhang J, Wang X et al (2017) Cloning and characterization of an insect apolipoprotein (apolipophorin-II/I) involved in the host immune response of Antheraea Pernyi. Dev Comp Immunol 77:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2017.08.010
Kamareddine L, Nakhleh J, Osta MA (2016) Functional interaction between apolipophorins and complement regulate the mosquito immune response to systemic infections. J Innate Immun 8(3):314–326. https://doi.org/10.1159/000443883
Mayans O, Benian GM, Simkovic F, Rigden DJ (2013) Mechanistic and functional diversity in the mechanosensory kinases of the titin-like family. Biochem Soc Trans 41(4):1066–1071. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20130085
Riddell CE, Lobaton Garces JD, Adams S, Barribeau SM, Twell D, Mallon EB (2014) Differential gene expression and alternative splicing in insect immune specificity. BMC Genomics 15(1):1031. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1031
Galetto L, Abba S, Rossi M, Vallino M, Pesando M, Arricau-Bouvery N et al (2018) Two Phytoplasmas Elicit different responses in the insect vector Euscelidius Variegatus Kirschbaum. Infect Immun 86(5). https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00042-18
Zhang YL, Xue RY, Cao GL, Zhu YX, Pan ZH, Gong CL (2013) Shotgun proteomic analysis of wing discs from the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori) during metamorphosis. Amino Acids 45(5):1231–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1588-8
Zurovcova M, Benes V, Zurovec M, Kucerova L (2019) Expansion of imaginal disc growth factor gene family in Diptera reflects the evolution of Novel functions. Insects 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100365
Kucerova L, Broz V, Arefin B, Maaroufi HO, Hurychova J, Strnad H et al (2016) The Drosophila chitinase-like protein idgf3 is involved in protection against nematodes and in wound healing. J Innate Immun 8(2):199–210. https://doi.org/10.1159/000442351
Brown MD, Sacks DB (2009) Protein scaffolds in MAP kinase signalling. Cell Signal 21(4):462–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.11.013
Di Lelio I, Varricchio P, Di Prisco G, Marinelli A, Lasco V, Caccia S et al (2014) Functional analysis of an immune gene of Spodoptera littoralis by RNAi. J Insect Physiol 64:90–. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.**sphys.2014.03.008
Pascale M, Laurino S, Vogel H, Grimaldi A, Monne M, Riviello L et al (2014) The Lepidopteran endoribonuclease-U domain protein P102 displays dramatically reduced enzymatic activity and forms functional amyloids. Dev Comp Immunol 47(1):129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2014.07.009
Falabella P, Riviello L, Pascale M, Lelio ID, Tettamanti G, Grimaldi A et al (2012) Functional amyloids in insect immune response. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 42(3):203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.11.011
Lim SG, Suk K, Lee WH (2020) LETMD1 regulates phagocytosis and inflammatory responses to Lipopolysaccharide via reactive oxygen species generation and NF-kappaB activation in macrophages. J Immunol 204(5):1299–1309. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1900551
Kong L, Lu A, Guan J, Yang B, Li M, Hillyer JF et al (2015) Thermolysin damages animal life through degradation of plasma proteins enhanced by rapid cleavage of serpins and activation of proteases. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 88(1):64–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.21178
Andrejko M, Mizerska-Dudka M (2012) Effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase B on level and activity of immune proteins/peptides of Galleria mellonella hemolymph. J Insect Sci 12:88. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.012.8801
Mollah MMI, Kim Y (2020) Virulent secondary metabolites of entomopathogenic bacteria genera, Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus, inhibit phospholipase A(2) to suppress host insect immunity. BMC microbiology. 20(1):359. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-02042-9
Antonello AM, Sartori T, Silva MB, Prophiro JS, **e-Filho P, Heermann R et al (2019) Anti-trypanosoma activity of bioactive metabolites from Photorhabdus luminescens and Xenorhabdus nematophila. Exp Parasitol 204:107724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2019.107724
Darsouei R, Karimi J, Dunphy GB (2019) Functional characterization of outer membrane proteins (OMPs) in Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens through Insect Immune Defense reactions. Insects 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100352
Sanda NB, Hou Y (2023) The symbiotic Bacteria-Xenorhabdus nematophila All and Photorhabdus luminescens H06 strongly affected the phenoloxidase activation of Nipa Palm Hispid, Octodonta nipae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) Larvae. Pathogens 12(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12040506
Eleftherianos I, ffrench-Constant RH, Clarke DJ, Dowling AJ, Reynolds SE (2010) Dissecting the immune response to the entomopathogen Photorhabdus. Trends Microbiol 18(12):552–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2010.09.006
Kim Y, Ji D, Cho S, Park Y (2005) Two groups of entomopathogenic bacteria, Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus, share an inhibitory action against phospholipase A2 to induce host immunodepression. J Invertebr Pathol 89(3):258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2005.05.001
Acknowledgements
Mass spectrometric analysis of products of Abz-RSVIK(Dnp) hydrolysis by PrtSt were performed using the equipment of the Advanced Mass Spectrometry Core Facility at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech, Moscow, Russia).
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 24-24-00122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Ilya V. Demidyuk; Data curation: Maria A. Karaseva; Formal analysis: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria A. Karaseva, Igor M. Berdyshev, Ksenia N. Chukhontseva, Ilya V. Demidyuk; Funding acquisition: Sergey V. Kostrov, Ilya V. Demidyuk; Investigation: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria (A) Karaseva, Igor M. Berdyshev, Ksenia N. Chukhontseva, Olga V. Pobeguts, Maria А. Galyamina, Igor P. Smirnov, Nikita (B) Polyakov, Maria G. Zavialova; Methodology: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria (A) Karaseva, Igor M. Berdyshev, Ksenia N. Chukhontseva, Olga V. Pobeguts, Maria А. Galyamina, Nikita (B) Polyakov, Maria G. Zavialova, Ilya V. Demidyuk; Project administration: Ilya V. Demidyuk; Supervision: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Sergey V. Kostrov, Ilya V. Demidyuk; Validation: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria A. Karaseva; Visualization: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria A. Karaseva, Igor M. Berdyshev, Olga V. Pobeguts, Maria А. Galyamina, Igor P. Smirnov, Maria G. Zavialova, Ilya V. Demidyuk; Writing – original draft: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria A. Karaseva, Igor M. Berdyshev, Olga V. Pobeguts, Maria А. Galyamina, Igor P. Smirnov, Maria G. Zavialova, Ilya V. Demidyuk; Writing – review & editing: Anastasia O. Svetlova, Maria A. Karaseva, Igor M. Berdyshev, Ksenia N. Chukhontseva, Olga V. Pobeguts, Maria А. Galyamina, Maria G. Zavialova, Sergey V. Kostrov, Ilya V. Demidyuk.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
No approval of research ethics committees was required to accomplish the goals of this study because experimental work was conducted with an unregulated insect species.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Svetlova, A.O., Karaseva, M.A., Berdyshev, I.M. et al. Protease S of entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus laumondii: expression, purification and effect on greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. Mol Biol Rep 51, 713 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09654-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09654-8