Abstract
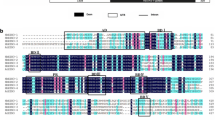
MYB family proteins regulate a variety of cellular processes in plants. Tap** panel dryness (TPD) in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) affects latex biosynthesis and causes serious losses to rubber producers. In this study, a novel SANT/MYB transcription factor gene down-regulated in TPD rubber tree, named as HbSM1, was isolated from rubber tree. The complete HbSM1 open reading frame (ORF) was 948 bp in length. The deduced HbSM1 protein is 315 amino acids. HbSM1 belonged to 1RMYB subfamily with a single SANT domain. Sequence alignment revealed that HbSM1 had high homology with MYB members from Ricinus communis and Manihot esculenta, with 72 and 78 % identity, respectively. Moreover, HbSM1 shared 56 % identity with Glycine max GmMYB176. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that HbSM1, GmMYB176, rice OsMYBS2, and OsMYBS3 fell into the same cluster with 93 % bootstrap support value. Comparing expression among different tissues demonstrated that HbSM1 was ubiquitously expressed in all tissues, but it appeared to be preferentially expressed in leaf and latex. Furthermore, HbSM1 transcripts were significantly induced by various phytohormones (including gibberellic acid, ethephon, methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, and abscisic acid) and wounding treatments. These results suggested that HbSM1 might play multiple roles in plant development via different phytohormones signaling pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feller A, Machemer K, Braun EL, Grotewold E (2011) Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J 66:94–116
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:447–456
Ogata K, Morikawa S, Nakamura H, Hojo H, Yoshimura S et al (1995) Comparison of the free and DNA-complexed forms of the DNA-binding domain from c-Myb. Nat Struct Biol 2:309–320
Kranz HD, Denekamp M, Greco R, ** H, Leyva A et al (1998) Towards functional characterisation of the members of the R2R3-MYB gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:263–276
Rosinski JA, Atchley WR (1998) Molecular evolution of the Myb family of transcription factors: evidence for polyphyletic origin. J Mol Evol 46:74–83
** H, Martin C (1999) Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol Biol 41:577–585
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C et al (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15:573–581
Riechmann JL, Ratcliffe OJ (2000) A genomic perspective on plant transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:423–434
Chen Y, Yang X, He K, Liu M, Li J et al (2006) The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Mol Biol 60:107–124
Du H, Yang S, Liang Z, Feng B, Liu L et al (2012) Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12:106
Cai H, Tian S, Dong H (2012) Large scale in silico identification of MYB family genes from wheat expressed sequence tags. Mol Biotechnol 52:184–192
Ito M (2005) Conservation and diversification of three-repeat Myb transcription factors in plants. J Plant Res 118:61–69
Alabadi D, Oyama T, Yanovsky MJ, Harmon FG, Mas P et al (2001) Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 293:880–883
Wada T, Tachibana T, Shimura Y, Okada K (1997) Epidermal cell differentiation in Arabidopsis determined by a Myb homolog, CPC. Science 277:1113–1116
Ye H, Li L, Guo H, Yin Y (2012) MYBL2 is a substrate of GSK3-like kinase BIN2 and acts as a corepressor of BES1 in brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:20142–20147
Dubos C, Le Gourrierec J, Baudry A, Huep G, Lanet E et al (2008) MYBL2 is a new regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 55:940–953
Aasland R, Stewart AF, Gibson T (1996) The SANT domain: a putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem Sci 21:87–88
Grune T, Brzeski J, Eberharter A, Clapier CR, Corona DF et al (2003) Crystal structure and functional analysis of a nucleosome recognition module of the remodeling factor ISWI. Mol Cell 12:449–460
Boyer LA, Langer MR, Crowley KA, Tan S, Denu JM et al (2002) Essential role for the SANT domain in the functioning of multiple chromatin remodeling enzymes. Mol Cell 10:935–942
Boyer LA, Latek RR, Peterson CL (2004) The SANT domain: a unique histone-tail-binding module? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:158–163
Bandurski RS, Teas HJ (1957) Rubber biosynthesis in latex of Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Physiol 32:643–648
de Faÿ E, Jacob JL (1989) Symptomatology, histological and cytological aspects of the bark dryness disease. In: d’Auzac J, Jacob JL, Chrestin H (eds) Physiology of rubber tree latex. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 407–430
Chrestin H (1989) Biochemical aspects of bark dryness induced by overstimulation of rubber tree with Ethrel. In: d’Auzac J, Jacob JL, Chrestin H (eds) Physiology of rubber tree latex. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 341–441
Faridah Y, Siti Arija M, Ghandimathi H (1996) Changes in some physiological latex parameters in relation to over exploitation and onset of induced tap** panel dryness. J Nat Rubber Res 10:182–186
Chen S, Peng S, Huang G, Wu K, Fu X et al (2003) Association of decreased expression of a Myb transcription factor with the TPD (tap** panel dryness) syndrome in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Mol Biol 51:51–58
Venkatachalam P, Thulaseedharan A, Raghothama K (2007) Identification of expression profiles of tap** panel dryness (TPD) associated genes from the latex of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). Planta 226:499–515
Venkatachalam P, Thulaseedharan A, Raghothama K (2009) Molecular identification and characterization of a gene associated with the onset of tap** panel dryness (TPD) syndrome in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell.) by mRNA differential display. Mol Biotechnol 41:42–52
Li D, Deng Z, Chen C, ** panel dryness from Hevea brasiliensis latex using suppression subtractive hybridization. BMC Plant Biol 10:140
Peng S, Wu K, Huang G, Chen S (2011) HbMyb1, a Myb transcription factor from Hevea brasiliensis, suppresses stress induced cell death in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:1429–1435
Lee GI, Howe GA (2003) The tomato mutant spr1 is defective in systemin perception and the production of a systemic wound signal for defense gene expression. Plant J 33:567–576
Xu J, Aileni M, Abbagani S, Zhang P (2010) A reliable and efficient method for total RNA isolation from various members of spurge family (Euphorbiaceae). Phytochem Anal 21:395–398
Letunic I, Copley RR, Schmidt S, Ciccarelli FD, Doerks T et al (2004) SMART 4.0: towards genomic data integration. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D142–D144
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2002) Multiple sequence alignment using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr Protoc Bioinform Chapter 2: Unit 2 3
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Qin B (2013) The function of Rad6 gene in Hevea brasiliensis extends beyond DNA repair. Plant Physiol Biochem 66:134–140
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△CT Method. Methods 25:402–408
Rubio-Somoza I, Martinez M, Diaz I, Carbonero P (2006) HvMCB1, a R1MYB transcription factor from barley with antagonistic regulatory functions during seed development and germination. Plant J 45:17–30
Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987) The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J 6:3553–3558
Yi J, Derynck MR, Li X, Telmer P, Marsolais F et al (2010) A single-repeat MYB transcription factor, GmMYB176, regulates CHS8 gene expression and affects isoflavonoid biosynthesis in soybean. Plant J 62:1019–1034
Lu CA, Ho TH, Ho SL, Yu SM (2002) Three novel MYB proteins with one DNA binding repeat mediate sugar and hormone regulation of alpha-amylase gene expression. Plant Cell 14:1963–1980
Rose A, Meier I, Wienand U (1999) The tomato I-box binding factor LeMYBI is a member of a novel class of myb-like proteins. Plant J 20:641–652
Klee H (2003) Hormones are in the air. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10144–10145
Hao B, Wu J (2000) Laticifer differentiation in Hevea brasiliensis: induction by exogenous jasmonic acid and linolenic acid. Ann Bot 85:37–43
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation Program of China (31300503 and 31460197), the Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (CARS-34-GW8), the Midwest University Project (MWECSP-RT08, ZXBJH-XK004, and ZXBJH-XK005), and Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (313064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bi Qin and Yu Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, B., Zhang, Y. & Wang, M. Molecular cloning and expression of a novel MYB transcription factor gene in rubber tree. Mol Biol Rep 41, 8169–8176 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3717-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3717-1