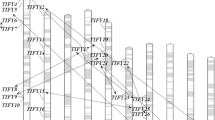
Abstract
The MYB proteins constitute one of the largest transcription factor families in plants. Much research has been performed to determine their structures, functions, and evolution, especially in the model plants, Arabidopsis, and rice. However, this transcription factor family has been much less studied in wheat (Triticum aestivum), for which no genome sequence is yet available. Despite this, expressed sequence tags are an important resource that permits opportunities for large scale gene identification. In this study, a total of 218 sequences from wheat were identified and confirmed to be putative MYB proteins, including 1RMYB, R2R3-type MYB, 3RMYB, and 4RMYB types. A total of 36 R2R3-type MYB genes with complete open reading frames were obtained. The putative orthologs were assigned in rice and Arabidopsis based on the phylogenetic tree. Tissue-specific expression pattern analyses confirmed the predicted orthologs, and this meant that gene information could be inferred from the Arabidopsis genes. Moreover, the motifs flanking the MYB domain were analyzed using the MEME web server. The distribution of motifs among wheat MYB proteins was investigated and this facilitated subfamily classification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh, K., Foley, R. C., & Onate-Sanchez, L. (2002). Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 5, 430–436.
Riechmann, J. L., Heard, J., Martin, G., Reuber, L., Jiang, C., Keddie, J., et al. (2000). Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science, 290, 2105–2110.
Stracke, R., Werber, M., & Weisshaar, B. (2001). The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 4, 447–456.
**, H., & Martin, C. (1999). Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Molecular Biology, 41, 577–585.
Rosinski, J. A., & Atchley, W. R. (1998). Molecular evolution of the Myb family of transcription factors: evidence for polyphyletic origin. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 46, 74–83.
Dubos, C., Stracke, R., Grotewold, E., Weisshaar, B., Martin, C., & Lepiniec, L. (2010). MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 15, 573–581.
Schaffer, R., Landgraf, J., Accerbi, M., Simon, V., Larson, M., & Wisman, E. (2001). Microarray analysis of diurnal and circadian-regulated genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 13, 113–123.
Simon, M., Lee, M. M., Lin, Y., Gish, L., & Schiefelbein, J. (2007). Distinct and overlap** roles of single-repeat MYB genes in root epidermal patterning. Developmental Biology, 311, 566–578.
Matsui, K., Umemura, Y., & Ohme-Takagi, M. (2008). AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal, 55, 954–967.
Ito, M. (2005). Conservation and diversification of three-repeat Myb transcription factors in plants. Journal of Plant Research, 118, 61–69.
Wilkins, O., Nahal, H., Foong, J., Provart, N. J., & Campbell, M. M. (2009). Expansion and diversification of the Populus R2R3-MYB family of transcription factors. Plant Physiology, 149, 981–993.
Matus, J. T., Aquea, F., & Arce-Johnson, P. (2008). Analysis of the grape MYB R2R3 subfamily reveals expanded wine quality-related clades and conserved gene structure organization across Vitis and Arabidopsis genomes. BMC Plant Biology, 8, 83.
Yanhui, C., **aoyuan, Y., Kun, H., Meihua, L., Jigang, L., Zhaofeng, G., et al. (2006). The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: Expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Molecular Biology, 60, 107–124.
Nagaraj, S. H., Gasser, R. B., & Ranganathan, S. (2007). A hitchhiker’s guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis. Brief Bioinformatics, 8, 6–21.
Nagaraj, S. H., Gasser, R. B., & Ranganathan, S. (2008). Needles in the EST haystack: large-scale identification and analysis of excretory-secretory (ES) proteins in parasitic nematodes using expressed sequence tags (ESTs). PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2, e301.
Xu, Y. L., He, P., Zhang, L., Fang, S. Q., Dong, S. L., Zhang, Y. J., et al. (2009). Large-scale identification of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins from expressed sequence tags in insects. BMC Genomics, 10, 632.
Boutrot, F., Chantret, N., & Gautier, M. F. (2008). Genome-wide analysis of the rice and Arabidopsis non-specific lipid transfer protein (nsLtp) gene families and identification of wheat nsLtp genes by EST data mining. BMC Genomics, 9, 86.
Chen, R. M., Ni, Z. F., Nie, X. L., Qin, Y. X., Dong, G. Q., & Sun, Q. X. (2005). Isolation and characterization of genes encoding Myb transcription factor in wheat (Triticum aestivem L.). Plant science, 169, 1146–1154.
Morimoto, R., Nishioka, E., Murai, K., & Takumi, S. (2009). Functional conservation of wheat orthologs of maize rough sheath1 and rough sheath2 genes. Plant Molecular Biology, 69, 273–285.
Huang, X., & Madan, A. (1999). CAP3: A DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Research, 9, 868–877.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596–1599.
Bailey, T. L., Williams, N., Misleh, C., & Li, W. W. (2006). MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Research, 34, W369–W373.
Singh, V. K., Mangalam, A. K., & Dwivedi, S. (1998). S. Naik, Primer premier: Program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence, 24, 318–319.
Zimmermann, P., Hirsch-Hoffmann, M., Hennig, L., & Gruissem, W. (2004). GENEVESTIGATOR. Arabidopsis microarray database, analysis toolbox. Plant Physiology, 136, 2621–2632.
Meissner, R. C., **, H., Cominelli, E., Denekamp, M., Fuertes, A., Greco, R., et al. (1999). Function search in a large transcription factor gene family in Arabidopsis: Assessing the potential of reverse genetics to identify insertional mutations in R2R3 MYB genes. Plant Cell, 11, 1827–1840.
Remm, M., Storm, C. E., & Sonnhammer, E. L. (2001). Automatic clustering of orthologs and in-paralogs from pairwise species comparisons. Journal of Molecular Biology, 314, 1041–1052.
Li, L., Stoeckert, C. J., Jr., & Roos, D. S. (2003). OrthoMCL: Identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Research, 13, 2178–2189.
Deluca, T. F., Wu, I. H., Pu, J., Monaghan, T., Peshkin, L., Singh, S., et al. (2006). Roundup: A multi-genome repository of orthologs and evolutionary distances. Bioinformatics, 22, 2044–2046.
Jensen, L. J., Julien, P., Kuhn, M., von Mering, C., Muller, J., Doerks, T., et al. (2008). eggNOG: Automated construction and annotation of orthologous groups of genes. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, D250–D254.
Altenhoff, A. M., & Dessimoz, C. (2009). Phylogenetic and functional assessment of orthologs inference projects and methods. PLoS Computational Biology, 5, e1000262.
Fang, J., Haasl, R. J., Dong, Y., & Lushington, G. H. (2005). Discover protein sequence signatures from protein–protein interaction data. BMC Bioinformatics, 6, 277.
Zhang, L., Zhao, G., Jia, J., Liu, X., & Kong, X. (2011). Molecular characterization of 60 isolated wheat MYB genes and analysis of their expression during abiotic stress. Journal of Experimental Botany. doi:10.1093/jxb/err264.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Key Basic Scientific Study and Development Plan (973 plan; grant no. 2012CB114003), Natural Science Foundation (grant no. 31171830), and Jiangsu Provincial Priority Academic Program Development of Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12033_2011_9486_MOESM4_ESM.tif
AF4. Phylogenetic tree constructed with MYB domains from wheat, rice and Arabidopsis R2R3-type MYB proteins. (TIFF 1667 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Tian, S. & Dong, H. Large Scale In Silico Identification of MYB Family Genes from Wheat Expressed Sequence Tags. Mol Biotechnol 52, 184–192 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-011-9486-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-011-9486-3