Abstract
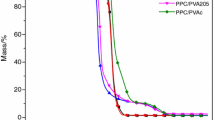
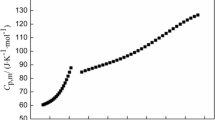
Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) is a binder for electrically controlled solid propellants (ECSPs), whose combustion strongly depends on their decomposition characteristics. Thus, the effects of heating rate, pyrolysis temperature, and lithium perchlorate content on the thermal decomposition behavior and products of PVA and LiClO4/PVA composites were investigated via thermogravimetry (TG) and pyrolysis/gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py/GC/MS). The TG curves showed that the heating rate significantly influences the thermal decomposition behavior; according to the Py/GC/MS results, the major pyrolysis products of PVA were water, acetaldehyde, 2-butenal, and 2,4-hexadienal at 573 K and acetaldehyde, cyclic olefinic compounds, and aromatic hydrocarbons at 1173 K. The results also revealed that depolymerization is among the main decomposition mechanisms of LiClO4/PVA composites and using the optimal LiClO4 content (40–56 mass%) could enhance the combustion efficiency of ECSPs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawka WN. Highly insensitive, solid state, electrically-controlled propellants for divert propulsion. Digital Solid State Propulsion LLC, N06–181; (http://www.dsspropulsion.com).
Sawka WN. Controllable digital solid state cluster thruster rocker propulsion and gas generation. US: 0134924 Patent 2008-5-5.
Matthew SG, Joshua LR, Shae W, Jason T. Plasma plume characterization of electric solid propellant pulsed microthrusters. J Propul Power. 2016;33:1–11. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2015-4185.
Sawka WN. Family of modifiable high performance electrically controlled propellant and explosives. US: 0067789 Patent. 2009-05-15.
Glascock MS, Rovey JL. Plasma plume characterization of electric solid propellant pulsed microthrusters. Propulsion and Energy Forum 51st AIAA/ SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, 2015. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2015-4185
Sawka WN, McPherso M. Electrical solid propellants: a safe, micro to macro propulsion technology. In: 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference, 2013. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2013-4168
Sawka WN, Katzakian AJ, Grix C. Solid state digital propulsion cluster thrusters for small satellites using high performance electrically controlled extinguishable solid propellants. 19th annual AIAA/USU conference on small satellites, 2005. http://hdl.handle.net/2060/20050223573.
Amrousse R. Hydroxylammonium Nitrate (HAN)-based Green propellant as alternative energy resource for potential hydrazine substitution: from lab scale to pilot plant scale-up. Combust Flame. 2017;176:334–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.11.011.
Amrousse R. New HAN-based mixtures for reaction control system and low toxic spacecraft propulsion subsystem: thermal decomposition and possible thruster applications. Combust Flame. 2015;162:2686–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.03.026.
Siddaiah T, Pravakar O, Gopal NO, Ramu C, Nagabhushana H. Thermal, structural, optical and electrical properties of PVA/MAA: EA polymer blend filled with different concentrations of lithium perchlorate. J Sci Adv Mater Dev. 2018;3:456–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.11.004.
Hirankumar G, Mehta N. Effect of incorporation of different plasticizers on structural and ion transport properties of PVA-LiClO4 based electrolytes. Heliyon. 2018;4: e00992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00992.
Zugic DL, Perovic IM, Nikolic VM. Enhanced performance of the solid alkaline fuel cell using PVA-KOH membrane. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2013;8:949–57.
Hong HJ, Li S, Zhou XW. Non-isothermal decomposition mechanism and kinetics of LiClO4 in nitrogen. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2010;26:300–3. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.201090321.
Tellekamp MB. Lithium perchlorate as a solid/liquid state oxygen source for molecular beam epitaxy. Thesis. School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Georgia Institute of Technology, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/1853/55544.
Golofit K, Zysk T. Thermal decomposition properties and compatibility of CL-20 with binders HTPB, PBAN, GAP and polyNIMMO. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1931–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4418-2.
Baraker BM, Lobo B. Multistage thermal decomposition in films of cadmium chloride-doped PVA–PVP polymeric blend. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134:879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7289-5.
Taghizadeh MT, Yeganeh N, Rezaei M. The investigation of thermal decomposition pathway and products of poly (vinyl alcohol) by TG-FTIR. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015;132(42117):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42117.
He ZC, **a ZX, Hu JX. Thermodynamic properties of polyvinyl alcohol binder of electrically controlled solid propellant. J Polym Resear. 2019;26:219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1894-2.
Pogue RT, Ackley KL, Majidi V. Evaluation of high molecular weight species produced during thermal degradation of poly (vinyl alcohol). Int J Polym Anal Ch. 1996;3:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236669708032764.
Beck WH. Pyrolysis studies of polymeric materials used as binders in composite propellants: a review. Combust Flame. 1987;70:171–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-2180(87)90077-0.
Chaturvedi S, Dave PN. Solid propellants: AP/HTPB composite propellants. Arab J Chem. 2019;12:2061–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.033.
Siddaiah T, Ojha P, Gopal NO. Thermal, structural, optical and electrical properties of PVA/MAA: EA polymer blend filled with different concentrations of lithium perchlorate. J Sci Adv Mater Dev. 2018;3:456–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.11.004.
Tsuchiya Y, Sumi K. Thermal decomposition products of poly (vinyl alcohol). J Polym Sci Part Part A-1. 1970;7:3151–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1969.150070302.
Yang HG, Xu SB, Jiang L, Dan Y. Thermal decomposition behavior of poly (vinyl alcohol) with different hydroxyl content. J Macro Sci Part B Phys. 2012;51:464–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2011.597687.
Gilman JW, Vanderhart DL, Kashiwagi T. Thermal decomposition chemistry of poly (vinyl alcohol). ACS Symp Ser. 1995;599:161–85. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1995-0599.ch011.
Ettre K, Varadi PF. Pyrolysis-gas chromatographic technique. Effect of temperature on thermal degradation of polymers. Anal Chem. 1963;35:69–73. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60194a023.
Boddington T, Hongtu F, Laye PG, Nawaz M, Nelson DC. Thermal runaway by thermal analysis. Thermochim Acta. 1990;170:81–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(90)80526-5.
Sánchez-Rodriguez D, Farjas J, Roura P. The critical conditions for thermal explosion in a system heated at a constant rate. Combust Flame. 2017;186:211–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.08.008.
Rathod SG, Bhajantri R, Ravindrachary V, Poojary B, Pujari PK, Sheela T, Naik J. Influence of transport parameters on conductivity of lithium perchlorate-doped poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan composites. J Elastom Plast. 2015;48:442–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244315580457.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51706241).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., **a, Zx., Ma, Lk. et al. Study on the thermal decomposition behavior and products of poly(vinyl alcohol) and its LiClO4 composites via Py/GC/MS. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 7031–7042 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-11019-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-11019-3