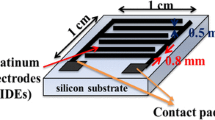
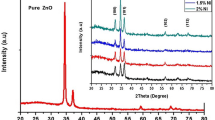
Abstract
This work presents an improvement in room temperature gas sensing properties of ZnO thin film samples as an impact of cobalt do**. The response of films towards various gases (xylene, toluene, isopropanol, methanol, ethanol and Acetone) were studied. Thin films samples were prepared using the spray pyrolysis technique. XRD patterns revealed hexagonal (wurtzite) structure of prepared film samples. UV–Vis spectra showed the reduction of the energy band gap with cobalt do**. Different modes in the Raman spectra were observed in the vibrational analysis of the samples. A spindle-like morphology with enhanced surface granularity is observed with cobalt incorporation. This research extensively studied the response of thin films to different acetone gas concentrations at room temperature. At 50 ppm acetone concentration, 3% Co doped ZnO thin films showed a maximum response of 185. Also, Co doped ZnO film shows good selectivity towards acetone as compared to other gases. The obtained results brought attention to the potential utilization of cobalt doped ZnO thin films in develo** gas sensing devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are not openly available due to reasons of sensitivity and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable.
References
A.M. Subramanian, S. Nagarajan, S. Vinod, K. Chakraborty, T. Sivagami, Theodore, Long-term impacts of climate change on coastal and transitional eco-systems in India: an overview of its current status, future projections, solutions, and policies. RSC Adv. 13, 12204–12228 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra07448f
E. David, V.-C. Niculescu, Volatile Organic compounds (VOCs) as environmental pollutants: occurrence and mitigation using nanomaterials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 18, 13147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413147
W. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Wu, X. Wang, X. Lv, G. Liu, Electrospun Nb-doped CeO2 nanofibers for humidity independent acetone sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 602, 154303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154303
X. Chang, S. Xu, S. Liu, N. Wang, S. Sun, X. Zhu et al., Highly sensitive acetone sensor based on WO3 nanosheets derived from WS2 nanoparticles with inorganic fullerene-like structures. Sens. Actuators B 343, 130135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130135
M. Dadkhah, Nanostructured metal oxide semiconductors towards greenhouse gas detection. Chemosensors 10(2), 57 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020057
Z. Jiang, B. Liu, L. Yu, Y. Tong, M. Yan, R. Zhang, W. Han, Research progresses in preparation methods and applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 956, 170316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170316
X. Zhou, A. Wang, Y. Wang, L. Bian, Z. Yang, Y. Bian, Y. Gong, X. Wu, N. Han, Y. Chen, Crystal-defect-dependent gas-sensing mechanism of the single ZnO Nanowire Sensors. ACS Sens. 3(11), 2385–2393 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b00792
P. Chesler, C. Hornoiu, MOX-Based resistive gas sensors with different types of sensitive materials (powders, pellets, films), used in Environmental Chemistry. Chemosensors. 11(2), 95 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020095
T. Zhou, T. Zhang, Recent progress of Nanostructured sensing materials from 0d to 3D: overview of structure–property-application relationship for gas sensors. Small Methods. 5(9), 2100515 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202100515
P. Nakarungsee, S. Srirattanapibul, C. Issro, I.-M. Tang, S. Thongmee, High performance cr doped ZnO by UV for NH3 Gas Sensor. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 314, 112230 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112230
K. Suganthi, E. Vinoth, L. Sudha, P. Bharathi, M. Navaneethan, Manganese (mn 2+) doped hexagonal prismatic zinc oxide (ZnO) nanostructures for chemiresistive NO2 sensor. Sens. Actuators B 380, 133293 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133293
R. John, A. Alice, J. Ruban Kumar, Shruthi, M.V. Ramana, Reddy, FeXZn1-xOy as room temperature dual sensor for formaldehyde and ammonia gas detection. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 141, 109506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109506
S. Pan, Y. Guo, G. Chen, L. Sun, J. Huang, L. Wang, L. Cheng, MOFs-derived synthesis of Ni-doped ZnO nanostructutred material towards excellent n-butanol sensing performance and long-term stability. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33(10), 7501–7514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07888-5
S.D. Lokhande, M.B. Awale, V.D. Mote, Optical and gas sensing properties of Cu-Doped ZnO nanocrystalline thin films for sensor applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33, 25063–25077 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09213-6
W. Niu, K. Kang, Y. Ou, Y. Ding, B. Du, X. Guo, Y. Tan et al., Cobalt ions Induced morphology control of metal-organic framework-derived indium oxide nanostructures for high performance hydrogen sulfide gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 381, 133347 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133347
Y. Luo, A. Ly, D. Lahem, D.M. Justin, A.-C. Martin, C. Romain, C. Zhang, M. Debliquy, Role of cobalt in Co-ZnO nanoflower gas sensors for the detection of low concentration of vocs. Sens. Actuators B 360, 131674 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131674
Y. Fan, Y. Xu, Y. Wang, Y. Sun, Fabrication and characterization of Co-doped ZnO Nanodiscs for Selective Tea Sensor applications with high response, high selectivity and ppb-level detection limit. J. Alloys Compd. 876, 160170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160170
J. Rodrigues, Detection of trimethylamine (TMA) gas using mixed shape cobalt doped ZnO nanostructure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 305, 127972 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127972
E. Chubenko, M.W. Alhamd, V. Bondarenko, Optical properties of hydrothermally deposited Ni and Co doped nanostructured ZnO thin films as scintillating coatings for beta-particles detection. J. Lumin. 247, 118860 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2022.118860
P. Kumar, P. Nisha, S. Sarkar, B.C. Singh, Mishra, R.S. Katiyar, The influence of post-growth heat treatment on the optical properties of pulsed laser deposited ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 128, 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05511-2
Y. Kim, Characterization of Ni–CO Thin Film and its applications to multifunctional substrates of flexible microdevices. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 333, 113295 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.113295
U.C. Matur, I.P. Duru, D. Akcan, Tracking Optical properties of ZnO:mg thin films: experimental and first principles calculations. Ceram. Int. 48(13), 19090–19097 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.199
H. Fayaz Rouhi, S.M. Rozati, Synthesis and investigating effect of tellurium-do** on physical properties of zinc oxide thin films by spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Phys. A (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05377-4
A.B. Workie, H.S. Ningsih, S.-J. Shih, A Comprehensive Review on the spray pyrolysis technique: historical context, operational factors, classifications, and product applications. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 170, 105915 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2023.105915
S.B. Rana, R.P. Singh, S. Arya, Structural, optical, magnetic and antibacterial study of pure and cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28(3), 2660–2672 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5843-0
P. Singh, N. Kumar, S.K. Singh, M. Singh, Singh, P. Tandon, Co-doped ZnO nanostructures for liquefied petroleum gas sensing at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34, 10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10344-7
V. Vinitha, M. Preeyanghaa, M. Anbarasu, B. Neppolian, V. Sivamurugan, Chemical recycling of polyester textile wastes using silver-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: an economical solution for circular economy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27567-0
A. Goktas, S. Modanlı, A. Tumbul, A. Kilic, Facile synthesis and characterization of ZnO, ZnO:Co, and ZnO/ZnO:Co nano rod-like homojunction thin films: role of crystallite/grain size and microstrain in photocatalytic performance. J. Alloys Compd. 893, 162334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162334
K. Singh, N.H. Kaur, P.K. Sharma, G. Singh, J. Singh, ZnO and cobalt decorated ZnO NPS: synthesis, photocatalysis and antimicrobial applications. Chemosphere 313, 137322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137322
M. Awale, S.D. Lokhande, S.S. Jadhav, S.B. Kadam, V.D. Mote, A.B. Kadam, Effect on ethanol sensing ability of zinc oxide thin films with manganese do**. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10407-9
M. Ashokkumar, C. Muthusamy, Role of ionic radii and electronegativity of co-dopants (Co, Ni and Cr) on properties of Cu doped ZnO and evaluation of in-vitro cytotoxicity. Surf. Interfaces 30, 101968 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101968
S.D. Lokhande, M.B. Awale, G. Umadevi, V.D. Mote, Effect of Ni do** on structural, optical and gas sensing properties of ZnO films for the development of acetone sensor devices. Mater. Chem. Phys. 301, 127667 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127667
B. Altun, I.K. Er, A.O. Çağırtekin, A. Ajjaq, F. Sarf, S. Acar, Effect of cd dopant on structural, optical and CO2 gas sensing properties of ZnO thin film sensors fabricated by chemical bath deposition method. Appl. Phys. A 127, 9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04843-9
A.L. Naim, A.F.A. Solieman, E.R. Shaaban, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline thin films for spintronic devices. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(4), 3613–3621 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02916-8
N. Ben Elkamel, Imen, A. Hamdaoui, R. Mezni, Ajjel, L. Beji, High responsivity and 1/f noise of an ultraviolet photodetector based on Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 8(56), 32333–32343 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05567j
S. Kammoun, J. El Ghoul, Structural and optical investigation of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles for nanooptoelectronic devices. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(6), 7215–7225 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05430-7
T. Elavarasan, S. Ernest, S. Fairose, Influence of cobalt do** on the structural optical topographical and sensing properties of spray deposited zinc oxide thin films. Mater. Today: Proceed. 38, 2720–2724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.529
P. Kumar, V. Chauhan, P.C. Panday, Role of dysprosium do** concentration on structural deformation of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 621, 413313 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2021.413313
E. Naik, H.S. Indrajith, M.S. Bhojya Naik, Sarvajith, E. Pradeepa, Co-precipitation synthesis of cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles: characterization and their applications for biosensing and antibacterial studies. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 130, 108678 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108678
S. Jaballah, M. Benamara, H. Dahman, A. Ly, D. Lahem, M. Debliquy, L. El Mir, Effect of Mg-do** ZnO nanoparticles on detection of low ethanol concentrations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 255, 123643 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123643
S. Lal, R. Verma, A. Chauhan, J. Dhatwalia, I. Guleria, S. Ghotekar, S. Thakur et al., Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and photocatalytic activity of green synthesized ZnO-NPS from Myrica esculenta fruits extract. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 141, 109518 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109518
Z. Aghagoli, M. Ardyanian, Synthesis and study of the structure, magnetic, optical and methane gas sensing properties of cobalt doped zinc oxide microstructures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(9), 7130–7141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8701-4
B. Salameh, A.M. Alsmadi, M. Shatnawi, Effects of Co concentration and annealing on the magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO films: role of oxygen vacancies on the ferromagnetic ordering. J. Alloys Compd. 835, 155287 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155287
P. Batista-Grau, R. Sánchez-Tovar, R.M. Fernández-Domene, J. García-Antón, Formation of ZnO nanowires by anodization under hydrodynamic conditions for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Surf. Coat. Technol. 381, 125197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.125197
M. Murthy, V. Narasimha, G. Ganesh, S. Ravinder, G. Anusha, Chandrakala, C.J. Sreelatha, Sol–Gel synthesized ZnO thin films doped with Rb and Al for self-cleaning antibacterial applications. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06044-7
J. Sahu, S. Soni, S. Kumar, B. Dalela, P.A. Alvi, S.S. Sharma, D.M. Phase, M. Gupta, S. Kumar, S. Dalela, Defects and oxygen vacancies tailored structural, optical and electronic structure properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticle samples probed using soft X-Ray absorption spectroscopy. Vacuum. 179, 109538 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109538
F.A. Taher, E. Abdeltwab, Shape-controlled synthesis of nanostructured Co-doped ZnO thin films and their magnetic properties. CrystEngComm 20(38), 5844–5856 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ce00738a
M. Kaur, V. Kumar, P. Kaur, M. Lal, P. Negi, R. Sharma, Effect on the dielectric properties due to in–N co-do** in ZnO particles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(7), 8991–9004 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05570-w
A. Bashir, A. Majeed, S. Naseem, Investigation of Structural and optical parameters of Yttrium-doped ZnO thin films prepared via spin coating of simple aqueous solution. Bull. Mater. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02391-9
V.M. Vimuna, R. Sreeja Sreedharan, R. Resmi Krishnan, V.S. Kavitha, S.R. Chalana, S. Suresh, V.P. Mahadevan Pillai, Study on the structural, morphological and optical properties of RF sputtered gallium doped zinc oxide thin films. Mater. Today: Proceed. 4(2), 4417–4433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.04.014
P.P. Patel, P.J. Hanumantha, O.I. Velikokhatnyi, M.K. Datta, D. Hong, B. Gattu, J.A. Poston, A. Manivannan, P.N. Kumta, Nitrogen and cobalt co-doped zinc oxide nanowires—viable photoanodes for hydrogen generation via photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Power Sources 299, 11–24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.08.027
J. Hu, F. Gao, Z. Zhao, S. Sang, P. Li, W. Zhang, **ongtu Zhou, and, Y. Chen, Synthesis and characterization of cobalt-doped ZnO microstructures for methane gas sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 363, 181–188 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.024
J. Xuan, G. Zhao, Q. Gong, L. Wang, J. Ren, M. Sun, T. Zhou, F. **ng, B. Liu, Fabrication of in-situ grown and Pt-decorated ZnO nanoclusters on new-type FTO electrode for room-temperature detection of low-concentration H2S. J. Alloys Compd. 860, 158499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158499
T. Karthik, M. Venkata, A. Olvera, R.R. Maldonado, Biswal, Undoped and nickel-doped zinc oxide thin films deposited by dip coating and ultrasonic spray pyrolysis methods for propane and carbon monoxide sensing applications. Sensors 20(23), 6879 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236879
K. Krishna, G. Gopi, S. Umadevi, Parne, N. Pothukanuri, Zinc oxide based gas sensors and their derivatives: a critical review. J. Mater. Chem. C 11(12), 3906–3925 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2tc04690c
A. Hastir, N. Kohli, Temperature dependent selective and sensitive terbium doped ZnO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B 231, 110–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.03.001
Y. Li, S. Wang, P. Hao, J. Tian, H. Cui, X. Wang, Soft-templated formation of double-shelled ZnO hollow microspheres for acetone gas sensing at low concentration/near room temperature. Sens. Actuators: Chem. 273, 751–759 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.06.110
W. Zhang, L. Song, D. Zhao, T. Liu, H. Jiang, W. Yang, B. Zhao, W. Huang, P. Wang, L. Sui, Construction of hierarchical ZnO Flower-like structure for Boost H2S detection at low temperature. Sens. Actuators B 385, 133728 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133728
C.-N. Wang, Y.L. Li, F.L. Gong, Y.H. Zhang, S.-M. Fang, H.-L. Zhang, Advances in Doped ZnO nanostructures for gas sensor. Chem. Record 20, 1553–1567 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202000088
R.C. Ramola, S. Negi, R.C. Singh, F. Singh, Gas sensing response of ion beam irradiated Ga-doped ZnO thin films. Sci. Rep. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-26948-8
S. Sun, M. Wang, X. Chang, Y. Jiang, D. Zhang, D. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Lei, W18O49/Ti3c2tx mxene nanocomposites for highly sensitive acetone gas sensor with low detection limit. Sens. Actuators B 304, 127274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127274
X. Kou, N. **. Sens. Actuators B 256, 861–869 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.011
S. Zhang, M. Yang, K. Liang, A. Turak, B. Zhang, D. Meng, C. Wang, F. Qu, W. Cheng, M. Yang, An acetone gas sensor based on nanosized PT-loaded Fe2O3 nanocubes. Sens. Actuators B 290, 59–67 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.082
S. Cao, N. Sui, P. Zhang, T. Zhou, J. Tu, T. Zhang, TiO2 nanostructures with different crystal phases for sensitive acetone gas sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 607, 357–366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.215
Y. Gong, X. Wu, X. Li, A. Wang, M. Zhang, Y. Chen, Enhanced acetone sensing properties of pt@al-doped ZnO core-shell nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 329, 129–153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129153
El Z. Khalidi, B. Hartiti, M. Siadat, E. Comini, H.M. Arachchige, S. Fadili, P. Thevenin, Acetone sensor based on Ni doped ZnO nanostructures: growth and sensing capability. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(8), 7681–7690 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01083-9
Y. Chen, H. Li, D. Huang, X. Wang, Y. Wang, W. Wang, M. Yi, Q. Cheng, Y. Song, G. Han, Highly sensitive and selective acetone gas sensors based on modified ZnO nanomaterials. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 148, 106807 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.106807
J. Du, R. Zhao, S. Chen, H. Wang, J. Li, Z. Zhu, Self-assembly of gridlike zinc oxide lamellae for chemical-sensing applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 5870–5878 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/am509139f
H. Zhang, S. Wu, J. Liu, Y. Cai, C. Liang, Laser irradiation-induced Au–ZnO nanospheres with enhanced sensitivity and stability for ethanol sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 22503–22508 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cp03487j
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MBA—Synthesis, characterization, analysis, formal writing, SDL—Analysis, final writing, SBK—Final drafting, VDM—Supervision of scientific, editing, ABK—Supervision, editing and reviewing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to this article’s content. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Awale, M., Lokhande, S.D., Kadam, S.B. et al. Highly sensitive and selective room temperature acetone sensing properties of Co doped ZnO nanostructure films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 1209 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12912-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12912-x