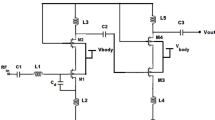
Abstract
This paper presents an optimum design of an ultra-wideband (UWB) 2.5–10.5-GHz low-noise amplifier (LNA) in 180-nm and 65-nm radiofrequency (RF)-complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) technology. A novel input matching network employing resistive–inductive feedback and a noise-canceling technique is proposed to achieve broadband matching as well as a low noise figure (NF). Moreover, a current-reused structure and the inductive peaking technique are applied in the proposed LNA to reduce its power consumption and provide high, flat gain. The proposed UWB-LNA is optimized using heuristic multiobjective optimization based on inclined planes system optimization (IPO) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) as simulation-based evolutionary techniques. The proposed UWB-LNA is designed and simulated using HSPICE and Cadence Spectre RF. The postlayout simulation results show an input return loss (S11) of less than −10 dB, a flat power gain (S21) of 13.2 ± 0.5 and 14 ± 0.5 dB, and an NF below 5 and 2.5 dB over the whole UWB band when implemented in 180-nm and 65-nm CMOS technology, respectively. The UWB-LNA consumes 7.2 and 9.5 mW from a 1.8-V power supply when implemented in 180-nm and 65-nm CMOS technology, respectively.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, Y.-H., Chen, Y.-J.E., Heo, D.: A 0.6-V low power UWB CMOS LNA. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 17(3), 229–231 (2007)
Zhang, Z., Dinh, A., Chen, L., et al.: Wide range linearity improvement technique for linear wideband LNA. IEICE Electron. Express 14(4), 1–10 (2017)
Sahafi, A., Sobhi, J., Koozehkanani, Z.D.: Linearity improvement of gm-boosted common gate LNA: analysis to design. Microelectron. J. 56, 156–162 (2016)
Ballweber, B., Gupta, R., Allstot, D.: A fully integrated 0.5–5.5 GHz CMOS distributed amplifier. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 35(2), 231–239 (2000)
Shin, S.-C., Lin, C.-S., Tsai, M.-D., et al.: A low-voltage and variable-gain distributed amplifier for 3.1–10.6 GHz UWB systems. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 16(4), 179–181 (2006)
Bhattacharyya, K., Deen, M.: Microwave CMOS traveling wave amplifiers: performance and temperature effects. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 14(4), 142–144 (2004)
Jussila, J., Sivonen, P.: A 1.2-V highly linear balanced noise-cancelling LNA in 0.13 µm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 43(3), 579–587 (2008)
Blaakmeer, S.C., Klumperink, E.A.M., Leenaerts, D.M.W., et al.: Wideband balun-LNA with simultaneous output balancing, noise-cancelling and distortion-cancelling. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 43(6), 1341–1350 (2008)
Nguyen, T.-K., Kim, C.-H., Ihm, G.-J., et al.: CMOS low-noise amplifier design optimization techniques. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 52(5), 1433–1442 (2004)
Papadimitriou, A., Bucher, M.: Multi-objective low-noise amplifier optimization using analytical model and genetic computation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(12), 4963–4993 (2017)
Kolakaluri, S., Nagura, S.S., Kar, R., et al.: Optimization of low noise amplifier using particle swarm optimization. In: 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT), Chennai, 2016, pp. 2055–2058
Mallick, S., Akhil, J.R., Dasgupta, A., , et al.: Optimal design of 5.5 GHz CMOS LNA using hybrid fitness based adaptive De with PSO. In: International Electrical Engineering Congress (IEECON), Pattaya, 2017, pp. 1–4 (2017)
Joshi, D., Dash, S., Malhotra, A., et al.: Optimization of 2.4 GHz CMOS low noise amplifier using hybrid particle swarm optimization with Lévy flight. In: 2017 30th International Conference on VLSI Design and 2017 16th International Conference on Embedded Systems (VLSID), Hyderabad, 2017, pp. 181–186
Bhale, V.: Design and optimization of CMOS 0.18 μm low noise amplifier for wireless applications. Int. J. Inf. Electron. Eng. 4(2), 92–97 (2014)
Ghosh, S., De, B.P., Kar, R., et al.: Optimal design of a 5.5-GHz low-power high-gain CMOS LNA using the flower pollination algorithm. J. Comput. Electron. 18(2), 737–747 (2019)
Li, Y.: A simulation-based evolutionary approach to LNA circuit design optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 209(1), 57–67 (2009)
Zandian, S., Khosravi, H., Bijari, A.: Design and heuristic optimization of a CMOS LNA for ultra-wideband receivers. In: 2019 27th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Yazd, Iran, 2019, pp. 243–248
Mozaffari, M.H., Abdy, H.: Zahiri, SH: IPO: an inclined planes system optimization algorithm. Comput. Inform. 35(1), 222–240 (2016)
Tripathi, P.K., Bandyopadhyay, S., Pal, S.K.: Multi-objective particle swarm optimization with time variant inertia and acceleration coefficients. Inf. Sci. 177(22), 5033–5049 (2007)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 1995, pp. 1942–1948
Lin, Y.-S., Chen, C.-Z., Yang, H.-Y., et al.: Analysis and design of a CMOS UWB LNA with dual-RLC-branch wideband input matching network. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 58(2), 287–296 (2010)
Wu, C.-H., Lin, Y.-S., Wang, C.-C.: A 3.1–10.6-GHz current-reused CMOS ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier using self-forward body bias and forward combining techniques. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 55(10), 2296–2302 (2013)
Arshad, S., Ramzan, R., Muhammad, K., et al.: A sub-10 mW, noise cancelling, wideband LNA for UWB applications. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69(1), 109–118 (2015)
Li, N., Feng, W., Li, X.: A CMOS 3–12 GHz ultra-wideband low noise amplifier by dual-resonance network. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 27(4), 383–385 (2017)
Lin, Y.-S., Wang, C.-C., Lee, G.-L., et al.: High-performance wideband low-noise amplifier using enhanced π-match input network. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 24(3), 200–202 (2014)
Saberkari, A., Kazemi, S., Shirmohammadli, V., et al.: gm-boosted flat gain UWB low noise amplifier with active inductor-based input matching network. Integration 52, 323–333 (2016)
Daryabari, F., Zahedi, A., Rezaei, A., et al.: Low-power ultra-wideband LNA employing CS–CD current-reuse and gain-controller resistor technique in 0.18 μm CMOS technology. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 101(2), 187–199 (2019)
Kumar, M.: Deolia, VK: A wideband design analysis of LNA utilizing complimentary common gate stage with mutually coupled common source stage. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 98(3), 575–585 (2018)
Luo, P., Liu, M., Chen, L., et al.: A 2.99 dB NF 15.6 dB gain 3–10 GHz ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier for UWB systems in 65 nm CMOS. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 101(3), 651–665 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bijari, A., Zandian, S. & Ebrahimipour, M. Optimum design of a new ultra-wideband LNA using heuristic multiobjective optimization. J Comput Electron 19, 1295–1312 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01513-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01513-6