Abstract
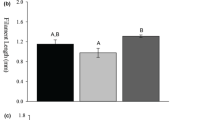
Fish are faced with a wide range of hydrostatic pressure (HP) in their natural habitats. Additionally, freshwater fish are occasionally exposed to rapid changes in HP due to heavy rainfall, flood and/or dam release. Accordingly, variations in HP are one of the most important environmental cues for fish. However, little information is available on how HP information is perceived and transmitted in the central nervous system of fish. The present study examined the effect of HP (water depth of 1.3 m) on the quantities of monoamines and their metabolites in the telencephalon, optic tectum, diencephalon, cerebellum (including partial mesencephalon) and vagal lobe (including medulla oblongata) of the goldfish, Carassius auratus, using high-performance liquid chromatography. HP affected monoamine and metabolite contents in restricted brain regions, including the telencephalon, cerebellum and vagal lobe. In particular, HP significantly increased the levels of dopamine (DA) in the telencephalon at 15 min and that of norepinephrine (NE) in the cerebellum at 30 min. In addition, HP also significantly increased locomotor activity at 15 and 30 min after HP treatment. It is possible that HP indirectly induces locomotion in goldfish via telencephalic DA and cerebellar NE neuronal activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atema J (1971) Structures and functions of the sense of taste in the catfish (Ictalurus natalis). Brain Behav Evol 4:273–294
Block BA, Booth D, Carey FG (1992) Direct measurement of swimming speeds and depth of blue marlin. J Exp Biol 166:267–284
Bonn U (1987) Distribution of monoamine-containing neurons in the brain of a teleost, Carassius auratus (Cyprinidae). J Hirnforsch 28:529–544
Contestabile A, Villani L, Bissoli R, Poli A, Migani P (1986) Cholinergic, GABAergic and excitatory amino acidic neurotransmission in the goldfish vagal lobe. Exp Brain Res 63:301–309
Corio M, Peute J, Steinbusch HWM (1991) Distribution of serotonin- and dopamine-immunoreactivity in the brain of the teleost Clarias gariepinus. J Chem Neuroanat 4:79–95
Damasceno-Oliveira A, Fernández-Durán B, Gonçalves J, Serrão P, Soares-Da-Silva P, Reis-Henriques MA, Coimbra J (2006) Effects of cyclic and constant hydrostatic pressure on norepinephrine and epinephrine levels in the brain of flounder. J Fish Biol 68:1300–1307
Damasceno-Oliveira A, Fernandez-Duran B, Goncalves J, Serrao P, Soares-da-Silva P, Reis-Henriques MA, Coimbra J (2007) Effects of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on the brain biogenic amines concentrations in the flounder, Platichthys flesus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 153:385–389
De Pedro N, Pinillos ML, Valenciano AI, Alonso-Bedate M, Delgado MJ (1998) Inhibitory effect of serotonin on feeding behavior in goldfish: involvement of CRF. Peptides 19:505–511
Dietrich M, Hofmann MH, Bleckmann H (2002) Effects of dopaminergic drugs and telencephalic ablation on eye movements in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Brain Res Bull 57:393–395
Fenwick JC (1970) Brain serotonin and swimming activity in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Comp Biochem Physiol 32:803–806
Finger TE (2008) Sorting food from stones: the vagal taste system in goldfish, Carassius auratus. J Comp Physiol A 194:135–143
Fraser PJ, Macdonald AG (1994) Crab hydrostatic pressure sensors. Nature 371:383–384
Fraser PJ, Shelmerdine RL (2002) Dogfish hair cells sense hydrostatic pressure. Nature 415:495–496
Fraser PJ, Cruickshank SF, Shelmerdine RL (2003) Hydrostatic pressure effects on vestibular hair cell afferents in fish and crustacea. J Vestib Res 13:235–242
Fremberg M, van Veen T, Hartwig HG (1977) Formaldehyde-induced fluorescence in the telencephalon and diencephalon of the eel (Anguilla anguilla l.). A fluorescence-microscopic and microspectrofluorometric investigation with special reference to the innervation of the pituitary. Cell Tissue Res 176:1–22
Gardette R, Krupa M, Crepel F (1987) Differential effects of serotonin on the spontaneous discharge and on the excitatory amino acid-induced responses of deep cerebellar nuclei neurons in rat cerebellar slices. Neuroscience 23:491–500
Geffard M, Kah O, Onteniente B, Seguela P, Le Moal M, Delaage M (1984) Antibodies to dopamine: radioimmunological study of specificity in relation to immunocytochemistry. J Neurochem 42:1593–1599
Gibson RN (1970) The tidal rhythm of activity of Coryphoblennius galerita (L.) (Teleostei, Blenniidae). Anim Behav 18:539–543
Gibson RN (1984) Hydrostatic pressure and the rhythmic behaviour of intertidal marine fishes. Trans Am Fish Soc 113:479–483
Gibson RN (1992) Tidally-synchronised behaviour in marine fishes. In: Ali MA (ed) Rhythms in fishes. Springer, New York, pp 63–81
Gnegy ME (2012) Catecholamine. In: Brady ST, Siegel GJ, Albers RW, Price DL (eds) Basic neurochemistry: Principles of molecular, cellular, and medical neurobiology. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 283–293
Godø OR, Michalsen K (2000) Migratory behaviour of north-east Arctic cod, studied by use of data storage tags. Fish Res 48:127–140
Go** G, Pollard HB, Adeyemo OM, Kuijpers GA (1995) Effect of MPTP on dopaminergic neurons in the goldfish brain: a light and electron microscope study. Brain Res 687:35–52
Gotow T, Triller A, Korn H (1990) Differential distribution of serotoninergic inputs on the goldfish Mauthner cell. J Comp Neurol 292:255–268
Hensler JG (2012) Serotonin. In: Brady ST, Siegel GJ, Albers RW, Price DL (eds) Basic neurochemistry: Principles of molecular, cellular, and medical neurobiology. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 300–322
Hornby PJ, Piekut DT (1990) Distribution of catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes in goldfish brains: presumptive dopamine and norepinephrine neuronal organization. Brain Behav Evol 35:49–64
Ikenaga T, Yoshida M, Uematsu K (2005) Morphology and immunohistochemistry of efferent neurons of the goldfish corpus cerebelli. J Comp Neurol 487:300–311
Ikenaga T, Yoshida M, Uematsu K (2006) Cerebellar efferent neurons in teleost fish. Cerebellum 5:268–274
Janssen J, Brandt SB (1980) Feeding ecology and vertical migration of adult alewives (Alosa pseudoharengus) in lake Michigan. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:177–184
Kah O, Chambolle P (1983) Serotonin in the brain of the goldfish, Carassius auratus. An immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 234:319–333
Kapsimali M, Vidal B, Gonzalez A, Dufour S, Vernier P (2000) Distribution of the mRNA encoding the four dopamine D1 receptor subtypes in the brain of the european eel (Anguilla anguilla): comparative approach to the function of D1 receptors in vertebrates. J Comp Neurol 419:320–343
Koizumi I, Kanazawa Y, Tanaka Y (2013) The fishermen were right: experimental evidence for tributary refuge hypothesis during floods. Zool Sci 30:375–379
Lee M, Strahlendorf JC, Strahlendorf HK (1985) Modulatory action of serotonin on glutamate-induced excitation of cerebellar purkinje cells. Brain Res 361:107–113
Lillesaar C (2011) The serotonergic system in fish. J Chem Neuroanat 41:294–308
Linard B, Bennani S, Jego P, Saligaut C (1996) Tyrosine hydroxylase activity and dopamine turnover of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) brain: the special status of the hypothalamus. Fish Physiol Biochem 15:41–48
Macdonald AG, Gilchrist I, Wardle CS (1987) Effect of hydrostatic pressure on the motor activity of fish from shallow water and 900 m depths: some results of challenger cruise 6B/85. Comp Biochem Physiol 88:543–547
Matsumoto N, Yoshida M, Uematsu K (2007) Effects of partial ablation of the cerebellum on sustained swimming in goldfish. Brain Behav Evol 70:105–114
McCleave JD, Arnold GP (1999) Movements of yellow- and silver-phase European eels (Anguilla anguilla L.) tracked in the western North Sea. ICES J Mar Sci 56:510–536
Mok EY, Munro AD (1998) Effects of dopaminergic drugs on locomotor activity in teleost fish of the genus Oreochromis (Cichlidae): involvement of the telencephalon. Physiol Behav 64:227–234
Morita Y, Ito H, Masai H (1980) Central gustatory paths in the crucian carp, Carassius carassius. J Comp Neurol 191:119–132
Nilsson GE (1989) Regional distribution of monoamines and monoamine metabolites in the brain of the crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.). Comp Biochem Physiol C 94:223–228
Nishi K, Kondo T, Narabayashi H (1991) Destruction of norepinephrine terminals in 1-metyl-4phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-treated mice reduces locomotor activity induced by L-DOPA. Neurosci Lett 123:244–247
Northcott SJ (1991) A comparison of circatidal rhythmicity and entrainment by hydrostatic pressure cycles in the rock goby, Gobius paganellus L. and the shanny, Lipophrys pholis (L.). J Fish Biol 39:25–33
Northcott SJ, Gibson RN, Morgan E (1991a) Phase responsiveness of the activity rhythm of Lipophrys pholis (L.) (Teleostei) to a hydrostatic pressure pulse. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 148:47–57
Northcott SJ, Gibson RN, Morgan E (1991b) The effect of tidal cycles of hydrostatic pressure on the activity of Lipophrys pholis (L.) (Teleostei). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 148:35–45
Nunn AD, Copp GH, Vilizzi L, Carter MG (2010) Seasonal and diel patterns in the migrations of fishes between a river and a floodplain tributary. Ecol Freshw Fish 19:153–162
Olcese JM, Hall TR, Figueroa HR, de Vlaming VL (1979) Hypothalamic monoamine oxidase, a component in the serotonergic control of pituitary prolactin content in Carassius auratus L. Gen Comp Endocrinol 38:309–313
Pollard HB, Dhariwal K, Adeyemo OM, Markey CJ, Caohuy H, Levine M, Markey S, Youdim MB (1992) A parkinsonian syndrome induced in the goldfish by the neurotoxin MPTP. FASEB J 6:3108–3116
Pollard HB, Kuijpers GA, Adeyemo OM, Youdim MB, Go** G (1996) The MPTP-induced parkinsonian syndrome in the goldfish is associated with major cell destruction in the forebrain and subtle changes in the optic tectum. Exp Neurol 142:170–178
Raffaelli D, Richner H, Summers R, Northcott S (1990) Tidal migrations in the flounder (Platichthys flesus). Mar Behav Physiol 16:249–260
Roberts BL, van Rossem A, de Jager S (1992) The influence of cerebellar lesions on the swimming performance of the trout. J Exp Biol 167:171–178
Sebert P, Barthelemy L, Caroff J (1985) Serotonin levels in fish brain: effects of hydrostatic pressure and water temperature. Experientia 41:1429–1430
Sebert P, Barthelemy L, Caroff J (1986) Catecholamine content (as measured by the HPLC method) in brain and blood plasma of the EEL: effects of 101 ATA hydrostatic pressure. Comp Biochem Physiol C 84:155–157
Sébert ME, Weltzien FA, Moisan C, Pasqualini C, Dufour S (2008) Dopaminergic systems in the European eel: characterization, brain distribution, and potential role in migration and reproduction. In: Dufour S, Prévost E, Rochard E, Williot P (eds) Fish and diadromy in Europe (ecology, management, conservation). Springer, Netherlands, pp 27–46
Somoza GM, Peter RE (1991) Effects of serotonin on gonadotropin and growth hormone release from in vitro perifused goldfish pituitary fragments. Gen Comp Endocrinol 82:103–110
Strahlendorf JC, Lee M, Strahlendorf HK (1989) Modulatory role of serotonin on GABA-elicited inhibition of cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuroscience 30:117–125
Takemura A, Uchimura M, Shibata Y (2010a) Dopaminergic activity in the brain of a tropical wrasse in response to changes in light and hydrostatic pressure. Gen Comp Endocrinol 166:513–519
Takemura A, Rahman MS, Park YJ (2010b) External and internal controls of lunar-related reproductive rhythms in fishes. J Fish Biol 76:7–26
Takemura A, Shibata Y, Takeuchi Y, Hur SP, Sugama N, Badruzzaman M (2012) Effects of hydrostatic pressure on monoaminergic activity in the brain of a tropical wrasse, Halicoeres trimaculatus: possible implication for controlling tidal-related reproductive activity. Gen Comp Endocrinol 175:173–179
Tanaka H, Naito Y, Davis ND, Urawa S, Ueda H, Fukuwaka M (2005) First record of the at-sea swimming speed of a Pacific salmon during its oceanic migration. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 291:307–312
Thompson RH, Menard A, Pombal M, Grillner S (2008) Forebrain dopamine depletion impairs motor behavior in lamprey. Euro J Neurosci 27:1452–1460
Vetillard A, Benanni S, Saligaut C, Jego P, Bailhache T (2002) Localization of tyrosine hydroxylase and its messenger RNA in the brain of rainbow trout by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol 449:374–389
Vidal B, Pasqualini C, Le Belle N, Holland MC, Sbaihi M, Vernier P, Zohar Y, Dufour S (2004) Dopamine inhibits luteinizing hormone synthesis and release in the juvenile European EEL: a neuroendocrine lock for the onset of puberty. Biol Reprod 71:1491–1500
Weinreb O, Youdim MB (2007) A model of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in the goldfish. Nat Proto 2:3016–3021
Wollmuth LP, Crawshaw L, Panayiotides-Djaferis H (1989) The effects of dopamine on temperature regulation in goldfish. J Comp Physiol B 159:83–89
Yoshida M, Nagatsu I, Kawakami-Kondo Y, Karasawa N, Spatz M, Nagatsu T (1983) Monoaminergic neurons in the brain of goldfish as observed by immunohistochemical techniques. Experientia 39:1171–1174
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ms. Chihiro Yamauchi, University of the Ryukyus, and Dr. Yoriko Akimoto, Mr. Takahiro Nakashita, Mr. Seiya Mochinaga and Mr. Takeshi Yoshihara, Kyushu University, for their support and help in sampling. Dr. Sethu Selvaraj, Kyushu University, Dr. Takeshi Onuma, Osaka University, and Mr. Makoto Yoshida, The University of Tokyo, provided stimulating discussions and helpful advice. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS fellows (Grant Numbers 10J02886 and 12J02083) to TI from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikegami, T., Takemura, A., Choi, E. et al. Increase in telencephalic dopamine and cerebellar norepinephrine contents by hydrostatic pressure in goldfish: the possible involvement in hydrostatic pressure-related locomotion. Fish Physiol Biochem 41, 1105–1115 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0072-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0072-7