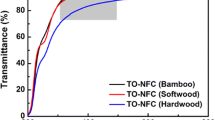
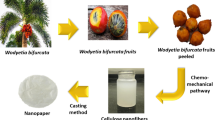
Abstract
Mechanochemical methods for cellulose processing have gained significant attention for the higher efficiency and the potential for special applications. Cellulose pulp fibers from different sources including softwood, hardwood and bamboo were selected as starting materials in this study, because the performance and sustainability of cellulose based materials are highly dependent on their sources. They were successfully defibrillated and functionalized in one-step by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES)-assisted ball milling method. The morphology, chemical structure and crystal structure of the cellulose fibers before and after modification were characterized. Translucent cellulose films with high haze (about 94.8%) were prepared through vacuum-assisted filtration. The test results show that the addition of APTES plays a significant role in enhancing the performance of cellulose films, not only weakening the hydrophilicity (water contact angle of up to 88°), but also enhancing the transparency (transmittance of up to 78%), thermal stability and mechanical properties. These demonstrate that the APTES-assisted ball milling method is an effective way to tailor the structure of cellulose fibers due to its easy operation and wide applicability. In addition, softwood and bamboo films that show relatively higher comprehensive performance on the radar chart have higher application value in the packaging, composite materials and other fields. This work provides guidance for the design and efficient preparation of high-performance cellulose materials.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data is provided within the manuscript and supplementary information files.
References
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA et al (2011) Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: a novel approach. Carbohydr Polym 86(4):1468–1475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.034
Ahvenainen P, Kontro I, Svedström K (2016) Comparison of sample crystallinity determination methods by X-ray diffraction for challenging cellulose I materials. Cellulose 23(2):1073–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0881-6
Albornoz-Palma G, Ching D, Valerio O et al (2020) Effect of lignin and hemicellulose on the properties of lignocellulose nanofibril suspensions. Cellulose 27(18):10631–10647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03304-5
Alongi J, Camino G, Malucelli G (2013) Heating rate effect on char yield from cotton, poly(ethylene terephthalate) and blend fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 92(2):1327–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.10.029
Andresen M, Johansson L-S, Tanem BS et al (2006) Properties and characterization of hydrophobized microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 13(6):665–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-006-9072-1
Balk M, Sofia P, Neffe AT et al (2023) Lignin, the lignification process, and advanced, Lignin-based materials. Int J Mol Sci 24(14):11668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411668
Benaimeche O, Seghir NT, Sadowski Ł et al (2020) The utilization of vegetable fibers in cementitious materials. In: Hashmi S, Choudhury IA (eds) Encyclopedia of Renewable and Sustainable Materials. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 649–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-803581-8.11596-6
Bhushan B, Jung YC (2011) Natural and biomimetic artificial surfaces for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning, low adhesion, and drag reduction. Prog Mater Sci 56(1):1–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.04.003
Bian H, Gao Y, Wang R et al (2018) Contribution of lignin to the surface structure and physical performance of cellulose nanofibrils film. Cellulose 25(2):1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1658-x
Brännvall E, Aulin C (2022) CNFs from softwood pulp fibers containing hemicellulose and lignin. Cellulose 29(9):4961–4976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04585-8
Chen YF, Geng BY, Ru J et al (2017) Comparative characteristics of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers and resulting nanopapers from bamboo, softwood, and hardwood pulps. Cellulose 24(11):4831–4844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1478-4
Chen S, Song YJ, Xu F (2018) Highly transparent and hazy cellulose nanopaper simultaneously with a self-cleaning superhydrophobic surface. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6(4):5173–5181. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04814
Chen CH, Li C, Yu DY et al (2022) A facile method to prepare superhydrophobic nanocellulose-based aerogel with high thermal insulation performance via a two-step impregnation process. Cellulose 29(1):245–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04275-x
Cheng Y, Hui LF, Li M et al (2023) Reactive ammonium phosphite flame retardant in improving the flame retardancy of air filter paper. Cellulose 30(10):6571–6587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05262-0
Chinga-Carrasco G (2013) Optical methods for the quantification of the fibrillation degree of bleached MFC materials. Micron 48:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2013.02.005
Chu Y, Sun Y, Wu W et al (2020) Dispersion properties of nanocellulose: a review. Carbohydr Polym 250:116892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116892
Correa CL, Midorikawa GEO, Filho EXF et al (2020) Transcriptome profiling-based analysis of carbohydrate-active enzymes in aspergillus terreus involved in plant biomass degradation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:564527. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.564527
Dhali K, Daver F, Cass P et al (2022) Surface modification of the cellulose nanocrystals through vinyl silane grafting. Int J Biol Macromol 200:397–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.079
Douard L, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2022) Extraction of carboxylated nanocellulose by combining mechanochemistry and NADES. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10(39):13017–13025. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c02783
Duan R, Tong JY, Sutton AJ et al (2023) Origami plot: a novel multivariate data visualization tool that improves radar chart. J Clin Epidemiol 156:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2023.02.020
Eyckens DJ, Arnold CL, Randall JD et al (2019) Fiber with butterfly wings: creating colored carbon fibers with increased strength, adhesion, and reversible malleability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(44):41617–41625. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b11826
Frank BP, Durkin DP, Caudill ER et al (2018) Impact of silanization on the structure, dispersion properties, and biodegradability of nanocellulose as a nanocomposite filler. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1(12):7025–7038. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b01819
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gu L, Jiang B, Song J et al (2018) Effect of lignin on performance of lignocellulose nanofibrils for durable superhydrophobic surface. Cellulose 26(2):933–944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2129-0
Guan Y, He H, Tang D et al (2024) Functional cellulose paper with high transparency, high haze, and UV-blocking for perovskite solar cells. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 7(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-023-00823-0
Guo RQ, Zhang LX, Lu Y et al (2020) Research progress of nanocellulose for electrochemical energy storage: a review. J Energy Chem 51:342–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2020.04.029
He MY, Sun YH, Han BX (2013) Green carbon science: scientific basis for integrating carbon resource processing, utilization, and recycling. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(37):9620–9633. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201209384
He W, Zhang Z, Zheng Y et al (2020) Preparation of aminoalkyl-grafted bacterial cellulose membranes with improved antimicrobial properties for biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 108(5):1086–1098. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36884
Hu M, Luber EJ, Buriak JM (2020) Reconsidering X–ray photoelectron spectroscopy quantification of substitution levels of monolayers on unoxidized silicon surfaces. J Phys Chem C 124(30):16461–16477. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04101
Huang L, Wu Q, Wang Q et al (2020) Interfacial crystals morphology modification in cellulose fiber/polypropylene composite by mechanochemical method. Compos Part A 130:105765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105765
Jiang B, Chen C, Liang Z et al (2019) Lignin as a wood-inspired binder enabled strong, water stable, and biodegradable paper for plastic replacement. Adv Funct Mater 30(4):1906307. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201906307
**g MF, Zhang LJ, Fan ZB et al (2022) Markedly improved hydrophobicity of cellulose film via a simple one-step aminosilane-assisted ball milling. Carbohydr Polym 275:118701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118701
Kim H, Youn JR, Song YS (2018) Eco-friendly flame retardant nanocrystalline cellulose prepared via silylation. Nanotechnology 29(45):455702. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aadc87
Kuga S, Wu M (2019) Mechanochemistry of cellulose. Cellulose 26(1):215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2197-1
Lamm ME, Li K, Ker D et al (2022) Exploiting chitosan to improve the interface of nanocellulose reinforced polymer composites. Cellulose 29(7):3859–3870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04327-2
Li HS, Chen B, Kulachenko A et al (2023) A comparative study of lignin-containing microfibrillated cellulose fibers produced from softwood and hardwood pulps. Cellulose 31(2):907–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05674-y
Lichtenstein K, Lavoine N (2017) Toward a deeper understanding of the thermal degradation mechanism of nanocellulose. Polym Degrad Stab 146:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.09.018
Liu YZ, Guo BT, **a QQ et al (2017) Efficient cleavage of strong hydrogen bonds in cotton by deep eutectic solvents and facile fabrication of cellulose nanocrystals in high yields. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(9):7623–7631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00954
Liu X, Li Y, Ewulonu CM et al (2019) Mild alkaline pretreatment for isolation of native-like lignin and lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers (LCNF) from crop waste. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(16):14135–14142. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02800
Liu H, Xu Y, Zhao X et al (2022) Lightweight leaf-structured carbon nanotubes/graphene foam and the composites with polydimethylsiloxane for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 191:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.01.051
Liu J, **ao P, Kuga S et al (2023) Preparation of cationic lignocellulose nanofibers from reed straw via mechanochemical method and its application. Cellulose 30(11):7251–7264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05328-z
Lourenço A, Pereira H (2018) Compositional variability of lignin in biomass. In: Poletto M (ed) Lignin - Trends and Applications. IntechOpen, London, pp 65–98. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71208
Lv PF, Lu XM, Wang L et al (2021) Nanocellulose-based functional materials: from chiral photonics to soft actuator and energy storage. Adv Funct Mater 31(45):2104991. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202104991
Mark JE (2009) Polymer Data Handbook. Oxford University Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780195181012.001.0001
Muhammad A, Rahman MR, Hamdan S et al (2019) Recent developments in bamboo fiber-based composites: a review. Polym Bull 76(5):2655–2682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2493-9
Nagarajan KJ, Ramanujam NR, Sanjay MR et al (2021) A comprehensive review on cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibers: pretreatment, preparation, and characterization. Polym Compos 42(4):1588–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25929
Nair SS, Yan N (2015) Effect of high residual lignin on the thermal stability of nanofibrils and its enhanced mechanical performance in aqueous environments. Cellulose 22(5):3137–3150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0737-5
Nelson ML, O’Connor RT (1964a) Relation of certain infrared bands to cellulose crystallinity and crystal lattice type. Part II. A new infrared ratio for estimation of crystallinity in celluloses I and II. J Appl Polym Sci 8(3):1325–1341. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1964.070080323
Nelson ML, O’Connor RT (1964b) Relation of certain infrared bands to cellulose crystallinity and crystal latticed type. Part I. Spectra of lattice types I, II, III and of amorphous cellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 8(3):1311–1324. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1964.070080322
Ogden CA, Ileleji KE, Johnson KD (2019) Fuel property changes of switchgrass during one-year of outdoor storage. Biomass Bioenergy 120:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.11.030
Pan R, Cheng Y, Pei Y et al (2023) Cellulose materials with high light transmittance and high haze: a review. Cellulose 30(8):4813–4826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05172-1
Piras CC, Fernández-Prieto S, De Borggraeve WM (2019) Ball milling: a green technology for the preparation and functionalisation of nanocellulose derivatives. Nanoscale Adv 1(3):937–947. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8na00238j
Ramage MH, Burridge H, Busse-Wicher M et al (2017) The wood from the trees: the use of timber in construction. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 68:333–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.107
Sabara Z, Mutmainnah A, Kalsum U et al (2022) Sugarcane bagasse as the source of nanocrystalline cellulose for gelatin-free capsule shell. Int J Biomater 2022:9889127. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9889127
Santander P, Butter B, Oyarce E et al (2021) Lignin-based adsorbent materials for metal ion removal from wastewater: a review. InD Crops Prod 167:113510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113510
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE et al (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-Ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Tanpichai S, Biswas SK, Witayakran S et al (2019) Water hyacinth: a sustainable lignin-poor cellulose source for the production of cellulose nanofibers. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(23):18884–18893. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04095
Tarrés Q, Ehman NV, Vallejos ME et al (2017) Lignocellulosic nanofibers from triticale straw: the influence of hemicelluloses and lignin in their production and properties. Carbohydr Polym 163:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.017
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991) Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74(10):3583–3597. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(91)78551-2
Vasiljević J, Jerman I, Jakša G et al (2015) Functionalization of cellulose fibres with DOPO-polysilsesquioxane flame retardant nanocoating. Cellulose 22(3):1893–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0599-x
Vilela C, Silvestre AJD, Figueiredo FML et al (2019) Nanocellulose-based materials as components of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Mater Chem A 7(35):20045–20074. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta07466j
Wohlhauser S, Delepierre G, Labet M et al (2018) Grafting polymers from cellulose nanocrystals: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Macromolecules 51(16):6157–6189. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.8b00733
Yang B, Zhang MY, Lu ZQ et al (2019) Comparative study of aramid nanofiber (ANF) and cellulose nanofiber (CNF). Carbohydr Polym 208:372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.086
Yang C, Zhu Y, Tian Z et al (2024) Preparation of nanocellulose and its applications in wound dressing: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 254:127997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127997
Zhang LY, Tsuzuki T, Wang XG (2015) Preparation of cellulose nanofiber from softwood pulp by ball milling. Cellulose 22(3):1729–1741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0582-6
Zhang TL, Wu M, Kuga S et al (2020) Cellulose nanofibril-based flame retardant and its application to paper. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(27):10222–10229. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02892
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Wan Z et al (2023) Mechanochemical fabrication of geopolymer composites based on the reinforcement effect of microfibrillated cellulose. Ceram Int 49(1):503–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.017
Zhu HL, Parvinian S, Preston C et al (2013) Transparent nanopaper with tailored optical properties. Nanoscale 5(9):3787–3792. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr00520h
Zhu Y, Liu J, Lv W et al (2020) Revisiting alkaline pretreatment of lignocellulose: understanding the structural evolution of three components. Adv Sustainable Syst 4(10):2000067. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202000067
Zhu FL, Li X, Feng QQ (2021) Thermal decomposed behavior and kinetic study for untreated and flame retardant treated regenerated cellulose fibers using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 145(2):423–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09780-y
Zhu Z, Wang W, Liu Z et al (2022) High-strength, lightweight and sustainable lignin contained cellulose nanofiber bulk materials for plastic replacement. Ind Crops Prod 185:115106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115106
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52203107 and 52073261), the Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (22A430010).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (52203107 and 52073261). Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (22A430010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Like Ma: Investigation, Methodology, Writing - original draft. Yaohui Hou: Investigation. Ruiting Jiang: Investigation. Yue Ren: Methodology. Yaming Wang: Methodology, Funding acquisition. Chuntai Liu: Resources, Supervision. Changyu Shen: Resources, Supervision. Mengfan **g: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All the authors consent for the publication of this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 2.41 MB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Hou, Y., Jiang, R. et al. Defibrillation and functionalization of cellulose fibers from different sources in one-step via a mechanochemical method. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-06000-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-06000-w