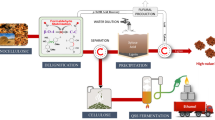
Abstract
In this study, biomass-derived organic solvents (GVL, THF, and ethanol) were used to pretreat lignocellulosic biomass to facilitate the extraction of lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis of glucan. Under the same pretreatment conditions (120 °C, 30 min, 0.5 wt% H2SO4), the GVL cosolvent exhibited a high lignin removal value of 62.80%. The enzymatic saccharification of residual cellulose-rich solid reached 82.59%. The extracted lignin showed a low molecular weight of 3264 g/mol and a good chemical structure according to characterization by SEM, FT-IR, GPC, and 2D-HSQC NMR. Moreover, a QC calculation was performed to explore the interactions between the lignin model compound and solvent molecules to understand the reasons for the differences in lignin dissolution of these three solvents. The H···OH length and bonding energy (ΔE) in the complex of VG-GVL were calculated to be 1.852 Å and 19.4 kcal/mol, respectively. The results indicated that a strong hydrogen bonding interaction was formed between VG and GVL, which explained why GVL had a higher lignin removal capacity than the other solvents under the same pretreatment conditions. In summary, the current study provided a valuable reference for lignocellulose pretreatment toward the extraction of lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis of glucan.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials are provided in full in the results section of this paper.
References
Arnold JC (2003) Environmental effects on crack growth in polymers. In: Milne I, Ritchie RO, Karihaloo B (eds) Compr Struct Integr. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 281–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-043749-4/06123-1
Asadi N, Zilouei H (2017) Optimization of organosolv pretreatment of rice straw for enhanced biohydrogen production using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol 227:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.073
Chen J, Tan X, Miao C, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Zhuang X (2021) A one-step deconstruction-separation organosolv fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass using acetone/phenoxyethanol/water ternary solvent system. Bioresour Technol 342:125963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125963
Chen L et al (2022) New insight into lignin aggregation guiding efficient synthesis and functionalization of a lignin nanosphere with excellent performance. Green Chem 24:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc03651c
Cheng Y-S, Mutrakulcharoen P, Chuetor S, Cheenkachorn K, Tantayotai P, Panakkal EJ, Sriariyanun M (2020) Recent situation and progress in biorefining process of lignocellulosic biomass: toward green economy. Appl Sci Eng Progress. https://doi.org/10.14416/j.asep.2020.08.002
Constant S et al (2016) New insights into the structure and composition of technical lignins: a comparative characterisation study. Green Chem 18:2651–2665. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC03043A
Faiz Norrrahim MN, Ilyas RA, Nurazzi NM, Asmal Rani MS, Nur Atikah MS, Shazleen SS (2021) Chemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for the production of bioproducts: an overview. Appl Sci Eng Progress. https://doi.org/10.14416/j.asep.2021.07.004
Frisch M et al (2009) Gaussian, Inc. Wallingford CT, Wallingford CT
Hrůzová K, Matsakas L, Rova U, Christakopoulos P (2021) Organosolv fractionation of spruce bark using ethanol–water mixtures: towards a novel bio-refinery concept. Bioresour Technol 341:125855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125855
Ji H, Dong C, Yang G, Pang Z (2018) Valorization of lignocellulosic biomass toward multipurpose fractionation: furfural, phenolic compounds, and ethanol. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:15306–15315. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03766
Ji H, Lv P (2020) Mechanistic insights into the lignin dissolution behaviors of a recyclable acid hydrotrope, deep eutectic solvent (DES), and ionic liquid (IL). Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC02760B
Jiang Z, Zhao P, Hu C (2018) Controlling the cleavage of the inter- and intra-molecular linkages in lignocellulosic biomass for further biorefining: a review. Bioresour Technol 256:466–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.061
Kawamata Y et al (2021) Uniqueness of biphasic organosolv treatment of soft- and hardwood using water/1-butanol co-solvent. Ind Crops Prod 159:113078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113078
Kim D-E, Pan X (2010) Preliminary study on converting hybrid poplar to high-value chemicals and lignin using organosolv ethanol process. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:12156–12163. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101671r
Labauze H, Benjelloun-Mlayah B (2021) Kinetics of xylan hydrolysis using an acetic and formic acid-based organosolv pretreatment. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100690
Li P, Ji H, Shan L, Dong Y, Pang Z (2020) Insights into delignification behavior using aqueous p-toluenesulfonic acid treatment: comparison with different biomass species. Cellulose 27:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03481-3
Lv P, Han Z, Chu Y, Ji H (2021) A cosolvent pretreatment: effect of solvent–water on enzymatic hydrolysis of glucan, lignin structure, and dynamics. Cellulose 28:9051–9067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04121-0
Mäki-Arvela P, Anugwom I, Virtanen P, Sjöholm R, Mikkola JP (2010) Dissolution of lignocellulosic materials and its constituents using ionic liquids—a review. Ind Crops Prod 32:175–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.04.005
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) Performance of SM6, SM8, and SMD on the SAMPL1 test set for the prediction of small-molecule solvation free energies. J Phys Chem B 113:4538–4543. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp809094y
Medronho B, Romano A, Miguel MG, Stigsson L, Lindman B (2012) Rationalizing cellulose (in)solubility: reviewing basic physicochemical aspects and role of hydrophobic interactions. Cellulose 19:581–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9644-6
Rachamontree P, Douzou T, Cheenkachorn K, Sriariyanun M, Rattanaporn K (2020) Furfural: a sustainable platform chemical and fuel. Appl Sci Eng Progress. https://doi.org/10.14416/j.asep.2020.01.003
Sharma V et al (2022) Deep eutectic solvents as promising pretreatment agents for sustainable lignocellulosic biorefineries: a review. Bioresour Technol 360:127631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127631
Shen X, Sun R (2021) Recent advances in lignocellulose prior-fractionation for biomaterials, biochemicals, and bioenergy. Carbohydr Polym 261:117884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117884
Shinde VM, Patil GN, Katariya A, Mahajan YS (2015) Production of tetrahydrofuran by dehydration of 1,4-butanediol using amberlyst-15: batch kinetics and batch reactive distillation. Chem Eng Process 95:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2015.06.016
Shuai L, Questell-Santiago YM, Luterbacher JS (2016) A mild biomass pretreatment using γ-valerolactone for concentrated sugar production. Green Chem 18:937–943. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc02489g
Singh R, Srivastava V, Chaudhary K, Gupta P, Prakash A, Balagurumurthy B, Bhaskar T (2015) Conversion of rice straw to monomeric phenols under supercritical methanol and ethanol. Bioresour Technol 188:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.001
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab Anal Proced 1617:1–16
Sriariyanun M, Heitz JH, Yasurin P, Asavasanti S, Tantayotai P (2019) Itaconic acid: a promising and sustainable platform chemical? Appl Sci Eng Progress 12:75–82. https://doi.org/10.14416/j.asep.2019.05.002
Tang X et al (2014) Production of γ-valerolactone from lignocellulosic biomass for sustainable fuels and chemicals supply. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 40:608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.209
Teramura H, Sasaki K, Oshima T, Kawaguchi H, Ogino C, Sazuka T, Kondo A (2018) Effective usage of sorghum bagasse: optimization of organosolv pretreatment using 25% 1-butanol and subsequent nanofiltration membrane separation. Bioresour Technol 252:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.100
Thoresen PP, Matsakas L, Rova U, Christakopoulos P (2020) Recent advances in organosolv fractionation: towards biomass fractionation technology of the future. Bioresour Technol 306:123189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123189
Wang Y-Y, Li M, Wyman CE, Cai CM, Ragauskas AJ (2018) Fast fractionation of technical lignins by organic cosolvents. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:6064–6072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04546
Wu Y, Ji H, Ji X, Tian Z, Chen J (2020) Fibrillating wood chips to facilitate high-valued lignin extraction and high titer ethanol production. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112153
**e LF, Ye CC, Ju XH, Zhao FQ (2012) Theoretical study on dimers of 2,6-diamino-3,5-dinitropyridine and its N-oxide. J Struct Chem 53:659–664. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476612040075
Yuan S, Ji X, Ji H, Tian Z, Chen J (2019) An optimum combined severity factor improves both the enzymatic saccharification yield and the functional lignin structure. Cellulose 26:4731–4742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02442-9
Zhang Z (2016) Synthesis of γ-Valerolactone from Carbohydrates and its applications. Chemsuschem 9:156–171. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201501089
Zhang Z, Harrison M, Rackemann D, Doherty W, O’Hara I (2016) Organosolv pretreatment of Plant Biomass for enhanced enzymatic saccharification. Green Chem 18:360–381. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC02034D
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG (2008) Density functionals with broad applicability in chemistry. Acc Chem Res 41:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar700111a
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG (2011) Applications and validations of the Minnesota density functionals. Chem Phys Lett 502:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2010.11.060
Zhou Q, Li Y (2015) The real role of N-Heterocyclic carbene in reductive functionalization of CO2: an alternative understanding from Density Functional Theory Study. J Am Chem Soc 137:10182–10189. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b03651
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express thanks for the supports from the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFC1905900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32230070), Shandong Natural Science Foundation & Major Basic Research Project (Grant No. ZR2021ZD38), **an Innovation Team (Grant No. 2021GXRC023), the QUTJBZ Program (No. 2022JBZ01-05), the Taishan Industrial Experts Program, and Taishan Scholars Program.
Funding
National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFC1905900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32230070), Shandong Natural Science Foundation & Major Basic Research Project (Grant No. ZR2021ZD38), **an Innovation Team (Grant No. 2021GXRC023), the QUTJBZ Program (No. 2022JBZ01-05), the Taishan Industrial Experts Program, and Taishan Scholars Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yan Wu conducted all the experiment and wrote paper. HJ revised this paper. XJ conceived the experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Ji, H. & Ji, X. Biomass pretreatment using biomass-derived organic solvents facilitates the extraction of lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis of glucan. Cellulose 30, 2859–2872 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05061-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05061-7