Abstract
A voltammetric sensor for both the individual and the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid (AA), uric acid (UA) and folic acid (FA) is described. It is based on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) that was modified with bentonite (Bnt) that was first functionalized with cysteine (Cys) to which gold nanoparticles were linked. The resulting material (referred to as Au-Cys-Bnt) and the other materials were characterized by UV-vis spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy dispersive X-ray analysis and electrochemical methods. The XRD peak positions of bentonite and Cys-functionalized bentonite prove the incorporation of Cys into bentonite. The XPS spectrum of Au-Cys-Bnt confirms the interaction of gold nanoparticles with the thiol group of Cys. The modified GCE displays high electrocatalytic activity for the oxidation of AA, UA and FA, typically at 0.19, 0.41, and 0.73 V (vs. SCE), respectively. Differential pulse voltammetric data show a linear response that covers the 1 μM to 25 mM concentration range for AA, the 1 to 200 μM concentration range for UA, and two linear ranges for FA, one from 5 to 100 μM and one from 100 μM to 1.5 mM. The sensor was applied to the determination of AA, UA and FA in (spiked) multi-vitamin syrup, bird serum and milk samples.

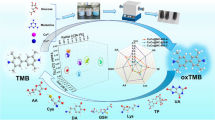
Schematic of a sensor for simultaneous and individual electrochemical determination of ascorbic, uric, and folic acids in real samples. The sensor consists of a glassy carbon electrode that was modified with a nanocomposite prepared from bentonite that was first functionalized with cysteine to which gold nanoparticles were linked.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pramanik S, Murphy BP, Osman NAA (2013) Developments of immobilized surface modified piezoelectric crystal biosensors for advanced applications. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:8863–8892
Jia X, Dong S, Wang E (2016) Engineering the bioelectrochemical interface using functional nanomaterials and microchip technique toward sensitive and portable electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 76:80–90
Pu L, Baig M, Maheshwari V (2016) Nanoparticle chains as electrochemical sensors and electrodes. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:2697–2705
Saxena U, Das AK (2016) Nanomaterials towards fabrication of cholesterol biosensors: key roles and design approaches. Biosens Bioelectron 75:196–205
Gupta R, Ganesan V (2015) Gold nanoparticles impregnated mesoporous silica spheres forsimultaneous and selective determination of uric acid and ascorbic acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 219:139–145
Azad UP, Ganesan V (2010) Influence of metal nanoparticles on the electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose by poly(NiIIteta) modified electrodes. Electroanalysis 22(5):575–583
Azad UP, Ganesan V, Pal M (2011) Catalytic reduction of organic dyes at gold nanoparticles impregnated silica materials: influence of functional groups and surfactants. J Nanopart Res 13:3951–3959
Yadav DK, Ganesan V, Sonkar PK, Gupta R, Rastogi PK (2016) Electrochemical investigation of gold nanoparticles incorporated zinc based metal-organic framework for selective recognition of nitrite and nitrobenzene. Electrochim Acta 200:276–282
Aihara N, Torigoe K, Esumi K (1998) Preparation and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles in layered laponite suspensions. Langmuir 14(17):4945–4949
Yadav DK, Gupta R, Ganesan V, Sonkar PK, Rastogi PK (2016) Electrochemical sensing platform for hydrogen peroxide determination at low reduction potential using silver nanoparticle-incorporated bentonite clay. J Appl Electrochem 46:103–112
Rastogi PK, Ganesan V, Krishnamoorthi S (2013) A promising electrochemical sensing platform based on a silver nanoparticles decorated copolymer for sensitive nitrite determination. J Mater Chem A 2:933–943
Rastogi PK, Ganesan V, Krishnamoorthi S (2014) Palladium nanoparticles decorated gaur gum based hybrid material for electrocatalytic hydrazine determination. Electrochim Acta 125:593–600
Sonkar PK, Ganesan V (2015) Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle-anchored amine-functionalized mesoporous silica for electrocatalytic determination of nitrite. J Solid State Electrochem 19:2107–2115
Rastogi PK, Ganesan V, Krishnamoorthi S (2014) Palladium nanoparticles incorporated polymer-silica nanocomposite based electrochemical sensing platform for nitrobenzene detection. Electrochim Acta 147:442–450
Mousty C (2004) Sensors and biosensors based on clay-modified electrodes-new trends. Appl Clay Sci 27:159–177
Ensafi AA, Bafrooei EH, Dinari M, Mallakpour S (2014) Improved immobilization of DNA to graphite surfaces, using amino acid modified clays. J Mater Chem B 2:3022–3028
Majzik A, Fulop L, Csapo E, Bogar F, Martinek T, Penke B, Biro G, Dekany I (2010) Functionalization of gold nanoparticles with amino acid, β-amyloid peptides and fragment. Colloids Surf, B 81:235–241
Gigante A, Chillemi C, Bevilacqua C, Greco F (2003) Effect of elastin-derived peptide on Achilles tendon healing: an experimental study. J Mater Sci Mater Med 14:717–720
Miksa MAP, Writer MJ, Sarkar S, Meng QH, Barker SE, Shamlou PA, Hailes HC, Hart SL, Tabor AB (2007) Targeting lipopolyplexes using bifunctional peptides incorporating hydrophobic spacer amino acids: synthesis, transfection, and biophysical studies. Bioconjug Chem 18(6):1800–1810
Tosi G, Costantino L, Rivasi F, Ruozi B, Leo E, Vergoni AV, Tacchi R, Bertolini A, Vandelli MA, Forni F (2007) Targeting the central nervous system: in vivo experiments with peptide-derivatized nanoparticles loaded with Loperamide and rhodamine-123. J Control Release 122:1–9
Aryal S, Remant BKC, Dharmaraj N, Bhattarai N, Kim CH, Kim HY (2006) Spectroscopic identification of S-au interaction in cysteine capped gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta A 63:160–163
Mallakpour S, Dinari M (2011) Preparation and characterization of new organoclays using natural amino acids and Cloisite Na+. Appl Clay Sci 51:353–359
Abdelwahab AA, Shim YB (2015) Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and folic acid based on activated graphene/MWCNT nanocomposite loaded Au nanoclusters. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:659–665
Nie T, Lu L, Bai L, Xu J, Zhang K, Zhang O, Wen Y, Wu L (2013) Simultaneous determination of folic acid and uric acid under coexistence of l-ascorbic acid using a modified electrode based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes composite. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:7016–7029
Li Y, Lin H, Peng H, Qi R, Luo C (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with MoS2 nanosheets and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 183:2517–2523
Azad UP, Turllapati S, Rastogi PK, Ganesan V (2014) Tris(1,10-phenanthroline)iron(II)-bentonite film as efficientelectrochemical sensing platform for nitrite determination. Electrochim Acta 127:193–199
Ghosh PK, Bard AJ (1983) Clay-modified electrodes. J Am Chem Soc 105:5691–5693
Ege D, Ghosh PK, White JR, Equey JF, Bard AJ (1985) Clay modified electrodes. 3. Electrochemical and electron spin resonance studies of montmorillonite layers. J Am Chem Soc 107:5644–5652
Lacina K, Novotny J, Moravec Z, Skladal P (2015) Interaction of ferroceneboronic acid with diols at aqueous and non-aqueous conditions - signalling and binding abilities of an electrochemical probe for saccharides. Electrochim Acta 153:280–286
Yang YJ (2015) One-pot synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/zinc sulfidenanocomposite at room temperature for simultaneous determinationof ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:750–759
Yang YJ, Li W (2014) CTAB functionalized grapheme oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite modified electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and nitrite. Biosens Bioelectron 56:300–306
**ng L, Ma Z (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 183:257–263
Mei LP, Feng JJ, Wu L, Chen JR, Shen L, **e Y, Wang AJ (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with porous Cu2O nanospheres on reduced graphene oxide support for simultaneous sensing of uric acid and dopamine with high selectivity over ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 183:2039–2046
Wang C, Yuan R, Chai Y, Chen S, Hu F, Zhang M (2012) Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and tryptophan on gold nanoparticles/overoxidized-polyimidazole composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal Chim Acta 741:15–20
Wu F, Huang T, Hu Y, Yang X, Quyang Y, **e Q (2016) Differential pulse voltammetric simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid on a glassy carbon electrode modified with electroreduced graphene oxide and imidazolium groups. Microchim Acta 183:2539–2546
Acknowledgements
Financial support from CSIR (01(2708)/13/EMR-II), UGC (42-271/2013 (SR)) and DST (SR/NM/NS-2012/2013(G)), New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged. DKY acknowledges UGC for junior research fellowship (JRF). We thank Prof. O. N. Srivastava, Banaras Hindu University for SEM and TEM studies. We thank Ms. Dipika Roy for her assistance during the initial stage of this study in synthesis and characterization of the material and in the electrocatalysis of folic acid. We thank the reviewers for their valuable suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.22 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, D.K., Gupta, R., Ganesan, V. et al. Individual and simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, uric acid and folic acid by using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticles linked to bentonite via cysteine groups. Microchim Acta 184, 1951–1957 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2186-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2186-3