Abstract
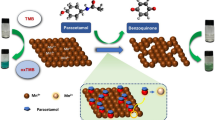
Amlodipine (AM) is a long active calcium channel blocker used to relax blood vessels by preventing calcium ion transport into the vascular walls and its supporting molecules acetaminophen (AP) and ascorbic acid (AA) are recommended for hypertension control and prevention. Considering their therapeutic importance and potential side effects due to over dosage, we have fabricated a sensor for individual and simultaneous determination of AA, AP, and AM in pharmaceuticals and human urine using novel Zn-doped Ca2CuO3 nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Optimally doped Ca2CuO3 (2.5 wt% Zn at Cu site) enhanced the detection of target molecules over much wider concentration ranges of 50 to 3130 µM for AA, 0.25 to 417 µM for AP, and 0.8 to 354 µM for AM with the corresponding lowest detection limits of 14 µM, 0.05 µM, and 0.07 µM, respectively. Furthermore, the Zn-Ca2CuO3/GCE exhibited excellent selectivity and high sensitivity even in the presence of several potential interfering agents. The usefulness of the developed electrode was tested using an amlodipine besylate tablet and urine samples of seven hypertension patients under medication. The results confirmed the presence of a significant amount of AP and AM in six patients’ urine samples indicating that the personalized medication is essential and the quantum of medication need to be fixed by knowing the excess medicines excreted through urine. Thus, the Zn-Ca2CuO3/GCE with a high recovery percentage and good sensitivity shall be useful in the pharmaceutical and biomedical sectors.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Jadon N, Jain R, Pandey A (2017) Electrochemical analysis of amlodipine in some pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluid using disposable pencil graphite electrode. J Electroanal Chem 788:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.01.055
Naikoo GA, Pandit UJ, Sheikh MUD et al (2020) Synergistic effect of carbon nanotubes, copper and silver nanoparticles as an efficient electrochemical sensor for the trace recognition of amlodipine besylate drug. SN Appl Sci 2:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2807-z
Firouzi M, Giahi M, Najafi M et al (2020) Electrochemical determination of amlodipine using a CuO-NiO nanocomposite/ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode as an electrochemical sensor. J Nanoparticle Res 23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05200-w
Atta NF, El-Ads EH, Galal A, Galal AE (2019) Electrochemical sensing platform based on nano-perovskite/glycine/carbon composite for amlodipine and ascorbic acid drugs. Electroanalysis 31:448–460. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800577
Sudha K, Elangovan A, Jeevika A et al (2021) Electroanalytical detection of amlodipine in urine and pharmaceutical samples using Ag-Ce2(WO4)3@CNF nanocomposite-modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchem J 165:106138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106138
Švorc L, Cinková K, Sochr J et al (2014) Sensitive electrochemical determination of amlodipine in pharmaceutical tablets and human urine using a boron-doped diamond electrode. J Electroanal Chem 728:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2014.06.038
Madhuri C, Manohara Reddy YV, Prabhakar Vattikuti SV et al (2019) Trace-level determination of amlodipine besylate by immobilization of palladium-silver bi-metallic nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide as an electrochemical sensor. J Electroanal Chem 847:113259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113259
Lou BS, Rajaji U, Chen SM, Chen TW (2020) A simple sonochemical assisted synthesis of NiMoO4/chitosan nanocomposite for electrochemical sensing of amlodipine in pharmaceutical and serum samples. Ultrason Sonochem 64:104827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104827
Doulache M, Bakirhan NK, Saidat B, Ozkan SA (2020) Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on polyglycine modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous determination of amlodipine and ramipril from biological samples. J Electrochem Soc 167:027511. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab68cd
Upreti V, Ratheesh VR, Dhull P, Handa A (2013) Shock due to amlodipine overdose. Indian J Crit Care Med 17:375–377. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-5229.123452
Khairy M, Khorshed AA, Rashwan FA et al (2017) Sensitive determination of amlodipine besylate using bare/unmodified and DNA-modified screen-printed electrodes in tablets and biological fluids. Sens Actuators B Chem 239:768–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.07.165
Kang X, Wang J, Wu H et al (2010) A graphene-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of paracetamol. Talanta 81:754–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.01.009
Luo J, Fan C, Wang X et al (2013) A novel electrochemical sensor for paracetamol based on molecularly imprinted polymeric micelles. Sens Actuators B Chem 188:909–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.07.088
Solanki PR, Kaushik A, Agrawal VV, Malhotra BD (2011) Nanostructured metal oxide-based biosensors. NPG Asia Mater 3:17–24
Sun D, Zhang Y, Wang F et al (2009) Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, uric acid and xanthine based on the surface enhancement effect of mesoporous silica. Sens Actuators B Chem 141:641–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.07.043
Zhao D, Yu G, Tian K, Xu C (2016) A highly sensitive and stable electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection towards ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid based on the hierarchical nanoporous PtTi alloy. Biosens Bioelectron 82:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.03.074
Wang C, Du J, Wang H et al (2014) A facile electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and au nanoplates modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens Actuators B Chem 204:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.077
Atta NF, Galal A, Ahmed YM, El-Ads EH (2019) Design strategy and preparation of a conductive layered electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dobutamine, acetaminophen and amlodipine. Sens Actuators B Chem 297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126648
Veerapandi G, Lavanya N, Sekar C (2023) Ca2CuO3 perovskite nanomaterial for electrochemical sensing of four different analytes in the xanthine derivatives family. Mater Chem Phys 295:127076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.127076
Lavanya N, Sekar C, Murugan R, Ravi G (2016) An ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of xanthine, hypoxanthine and uric acid based on Co doped CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 65:278–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.033
Rosner H, Eschrig H, Hayn R et al (1997) Electronic structure and magnetic properties of the linear chain cuprates Sr2CuO3 and Ca2CuO3. Phys Rev B - Condens Matter Mater Phys 56:3402–3412. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.56.3402
Zhu D, Ma H, Pang H et al (2018) Facile fabrication of a non-enzymatic nanocomposite of heteropolyacids and CeO2@Pt alloy nanoparticles doped reduced graphene oxide and its application towards the simultaneous determination of xanthine and uric acid. Electrochim Acta 266:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.01.185
Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Serban AI, Fafaneata C (2014) Electrochemical methods for ascorbic acid determination. Electrochim Acta 121:443–460
El-Said WA, Nasr O, Soliman AIA et al (2021) Fabrication of polypyrrole/Au nanoflowers modified gold electrode for highly sensitive sensing of paracetamol in pharmaceutical formulation. Appl Surf Sci Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2021.100065. 4:
Dehdashti A, Babaei A (2020) Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor based on Pt doped NiO nanoparticles/MWCNTs nanocomposite modified electrode for simultaneous sensing of piroxicam and amlodipine. Electroanalysis 32:1017–1024. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201900580
Atta NF, Galal A, El-Gohary ARM (2022) Electrochemical sensing of dobutamine, paracetamol, amlodipine, and daclatasvir in serum based on thiourea SAMs over nano-gold particles-CNTs composite. New J Chem 46:12265–12277. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2nj01822e
Eskiköy Bayraktepe D, Yazan Z (2020) Application of single-use electrode based on nano-clay and MWCNT for simultaneous determination of acetaminophen, ascorbic acid and acetylsalicylic acid in pharmaceutical dosage. Electroanalysis 32:1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201900601
Akbari Javar H, Mahmoudi-Moghaddam H, Garkani-Nejad Z, Dehghannoudeh G (2022) Grass-like Pt-doped NiCo2O4 modified electrode for electrochemical detection of amlodipine. Meas J Int Meas Confed 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.110790
Deng P, Feng J, **ao J et al (2021) Application of a simple and sensitive electrochemical sensor in simultaneous determination of paracetamol and ascorbic acid. J Electrochem Soc 168:096501. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ac1e59
Funding
The authors acknowledge DST sponsored Indo-Sri Lanka project (DST/INT/SL/P-30/2021) and MHRD-RUSA 2.0 (No. F.24–51/2014-U, Policy (TN-Multi-Gen), dated: 09.10.2018) for financial assistance. The authors also thank Mr. S. Arunachalam for many stimulating discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Urine samples for this research have been collected from the Government Hospital in Karaikudi, where doctors conduct clinical tests that meet ethical norms and protect participants’ rights and well-being. As a result, ethical approval may not always be necessary for the use of human urine samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Veerapandi, G., Sekar, C. Binder-free and efficient voltammetric sensor based on Zn-Ca2CuO3 nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of amlodipine, acetaminophen, and ascorbic acid in hypertension patients. Microchim Acta 191, 409 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06473-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06473-3