Abstract
Main conclusion
44 wheat LOX genes were identified by silico genome-wide search method. TaLOX5, 7, 10, 24, 29, 33 were specifically expressed post aphid infestation, indicating their participation in wheat-aphid interaction.
Abstract
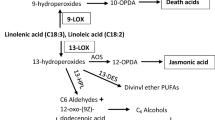
In plants, LOX genes play important roles in various biological progresses including seed germination, tuber development, plant vegetative growth and most crucially in plant signal transduction, stress response and plant defense against plant diseases and insects. Although LOX genes have been characterized in many species, the importance of the LOX family in wheat has still not been well understood, hampering further improvement of wheat under stress conditions. Here, we identified 44 LOX genes (TaLOXs) in the whole wheat genome and classified into three subfamilies (9-LOXs, Type I 13-LOXs and Type II 13-LOXs) according to phylogenetic relationships. The TaLOXs belonging to the same subgroup shared similar gene structures and motif organizations. Synteny analysis demonstrated that segmental duplication events mainly contributed to the expansion of the LOX gene family in wheat. The results of protein–protein interaction network (PPI) and miRNA-TaLOXs predictions revealed that three TaLOXs (TaLOX20, 22 and 37) interacted mostly with proteins related to methyl jasmonate (MeJA) signaling pathway. The expression patterns of TaLOXs in different tissues (root, stem, leaf, spike and grain) under diverse abiotic stresses (heat, cold, drought, drought and heat combined treatment, and salt) as well as under diverse biotic stresses (powdery mildew pathogen, Fusarium graminearum and stripe rust pathogen) were systematically analyzed using RNA-seq data. We obtained aphid-responsive candidate genes by RNA-seq data of wheat after the English grain aphid infestation. Aphid-responsive candidate genes, including TaLOX5, 7, 10, 24, 29 and 33, were up-regulated in the wheat aphid-resistant genotype (Lunxuan144), while they were little expressed in the susceptible genotype (Jimai22) during late response (48 h and 72 h) to the English grain aphid infestation. Meanwhile, qRT-PCR analysis was used to validate these aphid-responsive candidate genes. The genetic divergence and diversity of all the TaLOXs in bread wheat and its relative species were investigated by available resequencing data. Finally, the 3D structure of the TaLOX proteins was predicted based on the homology modeling method. This study not only systematically investigated the characteristics and evolutionary relationships of TaLOXs, but also provided potential candidate genes in response to the English grain aphid infestation and laid the foundation to further study the regulatory roles in the English grain aphid infestation of LOX family in wheat and beyond.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the datasets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- Fst :
-
The fixation index
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- LOX:
-
Lipoxygenase linoleate: oxygen oxidoreductase, EC:1.13.11.12
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- PLAT/LH2 domain:
-
Polycystin-1, lipoxygenase, alpha-toxin/lipoxygenase homology domain
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein interaction
References
Akdogan G, Tufekci ED, Uranbey S, Unver T (2016) miRNA-based drought regulation in wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 16(3):221–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0452-1
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22(2):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti770
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Web Server issue):202–208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Bailly C, Bogatek-Leszczynska R, Come D, Corbineau F (2002) Changes in activities of antioxidant enzymes and lipoxygenase during growth of sunflower seedlings from seeds of different vigour. Seed Sci Res 12(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1079/SSR200197
Bannenberg G, Martinez M, Hamberg M, Castresana C (2009) Diversity of the enzymatic activity in the lipoxygenase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Lipids 44(2):85–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-008-3245-7
Bell E, Creelman RA, Mullet JE (1995) A chloroplast lipoxygenase is required for wound-induced jasmonic acid accumulation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(19):8675–8679. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.19.8675
Bohnert HJ, Nelson DE, Jensen RG (1995) Adaptations to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7(7):1099–1111. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7.1071
Brash AR (1999) Lipoxygenases: occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate. J Biol Chem 274(34):23679–23682. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.34.23679
Caldelari D, Wang G, Farmer EE, Dong X (2011) Arabidopsis lox3 lox4 double mutants are male sterile and defective in global proliferative arrest. Plant Mol Biol 75(1–2):25–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9701-9
Christensen SA, Nemchenko A, Borrego E, Murray I, Sobhy IS, Bosak L, DeBlasio S, Erb M, Robert CA, Vaughn KA, Herrfurth C, Tumlinson J, Feussner I, Jackson D, Turlings TC, Engelberth J, Nansen C, Meeley R, Kolomiets MV (2013) The maize lipoxygenase, ZmLOX10, mediates green leaf volatile, jasmonate and herbivore-induced plant volatile production for defense against insect attack. Plant J 74(1):59–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12101
Christensen SA, Huffaker A, Kaplan F, Sims J, Ziemann S, Doehlemann G, Ji L, Schmitz RJ, Kolomiets MV, Alborn HT (2015) Maize death acids, 9-lipoxygenase-derived cyclopente(a)nones, display activity as cytotoxic phytoalexins and transcriptional mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 12(36):11407–11412. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511131112
Constantino NN, Mastouri F, Damarwinasis R, Borrego EJ, Moran-Diez ME, Kenerley CM, Gao X, Kolomiets MV (2013) Root-expressed maize lipoxygenase 3 negatively regulates induced systemic resistance to Colletotrichum graminicola in shoots. Front Plant Sci 4:510. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00510
Cui L, Yang G, Yan J, Pan Y, Nie X (2019) Genome-wide identification, expression profiles and regulatory network of MAPK cascade gene family in barley. BMC Genomics 20(1):750. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6144-9
Dai X, Zhuang Z, Zhao P (2018) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W49–W54. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky316
Dedryver CA, Gallic J, Haack L, Halkett F, Outreman Y, Simon J (2008) Seasonal and annual genotypic variation and the effect of climate on population genetic structure of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae in northern France. Bull Entomol Res. 98(2):159–168. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485307005500
Doebley JF, Gaut BS, Smith BD (2006) The molecular genetics of crop domestication. Cell 127(7):1309–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.006
Feng B, Dong Z, Xu Z, An X, Qin H, Wu N, Wang D, Wang T (2010) Molecular analysis of lipoxygenase ( LOX ) genes in common wheat and phylogenetic investigation of LOX proteins from model and crop plants. J Cereal Sci 52(3):387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2010.06.019
Fernandez-Calvo P, Chini A, Fernandez-Barbero G, Chico JM, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Geerinck J, Eeckhout D, Schweizer F, Godoy M, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Pauwels L, Witters E, Puga MI, Paz-Ares J, Goossens A, Reymond P, De Jaeger G, Solano R (2011) The Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factors MYC3 and MYC4 are targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in the activation of jasmonate responses. Plant Cell 23(2):701–715. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.075788
Feussner I, Wasternack C (2002) The lipoxygenase pathway. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:275–297. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135248
Gill BS, Appels R, Botha-Oberholster AM, Buell CR, Bennetzen JL, Chalhoub B, Chumley F, Dvorak J, Iwanaga M, Keller B, Li W, McCombie WR, Ogihara Y, Quetier F, Sasaki T (2004) A workshop report on wheat genome sequencing: International genome research on wheat consortium. Genetics 168(2):1087–1096. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.034769
Glauser G, Dubugnon L, Mousavi SA, Rudaz S, Wolfender JL, Farmer EE (2009) Velocity estimates for signal propagation leading to systemic jasmonic acid accumulation in wounded Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem. 284(50):34506–34513. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.061432
Gouinguene SP, Turlings TC (2002) The effects of abiotic factors on induced volatile emissions in corn plants. Plant Physiol 129(3):1296–1307. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.001941
Hao C, Jiao C, Hou J, Li T, Liu H, Wang Y, Zheng J, Liu H, Bi Z, Xu F, Zhao J, Ma L, Wang Y, Majeed U, Liu X, Appels R, Maccaferri M, Tuberosa R, Lu H, Zhang X (2020) Resequencing of 145 landmark cultivars reveals asymmetric sub-genome selection and strong founder genotype effects on wheat breeding in China. Mol Plant 13(12):1733–1751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.09.001
Hernandez-Garcia CM, Finer JJ (2014) Identification and validation of promoters and cis-acting regulatory elements. Plant Sci. 217–218:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.12.007
Itoh A, Howe GA (2001) Molecular cloning of a divinyl ether synthase: identification as a CYP74 cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem 276(5):3620–3627. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008964200
** HS, Van K, Dong HK, Kim KD, Jang YE, Choi BS, Kim MY, Lee SH (2008) The lipoxygenase gene family: a genomic fossil of shared polyploidy between Glycine max and Medicago truncatula. BMC Plant Biol 8:133. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-8-133
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 20. Bioinformatics. 23(21):2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Lee T, Yang S, Kim E, Ko Y, Hwang S, Shin J, Shim JE, Shim H, Kim H, Kim C, Lee I (2015) AraNet v2: an improved database of co-functional gene networks for the study of Arabidopsis thaliana and 27 other nonmodel plant species. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D996-1002. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1053
Lei P, Wei X, Gao R, Huo F, Nie X, Tong W, Song W (2021) Genome-wide identification of PYL gene family in wheat: evolution, expression and 3D structure analysis. Genomics 113(2):854–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.12.017
Lescot M, Dehais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouze P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li J, Li Y, Ma L (2021) Recent advances in CRISPR/Cas9 and applications for wheat functional genomics and breeding. Abiotech 2(4):375–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-021-00042-5
Liu SQ, Liu XH, Jiang LW (2011) Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the lipoxygenase gene family in cucumber. Genet Mol Res 10(4):2613–2636. https://doi.org/10.4238/2011.November.17.4
Liu XL, Yang XF, Wang CY, Wang YJ, Zhang H, Ji WQ (2012) Molecular map** of resistance gene to English grain aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) in Triticum durum wheat line C273. Theor Appl Genet 124(2):287–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1704-7
Liu F, Li H, Wu J, Wang B, Tian N, Liu J, Sun X, Wu H, Huang Y, Lu P, Cheng C (2021) Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of lipoxygenase gene family in banana. Sci Rep 11(1):9948. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89211-6
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ma F, Yang X, Shi Z, Miao X (2020) Novel crosstalk between ethylene- and jasmonic acid-pathway responses to a piercing-sucking insect in rice. New Phytol 225(1):474–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16111
Marco B, Stefan B, Andrew W, Konstantin A, Gabriel S, Tobias S, Florian K, Gallo CT, Martino B, Lorenza B (2014) SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W252–W258. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku340
Mariutto M, Duby F, Adam A, Bureau C, Fauconnier ML, Ongena M, Thonart P, Dommes J (2011) The elicitation of a systemic resistance by Pseudomonas putida BTP1 in tomato involves the stimulation of two lipoxygenase isoforms. BMC Plant Biol 11(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-29
Melan MA, Dong X, Endara ME, Davis KR, Ausubel FM, Peterman TK (1993) An Arabidopsis thaliana lipoxygenase gene can be induced by pathogens, abscisic acid, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Physiol 101(2):441–450. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.101.2.441
Mittler R, Blumwald E (2010) Genetic engineering for modern agriculture: challenges and perspectives. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61(1):443–462. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112116
Montillet JL, Leonhardt N, Mondy S, Tranchimand S, Rumeau D, Boudsocq M, Garcia AV, Douki T, Bigeard J, Laurière C, Chevalier A, Castresana C, Hirt H (2013) An abscisic acid-independent oxylipin pathway controls stomatal closure and immune defense in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 11(3):e1001513. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001513
Nafie E, Hathout T, Mokadem AL, Al Shyma (2011) Jasmonic acid elicits oxidative defense and detoxification systems in Cucumis melo L. cells. Braz J Plant Physiol. 23(2):161–174. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202011000200008
Nalam VJ, Keeretaweep J, Sarowar S, Shah J (2012) Root-derived oxylipins promote green peach aphid performance on Arabidopsis foliage. Plant Cell 24(4):1643–1653. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.094110
Nalam VJ, Keereetaweep J, Shah J (2013) The green peach aphid, Myzus persicae, acquires a LIPOXYGENASE5-derived oxylipin from Arabidopsis thaliana, which promotes colonization of the host plant. Plant Signal Behav 8(1):e22735. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.22735
Ogunola OF, Hawkins LK, Mylroie E, Kolomiets MV, Borrego E, Tang JD, Williams WP, Warburton ML (2017) Characterization of the maize lipoxygenase gene family in relation to aflatoxin accumulation resistance. PLoS One 12(7):e0181265. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181265
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang TC, Mendell JT, Salzberg SL (2015) StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol 33(3):290–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3122
Pigolev AV, Miroshnichenko DN, Pushin AS, Terentyev VV, Boutanayev AM, Dolgov SV, Savchenko TV (2018) Overexpression of Arabidopsis OPR3 in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) alters plant development and freezing tolerance. Int J Mol Sci. 19(12):3989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123989
Poosapati S, Poretsky E, Dressano K, Ruiz M, Vazquez A, Sandoval E, Estrada-Cardenas A, Duggal S, Lim JH, Morris G, Szczepaniec A, Walse SS, Ni X, Schmelz EA, Huffaker A (2022) A sorghum genome-wide association study (GWAS) identifies a WRKY transcription factor as a candidate gene underlying sugarcane aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) resistance. Planta 255(2):37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03814-x
Sarde SJ, Kumar A, Remme RN, Dicke M (2018) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression of lipoxygenase gene family in pepper. Plant Mol Biol 98(4–5):375–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0785-y
Shaban M, Ahmed MM, Sun H, Ullah A, Zhu L (2018) Genome-wide identification of lipoxygenase gene family in cotton and functional characterization in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Genomics 19(1):599. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4985-2
Shahzad MW, Razaq M, Hussain A, Yaseen M, Afzal M, Mehmood MK (2013) Yield and yield components of wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) affected by aphid feeding and sowing time at Multan, Pakistan. Pakistan J Bot. 45(6):2005–2011
Shewry PR (2009) Wheat. J Exp Bot 60(6):1537–1553. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp058
Shrestha K, Pant S, Huang Y (2021) Genome-wide identification and classification of lipoxygenase gene family and their roles in sorghum-aphid interaction. Plant Mol Biol 105(4–5):527–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01107-7
Smith CM, Boyko EV (2010) The molecular bases of plant resistance and defense responses to aphid feeding: current status. Entomol Exp Appl 122(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1570-7458.2006.00503.x
Stenzel I, Otto M, Delker C, Kirmse N, Schmidt D, Miersch O, Hause B, Wasternack C (2012) ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE (AOC) gene family members of Arabidopsis thaliana: tissue- and organ-specific promoter activities and in vivo heteromerization. J Exp Bot 63(17):6125–6138. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers261
Thackray DJ, Diggle AJ, Jones RAC (2010) BYDV PREDICTOR: a simulation model to predict aphid arrival, epidemics of barley yellow dwarf virus and yield losses in wheat crops in a mediterranean-type environment. Plant Pathol 58(1):186–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.01950.x
Tzin V, Fernandez-Pozo N, Richter A, Schmelz EA, Schoettner M, Schafer M, Ahern KR, Meihls LN, Kaur H, Huffaker A, Mori N, Degenhardt J, Mueller LA, Jander G (2015) Dynamic maize responses to aphid feeding are revealed by a time series of transcriptomic and metabolomic assays. Plant Physiol 169(3):1727–1743. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01039
Uhrig JF (2006) Protein interaction networks in plants. Planta 224(4):771–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0260-x
Ul Hassan MN, Zainal Z, Ismail I (2015) Green leaf volatiles: biosynthesis, biological functions and their applications in biotechnology. Plant Biotechnol J 13(6):727–739. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12368
Umate P (2011) Genome-wide analysis of lipoxygenase gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Signal Behav 6(3):335–338. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.3.13546
Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhao Y, Han G, Zhu S (2015) Systematic analysis of maize class III peroxidase gene family reveals a conserved subfamily involved in abiotic stress response. Gene 566(1):95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.041
Wang M, Tu L, Lin M, Lin Z, Wang P, Yang Q, Ye Z, Shen C, Li J, Zhang L, Zhou X, Nie X, Li Z, Guo K, Ma Y, Huang C, ** S, Zhu L, Yang X, Min L, Yuan D, Zhang Q, Lindsey K, Zhang X (2017) Asymmetric subgenome selection and cis-regulatory divergence during cotton domestication. Nat Genet 49(4):579–587. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3807
Woldemariam MG, Ahern K, Jander G, Tzin V (2018) A role for 9-lipoxygenases in maize defense against insect herbivory. Plant Signal Behav 13(1):e1422462. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2017.1422462
**ong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell. 14(Suppl (Suppl)):S165-183. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.000596
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57(1):781–803. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105444
Yan L, Zhai Q, Wei J, Li S, Wang B, Huang T, Du M, Sun J, Kang L, Li CB, Li C (2013) Role of tomato lipoxygenase D in wound-induced jasmonate biosynthesis and plant immunity to insect herbivores. PLoS Genet 9(12):e1003964. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003964
Yan J, Zhao C, Zhou J, Yang Y, Wang P, Zhu X, Tang G, Bressan RA, Zhu JK (2016) The miR165/166 mediated regulatory module plays critical roles in ABA homeostasis and response in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 12(11):e1006416. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006416
Yang G, Pan W, Zhang R, Pan Y, Guo Q, Song W, Zheng W, Nie X (2021) Genome-wide identification and characterization of caffeoyl-coenzyme A O-methyltransferase genes related to the fusarium head blight response in wheat. BMC Genomics 22(1):504. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07849-y
Zarate SI, Kempema LA, Walling LL (2007) Silverleaf whitefly induces salicylic acid defenses and suppresses effectual jasmonic acid defenses. Plant Physiol 143(2):866–875. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.090035
Zeb Q, Badshah H, Ali H, Shah RA, Rehman M (2011) Population of aphids on different varieties/lines of wheat and their effect on yield and thousands grain weight. Sarhad J Agric 27:443–450
Zhang X, Wang G, Qu X, Wang M, Guo H, Zhang L, Li T, Wang Y, Zhang H, Ji W (2022) A truncated CC-NB-ARC gene TaRPP13L1-3D positively regulates powdery mildew resistance in wheat via the RanGAP-WPP complex-mediated nucleocytoplasmic shuttle. Planta 255(3):60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-022-03843-0
Zhou M, Tang W (2019) MicroRNA156 amplifies transcription factor-associated cold stress tolerance in plant cells. Mol Genet Genomics 294(2):379–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1516-4
Zhou G, Ren N, Qi J, Lu J, **ang C, Ju H, Cheng J, Lou Y (2014) The 9-lipoxygenase Osr9-LOX1 interacts with the 13-lipoxygenase-mediated pathway to regulate resistance to chewing and piercing-sucking herbivores in rice. Physiol Plant 152(1):59–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12148
Zhou Y, Zhao X, Li Y, Xu J, Lu F (2020) Triticum population sequencing provides insights into wheat adaptation. Nat Genet 52(12):1412–1422. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00722-w
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the available public data that were used in our studies. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation China (No. 31871614), the Key R & D program of Shaanxi Province (2022NY-183) and Crop Germplasm Resources Protection (No. 2019NWB036-02-1).
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation China, No. 31871614, Wanquan Ji, the Key R & D program of Shaanxi Province, 2022NY-183, Wanquan Ji, Crop Germplasm Resources Protection, No. 2019NWB036-02-1, Wanquan Ji.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Luo, Y., Yu, J. et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of lipoxygenase genes related to the English grain aphid infestation response in wheat. Planta 257, 84 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04114-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04114-2