Abstract
Main conclusion
For the first time we provide a study on the physiological, ultrastructural and molecular effects of salt stress on a terrestrial symbiotic green microalga, Trebouxia sp. TR9.
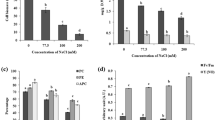
Although tolerance to saline conditions has been thoroughly studied in plants and, to an extent, free-living microalgae, scientific data regarding salt stress on symbiotic lichen microalgae is scarce to non-existent. Since lichen phycobionts are capable of enduring harsh, restrictive and rapidly changing environments, it is interesting to study the metabolic machinery operating under these extreme conditions. We aim to determine the effects of prolonged exposure to high salt concentrations on the symbiotic phycobiont Trebouxia sp. TR9, isolated from the lichen Ramalina farinacea. Our results suggest that, when this alga is confronted with extreme saline conditions, the cellular structures are affected to an extent, with limited chlorophyll content loss and photosynthetic activity remaining after 72 h of exposure to 5 M NaCl. Furthermore, this organism displays a rather different molecular response compared to land plants and free-living halophile microalgae, with no noticeable increase in ABA levels and ABA-related gene expression until the external NaCl concentration is raised to 3 M NaCl. Despite this, the ABA transduction pathway seems functional, since the ABA-related genes tested are responsive to exogenous ABA. These observations could suggest that this symbiotic green alga may have developed alternative molecular pathways to cope with highly saline environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez R, del Hoyo A, Díaz-Rodríguez C et al (2015) Lichen rehydration in heavy metal-polluted environments: Pb modulates the oxidative response of both Ramalina farinacea thalli and its isolated microalgae. Microb Ecol 69:698–709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0524-0
Archibald PA (1977) Physiological characteristics of Trebouxia (Chlorophyceae, Chlorococcales) and Pseudotrebouxia (Chlorophyceae, Chlorosarcinales). Phycologia 16:295–300. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-16-3-295.1
Armstrong RA (2017) Adaptation of lichens to extreme conditions. In: Kumar V, Shukla S, Kumar N (eds) Plant adaptation strategies in changing environment. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 1–27
Arup U (1995) Littoral species of Caloplaca in North America: a summary and a key. Bryologist 98:129–140. https://doi.org/10.2307/3243649
Aschenbrenner IA, Cernava T, Berg G, Grube M (2016) Understanding microbial multi-species symbioses. Front Microbiol 7:180. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00180
Balarinová K, Barták M, Hazdrová J, Hájek J, Jílková J (2014) Changes in photosynthesis, pigment composition and glutathione contents in two Antarctic lichens during a light stress and recovery. Photosynthetica 52:538–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-014-0060-7
Biosca EG, Flores R, Santander RD, Díez-Gil JL, Barreno E (2016) Innovative approaches using lichen enriched media to improve isolation and culturability of lichen associated bacteria. PLoS One 11:e0160328. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160328
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Some soil algae from Enchanted Rock and related algal species. Phycol Stud 44(1):1–95
Borges L, Caldas S, Montes D’Oca MG, Abreu PC (2016) Effect of harvesting processes on the lipid yield and fatty acid profile of the marine microalga Nannochloropsis oculata. Aquac Rep 4:164–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2016.10.004
Brandt A, Posthoff E, de Vera J-P, Onofri S, Ott S (2016) Characterisation of growth and ultrastructural effects of the Xanthoria elegans photobiont after 1.5 years of space exposure on the International Space Station. Orig Life Evol Biosph 46:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11084-015-9470-1
Brányiková I, Maršálková B, Doucha J et al (2011) Microalgae—novel highly efficient starch producers. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:766–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23016
Callis J, Carpenter T, Sun CW, Vierstra RD (1995) Structure and evolution of genes encoding polyubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia. Genetics 139:921–939
Campenni L, Nobre BP, Santos CA et al (2013) Carotenoid and lipid production by the autotrophic microalga Chlorella protothecoides under nutritional, salinity, and luminosity stress conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1383–1393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4570-6
Casano LM, del Campo EM, García-Breijo FJ et al (2011) Two Trebouxia algae with different physiological performances are ever-present in lichen thalli of Ramalina farinacea. Coexistence versus competition? Environ Microbiol 13:806–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02386.x
Chettri M, Cook C, Vardaka E, Sawidis T, Lanaras L (1998) The effect of Cu, Zn and Pb on the chlorophyll content of the lichens Cladonia convoluta and Cladonia rangiformis. Environ Exp Bot 39:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(97)00024-5
Cornillon P-A (2012) R for statistics. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Cowan AK, Rose PD, Horne LG (1992) Dunaliella salina: a model system for studying the response of plant cells to stress. J Exp Bot 43:1535–1547. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/43.12.1535
Czechowski T, Stitt M, Altmann T, Udvardi MK, Scheible WR (2005) Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:5–17. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.063743
Danquah A, de Zelicourt A, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2014) The role of ABA and MAPK signaling pathways in plant abiotic stress responses. Biotechnol Adv 32:40–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.09.006
Delmail D, Labrousse P, Hourdin P et al (2013) Micropropagation of Myriophyllum alterniflorum (Haloragaceae) for stream rehabilitation: first in vitro culture and reintroduction assays of a heavy-metal hyperaccumulator immersed macrophyte. Int J Phytoremediation 15:647–662. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2012.723068
Dragone G, Fernandes BD, Abreu AP, Vicente AA, Teixeira JA (2011) Nutrient limitation as a strategy for increasing starch accumulation in microalgae. Appl Energy 88:3331–3335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.03.012
Duarte AWF, Passarini MRZ, Delforno TP et al (2016) Yeasts from macroalgae and lichens that inhabit the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol Rep 8:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12452
Durgbanshi A, Arbona V, Pozo O et al (2005) Simultaneous determination of multiple phytohormones in plant extracts by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 53:8437–8442. https://doi.org/10.1021/JF050884B
Einspahr KJ, Maeda M, Thompson GA (1988) Concurrent changes in Dunaliella salina ultrastructure and membrane phospholipid metabolism after hyperosmotic shock. J Cell Biol 107:529–538. https://doi.org/10.1083/JCB.107.2.529
Gasulla F, de Nova PG, Esteban-Carrasco A et al (2009) Dehydration rate and time of desiccation affect recovery of the lichenic algae Trebouxia erici: alternative and classical protective mechanisms. Planta 231:195–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1019-y
Gasulla F, Guéra A, Barreno E (2010) A simple and rapid method for isolating lichen photobionts. Symbiosis 51:175–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-010-0064-4
Gómez-Cadenas A, Arbona V, Jacas J, Primo-Millo E, Talon M (2002) Abscisic acid reduces leaf abscission and increases salt tolerance in citrus plants. J Plant Growth Regul 21:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-002-0013-4
Green TGA, Brabyn L, Beard C, Sancho LG (2012) Extremely low lichen growth rates in Taylor Valley, Dry Valleys, continental Antarctica. Polar Biol 35:535–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-011-1098-7
Grube M, Blaha J (2005) Halotolerance and lichen symbioses. In: Gunde-Cimerman N, Oren A, Plemenitaš A (eds) Adaptation to life at high salt concentrations in Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Springer, Berlin, pp 471–488
Guéra A, Calatayud A, Sabater B, Barreno E (2004) Involvement of the thylakoidal NADH-plastoquinone-oxidoreductase complex in the early responses to ozone exposure of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. J Exp Bot 56:205–218. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri024
Gustavs L, Eggert A, Michalik D, Karsten U (2010) Physiological and biochemical responses of green microalgae from different habitats to osmotic and matric stress. Protoplasma 243:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-009-0060-9
Hauser F, Rainer W, Schroeder JI (2011) Evolution of abscisic acid synthesis and signaling mechanisms. Curr Biol 21:346–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.015.Hauser
Hayashi H, Alia L, Mustardy L, Ida M, Murata N (1997) Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana with the codA gene for choline oxidase; accumulation of glycine betaine and enhanced tolerance to salt and cold stress. Plant J 12:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.12010133.x
Hiremath S, Mathad P (2010) Impact of salinity on the physiological and biochemical traits of Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck. J Algal Biomass Util 1:51–59
Hirsch R, Hartung W, Gimmler H (1989) Abscisic acid content of algae under stress. Bot Acta 102:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.1989.tb00113.x
Jameson P (1993) Plant hormones in the algae. Prog Phycol Res 9:239–279
Kibbe WA (2007) OligoCalc: an online oligonucleotide properties calculator. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W43–W46. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm234
Kirk PM, Cannon PF, David JC, Stalpers JA (2001) Ainsworth and Bisby’s dictionary of the fungi, 9th edn. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK
Kline KG, Barrett-Wilt GA, Sussman MR (2010) In planta changes in protein phosphorylation induced by the plant hormone abscisic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15986–15991. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1007879107
Koizumi M, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Tsuji H, Shinozaki K (1993) Structure and expression of two genes that encode distinct drought-inducible cysteine proteinases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 129:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(93)90266-6
Krause GH, Weis E (1991) Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: the basics. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:313–349. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.42.060191.001525
Lan SB, Wu L, Zhang DL, Hu CX, Liu YD (2010) Effects of drought and salt stresses on man-made cyanobacterial crusts. Eur J Soil Biol 46:381–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2010.08.002
Leavitt SD, Kraichak E, Nelsen MP et al (2015) Fungal specificity and selectivity for algae play a major role in determining lichen partnerships across diverse ecogeographic regions in the lichen-forming family Parmeliaceae (Ascomycota). Mol Ecol 24:3779–3797. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13271
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/METH.2001.1262
Lu Y, Xu J (2015) Phytohormones in microalgae: a new opportunity for microalgal biotechnology? Trends Plant Sci 20:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.01.006
Malaspina P, Giordani P, Pastorino G, Modenesi P, Mariotti MG (2015) Interaction of sea salt and atmospheric pollution alters the OJIP fluorescence transient in the lichen Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf. Ecol Indic 50:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.015
Mane AV, Karadge BA, Samant JS (2010) Salt stress induced alteration in photosynthetic pigments and polyphenols of Pennisetum alopecuroides (L.). J Ecophysiol Occup Health 10:177–182. https://doi.org/10.18311/jeoh/2010/18339
Maphangwa KW, Musil CF, Raitt L, Zedda L (2012) Experimental climate warming decreases photosynthetic efficiency of lichens in an arid South African ecosystem. Oecologia 169:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-2184-9
Margulis L, Barreno E (2003) Looking at lichens. Bioscience 53:776–778. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053%5b0776:lal%5d2.0.co;2
Maršálek B, Zahradníčková H, Hronková M (1992) Extracellular abscisic acid produced by cyanobacteria under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 139:506–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)80503-1
Martínez-Alberola F (2015) Genome characterization of the symbiotic microalga Trebouxia sp. TR9 isolated from the lichen Ramalina farinacea (L.) Ach. by means of NGS techniques. PhD Dissertation. Universitat de València. http://roderic.uv.es/handle/10550/48824
Mishra A, Jha B (2009) Isolation and characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from micro-algae Dunaliella salina under salt stress. Bioresour Technol 100:3382–3386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.02.006
Molins A, Moya P, García-Breijo FJ, Reig-Arminana J, Barreno E (2018) A multi-tool approach to assess microalgal diversity in lichens: isolation, Sanger sequencing, HTS and ultrastructural correlations. Lichenologist 50:123–138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0024282917000664
Moya P, Molins A, Martínez-Alberola F, Muggia L, Barreno E (2017) Unexpected associated microalgal diversity in the lichen Ramalina farinacea is uncovered by pyrosequencing analyses. PLoS One 12:e0175091. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175091
Nash TH III, Lange OL (1988) Responses of lichens to salinity: concentration and time-course relationships and variability among Californian species. New Phytol 109:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1988.tb04206.x
Neale PJ, Melis A (1989) Salinity-stress enhances photoinhibition of photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Plant Physiol 134:619–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(89)80158-0
Negrão S, Schmöckel SM, Tester M (2017) Evaluating physiological responses of plants to salinity stress. Ann Bot 119:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcw191
Qiao K, Takano T, Liu S (2015) Discovery of two novel highly tolerant NaHCO3 Trebouxiophytes: identification and characterization of microalgae from extreme saline–alkali soil. Algal Res 9:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.03.023
Ruzin SE (2000) Plant microtechnique and microscopy. New Phytol 148:57–58
Schwartz SH, Tan BC, Gage DA, Zeevaart JAD, McCarty DR (1997) Specific oxidative cleavage of carotenoids by VP14 of maize. Science 276:1872–1874. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5320.1872
Škaloud P, Peksa O (2010) Evolutionary inferences based on ITS rDNA and actin sequences reveal extensive diversity of the common lichen alga Asterochloris (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta). Mol Phylogenet Evol 54:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMPEV.2009.09.035
Spribille T, Tuovinen V, Resl P et al (2016) Basidiomycete yeasts in the cortex of ascomycete macrolichens. Science 353:488–492. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8287
Stepien P, Johnson GN (2009) Contrasting responses of photosynthesis to salt stress in the glycophyte Arabidopsis and the halophyte Thellungiella: role of the plastid terminal oxidase as an alternative electron sink. Plant Physiol 149:1154–1165. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.132407
Takagi M, Karseno YT (2006) Effect of salt concentration on intracellular accumulation of lipids and triacylglyceride in marine microalgae Dunaliella cells. J Biosci Bioeng 101:223–226. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.223
Takahagi T, Yamamoto Y, Kinoshita Y, Takeshita S, Yamada T (2002) Inhibitory effects of sodium chloride on induction of tissue cultures of lichens of Ramalina species. Plant Biotechnol 19:53–55. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.19.53
Tietz A, Kasprik W (1986) Identification of abscisic acid in a green alga. Biochem Physiol Pflanz 181:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-3796(86)80093-2
Wani SH, Kumar V, Shriram V, Sah SK (2016) Phytohormones and their metabolic engineering for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Crop J 4:162–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2016.01.010
Wellburn AR, Lichtenthaler H (1984) Formulae and program to determine total carotenoids and chlorophylls A and B of leaf extracts in different solvents. In: Sybesma C (ed) Advances in photosynthesis research. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 9–12
Zhang J, Jia W, Yang J, Ismail AM (2006) Role of ABA in integrating plant responses to drought and salt stresses. Field Crop Res 97:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.08.018
Acknowledgements
Supported by the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MINECO, Spain) and FEDER (CGL2016-79158-P), and the PROMETEO Excellence in Research Program (Generalitat Valenciana, Spain) (PROMETEO/2017/039). Funding for Ernesto Hinojosa-Vidal was also provided by MINECO (BES-2013-065511). We want to thank the technicians (Mª Teresa Mínguez and Nuria Cebrián) from the Servicio de Microscopía Electrónica (SCSIE) and Jardí Botànic (Universitat de Valencia) who helped us to perform the TEM process; Dr. Ángeles Calatayud (IVIA, Valencia) for her valuable remarks on fluorescence analysis and Guillermo Salvá who performed the earliest experiments and fluorescence measurements. Daniel Sheerin revised the English manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinojosa-Vidal, E., Marco, F., Martínez-Alberola, F. et al. Characterization of the responses to saline stress in the symbiotic green microalga Trebouxia sp. TR9. Planta 248, 1473–1486 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2993-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2993-8