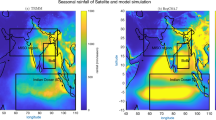
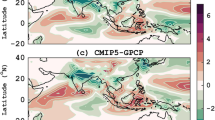
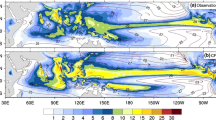
Abstract
The performances of four Chinese AGCMs participating in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) in the simulation of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation (BSISO) are assessed. The authors focus on the major characteristics of BSISO: the intensity, significant period, and propagation. The results show that the four AGCMs can reproduce boreal summer intraseasonal signals of precipitation; however their limitations are also evident. Compared with the Climate Prediction Center Merged Analysis of Precipitation (CMAP) data, the models underestimate the strength of the intraseasonal oscillation (ISO) over the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean (IO) during the boreal summer (May to October), but overestimate the intraseasonal variability over the western Pacific (WP). In the model results, the westward propagation dominates, whereas the eastward propagation dominates in the CMAP data. The northward propagation in these models is tilted southwest-northeast, which is also different from the CMAP result. Thus, there is not a northeast-southwest tilted rain belt revolution off the equator during the BSISO’s eastward journey in the models. The biases of the BSISO are consistent with the summer mean state, especially the vertical shear. Analysis also shows that there is a positive feedback between the intraseasonal precipitation and the summer mean precipitation. The positive feedback processes may amplify the models’ biases in the BSISO simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai, H., and K. R. Sperber, 2005: Regional heat sources and the active and break phases of boreal summer intraseasonal (30–50 day) variability. J. Atmos. Sci., 62, 2726–2748.
Bao, Q., G. X. Wu, Y. M. Liu, J. Yang, Z. Z. Wang, and T. J. Zhou, 2010: An introduction to the coupled model FGOALS1.1-s and its performance in East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 27, 1131–1142, doi: 10.1007/s00376-010-9177-1.
Bao, Q., and Coauthors, 2013: The flexible global oceanatmosphereland system model, spectral version 2: FGOALSs2. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 561–576, doi: 10.1007/s00376-012-2113-9.
Hsu, P. C., and T. Li, 2012: Role of the boundary layer moisture asymmetry in causing the eastward propagation of the Madden-Julian Oscillation. J. Climate, 25, 4914–4931.
Inness, P. M., J. M. Slingo, E. Guilyardi, and J. Cole, 2003: Simulation of the Madden-Julian oscillation in a coupled general circulation model. Part II: The role of the basic state. J. Climate, 16, 365–382.
Jia, X. L., C. Y. Li, N. F. Zhou, and J. Ling, 2009: The MJO in an AGCM with three different cumulus parameterization schemes. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans, 49, 141–163.
Jiang, J. H., and Coauthors, 2012: Evaluation of cloud and water vapor simulations in CMIP5 climate models using NASA “ATrain” satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res., 117, D14105, doi: 10.1029/2011JD017237.
Jiang, X., and T. Li, 2005: Reinitiation of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Climate, 18, 3777–3795.
Jiang, X., T. Li, and B. Wang, 2004: Structures and mechanisms of the northward propagating boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J. Climate, 17, 1022–1039.
Kemball-Cook, S., and B. Wang, 2001: Equatorial waves and airsea interaction in the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J. Climate, 14, 2923–2942.
Knutson, T. R., and K. M. Weickmann, 1987: 30–60-day atmospheric oscillations: Composite life cycles of convection and circulation anomalies. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 1407–1436.
Lau, K. M., and P. H. Chan, 1986: Aspects of the 40–50 day oscillation during the northern summer as inferred from the outgoing long-wave radiation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 114, 1354–1367.
Lau, W. K. M., and D. E. Waliser, Eds., 2005: Intraseasonal Variability of the Atmosphere-Ocean Climate System. Springer, Heidelberg, 614 pp.
Li, C. Y., Z. X. Long, and Q. Y. Zhang, 2001: Strong/weak summer monsoon activity over the South China Sea and atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 1146–1160.
Li, C. Y., X. L. Jia, J. A. Ling, W. Zhou, and C. D. Zhang, 2009: Sensitivity of MJO simulations to convective heating profiles. Climate Dyn., 32, 167–187.
Li, L. J., and Coauthors, 2013: The flexible global oceanatmosphereland system model, Grid-point Version 2: FGOALS-g2. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 543–560, doi: 10.1007/s00376-012-2140-6.
Li, T., X. Jia, and M. Dong, 2006: The importance of the atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation in the prediction of the weather and climate. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 64, 412–419. (in Chinese)
Liebmann, B., H. H. Hendon, and J. D. Glick, 1994: The relationship between tropical cyclones of the western Pacific and Indian Oceans and the Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 72, 401–411.
Lin, J. L., K. M. Weickman, G. N. Kiladis, B. E. Mapes, S. D. Schubert, M. J. Suarez, J. T. Bacmeister, and M. I. Lee, 2008: Subseasonal variability associated with Asian summer monsoon simulated by 14 IPCC AR4 coupled GCMs. J. Climate, 21, 4541–4567.
Maloney, E. D., and D. L. Hartman, 2001: The sensitivity of intraseasonal variability in the NCAR CCM3 to changes in convective parameterization. J. Climate, 14, 2015–2034.
Morrison, H., and A. Gettelman, 2008: A new two-moment bulk stratiform cloud microphysics scheme in the community atmosphere model, version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and numerical tests. J. Climate, 21, 3642–3659.
Nakazawa, T., 1986: Intraseasonal variations of OLR in the tropics during the FGGE year. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 64, 17–34.
Ray, P., and T. Li, 2013: Relative roles of circumnavigating waves and extratropics on the MJO and its relationship with the mean state. J. Atmos. Sci., 70, 876–893.
Saha, S., and Coauthors, 2006: The NCEP climate forecast system. J. Climate, 19, 3483–3517.
Saha, S., and Coauthors, 2010: The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 91, 1015–1057.
Seo, K.-H., J.-K. Schemm, C. Jones, and S. Moorthi, 2005: Forecast skill of the Tropical Intraseasonal Oscillation in the NCEP GFS dynamical extended range forecasts. Climate Dyn., 25, 265–284.
Seo, K.-H., J.-K. E. Schemm, W. Wang, and A. Kumar, 2007: The boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation simulated in the NCEP Climate Forecast System (CFS): The effect of sea surface temperature. Mon. Wea. Rev., 135, 1807–1827.
Sikka, D. R., and S. Gadgil, 1980: On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over Indian longitudes during the southwest monsoon. Mon. Wea. Rev., 108, 1840–1853.
Slingo, J. M., and Coauthors, 1996: Intraseasonal oscillation in 15 atmospheric general circulation models: Results from an AMIP diagnostic subproject. Climate Dyn., 12, 325–357.
Sperber, K. R., H. Annamalai, I.-S. Kang, A. Kitoh, A. Moise, A. Turner, B. Wang, and T. Zhou, 2013: The Asian summer monsoon: An intercomparison of CMIP5 vs. CMIP3 simulations of the late 20th century. Climate Dyn., 41, 2711–2744, doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1607-6.
Taylor, K. E., R. J. Stouffer, and G. A. Meehl, 2009: A summary of the CMIP5 experiment design. [Available online at http://cmip-pcmdi.llnl.gov/cmip5/docs/Taylor -CMIP5-design.pdf]
Teng, H., and B. Wang, 2003: Interannual variations of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the Asian-Pacific region. J. Climate, 16, 3572–3584.
Waliser, D. E., and Coauthors, 2003: AGCM simulations of intraseasonal variability associated with the Asian summer monsoon. Climate Dyn., 21, 423–446.
Wang, B., and H. Rui, 1990: Synoptic climatology of transient tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 44, 43–61.
Wang, B., and X. **e, 1997: A Model for the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation. J. Atmos. Sci., 54, 72–86.
Wheeler, M. C., and G. N. Kiladis, 1999: Convectively coupled equatorial waves: Analysis of clouds and temperature in the wavenumber-frequency domain. J. Atmos. Sci., 56, 374–399.
Wheeler, M. C., and H. Hendon, 2004: An All-Season Real-Time multivariate MJO index: Development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Mon. Wea. Rev., 132, 1917–1932.
Wu, Q. Z., J. M. Feng, W. J. Dong, L. N. Wang, D. Y. Ji, and H. Q. Cheng, 2013: Introduction of the CMIP5 experiments carried out by BNU-ESM. Progressus Inquisitiones de Mutatione Climatis, 9, 291–294.
Wu, T. W., R. C. Yu, and F. Zhang, 2008: A modified dynamic framework for the atmospheric spectral model and its application. J. Atmos. Sci., 65, 2235–2253.
Wu, T. W., and Coauthors, 2010: The Bei**g climate center for atmospheric general circulation model (BCC AGCM 2.0.1): Description and its performance for the present-day climate. Climate Dyn., 34, 123–147.
**e, P., and P. A. Arkin, 1997: Global precipitation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 78, 2539–2558.
**e, P., and Coauthors, 2003: GPCP pentad precipitation analyses: An experimental dataset based on gauge observations and satellite estimates. J. Climate, 16, 2197–2214.
Yang, J., Q. Bao, and X. C. Wang, 2013: Intensified eastward and northward propagation of tropical intraseasonal oscillation over the equatorial Indian Ocean in a global warming scenario. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 167–174, doi: 10.1007/s00376-012-1260-3.
Yasunari, T., 1979: Cloudiness fluctuations associated with the northern hemisphere summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 57, 227–242.
Yasunari, T., 1980: A quasi-stationary appearance of 30 to 40 day period in the cloudiness fluctuations during the summer monsoon over India. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 58, 225–229.
Zhang, C, M. Dong, S. Gualdi, H. H. Hendon, E. D. Maloney, A. Marshall, K. R. Sperber, and W. Wang, 2006: Simulations of the Madden-Julian oscillation by four pairs of coupled and uncoupled global models. Climate Dyn., 27, 573–592.
Zhang, G. J., and M. Mu, 2005: Effects of modifications to the Zhang-McFarlane convection parameterization on the simulation of the tropical precipitation in the national center for atmospheric research community climate model, version 3. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D09109, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005617.
Zhao, C. B., T. Li, and T. J. Zhou, 2013: Precursor signals and processes associated with MJO initiation over the Tropical Indian Ocean. J. Climate, 26, 291–307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Zhou, T., Song, L. et al. The boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation simulated by four Chinese AGCMs participating in the CMIP5 project. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 31, 1167–1180 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-3211-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-3211-7