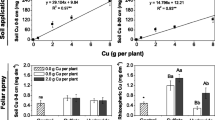
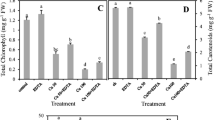
Abstract
In China, high copper (Cu) and low organic matter often occur in some citrus orchard soils. However, the underlying mechanisms by which humic acid (HA) stimulates growth and mitigates Cu toxicity of citrus seedlings are unclear. After being treated with 0, 0.1, or 0.5 mM sodium humate and 0.5 or 400 μM CuCl2 (Cu excess) for 24 weeks, sweet orange [Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck cv. Xuegan] seedlings were used to examine the impacts of HA-Cu interactions on seedling growth, nutrient uptake, leaf pigments, and photosynthetic performance that was revealed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. Copper excess reduced root, stem, and leaf dry weight (DW) by 42.4%, 65.4%, and 61.6%, respectively at 0 mM HA, and by 17.3%, 25.4%, and 31.4%, respectively at 0.5 mM HA; and that the levels of Cu in leaves, stems, and roots declined with elevating HA supply. Copper excess caused some rotten and dead fibrous roots at 0 mM HA, but not at 0.5 mM HA. Adding HA lowered Cu uptake per root DW (UPR), the levels of Cu in leaves, stems, and roots, and the competition of Cu2+ with Mg2+ and Fe2+, and therefore mitigated root impairment caused by Cu excess. The HA-mediated alleviation of root damage caused by Cu excess increased the uptake per plant and UPR of nitrogen, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, sulfur, boron, and manganese, and therefore alleviated Cu excess-induced decline in seedling growth, impairment to leaf photosynthetic electron transport chains, and decrease in leaf pigments. For 0.5 μM Cu-treated seedlings, adding HA promoted seedling growth by improving root nutrient uptake and leaf photosynthetic performance. Cu excess aggravated the impacts of HA supplementation on seedling growth, leaf photosynthetic performance, and root nutrient uptake.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162
Akinci Ş, Büyükkeskin T, Eroğlu A, Erdoğan BE (2009) The effect of humic acid on nutrient composition in broad bean (Vicia faba L.) roots. Not Sci Biol 1:81–87
Albano JP, Bowman KD, Wilson PC (2013) Differential response of citrus rootstocks to CuEDTA concentration in sand culture. J Appl Horti 15:81–86
Baldi E, Miotto A, Ceretta CA, Brunetto G, Muzzi E, Sorrenti G, Quartieri M, Toselli M (2018) Soil application of P can mitigate the copper toxicity in grapevine: physiological implications. Sci Horti 238:400–407
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Function of nutrients: micronutrients. In: Marschner P (ed) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic, Amsterdam, pp 191–248
Cai L-Y, Zhang J, Ren Q-Q, Lai Y-H, Peng M-Y, Deng C-L, Ye X, Yang L-T, Huang Z-R, Chen L-S (2021) Increased pH-mediated alleviation of copper-toxicity and growth response function in Citrus sinensis seedlings. Sci Horti 288:110310
Canellas LP, Olivares FL, Aguiar NO, Jones DL, Nebbioso A, Mazzei P, Piccolo A (2015) Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci Horti 196:15–27
Chen L-S, Cheng L (2010) The acceptor side of photosystem II is damaged more severely than the donor side of photosystem II in ‘Honeycrisp’ apple leaves with zonal chlorosis. Acta Physiol Plant 32:253–261
Chen AH, Jiao BN, Wang CQ (2011) Extraction of mineral elements from citrus leaves with boiling hydrochloric acid. J Fruit Sci 28:1107–1110
Chen BC, Ho PC, Juang KW (2013) Alleviation effects of magnesium on copper toxicity and accumulation in grapevine roots evaluated with biotic ligand models. Ecotoxicology 22:174–183
Chen M, Fang X, Wang Z, Shangguan L, Liu T, Chen C, Liu Z, Ge M, Zhang C, Zheng T, Fang J (2021) Multi-omics analyses on the response mechanisms of ‘Shine Muscat’ grapevine to low degree of excess copper stress (Low-ECS). Environ Pollut 286:117278
Chen X-F, Hua D, Zheng Z-C, Zhang J, Huang W-T, Chen H-H, Huang Z-R, Yang L-T, Ye X, Chen L-S (2022) Boron-mediated amelioration of copper-toxicity in sweet orange [Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck cv. Xuegan] seedlings involved reduced damage to roots and improved nutrition and water status. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 234:113423
Chen H-H, Zheng Z-C, Chen W-S, Rao R-Y, Chen X-F, Ye X, Guo J, Yang L-T, Chen L-S (2023) Regulation on copper-tolerance in Citrus sinensis seedlings by boron addition: insights from root exudates, related metabolism, and gene expression. J Hazard Mater 459:132277
Chen H-H, Zheng Z-C, Hua D, Chen X-F, Huang Z-R, Guo J, Yang L-T, Chen L-S (2024) Boron-mediated amelioration of copper toxicity in Citrus sinensis seedlings involved reduced concentrations of copper in leaves and roots and their cell walls rather than increased copper fractions in their cell walls. J Hazard Mater 467:133738
Cheng C, Zhang SQ, Lin WJ, Chen HH, Lin F, Zhu DH, Chen LS, Li Y, Guo JX (2018) Soil copper (Cu) nutrient status and its influencing factors in pomelo orchards in **he county, Fujian province. J Fruit Sci 35:301–310
Chrysargyris A, Maggini R, Incrocci L, Pardossi A (2021) Copper tolerance and accumulation on Pelargonium graveolens L’Hér grown in hydroponic culture. Plants 10:1663
David PP, Nelson PV, Sanders DC (1994) A humic acid improves growth of tomato seedling in solution culture. J Plant Nutr 17:173–184
El-Hoseiny HM, Helaly MN, Elsheery NI, Alam-Eldein SM (2020) Humic acid and boron to minimize the incidence of alternate bearing and improve the productivity and fruit quality of mango trees. HortScience 55:1026–1037
Elsheery NI, Sunoj VSJ, Wen Y, Zhu JJ, Muralidharan G, Cao KF (2020) Foliar application of nanoparticles mitigates the chilling effect on photosynthesis and photoprotection in sugarcane. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:50–60
Ennab HA, Mohamed AH, El-Hoseiny HM, Omar AA, Hassan IF, Gaballah MS, Khalil SE, Mira AM, Abd El-Khalek AF, Alam-Eldein SM (2023) Humic acid improves the resilience to salinity stress of drip-irrigated Mexican lime trees in saline clay soils. Agronomy 13:1680
Fagbenro JA, Agboola AA (1993) Effect of different levels of humic acid on the growth and nutrient uptake of teak seedlings. J Plant Nutr 16:1465–1483
Fan HM, Wang XW, Sun X, Li YY, Sun XZ, Zheng CS (2014) Effects of humic acid derived from sediments on growth, photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure in chrysanthemum. Sci Horti 177:118–123
Force L, Critchley C, van Rensen JJS (2003) New fluorescence parameters for monitoring photosynthesis in plants. Photosynth Res 78:17–33
Guo P, Qi Y-P, Cai Y-T, Yang T-Y, Yang L-T, Huang Z-R, Chen L-S (2018) Aluminum effects on photosynthesis, reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal detoxification in two citrus species differing in aluminum tolerance. Tree Physiol 38:1548–1565
Haghighi M, Teixeira da Silva JA (2013) Amendment of hydroponic nutrient solution with humic acid and glutamic acid in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) culture. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 59:642–648
Hemati A, Alikhani HA, Ajdanian L, Babaei M, Asgari Lajayer B, van Hullebusch ED (2022a) Effect of different enriched vermicomposts, humic acid extract and indole-3-acetic acid amendments on the growth of Brassica napus. Plants 11:227
Hemati A, Alikhani HA, Babaei M, Ajdanian L, Asgari Lajayer B, van Hullebusch ED (2022b) Effects of foliar application of humic acid extracts and indole acetic acid on important growth indices of canola (Brassica napus L.). Sci Rep 12:20033
Hippler FWR, Boaretto RM, Dovis VL, Quaggio JA, Azevedo RA, Mattos-Jr D (2018) Oxidative stress induced by Cu nutritional disorders in citrus depends on nitrogen and calcium availability. Sci Rep 8:1641
Huang W-T, **e Y-Z, Chen X-F, Zhang J, Chen H-H, Ye X, Guo J-X, Yang L-T, Chen L-S (2021) Growth, mineral nutrients, photosynthesis and related physiological parameters of citrus in response to nitrogen deficiency. Agronomy 11:1859
Huang W-T, Zheng Z-C, Hua D, Chen X-F, Zhang J, Chen H-H, Ye X, Guo J-X, Yang L-T, Chen L-S (2022) Adaptive responses of carbon and nitrogen metabolisms to nitrogen-deficiency in Citrus sinensis seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 22:370
Inaba S, Takenaka C (2005) Effects of dissolved organic matter on toxicity and bioavailability of copper for lettuce sprouts. Environ Int 31:603–608
Jiang H-X, Chen L-S, Zheng J-G, Han S, Tang N, Smith B-R (2008) Aluminum-induced effects on photosystem II photochemistry in citrus leaves assessed by the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. Tree Physiol 28:1863–1871
Jiang Y, Li Z, Dong Z, Dong X, Wang X, Wang S, Qiu X (2023) Study on the evolution of citrus planting area and yield pattern in China from 1978 to 2020. China Agri Inform 35:43–54
Juang KW, Lee YI, Lai HY, Chen BC (2014) Influence of magnesium on copper phytotoxicity to and accumulation and translocation in grapevines. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:36–42
Kalaji HM, Schansker G, Ladle RJ, Goltsev V, Bosa K, Allakhverdiev SI, Brestic M, Bussotti F, Calatayud A, Dąbrowski P, Elsheery NI, Ferroni L, Guidi L, Hogewoning SW, Jajoo A, Misra AN, Nebauer SG, Pancaldi S, Penella C, Poli D, Pollastrini M, Romanowska-Duda ZB, Rutkowska B, Serôdio J, Suresh K, Szulc W, Tambussi E, Yanniccari M, Zivcak M (2014) Frequently asked questions about in vivo chlorophyll fluorescence: practical issues. Photosynth Res 122:121–158
Kalaji HM, Bąba W, Gediga K, Goltsev V, Samborska IA, Cetner MD, Dimitrovam S, Piszcz U, Bielecki K, Karmowska K, Dankov K, Kompała-Bąba A (2018) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool for nutrient status identification in rapeseed plants. Photosynth Res 136:329–343
Katkat AV, Çelik H, Turan MA, Asyk BB (2009) Effects of soil and foliar applications of humic substances on dry weight and mineral nutrients uptake of wheat under calcareous soil conditions. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3:1266–1273
Kowalenko CG, Lavkulich LM (1976) A modified curcumin method for boron analysis of soil extracts. Can J Soil Sci 56:537–539
Kumar V, Pandita S, Sidhu GPS, Sharma A, Khanna K, Kaur P, Bali AS, Setia R (2021) Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 262:127810
Lajayer HA, Savaghebi G, Hadian J, Hatami M, Pezhmanmehr M (2017) Comparison of copper and zinc effects on growth, micro- and macronutrients status and essential oil constituents in pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium L.). Braz J Bot 40:379–388
Li Y, Han M-Q, Lin F, Ten Y, Lin J, Zhu D-H, Guo P, Weng Y-B, Chen L-S (2015) Soil chemical properties, ‘Guanximiyou’ pummelo leaf mineral nutrient status and fruit quality in the southern region of Fujian province. China J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 15:615–628
Li Q, Chen H-H, Qi Y-P, Ye X, Yang L-T, Huang Z-R, Chen L-S (2019) Excess copper effects on growth, uptake of water and nutrients, carbohydrates, and PSII photochemistry revealed by OJIP transients in citrus seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:30188–30205
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Lin ZH, Chen LS, Chen RB, Zhang FZ, Jiang HX, Tang N (2009) CO2 assimilation, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, carbohydrates and photosynthetic electron transport probed by the JIP-test, of tea leaves in response to phosphorus supply. BMC Plant Biol 9:43
Liu M, Li XH, Liu WB, Yang L, Li JX (2019) Effect of humic acid on nitrogen metabolism at tomato seedling stage. J Soil Water Conserv 33:327–331
Long A, Zhang J, Yang L-T, Ye X, Lai N-W, Tan L-L, Lin D, Chen L-S (2017) Effects of low pH on photosynthesis, related physiological parameters, and nutrient profiles of citrus. Front Plant Sci 8:185
Lu RK (1999) Methods of soil and agrochemistry analysis. China Agriculture Science & Technology Press, Bei**g
Massoud MB, Sakouhi L, Chaoui A (2019) Effect of plant growth regulators, calcium and citric acid on copper toxicity in pea seedlings. J Plant Nutr 42:1230–1242
Mo X, Chen C, Riaz M, Moussa MG, Chen X, Wu S, Tan Q, Sun X, Zhao X, Shi L, Hu C (2022) Fruit characteristics of citrus trees grown under different soil Cu levels. Plants 11:2943
Musante C, White JC (2012) Toxicity of silver and copper to Cucurbita pepo: differential effects of nano and bulk-size particles. Environ Toxicol 27:510–517
Nardi S, Pizzeghello D, Muscolo A, Vianello A (2002) Physiological effects of humic substances on higher plants. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1527–1536
Nardi S, Schiavon M, Francioso O (2021) Chemical structure and biological activity of humic substances define their role as plant growth promoters. Molecules 26:2256
Nazir F, Fariduddin Q, Hussain A, Khan TA (2021) Brassinosteroid and hydrogen peroxide improve photosynthetic machinery, stomatal movement, root morphology and cell viability and reduce Cu-triggered oxidative burst in tomato. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111081
Nikbakht A, Kafi M, Babalar M, **a YP, Luo AC, Etemadi N (2008) Effect of humic acid on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and postharvest life of gerbera. J Plant Nutr 31:2155–2167
Noor I, Sohail H, Sun J, Nawaz MA, Li G, Hasanuzzaman M, Liu J (2022) Heavy metal and metalloid toxicity in horticultural plants: tolerance mechanism and remediation strategies. Chemosphere 303:135196
Olaetxea M, Mora V, Bacaicoa E, Baigorri R, Garnica M, Fuentes M, Zamarreño AM, Spíchal L, García-Mina JM (2019) Root ABA and H+-ATPase are key players in the root and shoot growth-promoting action of humic acids. Plant Direct 3:e00175
Ondrasek G, Rengel Z, Romic D (2018) Humic acids decrease uptake and distribution of trace metals, but not the growth of radish exposed to cadmium toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 151:55–61
Ouzounidou G, Ilias I, Tranopoulou H, Karataglis S (1998) Amelioration of copper toxicity by iron on spinach physiology. J Plant Nutr 21:2089–2101
Pätsikkä E, Kairavuo M, Šeršen F, Aro EM, Tyystjärvi E (2002) Excess copper predisposes photosystem II to photoinhibition in vivo by outcompeting iron and causing decrease in leaf chlorophyll. Plant Physiol 129:1359–1367
Peng C, Zhang H, Fang H, Xu C, Huang HM, Wang Y, Sun LJ, Yuan XF, Chen YX, Shi JY (2015) Natural organic matter–induced alleviation of the phytotoxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) caused by copper oxide nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:1996–2003
Peng XX, Gai S, Cheng K, Yang F (2022) Roles of humic substances redox activity on environmental remediation. J Hazard Mater 435:129070
Peng M-Y, Ren Q-Q, Lai Y-H, Zhang J, Chen H-H, Guo J, Yang L-T, Chen L-S (2023) Integration of physiology, metabolome and transcriptome for understanding of the adaptive strategies to long-term nitrogen deficiency in Citrus sinensis leaves. Sci Horti 317:112079
Ren C, You JW, Qi YB, Huang GY, Hu HQ (2017) Effects of sulfur on toxicity and bioavailability of Cu for castor (Ricinus communis L.) in Cu-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:27476–27483
Rose MT, Patti AF, Little KR, Brown AL (2014) A meta-analysis and review of plant-growth response to humic substances: practical implications for agriculture. Adv Agron 124:37–89
Schmidt W, Bartels M, Tittel J, Fühner C (1997) Physiological effects on iron acquisition processes in Plantago. New Phytol 135:659–666
Selim E-M, Mosa AA (2012) Fertigation of humic substances improves yield andquality of broccoli and nutrient retention in a sandy soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 175:273–281
Setlik I, Allakhverdiev SI, Nedbal L, Setlikova E, Klimov VV (1990) Three types of photosystem II photoinactivation. 1. Damaging processes on the acceptor side. Photosynth Res 23:39–48
Shabbir Z, Sardar A, Shabbir A, Abbas G, Shamshad S, Khalid S, Murtaza G, Dumat C, Shahid M (2020) Copper uptake, essentiality, toxicity, detoxification and risk assessment in soil-plant environment. Chemosphere 259:127436
Shah ZH, Rehman HM, Akhtar T, Alsamadany H, Hamooh BT, Mujtaba T, Daur I, Al Zahrani Y, Alzahrani HAS, Ali S, Yang SH, Chung G (2018) Humic substances: determining potential molecular regulatory processes in plants. Front Plant Sci 9:263
Spark KM, Wells JD, Johnson BB (1997) The interaction of a humic acid with heavy metals. Aust J Soil Res 35:89–101
Srivastava A, Guisse B, Greppin H, Strasser RJ (1997) Regulation of antenna structure and electron transport in photosystem II of Pisum sativum under elevated temperature probed by the fast polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient: OKJIP. Biochim Biophys Acta 1320:95–106
Strasser RJ, Tsimilli-Micheal M, Srivastava A (2004) Analysis of the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. In: Papageorgiou GCG (ed) Chlorophyll a fluorescence: a signature of photosynthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 321–362
Sun Y, Yang T (2023) Investigating the use of synthetic humic-like acid as a soil amendment for metal-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:16719–16728
Tan KH, Nopamornbodi V (1979) Effect of different levels of humic acids on nutrient content and growth of corn (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 51:283–287
Tan KH, Tantiwiramanond D (1983) Effect of humic acids on nodulation and dry matter production of soybean, peanut and clover. Soil Sci Soc Amer J 47:1121–1124
Thomas G, Andresen E, Mattusch J, Hubáček KH (2016) Deficiency and toxicity of nanomolar copper in low irradiance—a physiological and metalloproteomic study in the aquatic plant Ceratophyllum demersum. Aquat Toxicol 177:226–236
Tiwari J, Ramanathan AL, Bauddh K, Korstad J (2023) Humic substances: structure, function and benefits for agroecosystems—a review. Pedosphere 33:237–249
Trentin E, Cesco S, Pii Y, Valentinuzzi F, Celletti S, Feil SB, Zuluaga MYA, Ferreira PAA, Ricachenevsky FK, Stefanello LO, De Conti L, Brunetto G, Mimmo T (2022) Plant species and pH dependent responses to copper toxicity. Environ Exp Bot 196:104791
Ullah SM, Gerzabek MH (1991) Influence of fulvic and humic acids on Cu- and V-toxicity to Zea mays (L.). Bodenkultur 42:123–134
van de Tol Castro TA, Berbara RLL, Tavares OCH, Mello DFDG, Pereira EG, Souza CDCB, Espinosa LM, García AC (2021) Humic acids induce a eustress state via photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism leading to a root growth improvement in rice plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:171–184
Wan H, Du J, He J, Lyu D, Li H (2019) Copper accumulation, subcellular partitioning and physiological and molecular responses in relation to different copper tolerance in apple rootstocks. Tree Physiol 39:1215–1234
Wang Z, Chen Y (1997) Alleviation of copper toxicity to maize by phosphorus fertilizer in purple soil. Pedosphere 7:281–288
Wang YM, Zhou DM, Yuan XY, Zhang XH, Li Y (2018) Modeling the interaction and toxicity of Cu–Cd mixture to wheat roots affected by humic acids, in terms of cell membrane surface characteristics. Chemosphere 199:76–83
Wang M, Yuan M, Zhu PP, Ling LL, He YZ, Fu XZ, Peng LZ (2020) Physiological response and tolerance to copper toxicity of four citrus rootstock seedlings. Acta Hort Sin 47:1969–1981
Wu S, Liang S, Hu C, Tan Q, Zhang J, Dong Z (2022) Ecological region division of soil based supplementary fertilization and decrement fertilization in China citrus orchards. J Huazhong Agri Univ 41(2):9–19
Yarmohammadi A, Khoramivafa M, Honarmand SJ (2019) Humic acid reduces the CuO and ZnO nanoparticles cellular toxicity in rapeseed (Brassica napus). Cell Mol Biol 65(4):29–36
Yruela I (2009) Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 36(5):409–430
Zhang J, Chen X-F, Huang W-T, Chen H-H, Lai N-W, Yang L-T, Huang Z-R, Guo J, Chen L-S (2022) Mechanisms for increased pH-mediated amelioration of copper toxicity in Citrus sinensis leaves using physiology, transcriptomics and metabolomics. Environ Exp Bot 196:104812
Zhang J, Huang W-L, Huang W-T, Chen X-F, Chen H-H, Ye X, Yang L-T, Chen L-S (2023) Roles of hormones in elevated pH-mediated mitigation of copper toxicity in Citrus sinensis revealed by targeted metabolome. Plants 12:2144
Zheng Z-C, Chen H-H, Yang H, Shen Q, Chen X-F, Huang W-L, Yang L-T, Guo J, Chen L-S (2024) Citrus sinensis manganese tolerance: insight from manganese-stimulated secretion of root exudates and rhizosphere alkalization. Plant Physiol Biochem 206:108318
Zhou X, Shi H, Shi Z, Han Q, Sun Y, Chen Y (2018) Effects of NaHA treatments on wheat seed germination and seedling growth under lead and cadmium stresses. Mol Plant Breed 16:4793–4801
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072511) and the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-26-01A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WTH, NWL, LTY, ZRH, and LSC designed the experiment; WTH performed the experiments, QS, HY, XFC, WLH, and HXW participated in the experiments; WTH wrote the first version of the manuscript; LSC reviewed, revised, and validated the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Boon Chin Tan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, WT., Shen, Q., Yang, H. et al. Effects of Humic Acid-Copper Interactions on Growth, Nutrient Absorption, and Photosynthetic Performance of Citrus sinensis Seedlings in Sand Culture. J Plant Growth Regul (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-024-11359-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-024-11359-y