Abstract
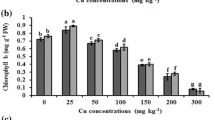
The biogeochemical cycling of sulfur (S) in soil has an important impact on the bioavailability of heavy metals and affects the utilization of soil polluted by heavy metals. In addition, S-containing compounds are involved in heavy metal detoxification. This study investigated the effects of S on the toxicity and bioavailability of copper (Cu) in castor (Ricinus communis L.) grown in Cu-contaminated mine tailings. The results showed that the application of S reduced the accumulation of Cu in castor and promoted its growth. With the addition of S, the malondialdehyde (MDA) content of castor leaves decreased significantly compared with control plants, indicating the alleviation of oxidative stress. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities and glutathione (GSH) content decreased significantly with the alleviation of oxidative stress. The sequential extraction of Cu fractions showed that the application of S significantly reduced the reducible Cu fraction, and increased the oxidizable Cu fraction. It also increased the residual Cu fraction in the soil. The transformation of chemical speciation reduced the bioavailability of Cu in soil, which then reduced the accumulation of Cu in castor. Our results demonstrated that S application was effective at promoting castor growth by reducing the bioavailability and uptake of Cu in Cu-contaminated mine tailings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astolfi S, Zuchi S, Passera C (2005) Effect of cadmium on H+ATPase activity of plasma membrane vesicles isolated from roots of different S-supplied maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Plant Sci 169:361–368
Astolfi S, Zuchi S, Neumann G et al (2012) Response of barley plants to Fe deficiency and Cd contamination as affected by S starvation. J Exp Bot 63(3):1241–1250
Borch T, Kretzschmar R, Kappler A et al (2010) Biogeochemical redox processes and their impact on contaminant dynamics. Environ Sci Technol 44(1):15–23
Brunetto G, Bastos de Melo GW, Terzano R et al (2016) Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: Rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity. Chemosphere 162:293–307
Choudhary SP, Bhardwaj R, Gupta BD et al (2010) Epibrassinolide induces changes in indole-3-acetic acid, abscisic acid and polyamine concentrations and enhances antioxidant potential of radish seedlings under copper stress. Physiol Plant 140(3):280–296
Choudhary SP, Oral HV, Bhardwaj R et al (2012) Interaction of brassinosteroids and polyamines enhances copper stress tolerance in Raphanus sativus. J Exp Bot 63(15):5659–5675
Da Silva NL, Maciel MRW, Batistella CB et al (2006) Optimization of biodiesel production from castor oil. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 130(1–3):405–414
Ferri A, Lancilli C, Maghrebi M et al (2017) The sulfate supply maximizing Arabidopsis shoot growth is higher under long- than short-term exposure to cadmium. Front Plant Sci 8:854
Flores-Cáceres ML, Hattab S, Hattab S et al (2015) Specific mechanisms of tolerance to copper and cadmium are compromised by a limited concentration of glutathione in alfalfa plants. Plant Sci 233:165–173
Fulda B, Voegelin A, Ehlert K et al (2013) Redox transformation, solid phase speciation and solution dynamics of copper during soil reduction and reoxidation as affected by sulfate availability. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 123:385–402
Gee G W, Bauder J W, Klute A (1986) USA. Particle-size analysis. Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Physical Mineralogical. Methods 383–411
Han D, Li X, **ong S et al (2013) Selenium uptake, speciation and stressed response of Nicotiana tabacum L. Environ Exp Bot 95:6–14
Han Y, Zhang L, Yang Y et al (2016) Pb uptake and toxicity to Iris halophila tested on Pb mine tailing materials. Environ Pollut 214:510–516
Hashem HA (2014) Cadmium toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters cytokinin content and antioxidant enzyme activities in soybean. Botany 92:1–7
Hodges DM, Andrews CJ, Johnson DA et al (1996) Antioxidant compound responses to chilling stress in differentially sensitive inbred maize lines. Physiol Plant 98(4):685–692
Hofacker AF, Voegelin A, Kaegi R et al (2013) Temperature-dependent formation of metallic copper and metal sulfide nanoparticles during flooding of a contaminated soil. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 103:316–332
Huang G, Su X, Rizwan MS et al (2016) Chemical immobilization of Pb, Cu, and Cd by phosphate materials and calcium carbonate in contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16845–16856
Kang W, Bao J, Zheng J et al (2015) Distribution and chemical forms of copper in the root cells of castor seedlings and their tolerance to copper phytotoxicity in hydroponic culture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(10):7726–7734
Khare R, Kumar S, Shukla T et al (2017) Differential sulphur assimilation mechanism regulates response of Arabidopsis thaliana natural variation towards arsenic stress under limiting sulphur condition. J Hazard Mater 337:198–207
Konno H, Nakato T, Nakashima S et al (2005) Lygodium japonicum fern accumulates copper in the cell wall pectin. J Exp Bot 56(417):1923–1931
Lancilli C, Giacomini B, Lucchini G et al (2014) Cadmium exposure and sulfate limitation reveal differences in the transcriptional control of three sulfate transporter (Sultr1; 2) genes in Brassica juncea. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):132
Lange B, Pourret O, Meerts P et al (2016) Copper and cobalt mobility in soil and accumulation in a metallophyte as influenced by experimental manipulation of soil chemical factors. Chemosphere 146:75–84
Ma T, Zhou L, Chen L et al (2016) Oxytetracycline toxicity and its effect on phytoremediation by Sedum plumbizincicola and Medicago sativa in metal-contaminated soil. J Agric Food Chem 64(42):8045–8053
Manceau A, Nagy KL, Marcus MA et al (2008) Formation of metallic copper nanoparticles at the soil− root interface. Environ Sci Technol 42(5):1766–1772
Martins LL, Mourato MP (2006) Effect of excess copper on tomato plants: growth parameters, enzyme activities, chlorophyll, and mineral content. J Plant Nutr 29(12):2179–2198
Morse JW, Luther GW (1999) Chemical influences on trace metal-sulfide interactions in anoxic sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:3373–3378
Mwamba TM, Li L, Gill RA et al (2016) Differential subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium and copper in Brassica napus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 134:239–249
Nakamura S, Suzui N, Nagasaka T et al (2013) Application of glutathione to roots selectively inhibits cadmium transport from roots to shoots in oilseed rape. J Exp Bot 64(4):1073–1081
Olivares AR, Carrillo-González R, González-Chávez MCA et al (2013) Potential of castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) for phytoremediation of mine tailings and oil production. J Environ Manag 114:316–323
Pinhero RG, Rao MV, Paliyath G et al (1997) Changes in activities of antioxidant enzymes and their relationship to genetic and paclobutrazol-induced chilling tolerance of maize seedlings. Plant Physiol 114(2):695–704
Ric De Vos CH, Vonk MJ, Vooijs R et al (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 98:853–858
Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Huang G et al (2016) Immobilization of Pb and Cu in polluted soil by superphosphate, multi-walled carbon nanotube, rice straw and its derived biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:15532–15543
Ryan BM, Kirby JK, Degryse F et al (2013) Copper speciation and isotopic fractionation in plants: uptake and translocation mechanisms. New Phytol 199(2):367–378
Samarth RM, Panwar M, Kumar M et al (2008) Evaluation of antioxidant and radical-scavenging activities of certain radioprotective plant extracts. Food Chem 106:868–873
Seth CS, Remans T, Keunen E et al (2012) Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a central role for glutathione. Plant Cell Environ 35(2):334–346
Sidhu GPS, Singh HP, Batish DR et al (2017) Tolerance and hyperaccumulation of cadmium by a wild, unpalatable herb Coronopus didymus (L.) Sm.(Brassicaceae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:209–215
Srivastava S, D’souza SF (2009) Increasing sulfur supply enhances tolerance to arsenic and its accumulation in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Technol 43:6308–6313
SSSC (Soil Science Society of China) (1999) Analysis methods for soil and agricultural chemistry. China Science and Technology Publishing House, Bei**g
Sun L, Zheng C, Yang J et al (2016) Impact of sulfur (S) fertilization in paddy soils on copper (Cu) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants under flooding conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 52(1):31–39
Wang YP, Li QB, Hui W et al (2008) Effect of sulphur on soil Cu/Zn availability and microbial community composition. J Hazard Mater 159(2):385–389
Wang C, Li G, Zhang Z et al (2013) Genetic diversity of castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) in Northeast China revealed by ISSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 51:301–307
Weber FA, Voegelin A, Kretzschmar R (2009) Multi-metal contaminated dynamics in temporarily flooded soil under sulfate limitation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:5513–5527
Wei S, Ma LQ, Saha U et al (2010) Sulfate and glutathione enhanced arsenic accumulation by arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Environ Pollut 158(5):1530–1535
Yang JX, Liu ZY, Wan XM et al (2016) Interaction between sulfur and lead in toxicity, iron plaque formation and lead accumulation in rice plant. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 128:206–212
Yin H, Tan N, Liu C et al (2016) The associations of heavy metals with crystalline iron oxides in the polluted soils around the mining areas in Guangdong Province, China. Chemosphere 161:181–189
Zhang M, Hu C, Zhao X et al (2012) Molybdenum improves antioxidant and osmotic-adjustment ability against salt stress in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Pekinensis). Plant Soil 355(1–2):375–383
Zhou W, Wan M, He P et al (2002) Oxidation of elemental sulfur in paddy soils as influenced by flooded condition and plant growth in pot experiment. Biol Fertil Soils 36:384–389
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (41371470) and the National Key Technology Support Program (2015BAD05B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roberto Terzano
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, C., You, J., Qi, Y. et al. Effects of sulfur on toxicity and bioavailability of Cu for castor (Ricinus communis L.) in Cu-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 27476–27483 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0306-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0306-6