Abstract
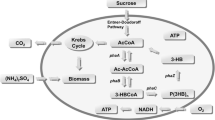
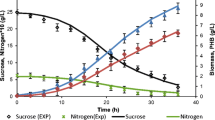
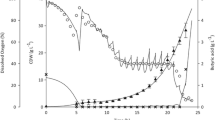
Successful scale-up of Bacillus subtilis culture for poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) production was performed in 5-l stirred-tank reactor using batch, fed-batch, and two-stage culture strategies. The kinetics of biomass production, substrate consumption, and PHB production were established in the stirred tank bioreactor in all the studies. A mathematical model was developed to investigate the role of limiting substrate on overall culture metabolism. A fed-batch strategy was predicted on the basis of computer simulations, for maximum PHB production. This was performed by extrapolation of batch model for predicting the feeding rate and suitable time of feeding. Substrate inhibition was studied and the substrate inhibition terms were incorporated in the model. The maximum cell biomass concentration in batch culture (24 h) and fed-batch culture (30 h) was 1.79 ± 0.03 g/l on dry cell weight (DCW) basis and 1.66 ± 0.050 g/l on DCW basis and the corresponding PHB content was 68.71% and 85.54% of DCW, respectively. Glucose was found to be the major limiting nutrient during the bioreactor culture. A two-stage culture, where cells were first grown in stage I in LBG media containing excess carbon and thereafter in stage II in OM media, showed biomass production of 1.95 ± 0.045 g/l at 4 h and PHB production of 93.33% of DCW at 16 h. A 9% increase in growth and 25% increase in PHB yield were obtained using two-stage culture with computer-simulated feeding strategy in the 5 l reactor. Oxygen limitation was overcome in modified two-stage culture to obtain a PHB production of 98% at 30 h.
Key points
• Polyhydroxybutyrate production was studied in a 5-l stirred-tank bioreactor using HPLC
• Mathematical model-assisted fed-batch strategy was implemented in bioreactor
• Two-stage fed-batch cultivation was implemented and PHB production was 93% of dry weight in Gram-positive bacteria





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Amon J, Titgemeyer F, Burkovski A (2010) Common patterns – unique features: nitrogen metabolism and regulation in Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:588–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00216.x
Aslam R, Saleem F, Saleem Y (2003) Biotechnological production of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) from Enterobacter aerogenes. Glob J Pure Appl Sci 1:1–8
Bergey DH, Holt JG (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland
Chaluvadi S, Ujjwal A, Singh RK (2019) Effect of torrefaction prior to biomass size reduction on ethanol production. Waste Biomass Valorization 10:3567–3577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0389-4
Gahlawat G, Srivastava AK (2013) Development of a mathematical model for the growth associated Polyhydroxybutyrate fermentation by Azohydromonas australica and its use for the design of fed-batch cultivation strategies. Bioresour Technol. 137:98–105 S0960–8524(13)00379–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.023
Ge L, Tan G-Y A, Wang L, Chen C-L, Li L, Tan S N, Wang J-Y (2016) Determination of monomeric composition in polyhydroxyalkanoates by liquid chromatography coupled with on-line mass spectrometry and off-line nuclear magnetic resonance. Talanta. 146: 107–113 ISSN 0039–9140
Gomaa EZ (2014) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) by Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli grown on cane molasses fortified with ethanol. Braz Arch Biol Technol 57:145–154
Gouda MK, Swellam AE, Omar SH (2001) Production of PHB by a Bacillus megaterium strain using sugarcane molasses and corn steep liquor as sole carbon and nitrogen sources. Microbiol Res 156:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1078/0944-5013-00104
Grothe E, Chisti Y (2000) Poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid) thermoplastic production by Alcaligenes latus: behavior of fed-batch cultures. Bioprocess Eng 22:441–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490050757
Grubelnik A, Wiesli L, Furrer P, Rentsch D, Hany R, Meyer VR (2008) A simple HPLC-MS method for the quantitative determination of the composition of bacterial medium chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Sep Sci 31:1739–1744. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800033
Hassan MA, Bakhiet EK, Hussein HR, Ali SG (2019) Statistical optimization studies for polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by novel Bacillus subtilis using agricultural and industrial wastes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:3497–3512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1900-y
Hezayen FF, Rehm BHA, Eberhardt R, Steinbüchel A (2000) Polymer production by two newly isolated extremely halophilic Archaea: application of a novel corrosion-resistant bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000394
Hiiro K, Tanaka T, Kawahara A, Adachi M, Fukushi K (1982) A new spectrophotometric determination of phosphorus in sea water based on the measurement of color intensity of membrane filters. Bunseki Kagaku 31:E401–E407. https://doi.org/10.2116/bunsekikagaku.31.11_E401
Ibrahim MHA, Steinbüchel A (2009) Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production from glycerol by Zobellella denitrificans MW1 via high-cell-density fed-batch fermentation and simplified solvent extraction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 75:6222–6231. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01162-09
Ibrahim MHA, Steinbüchel A (2010) High-cell-density cyclic fed-batch fermentation of a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-accumulating thermophile, Chelatococcus sp. strain MW10. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7890–7895. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01488-10
Jung K, Hazenberg W, Prieto M, Witholt B (2001) Two-stage continuous process development for the production of medium-chain-length poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates). Biotechnol Bioeng 72:19–24
Kanjanachumpol P, Kulpreecha S, Tolieng V, Thongchul N (2013) Enhancing polyhydroxybutyrate production from high cell density fed-batch fermentation of Bacillus megaterium BA-019. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 36:1463–1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0885-7
Khanna S, Srivastava AK (2006) Computer simulated fed-batch cultivation for over production of PHB: a comparison of simultaneous and alternate feeding of carbon and nitrogen. Biochem Eng J 27:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2005.08.006
Lazic M, Gudneppanavar R, Whiddon K, Sauvageau D, Stein LY, Konopka M (2022) In vivo quantification of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) in the alphaproteobacterial methanotroph. Methylocystis Sp Rockwell Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106:811–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11732-x
López JA, Naranjo JM, Higuita JC, Cubitto MA, Cardona CA, Villar MA (2012) Biosynthesis of PHB from a new isolated Bacillus megaterium strain: outlook on future developments with endospore forming bacteria. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 17:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0448-1
Miller GH (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mizuno K, Ohta A, Hyakutake M, Ichinomiya Y, Tsuge T (2010) Isolation of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria from a polluted soil and characterization of the isolated strain Bacillus cereus YB-4. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1335–1339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.01.033
Mohapatra S, Sarkar B, Samantaray DP, Daware A, Maity S, Pattnaik S, Bhattacharjee S (2017) Bioconversion of fish solid waste into PHB using Bacillus subtilis based submerged fermentation process. Environ Technol 38:3201–3208. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1291759
Monod J (1942) Recherches sur la Croissance des Cultures Bacte´riennes. Herman, Paris
Oehmen A, Keller-Lehmann B, Zeng RJ, Yuan Z, Keller J (2005) Optimisation of poly-β-hydroxyalkanoate analysis using gas chromatography for enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. J Chromatogr A 1070:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.02.020
Oh G, Moo-Young M, Chisti u, (1998) Automated fed-batch culture of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on on-line monitored maximum substrate uptake rate. Biochem Eng J 1:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(98)00004-7
Panda I, Balabantaray S, Sahoo SK, Patra N (2018) Mathematical model of growth and polyhydroxybutyrate production using microbial fermentation of Bacillus subtilis. Chem Eng Commun 205:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2017.1384923
Pandian SRK, Deepak V, Kalishwaralal K, Rameshkumar N, Jeyaraj M, Gurunathan S (2010) Optimization and fed-batch production of PHB utilizing dairy waste and sea water as nutrient sources by Bacillus megaterium SRKP-3. Bioresour Technol 101:705–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.040
Parveez GKA, Bahariah B, Ayub NH, Masani MYA, Rasid OA, Tarmizi AH, Ishak Z (2015) Production of polyhydroxybutyrate in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) mediated by microprojectile bombardment of PHB biosynthesis genes into embryogenic calli. Front Plant Sci 6:598–598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00598
Patwardhan PR, Srivastava AK (2004) Model-based fed-batch cultivation of R. eutropha for enhanced biopolymer production. Biochem Eng J 20:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2004.04.001
Rosenbrock HH (1960) An automatic method of finding the greatest or the least value of a function. J Comput 3:175–184
Salazar-Magallón JA, Huerta de la Peña A (2020) Production of antifungal saponins in an airlift bioreactor with a cell line transformed from Solanum chrysotrichum and its activity against strawberry phytopathogens. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 50:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2019.1676781
Sathiyanarayanan G, Saibaba G, Seghal Kiran G, Selvin J (2013) A statistical approach for optimization of polyhydroxybutyrate production by marine Bacillus subtilis MSBN17. Int J Biol Macromol 59:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.04.040
SolÓRzano L (1969) Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method 1 1 This research was fully supported by U.S. Atomic Energy Commission Contract No. ATS (11–1) GEN 10, P.A. 20 Limnology and Oceanography 14:799–801. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1969.14.5.0799
Sun Z, Ramsay JA, Guay M, Ramsay BA (2007) Carbon-limited fed-batch production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates from nonanoic acid by Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0655-4
Umesh M, Mani VM, Thazeem B, Preethi K (2018) Statistical optimization of process parameters for bioplastic (PHA) production by Bacillus subtilis NCDC0671 using orange peel-based medium. Iran J Sci Technol, Trans a: Sci 42:1947–1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0457-9
Valappil SP, Misra SK, Boccaccini AR, Keshavarz T, Bucke C, Roy I (2007) Large-scale production and efficient recovery of PHB with desirable material properties, from the newly characterised Bacillus cereus SPV. J Biotechnol 132:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.03.013
Verlinden RAJ, Hill DJ, Kenward MA, Williams CD, Radecka I (2007) Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Appl Microbiol 102:1437–1449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03335.x
Volesky B, Votruba J (1992) Modelling and optimization of fermentation processes. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Yadav J, Balabantaray S, Patra N (2017) Statistical optimization of fermentation conditions for the improved production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate from Bacillus subtilis. Chem Eng Commun 204:1122–1128. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2017.1347094
Zhang X, Zhao G, Li D, Li S, Hong Q (2014) Identification and evaluation of strain B37 of Bacillus subtilis antagonistic to sapstain fungi on poplar wood. Sci World J 149342:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/149342
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (JY) thanks the Ministry of Education, New Delhi (India) for providing a senior research fellowship for this research work. The authors thank Dr. R. Jayabalan for his help in the HPLC analysis of PHB.
Funding
The financial support for the study was by ECRA, SERB (Government of India) (Sanction number: ECR/2017/001113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experimental work of this research has been performed by JY. Modeling and simulation part was done by NP. This research work has been completed under the supervision of NP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participates or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, J., Patra, N. Modeling of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate production by Bacillus subtilis and its use for feed-forward bioreactor studies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 57–69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12266-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12266-6