Abstract
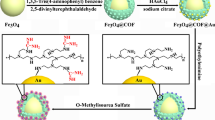
In this study, titanium (IV)-immobilized magnetic nanoparticles (Ti4+-PTL-MNPs) were firstly synthesized via a one-step aqueous self-assembly of lysozyme nanofilms for efficient phosphopeptide enrichment. Under physiological conditions, lysozymes readily self-organized into phase-transitioned lysozyme (PTL) nanofilms on Fe3O4@SiO2 and Fe3O4@C MNP surfaces with abundant functional groups, including –NH2, –COOH, –OH, and –SH, which can be used as multiple linkers to efficiently chelate Ti4+. The obtained Ti4+-PTL-MNPs possessed high sensitivity of 0.01 fmol μL−1 and remarkable selectivity even at a mass ratio of β-casein to BSA as low as 1:400 for phosphopeptide enrichment. Furthermore, the synthesized Ti4+-PTL-MNPs can also selectively identify low-abundance phosphopeptides from extremely complicated human serum samples and their rapid separation, good reproducibility, and excellent recovery were also proven. This one-step self-assembly of PTL nanofilms facilitated the facile and efficient surface functionalization of various nanoparticles for proteomes/peptidomes.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li XS, Yuan BF, Feng YQ. Recent advances in phosphopeptides enrichment: strategies and techniques. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem. 2016;78:70–83.
Li YN, Wang Y, Dong MM, Zou HF, Ye ML. Sensitive approaches for the assay of the global protein tyrosine phosphorylation in complex samples using a mutated SH2 domain. Anal Chem. 2017;89:2304–11.
Lyu JW, Wang Y, Mao JW, Yao YT, Wang SJ, Zheng Y, Ye ML. A pseudo-targeted MS method for the sensitive analysis of protein phosphorylation in protein complexes. Anal Chem. 2018;90:6214–21.
Li M, **ong Y, Qing G. Innovative chemical tools to address analytical challenges of protein phosphorylation and glycosylation. Acc Chem Res. 2023;56(18):2514–25.
Demon B, Aebersold R. Mass spectrometry and protein analysis. Science. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1126/science1124619.
Kennedy RT. The 2019 Reviews Issue. Anal Chem. 2019;91:1–1.
Han DQ, Yao ZP. Chiral mass spectrometry: An overview. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem. 2020;123: 115763.
Gao RF, Li J, Shi R, Zhang Y, Ouyang FZ, Zhang T, Hu LH, Xu GQ, Lian J. Highly sensitive detection of phosphopeptides with superparamagnetic Fe3O4 @mZrO2 core-shell microspheres-assisted mass spectrometry. J Mater Sci Technol. 2020;59:234–42.
Ng CC, Zhou Y, Yao ZP. Algorithms for de-novo sequencing of peptides by tandem mass spectrometry: A review. Anal Chim Acta. 2023;1268.
Cheng G, Zhang JL, Liu YL, Sun DH, Ni JZ. Synthesis of novel Fe3O4@SiO2@CeO2 microspheres with mesoporous shell for phosphopeptide capturing and labeling. Chem Commun. 2011;47:5732–4.
Lin H, Yuan K, Deng C. Preparation of a TiO2-NH2 modified MALDI plate for on-plate simultaneous enrichment of phosphopeptides and glycopeptides. Talanta. 2017;175:427–34.
Guo HH, Chen G, Ma JT, Jia Q. A triazine based organic framework with micropores and mesopores for use in headspace solid phase microextraction of phthalate esters. Microchim Acta. 2019;186:DOI: 101007/s00604–018–3060–7.
Zhang Y, Wang B, ** W, Wen Y, Nan L, Yang M, Liu R, Zhu Y, Wang C, Huang L, Song X, Wang Z. Sensitive and robust MALDI-TOF-MS glycomics analysis enabled by Girard’s reagent T on-target derivatization (GTOD) of reducing glycans. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1048:105–14.
Gao L, Uttamchandani M, Yao SQ. Comparative proteomic profiling of mammalian cell lysates using phosphopeptide microarrays. Chem Commun. 2012;48:2240–2.
Nilsson CL. Advances in quantitative phosphoproteomics. Anal Chem. 2012;84:735–46.
Alcolea MP, Cutillas PR. In-depth analysis of protein phosphorylation by multidimensional ion exchange chromatography and mass spectrometry. Methods in Mol Biol. 2010;658:111–26.
Yang S, Chang Y, Zhang H, Yu X, Shang W, Chen G, Chen DY, Gu Z. Enrichment of phosphorylated peptides with metal-organic framework nanosheets for serum profiling of diabetes and phosphoproteomics analysis. Anal Chem. 2018;90:13796–805.
Gao L, Tao J, Qi L, Jiang X, Shi H, Liu Y, Di B, Wang Y, Yan F. Synthesis of a metal oxide affinity chromatography magnetic mesoporous nanomaterial and development of a one-step selective phosphopeptide enrichment strategy for analysis of phosphorylated proteins. Anal Chim Acta. 2022;1195.
Wang Y, Li P, Xu W, Zhang D, Jia Q. Hydrophilic magnetic host-guest Ti-phenolic networks: a promising material for the highly sensitive enrichment of glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(22):4874–81.
Zhao Y, Xu W, Zheng H, Jia Q. Light, pH, and temperature triple-responsive magnetic composites for highly efficient phosphopeptide enrichment. Anal Chem. 2023;95(23):9043–51.
Wang Z, Wang J, Sun N, Deng C. A promising nanoprobe based on hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and immobilized metal affinity chromatography for capture of glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1067:1–10.
Xu Z, Wu Y, Wu H, Sun N, Deng C. Hydrophilic polydopamine-derived mesoporous channels for loading Ti (IV) ions for salivary phosphoproteome research. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1146:53–60.
Li N, Zhang L, Shi HL, Li JR, Zhang J, Zhang ZQ, Dang FQ. Specific enrichment of phosphopeptides by using magnetic nanocomposites of type Fe3O4@graphene oxide and Fe3O4@C coated with self-assembled oligopeptides. Microchim Acta. 2020;187:144.
Veleva VR, Cue BW, Todorova Jr. Benchmarking green chemistry adoption by the global pharmaceutical supply chain. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2018;6:2−14.
Wang H, Tian ZX. Facile synthesis of titanium (IV) ion immobilized adenosine triphosphate functionalized silica nanoparticles for highly specific enrichment and analysis of intact phosphoproteins. J Chromatogr A. 2018;1564:69–75.
Jiang DD, Li XQ, Ma JT, Jia Q. Development of Gd3+-immobilized glutathione-coated magnetic nanoparticles for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta. 2018;180:368–75.
Luo B, Zhou XX, Jiang PP, Yi QY, Lan F. PAMA-Arg brush-functionalized magnetic composite nanospheres for highly effective enrichment of phosphorylated biomolecules. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6:3969–78.
Liu R, Zhao J, Han Q, Hu X, Wang D, Zhang X, Yang P. One-step assembly of a biomimetic biopolymer coating for particle surface engineering. Adv Mater. 2018;30:1802851.
Wang K, Li N, Hai XM, Dang FQ. Lysozyme-mediated fabrication of well-defifined core-shell nanoparticle@metal-organic framework nanocomposites. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5:20765–70.
Pan MR, Sun YF, Zheng J, Yang WL. Boronic acid-functionalized core-shell-shell magnetic composite microspheres for the selective enrichment of glycoprotein. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:8351–8.
Zhang QQ, Hang YY, Jiang BY, Hu YJ, **e JJ, Gao X, Jia B, Shen HL, Zhang WJ, Yang PY. In situ synthesis of magnetic mesoporous phenolic resin for the selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2018;90:7357–63.
Liu J, Sun ZK, Deng YH, Zou Y, Li CY, Guo XH, **ong LQ, Gao Y, Li FY, Zhao DY. Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:5875–9.
Chen ZM, Geng ZR, Zhang ZY, Ren LB, Tao TX, Yang RC, Guo ZX. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles modified with -SO3H and -COOH groups for fast removal of Pb2+ Hg2+ and Cd2+ ions. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2014;3172−3177.
Yan YH, Zheng ZF, Deng CH, Zhang XM, Yang PY. Facile synthesis of Ti4+-immobilized Fe3O4@polydopamine core-shell microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun. 2013;49:5055–7.
Qi DW, Mao Y, Lu J, Deng CH, Zhang XM. Phosphate-functionalized magnetic microspheres for immobilization of Zr4+ ions for selective enrichment of the phosphopeptides. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217:2606–17.
Gu J, Su Y, Liu P, Li P, Yang P. An environmentally benign antimicrobial coating based on a protein supramolecular assembly. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;9:198–210.
Gu J, Miao S, Yan Z, Yang P. Multiplex binding of amyloid-like protein nanofilm to different material surfaces. Colloid Interface Sci Commun. 2018;22:42–8.
Wang HP, Jiao FL, Gao FY, Lv YY, Wu Q, Zhao Y, Shen YH, Zhang YJ, Qian XH. Titanium (IV) ion-modified covalent organic frameworks for specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta. 2017;166:133–40.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation Project of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020JZ-24), the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFB2103000), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201801006).
Funding
National Key R&D Program of China, 2019 YFB2103000, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, GK201801006, Natural Science Foundation Project of Shaanxi Province, No. 2020JZ-24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianru Li & Nan Li: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Yawen Hou: Investigation, Validation. Miao Fan & Yuxiu Zhang & Qiqi Zhang: Resources. Fuquan Dang: Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics statement
Human serum was obtained from Shaanxi Normal University Hospital. All the experiments were permitted by Human Research Ethics Board of Shaanxi Normal University (NO. 20150323). All participants provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, N., Hou, Y. et al. Facile fabrication of Ti4+-immobilized magnetic nanoparticles by phase-transitioned lysozyme nanofilms for enrichment of phosphopeptides. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 1657–1665 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05170-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05170-7