Abstract
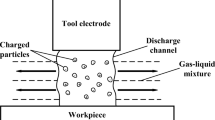
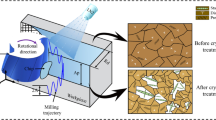
The ultrasonic and electrical discharge–assisted milling (US-EDAM) is a new machining method designed for machining difficult-to-cut materials. It combines two machining technologies: electrical discharge machining (EDM) and conventional milling with ultrasonic vibration. The EDM in the proposed method is used to soften the surface of the material to be machined and thereby reduce the cutting force. In the meanwhile, the ultrasonic vibration of the proposed method is used to improve the discharge efficiency of the EDM and reduce the cutting force. Likewise, the milling in the present method is used to remove the workpiece’s EDM-softened surface accurately and quickly. The effects of different machining methods (including the conventional milling (CM), the ultrasonic-assisted machining (USM), the electrical discharge–assisted machining (EDAM), and the US-EDAM) on the machined material’s surface topography, plastic deformation, microscopic appearance, surface microhardness, and residual stress on the surface were compared for different machining parameters. The results confirmed that the EDM in the US-EDAM softened the surface of the material to be removed and reduced the cutting force. Furthermore, the ultrasonic vibration assistance in the US-EDAM reduced the cutting force with intermittent cutting. Notably, the surface integrity of the machined workpiece under the US-EDAM was better than the ones under the other machining methods. Hence, the US-EDAM demonstrated its capability as a new hybrid machining combining EDM, ultrasonic vibration assistance, and milling.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The availability of data and material is available as requested to the authors.
Code availability
The code is available as requested to the authors.
References
Pervaiz S, Rashid A, Deiab I, Nicolescu M (2014) Influence of tool materials on machinability of titanium- and nickel-based alloys: a review. Mater Manuf Processes 29(3):219–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.880460
Shu Z, Huimin T (2011) Current status and prospects of titanium alloy processing. Metal Processing (Cold Processing) 17:2–5
Nurul-Amin AKM, Ismail AF, Nor Khairusshima MK (2007) Effectiveness of uncoated WC-Co and PCD inserts in end milling of titanium alloy—Ti–6Al–4V. J Mater Process Tech 192–193:147–158
Jawahir IS, Brinksmeier E, M’Saoubi R, Aspinwall DK, Outeiro JC, Meyer D, Jayal AD (2011) Surface integrity in material removal processes: recent advances. CIRP Ann 60(2):603–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2011.05.002
Liu C, Liu D, Zhang X, He G, Xu X, Ao N, Liu D (2019) On the influence of ultrasonic surface rolling process on surface integrity and fatigue performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Surf Coat Technol 370:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.04.080
Mondal A, Roy P, Mitra S (2020) Experimental investigation on electro discharge machining of Ti6Al4V alloy. Adv Mater Process Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068x.2020.1759913
Ho K, Newman S (2003) State of the art electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(13):1287–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0890-6955(03)00162-7
Li CP, Kim M-Y, Islam MM, Ko TJ (2016) Mechanism analysis of hybrid machining process comprising EDM and end milling. J Mater Process Technol 237:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.06.022
Li C, Xu M, Yu Z, Huang L, Li S, Li P, Ko TJ (2020) Electrical discharge-assisted milling for machining titanium alloy. J Mater Process Tech 285:116785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116785
Xu M, Li C, Kurniawan R, Park G, Chen J, Ko TJ (2022) Study on surface integrity of titanium alloy machined by electrical discharge-assisted milling. J Mater Process Technol 299:117334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117334
Kawalec M, Przestacki D, Bartkowiak K et al (2008) Laser assisted machining of aluminium composite reinforced by SiC particle. Int Congr Appl Lasers Electro-Opt. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5061278
Przestacki D, Szymański P (2011) Metallographic analysis of surface layer after turning with laser-assisted machining of composite A359/20SiCp. Composites 2:102–106
Przestacki D, Chwalczuk T (2017) The analysis of surface topography during turning of Waspaloy with the application of response surface method. MATEC Web Conf 136:02006. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201713602006
Kim E, Lee C (2019) A study on the optimal machining parameters of the induction assisted milling with Inconel 718. Materials 12(2):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020233
López de Lacalle LN, Sánchez JA, Lamikiz A, Celaya A (2004) Plasma assisted milling of heat-resistant superalloys. J Manuf Sci Eng 126(2):274. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1644548
Chen G, Ren C, Zou Y, Qin X, Lu L, Li S (2018) Mechanism for material removal in ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int J Mach Tool Manu. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2018.11.001
Chen W, Zheng L, **e W, Yang K, Huo D (2019) Modelling and experimental investigation on textured surface generation in vibration-assisted micro-milling. J Mater Process Tech 266:339–350
Khosrozadeh B, Shabgard M (2017) Effects of hybrid electrical discharge machining processes on surface integrity and residual stresses of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(5–8):1999–2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0601-x
Roy A, Silberschmidt VV (2014) Ultrasonically assisted machining of titanium alloys. Machining of Titanium Alloys. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43902-9_6
Kurniawan R, Thirumalai Kumaran S, Arumuga Prabu V, Zhen Y, Park KM, Kwak YI, Ko TJ (2017) Measurement of burr removal rate and analysis of machining parameters in ultrasonic assisted dry EDM (USEDAM) for deburring drilled holes in CFRP composite. Measurement 110:98–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.06.008
Hao T, Yang W, Yong L (2008) Vibration-assisted servo scanning 3D micro EDM. J Micromech Microeng 18(2):025011. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/18/2/025011
Gao C, Liu Z (2003) A study of ultrasonically aided micro-electrical-discharge machining by the application of workpiece vibration. J Mater Process Technol 139(1–3):226–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-0136(03)00224-3
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Deng J, Qin Y, Niu Z (2002) Ultrasonic vibration electrical discharge machining in gas. J Mater Process Tech 129(1–3):135–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-0136(02)00596-4
Liu J, Jiang X, Han X, Gao Z, Zhang D (2018) Effects of rotary ultrasonic elliptical machining for side milling on the surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2847-3
Liao Z, Abdelhafeez A, Li H, Yang Y, Diaz OG, Axinte D (2019) State-of-the-art of surface integrity in machining of metal matrix composites. Int J Mach Tool Manu. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.05.006
Oosthuizen T, Nunco K, Conradie P, Dimitrov D (2016) The effect of cutting parameters on surface integrity in milling Ti6-Al-4V. S Afr J Ind Eng. https://doi.org/10.7166/27-4-1199
Kurniawan R, Ahmed F, Ali S, Park GC, Ko TJ (2021) Analytical, FEA, and experimental research of 2D-vibration assisted cutting (2D-VAC) in titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07831-8
Sun J, Guo YB (2009) A comprehensive experimental study on surface integrity by end milling Ti–6Al–4V. J Mater Process Technol 209(8):4036–4042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.09.022
Abdullah A, Shabgard MR, Ivanov A, Shervanyi-Tabar MT (2008) Effect of ultrasonic-assisted EDM on the surface integrity of cemented tungsten carbide (WC-Co). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41(3–4):268–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1476-7
Ahmed F, Ko TJ, Kurniawan R, Kwack Y (2021) Machinability analysis of difficult-to-cut material during ultrasonic vibration-assisted ball end milling. Mater Manuf Process. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2021.1944194
Shabgard MR, Alenabi H (2015) Ultrasonic assisted electrical discharge machining of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mater Manuf Processes 30(8):991–1000. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1004686
Zhang M, Zhang D, Geng D, Shao Z, Liu Y, Jiang X (2019) Effects of tool vibration on surface integrity in rotary ultrasonic elliptical end milling of Ti–6Al–4V. J Alloy Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153266
Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang X, Huang T (2020) Experimental study on tool wear in ultrasonic vibration–assisted milling of C/SiC composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05060-z
Niu Y, Jiao F, Zhao B, Wang D (2017) Multiobjective optimization of processing parameters in longitudinal-torsion ultrasonic assisted milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(9–12):4345–4356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0871-3
Kitamura T, Kunieda M, Abe K (2015) Observation of relationship between bubbles and discharge locations in EDM using transparent electrodes. Precis Eng 40:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.09.009
Shitara T, Fujita K, Yan J (2020) Direct observation of discharging phenomena in vibration-assisted micro-electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04877-7
Gurrappa I (2003) Characterization of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V for chemical, marine and industrial applications. Mater Charact 51(2–3):131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2003.10.006
Arrazola P-J, Garay A, Iriarte L-M, Armendia M, Marya S, Le Maître F (2009) Machinability of titanium alloys (Ti6Al4V and Ti555.3). J Mater Process Tech 209(5):2223–2230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.06.020
Potomati F, Giordani EJ, Duarte LT, de Alcântara NG, Bolfarini C (2012) Fatigue behavior and physical characterization of surface-modified Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy by micro-arc oxidation. Mater Res 15(2):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-14392012005000012
Li H, Wang J (2015) An experimental study of abrasive waterjet machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81(1–4):361–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7245-5
Zhao B, Li P, Zhao C, Wang X (2019) Fractal characterization of surface microtexture of Ti6Al4V subjected to ultrasonic vibration assisted milling. Ultrasonics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2019.106052
Alharbi N (2022) Experimental study on designing optimal vibration amplitude in ultrasonic assisted incremental forming of AA6061-T6. Eng Sci Technol Int J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.07.004
Velásquez JDP, Tidu A, Bolle B, Chevrier P, Fundenberger J-J (2010) Sub-surface and surface analysis of high speed machined Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mat Sci Eng A 527(10–11):2572–2578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.12.018
Zhang M, Zhang D, Geng D, Liu J, Shao Z, Jiang X (2020) Surface and sub-surface analysis of rotary ultrasonic elliptical end milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Mater Des. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108658
Liang X, Liu Z, Wang B, Hou X (2018) Modeling of plastic deformation induced by thermo-mechanical stresses considering tool flank wear in high-speed machining Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Mech Sci 140:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.02.031
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (grant number NRF-2020R1A2B5B02001755). Furthermore, we acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51905169 and 51775184), the Hunan Education Department Project (18C0323), and the HUNST Project (E51781).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Moran Xu: writing—original draft, conceptualization, methodology, software, and formal analysis. Chang** Li: conceptualization, supervision, and methodology. Rendi Kurniawan: measurement, supervision, and data analysis. Jielin Chen: software, and validation. Ye In Kwak: project administration, and validation. Saood Ali: validation. Min Ki Choo: project administration. Tae Jo Ko: conceptualization, resources, supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Li, C., Kurniawan, R. et al. Ultrasonic and electrical discharge–assisted milling of the Ti-6Al-4 V alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 122, 1897–1917 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10010-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10010-y