Abstract
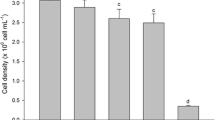
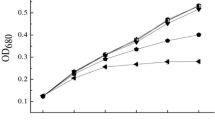
Effects of zinc on growth, cell morphology, oxidative stress, and zinc removal ability of the common phytoplankton species Desmodesmus communis were investigated at a concentration range of 0.25–160 mg L−1 zinc. Cell densities and chlorophyll content decreased in treated cultures, changes in coenobia morphology and elevated lipid peroxidation levels appeared above 2.5 mg L−1 zinc. The most effective zinc removal was observed at 5 mg L−1 zinc concentration, while maximal amount of removed zinc appeared in 15 mg L−1 zinc treated culture. Removed zinc is mainly bound on the cell surface. Dead biomass adsorbed more zinc than living biomass relative to unit of dry mass, but living biomass was more effective, relative to initial zinc content. This study comprehensively examines the zinc tolerance and removal ability of D. communis and demonstrates, in comparison with published literature, that these characteristics of different isolates of the same species can vary within a wide range.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilgrami KS, Kumar S (1997) Effects of copper, lead and zinc on phytoplankton growth. Biol Plant 39(2):315–317
Broadley MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A (2007) Zinc in plants. New Phytol 173(4):677–702
Chong AMY, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2000) Performance of different microalgal species in removing nickel and zinc from industrial wastewater. Chemosphere 41:251–257
Felföldy L (1987) A biológiai vízminősítés. 4. kiad. In: Vízügyi Hidrobiológia 16. – VGI, Budapest, 258
Güclü Z, Ertan ÖO (2012) Toxicity and removal of zinc in the three species (Acutodesmus obliquus, Desmodesmus subspicatus and Desmodesmus armatus) belonging to the Family, Scenedesmaceae (Chlorophyta). Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci 12:309–314
Hammer Ř, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4:9
Hassler CS, Behra R, Wilkinson KJ (2005) Impact of zinc acclimation on bioaccumulation and homeostasis in Chlorella kesslerii. Aquat Toxicol 74:139–149
Kessler E, Schäfer M, Hümmer C, Kloboucek A, Huss VAR (1997) Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characters for the taxonomy of the subgenera of Scenedesmus (Chlorococcales, Chlorophyta). Bot Acta 110(3):244–250
Krienitz L, Bock C (2012) Present state of the systematics of planktonic coccoid green algae of inland waters. Hydrobiologia 698:295–326
Monteiro CM, Marques AP, Castro PM, Malcata FX (2009) Characterization of Desmodesmus pleiomorphus isolated from a heavy metal-contaminated site: biosorption of zinc. Biodegradation 20(5):629–641
Monteiro CM, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2011a) Capacity of simultaneous removal of zinc and cadmium from contaminated media, by two microalgae isolated from a polluted site. Environ Chem Lett 9:511–517
Monteiro CM, Fonseca SC, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2011b) Toxicity of cadmium and zinc on two microalgae, Scenedesmus obliquus and Desmodesmus pleiomorphus, from Northern Portugal. J Appl Phycol 23:97–103
Monteiro CM, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2011c) Biosorption of zinc ions from aqueous solution by the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Environ Chem Lett 9:169–176
Omar HH (2002a) Bioremoval of zinc ions by Scenedesmus obliquus and Scenedesmus quadricauda and its effect on growth and metabolism. Int Biodeter Biodegr 50:95–100
Omar HH (2002b) Adsorption of zinc ions by Scenedesmus obliquus and S. quadricauda and its effect on growth and metabolism. Biol Plant 45(2):261–266
Radway JC, Wilde EW, Whitaker MJ, Weissman JC (2001) Screening of algal strains for metal removal capabilities. J Appl Phycol 13(5):451–455
Rojíčková-Padrtová R, Maršálek B (1999) Selection and sensitivity comparisons of algal species for toxicity testing. Chemosphere 38(14):3329–3338
Romera E, González F, Ballester A, Blázquez ML, Muñoz JA (2006) Biosorption with algae: a statistical review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 26(4):223–235
Starodub ME, Wong PTS (1987) Short term and long term studies on individual and combined toxicities of copper, zinc and lead to Scenedesmus quadricauda. Sci Total Environ 63:101–110
Travieso L, Cañizares RO, Borja R, Benítez F, Domínguez AR, Dupeyrón R, Valiente V (1999) Heavy metal removal by microalgae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 62(2):144–151
Tripathi BN, Gaur JP (2004) Relationship between copper- and zinc-induced oxidative stress and proline accumulation in Scenedesmus sp. Planta 219:397–404
Tripathi BN, Gaur JP (2006) Physiological behavior of Scenedesmus sp. during exposure to elevated levels of Cu and Zn and after withdrawal of metal stress. Protoplasma 229:1–9
Umisová D, Vìtovà M, Douskovà I, Bisovà K, Hlavovà M, Cizkovà M, Machàt J, Doucha J, Zachleder V (2009) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of selenium compounds in the green alga Scenedesmus quadricauda. BMC Plant Biol 9:58–74
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164(4):645–655
Visviki I, Rachlin JW (1991) The toxic action and interactions of copper and cadmium to the marine alga Dunaliella minuta, in both acute and chronic exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:271–275
Volesky B (1990) Removal and recovery of heavy metals by biosorption. In: Volesky B (ed) Biosorption of heavy metals, 1st edn. CRC Press, USA Boston, pp 7–43
Wase J, Forster CF (2003) Biosorbents for metal ions. Taylor & Francis e-Library, UK London
Wong MH, Kwan SH, Tam FY (1979) Comparative toxicity of manganese and zinc on Chlorella pyreonidosa, Chlorella salina and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Microbios Lett 12:37–46
Zar JH (1996) Biostatistical analysis, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Zhou GJ, Peng FQ, Zhang LJ, Ying GG (2012) Biosorption of zinc and copper from aqueous solutions by two freshwater green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(7):2918–2929
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the EU and co-financed by the European Social Fund under the project ENVIKUT (TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0043), by the Internal Research Project of the University of Debrecen and by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novák, Z., Jánószky, M., B-Béres, V. et al. Zinc Tolerance and Zinc Removal Ability of Living and Dried Biomass of Desmodesmus communis . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93, 676–682 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1374-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1374-7