Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to determine the removal of zinc and copper by two freshwater green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus and to investigate changes of algal ultrastructure and photosynthetic pigment.
Methods
Algal cells were exposed for 8 days to different initial zinc or copper concentrations. Heavy metal concentrations were detected by an atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Algal growth, ultrastructure, and photosynthetic pigment were analyzed by a microplate reader, transmission electron microscope, and spectrophotometer, respectively.
Results
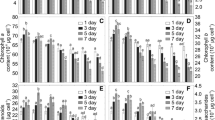
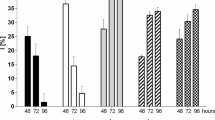
Low zinc and copper concentrations induced increase in algal growth, whereas application of high zinc and copper concentrations suppressed the growth of both algae. High metal concentrations also decreased the photosynthetic pigments and destroyed algal cell ultrastructure. The zinc removal efficiency by both algae increased rapidly during the first day and thereafter remained nearly constant throughout the experiment. The copper removal efficiency by both algae increased slowly during the whole experimental periods. In all cultures, the quantity of both metals removed intracellularly was much lower than the adsorbed quantity on the cell surface.
Conclusions
Both strains of the microalgae had proven effective in removing zinc and copper from aqueous solutions, with the highest removal efficiency being near 100%. In addition, C. pyrenoidosa appeared to be more efficient than S. obliquus for removing copper ions. On the contrary, S. obliquus appeared to be more efficient than C. pyrenoidosa for removing zinc ions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia SS, Goyal D (2007) Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresource Technol 98:2243–2257
Ajjabi LC, Chouba L (2009) Biosorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ from aqueous solutions by dried marine green macroalga Chaetomorpha linum. J Environ Manage 90:3485–3489
Ali I, Gupta VK (2006) Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat Protoc 1:2661–2667
Andrade LR, Salgado LT, Farina M, Pereira MS, Mourão PAS, Filho GMA (2004) Ultrastructure of acidic polysaccharides from the cell walls of brown algae. J Struct Biol 145:216–225
Barakat MA (2011) New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab J Chem 4:361–377
Chong AMY, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2000) Performance of different microalgal species in removing nickel and zinc from industrial wastewater. Chemosphere 41:251–257
Costa ACA, França FP (1998) The behaviour of the microalgae Tetraselmis chuii in cadmium-contaminated solutions. Aquacult Int 6:57–66
Debelius B, Forja JM, DelValls Á, Lubián LM (2009) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of copper and lead in five marine microalgae. Ecotox Environ Safe 72:1503–1513
Dönmez GÇ, Aksu Z, Öztürk A, Kutsal T (1999) A comparative study on heavy metal biosorption characteristics of some algae. Process Biochem 34:885–892
Doshi H, Seth C, Ray A, Kothari IL (2008) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by green algae. Curr Microbiol 56:246–255
Folgar S, Torres E, Pérez-Rama M, Cid A, Herrero C, Abalde J (2009) Dunaliella salina as marine microalga highly tolerant to but a poor remover of cadmium. J Hazard Mater 165:486–493
Franklin NM, Stauber JL, Markich SJ, Lim RP (2000) pH-Dependent toxicity of copper and uranium to a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.). Aquat Toxicol 48:275–289
Gekeler W, Grill E, Winnacher EL, Zenk MH (1988) Algae sequester heavy metals via synthesis of phytochelatin complexes. Arch Microbiol 150:197–202
Gupta VK, Ali I (2004) Removal of lead and chromium from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste. J Colloid Interf Sci 271:321–328
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008a) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by green algae Spirogyra species: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 152:407–414
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008b) Biosorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by non-living algal biomass Oedogonium sp. and Nostoc sp.—a comparative study. Colloid Surface B 64:170–178
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008c) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium(II) biosorption by nonliving algal biomass Oedogonium sp. from aqueous phase. J Hazard Mater 153:759–766
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008d) Sorption and desorption studies of chromium(VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J Hazard Mater 154:347–354
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 163:396–402
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Dwivedi MK, Mohan D (1997) Process development for the removal of zinc and cadmium from wastewater using slag—a blast furnace waste material. Separ Sci Technol 32:2883–2912
Gupta VK, Shrivastava AK, Jain N (2001) Biosorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions by green algae Spirogyra species. Wat Res 35:4079–4085
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Saini VK, Jain N (2006) Biosorption of copper(II) from aqueous solutions by Spirogyra species. J Colloid Interf Sci 296:59–63
Gupta VK, Carrott PJM, Ribeiro Carrott MML, Suhas (2009) Low-cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatment—a review. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 39:783–842
Harris PO, Ramelow GJ (1990) Binding of metal ions by particulate biomass derived from Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Environ Sci Technol 24:220–228
Howe G, Merchant S (1992) Heavy metal-activated synthesis of peptides in Chlamydomonas reinhaidtii. Plant Physiol 98:127–136
Khoshmanesh A, Lawson F, Prince IG (1996) Cadmium uptake by unicellular green microalgae. The Chem Eng J 62:81–88
Knauer K, Behra R, Sigg L (1997) Effects of free Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions on growth and metal accumulation in freshwater algae. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:220–229
Li HS, Sun Q, Zhao SJ, Zhang WH (2000) Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Higher Education Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Ma M, Zhu WZ, Wang ZJ, Witkamp GJ (2003) Accumulation, assimilation and growth inhibition of copper on freshwater alga (Scenedesmus subspicatus 86.81 SAG) in the presence of EDTA and fulvic acid. Aquat Toxicol 63:221–228
Macfie SM, Welbourn PM (2000) The cell wall as a barrier to uptake of metal ions in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyceae). Arch Environ Con Tox 39:413–419
Mata YN, Torres E, Blázquez ML, Ballester A, González F, Muñoz JA (2009) Gold(III) biosorption and bioreduction with the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. J Hazard Mater 166:612–618
Muyssen BTA, Janssen CR (2001) Zinc acclimation and its effect on the zinc tolerance of Raphidocelis subcapitata and Chlorella vulgaris in laboratory experiments. Chemosphere 45:507–514
Nourbakhsh M, Sağ Y, Özer D, Aksu Z, Kutsal T, Çağlar A (1994) A comparative study of various biosorbents for removal of chromium (VI) ions from industrial waste waters. Process Biochem 29:1–5
Özer A, Özer D, Ekiz HI (1999) Application of Freundlich and Langmuir models to multistage purification process to remove heavy metal ions by using Schizomeris leibleinii. Process Biochem 34:919–927
Pérez-Rama M, Alonso JA, López CH, Vaamonde ET (2002) Cadmium removal by living cells of the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica. Bioresource Technol 84:265–270
Scarano G, Morelli E (2002) Characterization of cadmium- and lead-phytochelatin complexes formed in a marine microalga in response to metal exposure. BioMetals 15:145–151
Şeker A, Shahwan T, Eroğlu AE, Yılmaz S, Demirel Z, Dalay MC (2008) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies for the biosorption of aqueous lead(II), cadmium(II) and nickel(II) ions on Spirulina platensis. J Hazard Mater 154:973–980
Solisio C, Lodi A, Torre P, Converti A, Borghi MD (2006) Copper removal by dry and re-hydrated biomass of Spirulina platensis. Bioresource Technol 97:1756–1760
Srivastava SK, Gupta VK, Mohan D (1997) Removal of lead and chromium by activated slag—a blast-furnace waste. J Environ Eng 123:461–468
Surosz W, Palinska KA (2004) Effects of heavy-metal stress on cyanobacterium Anabaena flos-aquae. Arch Environ Con Tox 48:40–48
Terry PA, Stone W (2002) Biosorption of cadmium and copper contaminated water by Scenedesmus abundans. Chemosphere 47:249–255
Twiss MR, Nalewajko C (1992) Influence of phosphorus nutrition on copper toxicity to three strains of Scenedesmus acutus (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 28:291–298
Wang WX, Dei RCH (2001) Effects of major nutrient additions on metal uptake in phytoplankton. Environ Pollut 111:233–240
Wang WX, Dei RCH, Xu Y (2001) Responses of Zn assimilation by coastal plankton to macronutrients. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1524–1534
Yan H, Pan G (2002) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of copper in three green microalgal species. Chemosphere 49:471–476
Yu RQ, Wang WX (2004) Biokinetics of cadmium, selenium, and zinc in freshwater alga Scenedesmus obliquus under different phosphorus and nitrogen conditions and metal transfer to Daphnia magna. Environ Pollut 129:443–456
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 41103057 and U1133005) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (grant no. 20110490932). This is a Contribution No. 1445 from GIG CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vinod Kumar Gupta
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, GJ., Peng, FQ., Zhang, LJ. et al. Biosorption of zinc and copper from aqueous solutions by two freshwater green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus . Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 2918–2929 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0800-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0800-9