Abstract
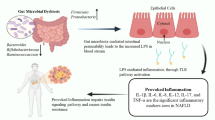
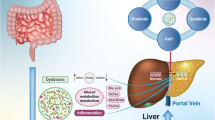
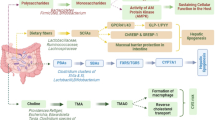
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a multifaceted disease allied with various metabolic disorders, obesity and dysbiosis. Gut microbiota plays an influential role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and other metabolic disorders. However, recent scientific upsurge emphasizes on the utility of beneficial gut microbiota and bacteriotherapy in the management of NAFLD. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is the contemporary therapeutic approach with state-of-the-art methods for the treatment of NAFLD. Other potential therapies include probiotics and prebiotics supplements which are based on alteration of gut microbes to treat NAFLD. In this review, our major focus is on the pathological association of gut microbiota with progression of NAFLD, historical aspects and recent advances in FMT with possible intervention to combat NAFLD and its associated metabolic dysfunctions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data and material regarding the material reported as self-citation by the authors in this Mini-review is available upon request.
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
Acetyl Co-A carboxylase
- AEs:
-
Adverse events
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CDI:
-
Clostridium difficile infection
- CD4:
-
Cluster of differentiation 4
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- DNL:
-
De novo lipogenesis
- FIAF:
-
Fasting-induced adipose factor
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acid
- FMT:
-
Fecal matter transplantation
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HDL-c:
-
High density lipoprotein cholesterol
- IR:
-
Insulin resistance
- LPL:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NAFLD:
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- NASH:
-
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- NF-kB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-B cells
- SCFA:
-
Short chain fatty acid
- SREBP:
-
Sterol regulatory element binding protein
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- VLDL:
-
Very low-density lipoprotein
References
Aller R, Izaola O, Primo D, de Luis D. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein variant (RS1800777) with liver histology in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Ann Nutr Metab. 2018;73:265–70. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493552.
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J, Bugianesi E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:1061–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109.
Fan JG, Kim SU, Wong VW. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J Hepatolol. 2017;67:862–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.257.
Tremaroli V, Bäckhed F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature. 2012;489:242. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11552.
Gérard P. Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:147–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2061-5.
Chen HT, Huang HL, Li YQ, Xu HM, Zhou YJ. Therapeutic advances in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a microbiota-centered view. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26(16):1901. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i16.1901.
Marotz CA, Zarrinpar A. Focus: microbiome—treating obesity and metabolic syndrome with fecal microbiota transplantation. Yale J Biol Med. 2016;89:383.
Iacono A, Raso GM, Canani RB, Calignano A, Meli R. Probiotics as an emerging therapeutic strategy to treat NAFLD: focus on molecular and biochemical mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem. 2011;22(8):699–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.10.002.
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004;101(44):15718–23. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407076101.
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006;444(7122):1027. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05414.
Bäckhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI. Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104(3):979–84. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605374104.
Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, Griffin NW, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241214.
Caesar R, Tremaroli V, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Cani PD, Bäckhed F. Crosstalk between gut microbiota and dietary lipids aggravates WAT inflammation through TLR signaling. Cell Metab. 2015;22:658–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.07.026.
Tiniakos DG, Vos MB, Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathology and pathogenesis. Ann Rev Pathol. 2010;5:145–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102132.
Onkar B, Savera A, Nirupma T, Gayatri R, Pawan K. Molecular and pathological events involved in the pathogenesis of diabetes associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2018.10.004.
Armstrong MJ, Adams LA, Canbay A, Syn WK. Extrahepatic complications of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2014;59:1174–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26717.
Yu J, Marsh S, Hu J, Feng W, Wu C. The pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and genetic background. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2862173.
Hochrath K, Schnabl B. Check your microbiota when taking the drug. J Hepatol. 2018;67:18–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29422.
Kolodziejczyk AA, Zheng D, Shibolet O, Elinav E. The role of the microbiome in NAFLD and NASH. EMBO Mol Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201809302.
Leung C, Rivera L, Furness JB, Angus PW. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:412.
Luedde T, Schwabe RF. NF-κB in the liver—linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:108–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2010.213.
De Groot PF, Frissen MN, de Clercq NC, Nieuwdorp M. Fecal microbiota transplantation in metabolic syndrome: history, present and future. Gut microbes. 2017;28:253–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2017.1293224.
Lebaka VR, Wee YJ, Narala VR, Joshi VK. Development of new probiotic foods—a case study on probiotic juices. Ther Probiot Unconv Foods. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814625-5.00004-2.
Zhang F, Luo W, Shi Y, Fan Z, Ji G. Should we standardize the 1,700-year-old fecal microbiota transplantation? Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:1755. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.251.
Zhou Y, Zheng T, Chen H. Microbial intervention as a novel target in treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51:2123–35. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495830.
Vrieze A, de Groot PF, Kootte RS, Knaapen M, Van Nood E, Nieuwdorp M. Fecal transplant: a safe and sustainable clinical therapy for restoring intestinal microbial balance in human disease? Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;27(1):127–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.003.
Todesco T, Rao AV, Bosello O, Knaapen M, Van Nood E, Nieuwdorp M. Propionate lowers blood glucose and alters lipid metabolism in healthy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;54:860–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/54.5.860.
Guo W, Wang P, Liu ZH, Ye P. Analysis of differential expression of tight junction proteins in cultured oral epithelial cells altered by Porphyromonas gingivalis, Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide, and extracellular adenosine triphosphate. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10:e8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijos.2017.51.
Hu S, Wang J, Wang J, Yang H, Yan X, Su L. Fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides improves insulin resistance by altering gut microbiota dysfunction. J Funct Foods. 2019;57:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.03.033.
Hardie DG, Carling D. The AMP-activated protein kinase: fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem. 1997;246(2):259–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00259.x.
Mogensen TH. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22(2):240–73. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00046-08.
Freeland KR, Wolever TM. Acute effects of intravenous and rectal acetate on glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY, ghrelin, adiponectin and tumour necrosis factor-α. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(3):460–6. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114509991863.
Lee J, Hong SW, Rhee EJ, Lee WY. GLP-1 receptor agonist and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):262–7.
Bull MJ, Plummer NT. Part 1: The human gut microbiome in health and disease. Integr Med. 2014;13:17.
Raman M, Ahmed I, Gillevet PM, Probert CS, Ratcliffe NM, Smith S, Greenwood R, Sikaroodi M, Lam V, Crotty P, Bailey J. Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:868–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.015.
Wong VW, Tse CH, Lam TT, Wong GL, Chim AM, Chu WC, Yeung DK, Law PT, Kwan HS, Yu J, Sung JJ. Molecular characterization of the fecal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis–a longitudinal study. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e62885.
Del Chierico F, Nobili V, Vernocchi P, Russo A, De Stefanis C, Gnani D, Furlanello C, Zandonà A, Paci P, Capuani G, Dallapiccola B. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology. 2017;65(2):451–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28572.
Silva HE, Teterina A, Comelli EM, Taibi A, Arendt BM, Fischer SE, Lou W, Allard JP. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with dysbiosis independent of body mass index and insulin resistance. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1466. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19753-9.
Wang B, Jiang X, Cao M, Ge J, Bao Q, Tang L, Chen Y, Li L. Altered fecal microbiota correlates with liver biochemistry in nonobese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32002.
Loomba R, Seguritan V, Li W, Long T, Klitgord N, Bhatt A, Dulai PS, Caussy C, Bettencourt R, Highlander SK, Jones MB. Gut microbiome-based metagenomic signature for non-invasive detection of advanced fibrosis in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Metab. 2017;25:1054–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.001.
Ponziani FR, Bhoori S, Castelli C, Putignani L, Rivoltini L, Del Chierico F, Sanguinetti M, Morelli D, Paroni Sterbini F, Petito V, Reddel S. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2018;69:107–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30036.
Bajaj JS, Fagan A, Sikaroodi M, White MB, Sterling RK, Gilles H, Heuman D, Stravitz RT, Matherly SC, Siddiqui MS, Puri P. Liver transplant modulates gut microbial dysbiosis and cognitive function in cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 2017;23(7):907–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.24754.
Yuan J, Chen C, Cui J, Lu J, Yan C, Wei X, Zhao X, Li N, Li S, Xue G, Cheng W. Fatty liver disease caused by high-alcohol-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cell Metab. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.08.018.
Jha R, Berrocoso JF. Dietary fiber and protein fermentation in the intestine of swine and their interactive effects on gut health and on the environment: a review. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 2016;212:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2015.12.002.
**n J, Zeng D, Wang H, Ni X, Yi D, Pan K, **g B. Preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 by attenuating inflammation and mitochondrial injury and improving gut environment in obese mice. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;c98:6817–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5752-1.
Jones ML, Martoni CJ, Prakash S. Cholesterol lowering and inhibition of sterol absorption by Lactobacillus reuteri NCIMB 30242: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012;22:699–711. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2012.126.
Fuentes MC, Lajo T, Carrión JM, Cuñé J. Cholesterol-lowering efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 7527, 7528 and 7529 in hypercholesterolaemic adults. Br J Nutr. 2013;109:1866–72. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451200373X.
Hadi A, Mohammadi H, Miraghajani M, Ghaedi E. Efficacy of synbiotic supplementation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials: synbiotic supplementation and NAFLD. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1458021.
Russo F, Chimienti G, Riezzo G, Pepe G, Petrosillo G, Chiloiro M, Marconi E. Inulin-enriched pasta affects lipid profile and Lp (a) concentrations in Italian young healthy male volunteers. Eur J Nutr. 2008;47:453–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-008-0748-1.
Van Loo J, Cummings J, Delzenne N, Englyst H, Franck A, Hopkins M, Kok N, Macfarlane G, Newton D, Quigley M, Roberfroid M. Functional food properties of non-digestible oligosaccharides: a consensus report from the ENDO project (DGXII AIRII-CT94-1095). Br J Nutr. 1999;81:121–32. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114599000252.
Bajaj JS, Kassam Z, Fagan A, Gavis EA, Liu E, Cox IJ, Kheradman R, Heuman D, Wang J, Gurry T, Williams R. Fecal microbiota transplant from a rational stool donor improves hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial. J Hepatol. 2017;66(6):1727–38.
Sharpton SR, Ajmera V, Loomba R. Emerging role of the gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from composition to function. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;17:296–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2018.08.065.
Suez J, Zmora N, Zilberman-Schapira G, Mor U, Dori-Bachash M, Bashiardes S, Zur M, Regev-Lehavi D, Brik RB, Federici S, Horn M. Post-antibiotic gut mucosal microbiome reconstitution is impaired by probiotics and improved by autologous FMT. Cell. 2018;174:1406–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.047.
Delaune V, Orci LA, Lacotte S, Peloso A, Schrenzel J, Lazarevic V, Toso C. Fecal microbiota transplantation: a promising strategy in preventing the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and improving the anti-cancer immune response. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18:1061–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/14712598.2018.1518424.
Schneider KM, Wirtz TH, Kroy D, Albers S, Neumann UP, Strowig T, Sellge G, Trautwein C. Successful fecal microbiota transplantation in a patient with severe complicated Clostridium difficile infection after liver transplantation. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2018;12:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481937.
Leylabadlo HE, Ghotaslou R, Kafil HS, Feizabadi MM, Moaddab SY, Farajnia S, Sheykhsaran E, Sanaie S, Shanehbandi D, Baghi HB. Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases: from role of gut microbiota to microbial-based therapies. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020;39(4):613–27.
Moreira GV, Azevedo FF, Ribeiro LM, Santos A, Guadagnini D, Gama P, Liberti EA, Saad MJ, Carvalho CR. Liraglutide modulates gut microbiota and reduces NAFLD in obese mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;62:143–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.07.009.
Angelberger S, Reinisch W, Makristathis A, Lichtenberger C, Dejaco C, Papay P, Novacek G, Trauner M, Loy A, Berry D. Temporal bacterial community dynamics vary among ulcerative colitis patients after fecal microbiota transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:1620. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.257.
Russell GH, Kaplan JL, Youngster I, Baril-Dore M, Schindelar L, Hohmann E, Winter HS. Fecal transplant for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection in children with and without inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;58:588–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000000283.
Wang S, Xu M, Wang W, Cao X, Piao M, Khan S, Yan F, Cao H, Wang B. Systematic review: adverse events of fecal microbiota transplantation. PLoS ONE. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161174.
Baxter M, Colville A. Adverse events in fecal microbiota transplant: a review of the literature. J Hosp Infect. 2016;92:117–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2015.10.024.
Craven L, Rahman A, Parvathy SN, Beaton M, Silverman J, Qumosani K, Hramiak I, Hegele R, Joy T, Meddings J, Urquhart B. Allogenic fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease improves abnormal small intestinal permeability: a randomized control trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(7):105510–65. https://doi.org/10.1430/ajg.0000000000000661.
Witjes JJ, Smits LP, Pekmez CT, Prodan A, Meijnikman AS, Troelstra MA, Bouter KE, Herrema H, Levin E, Holleboom AG, Winkelmeijer M. Donor fecal microbiota transplantation alters gut microbiota and metabolites in obese individuals with steatohepatitis. Hepatol Commun. 2020;4(11):1578–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1601.
Lechner S, Yee M, Limketkai BN, Pham EA. Fecal microbiota transplantation for chronic liver diseases: current understanding and future direction. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65(3):897–905.
Bajaj JS, Salzman NH, Acharya C, Sterling RK, White MB, Gavis EA, Fagan A, Hayward M, Holtz ML, Matherly S, Lee H. Fecal microbial transplant capsules are safe in hepatic encephalopathy: a phase 1, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology. 2019;70(5):1690–703.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Chitkara University for providing facilities and continuous support for writing this review article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SA, OB and PK: literature review: MG, NT and OB: review and editing: AK and TGS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All are aware of its submission to the Journal and its publication.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
There are no mandatory ethics documents associated with this mini review report.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, M., Krishan, P., Kaur, A. et al. Mechanistic and physiological approaches of fecal microbiota transplantation in the management of NAFLD. Inflamm. Res. 70, 765–776 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01480-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01480-z