Search
Search Results
-
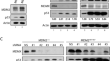
MDMX is essential for the regulation of p53 protein levels in the absence of a functional MDM2 C-terminal tail
BackgroundMDM2 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is able to ubiquitinate p53, targeting it for proteasomal degradation. Its homologue MDMX does not have...
-
The role of SIRT5 and p53 proteins in the sensitivity of colon cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agent 5-Fluorouracil
BackgroundIn the treatment of colorectal cancer, it is important to develop drug combinations that will increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy...

-
PRDX2 promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by increasing the ubiquitinated degradation of p53
Colorectal cancer is the most common gastrointestinal cancer and causes severe damage to human health. PRDX2 is a member of the peroxiredoxin family...

-
The RNA helicase Ddx21 controls Vegfc-driven developmental lymphangiogenesis by balancing endothelial cell ribosome biogenesis and p53 function
The development of a functional vasculature requires the coordinated control of cell fate, lineage differentiation and network growth. Cellular...

-
m5C-dependent cross-regulation between nuclear reader ALYREF and writer NSUN2 promotes urothelial bladder cancer malignancy through facilitating RABL6/TK1 mRNAs splicing and stabilization
The significance of 5-methylcytosine (m 5 C) methylation in human malignancies has become an increasing focus of investigation. Here, we show that m 5 C...

-
Cell-cycle arrest and senescence in TP53-wild type renal carcinoma by enhancer RNA-P53-bound enhancer regions 2 (p53BER2) in a p53-dependent pathway
TP53 is a classic tumor suppressor, but its role in kidney cancer remains unclear. In our study, we tried to explain the role of p53 in kidney cancer...

-
Mutant p53-reactivating compound APR-246 synergizes with asparaginase in inducing growth suppression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Asparaginase depletes extracellular asparagine in the blood and is an important treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) due to asparagine...

-
Investigating Conformational Dynamics and Allostery in the p53 DNA-Binding Domain Using Molecular Simulations
The p53 tumor suppressor is a multifaceted context-dependent protein, which is involved in multiple cellular pathways, with the ability to either...
-
Histone demethylase KDM4C controls tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by epigenetically regulating p53 and c-Myc
Glioblastoma is the most lethal brain tumor and its pathogenesis remains incompletely understood. KDM4C is a histone H3K9 demethylase that...

-
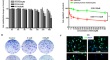
A carbazole compound, 9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3-carbaldehyde, plays an antitumor function through reactivation of the p53 pathway in human melanoma cells
p53, the major tumor suppressor, is frequently mutated in many cancers, and up to 84% of human melanomas harbor wild-type p53, which is considered to...
-
mTORC1 accelerates osteosarcoma progression via m6A-dependent stabilization of USP7 mRNA
Osteosarcoma (OS) is considered a sex steroid hormone-dependent bone tumor. The development and progression of OS are regulated by 17β-estradiol...

-
The regulatory roles of p53 in cardiovascular health and disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of mortality globally, so further investigation is required to identify its underlying...

-
Coronin 2B deficiency induces nucleolar stress and neuronal apoptosis
In eukaryotes, the nucleolus is the critical non-membranous organelle within nuclei that is responsible for ribosomal DNA (rDNA) transcription and...

-
Stabilization of CDK6 by ribosomal protein uS7, a target protein of the natural product fucoxanthinol
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) regulate the cell cycle, which is important for cell proliferation and development. Cyclins bind to and...

-
UFMylation maintains tumour suppressor p53 stability by antagonizing its ubiquitination
p53 is the most intensively studied tumour suppressor
1 . The regulation of p53 homeostasis is essential for its tumour-suppressive function2 ,3 ....
-
Dual regulation of p53 by the ribosome maturation factor SBDS
The Shwachman-Bodian Diamond syndrome (SBDS)-associated gene, SBDS , is involved in rRNA synthesis and ribosome maturation, but the role of SBDS in...

-
Sempervirine inhibits RNA polymerase I transcription independently from p53 in tumor cells
In the search of small molecules that can target MDM2/p53 pathway in testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs), we identified sempervirine...

-
Irradiation induces p53 loss of heterozygosity in breast cancer expressing mutant p53
Mutations in one allele of the TP53 gene in cancer early stages are frequently followed by the loss of the remaining wild-type allele (LOH) during...

-
Tubular β-catenin alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in acute kidney injury
Mitochondria take part in a network of intracellular processes that regulate homeostasis. Defects in mitochondrial function are key...

-
Sodium cantharidinate, a novel anti-pancreatic cancer agent that activates functional p53
Despite the use of many types of chemotherapies for pancreatic cancer, optimal efficacy has not been obtained so far. Pancreatic cancer shows a high...
