Abstract
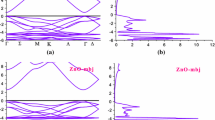
Optical response of Ti-doped (50%) hafnia (HfO2) has been studied, using first-principles calculations within the framework of density functional theory, to explore the feasibility of doped hafnia in photovoltaics. Density of states (DOS) of hafnia and doped hafnia are also presented to understand the role of Ti do** in reducing the bandgap of the base material from 5.77 to 2.33 eV leading to its applications in photovoltaic devices and UV detectors. Various optical properties like frequency-dependent dielectric constants and absorption coefficients are explained.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowther JE (2003) MRS Bull 28:189
Jaffe JE, Bachorz RA, Gutowski M (2005) Phys Rev B 72:144107
Zheng JX, Ceder G, Maxisch T, Chim WK, Choi WK (2007) Phys Rev B 75:104112
Nakhmedov EP, Nadimi E, Bouhassoune M, Radehaus C, Wieczorek K (2007) Phys Rev 75:115204
Caravaca MA, Mino JC, Perez VJ, Casali RA, Ponce CA (2009) J Phys Condens Matter 21:015501
Jiang H, Ricardo I, Abal G, Rinke P, Scheffler M (2010) Phys Rev B 81:085119
Zhang J, Oganov AR, Li X, Xue KH, Wang Z, Dong H (2015) Phys Rev B 92:184104
Blaha P, Schwarz K, Sorantin P, Rickey SB (1999) Comput Phys Commun 59:399
Perdew JP, Ruzsinszky A, Csonka GI, Vydrov OA, Scuseria GE, Constantin LA, Zhou X, Burke K (2008) Phys Rev Lett 100:136406-1–136406-4
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Prof. P. Blaha for providing the WIEN2k codes to our group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ahuja, U., Mali, D., Kumar, K., Soni, A. (2020). Use of Ti-Doped Hafnia in Photovoltaic Devices: Ab Initio Calculations. In: Kalam, A., Niazi, K., Soni, A., Siddiqui, S., Mundra, A. (eds) Intelligent Computing Techniques for Smart Energy Systems. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 607. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0214-9_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0214-9_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0213-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0214-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)