Abstract
Modern offshore and onshore green energy engineering includes energy harvesting—as a result, extensive experimental investigations, as well as safety and reliability analysis are crucial for design and engineering. For this study, several wind-tunnel experiments under realistic in situ wind speed conditions have been conducted to examine the performance of gallo** energy harvester. Next, a novel structural reliability approach is presented here that is especially well suited for multi-dimensional energy harvesting systems that have been either numerically simulated or analog observed during the representative time lapse, yielding an ergodic system time record. As demonstrated in this study, the advocated methodology may be used for risk assessment of dynamic system structural damage or failure. Furthermore, traditional reliability methodologies dealing with time series do not easily cope with the system’s high dimensionality, along with nonlinear cross-correlations between the system’s components. This study’s objective was to assess state-of-the-art reliability method, allowing efficient extraction of relevant statistical information, even from a limited underlying dataset. The methodology described in this study aims to assist designers when assessing nonlinear multidimensional dynamic energy harvesting system’s failure and hazard risks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Since wind energy is green and renewable, as advertised by global political agenda nowadays, energy harvesters (EH) became recently a popular research topic. Engineering research is also being done on micro- and nano-size EHs. Micro-scale wind energy is captured using piezoelectric, triboelectric, and electrostatic EHs; macro-scale wind energy is captured using an electromagnetic EH. Low-frequency EHs technology has been recently shown to be practical and advantageous. These innovations have been developed to supply energy to a variety of low-cost, low-power gadgets, including MEMS and Wireless Sensor Networks (WNS). It has been demonstrated that piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting (PVEH) is able to transform environmental mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy. Mechanical vibration is of an irregular and intermittent nature, resulting in aero-instability in the form of resonant vibrations. Thus, employing flow-induced vibrations (FIVs) to generate energy has been proven to be practical. Vortex-Induced Vibrations (VIV), wake gallo**, gallo**, and other related phenomena represent examples of FIVs. In the past decade, various investigations have utilized innovative experimental, numerical, and theoretical methods. In Albaladejo et al. (2010) the authors introduced a model for EH aero-instability coupling. In Mehmood et al. (2013) the authors presented the CFD approach to describe VIV Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters (VIVPEH). In Fazeres-Ferradosa et al. (2018a) the authors studied the Galerkin algorithm, applied to theoretical VIV piezoelectric EH features, with a series of laboratory tests carried out to examine the optimization process of a multifunctional VIVPEH device. In recent research (Dai et al., 2014) the authors have reported a transition from VIVPEH to GPEH, by adding 2 Y-shaped attachments. In Wang et al. (2019) the authors have used bistable and tristable features, subsequently examining GPEH nonlinear system response.
Energy harvesting systems are significant in both offshore and onshore applications. The hazards of ocean pollution are progressively rising as the oceanic industry increases. Devices for monitoring the water, such as various types of sensors, are created to address this kind of issue. Data can be gathered from remote locations and sent to local stations using sensors (Albaladejo et al., 2010; Zhao et al., 2019) have investigated the reliability and durability of the P1 MFC transducer, subjected to base excitations. In Wang et al. (2020) the authors reported experimental findings, where EH suffered damage at acceleration levels of 0.4 to 0.5 g. In Zhao and Yang (2018) the authors studied the EH performance of DuraAct (DuraAct P-876.A12 from Physik Instrumente GmbH & Co. KG.) piezo-sheet mounted EH on the railway, EH was reported to fail after about 100 cycles, under acceleration of 1 g. Next, in Daqaq (2015) the authors have applied a P-2 MFC sheet, using finite element method (FEM) and laboratory tests to study long-term fatigue life of EH. In Gaidai et al. (2006a). There have not been much studies done on the reliability of wind-induced vibrational EH dynamic performance, supported by experimental tests. Few studies have examined the EH system extreme performance and, consequently, reliability, and safety of EH operating conditions. Recent studies have typically concentrated on EH’s beam behavior under fatigue loadings, due to specific excitations, to estimate EH’s lifetime.
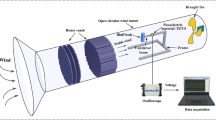
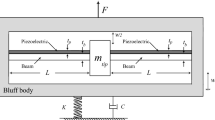
This study focuses on extreme value statistics of the GPEH dynamic system’s response. Both theoretical and experimental research have been done in order to examine the dynamic performance of particular gallo** EH. The experimental setup and specifics of the EH bluff body have been presented in Fig. 1. GPEH dynamic performance has been evaluated in a wind tunnel, using a circular inlet cross section. By installing a honeycomb structure within a wind tunnel’s settling chamber, having a diameter of 400 mm, steady incoming air flow was created, and wind speed ranged within 1 ≤ U ≤ 6 m/s. Piezoelectric sheet (Model: PZT-5, JiaYeShi, China) of 30 × 20 × 0.5 mm3 has been mounted on a substrate, made of aluminum, having dimensions of 200 × 25 × 0.5 mm3 when designing the GPEH cantilever. Free-end of the GPEH piezoelectric cantilever has been attached to a circular-sectioned bluff body (Wang et al., 2020). GPEH bluff body has been made of a hardened foam, having a length of 0.12 m, and a diameter of 0.03 m. Prototyped GPEH piezoelectric cantilever dam** ratio ζ has been measured, using the logarithmic decremental technique. For physical parameters of the GPEH experimental prototype, see Table 1, where \({C}_{p}\) is GPEH’s piezoelectric transducer clam** capacitance; \(M\) being GPEH’s bluff body effective mass; \({\zeta }_{1}\) GPEH’s dam** ratio; \({\omega }_{1}\)—GPEH’s natural vibrational frequency; \(\theta \)—equivalent electromechanical coefficient, for further details, see (Wang et al., 2020).
The free end of EH’s circular-sectioned bluff body has been attached to its piezoelectric cantilever (Albaladejo et al., 2010). Incoming wind speed U has been measured, using hot-wire anemometer (Model: 405i, Testo Co., USA). GPEH voltage output has been measured, using a digital oscilloscope (Model: DS1104S, RIGOL., China), for GPEH experimental setup see (Wang et al., 2019).
It is important to note that a GPEH’s intended use is to practically harvest low-speed wind energy: U ≤ 7 m/s, within the so-called “strong-breeze” region, Table 2.
Traditional propeller generators work better, when wind speed is high (7 m/s and above) because their motor size better matches these wind speeds.
Finally, it is worth mentioning a variety of other existing GPEH types: enhanced GPEH, having cooperative modes of collisions and vibrations, (Rugbjerg et al., 2006b); EH with self-regulating triboelectric nano-generators, self-powered wind speed sensor (Franck & Luc, 2011; Larsen et al., 2015; Mouslim et al., 2008; Teena et al., 2012); magnetically coupled water-proof piezoelectric-electromagnetic hybrid wind EH (Cheng et al., 2003; Cook & Harris, 2004; Ewans, 2014; Heffernan & Tawn, 2004; Jensen & Capul, 2006; Kim & Lee, 2015; Li et al., 2013; Zhao & Ono, 1999). This study is structured as follows: in the next section novel reliability methodology will be introduced, followed by the application of this reliability methodology to a particular GPEH device and its laboratory-recorded measurements.
Method
This section describes the Naess–Gaidai (NG) extrapolation approach (Gaidai et al. 2023a; Zhang et al. 2018), which is based on Weibull distribution with 3 parameters, and is applicable to a variety of unidimensional random system components. The requirement to do long-term statistical analysis for the structure of interest typically drives motivation for reliability study in engineering and design. The 3-parameter Weibull distribution is briefly introduced in the paragraph that follows. In reliability analysis, Weibull distribution has proved a potent choice: in contrast to exponential distribution, it offers a significantly wider application range. In reliability engineering, Weibull distribution is a viable substitute for both Gamma and Lognormal distributions. Weibull and exponential distributions have recently been given a number of weighted iterations in the literature
with \({\lambda }_{W},\beta ,\theta \) being the scale, shape, and minimum lifespan (location) parameters respectively, and \({\lambda }_{W}>0, \beta >0, x>\theta \). In lifetime data analysis, \(\theta \) is typically referred to as a threshold, guarantee time or a parameter, and \({\lambda }_{W}\) is the mean time to failure. NG method is based on adding 1 more parameter \(q\) to the 3-parameter Weibull’s distribution
with \(q>0\).Weibull distribution is well suited for modeling different environmental loadings, as well as structural reactions to such loadings. The distribution described by Eq. (2) will be referred to as “modified Weibull” or “4-parameter Weibull” in the sections that follow. As can be demonstrated, the essence of the NG technique—the modified Weibull distribution, happens to be a suitable approximation for empirical probability density function (PDF) tails, namely when \(x\to \infty \), for various engineering and design problems. As is customary in wind engineering, we will demonstrate the advocated approach in the sections that follow, by completing so-called short-term analyses for stationary environmental conditions. In situ scatter diagram, which will not be discussed in this study because it is being common knowledge, may be used for long-term analysis. In general, it is often challenging to assess realistic environmental system reliability function, using established theoretical reliability methodologies (Aarnes et al. 2012; Battjes and Groenendijk 2000; Bidlot and Janssen 2003; Cook and Harris 2004; Ferreira and Guedes 2000; Franck and Luc 2011; Gaidai et al. 2020, 2022; Zhao et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2019). Utilizing classic theoretical reliability approaches to assess a system’s reliability is not an easy and straightforward task. Typically, it is assumed that wind speeds represent an ergodic random process (quasi-stationary and homogenous) (Cheng et al., 2022; Gaidai & **ng, 2022a, b; Gaidai et al., 2022b, c, d, e, f, g, h; Xu et al., 2022). Think of an MDOF (multi-degree of freedom) EH system, subjected to in situ environmental loads (Balakrishna et al., 2022; Gaidai & **ng, 2022a, c; Gaidai et al., 2022c, d, e, g, h, i, j, k). Another option is to view the EH system process as being dependent on external (environmental) factors, whose temporal fluctuation may be modeled as ergodic processes. MDOF EH dynamic system being represented through its critical/key components \(\left(X\left(t\right), Y\left(t\right), Z\left(t\right),\dots \right)\) that have been measured/simulated over a representative time span \((0,T)\). One-dimensional system components global maxima over entire time lapse \((0,T)\) being denoted here as \({X}_{T}^{\text{max}}=\underset{0\le t\le T}{\text{max}}X\left(t\right)\), \({Y}_{T}^{\text{max}}=\underset{0\le t\le T}{\text{max}}Y\left(t\right)\), \({Z}_{T}^{\text{max}}=\underset{0\le t\le T}{\text{max}}Z\left(t\right), \dots \). By representative time lapse \(T\) one means large enough value of \(T\), with respect to dynamic system’s auto-correlation as well as relaxation time scales. Let \({X}_{1},\dots ,{X}_{{N}_{X}}\) be temporally consequent EH system component’s \(X(t)\) local maxima, recorded at discrete, monotonously increasing time instants \({t}_{1}^{X}<\dots <{t}_{{N}_{X}}^{X}\) within \((0,T)\) Analogous definition to follow for other MDOF EH system’s components \(Y\left(t\right), Z\left(t\right), \dots \) with \({Y}_{1},\dots ,{Y}_{{N}_{Y}};\) \({Z}_{1},\dots ,{Z}_{{N}_{Z}}\) etc. For simplicity, all EH system’s components local and hence global maxima are assumed to be positive. The target is now to accurately estimate the system’s failure/hazard/damage probability, namely probability/risk of exceedance
with
being target non-exceedance (survival) system probability, given critical values of EH system’s components \({\eta }_{X}\), \({\eta }_{Y}\), \({\eta }_{Z}\),…; with \(\cup \) being logical unity operation «or»; and \({p}_{{X}_{T}^{\text{max}}, { Y}_{T}^{\text{max}}, { Z}_{T}^{\text{max}} , \dots }\) being joint PDF of EH system component’s global maxima over entire observational time-span \((0,T)\). In practice, however, it is not feasible to assess directly the latter joint PDF \({p}_{{X}_{T}^{\text{max}}, { Y}_{T}^{\text{max}}, { Z}_{T}^{\text{max}} , \dots }\) due to the system’s high dimensionality, and underlying dataset limitations. More specifically, when either component \(X\left(t\right)\) exceeds \({\eta }_{X}\), or \(Y\left(t\right)\) exceeds \({\eta }_{Y}\), or \(Z\left(t\right)\) exceeds \({\eta }_{Z}\), etc., EH system is regarded as immediately failed. Fixed hazard/failure levels \({\eta }_{X}\), \({\eta }_{Y}\), \({\eta }_{Z}\),… being individual for each one-dimensional system’s component. \({X}_{{N}_{X}}^{\text{max}}=\text{max }\{{X}_{j}\hspace{0.17em};j=1,\dots ,{N}_{X}\}={X}_{T}^{\text{max}}\), \({Y}_{{N}_{Y}}^{\text{max}}=\text{max }\{{Y}_{j}\hspace{0.17em};j=1,\dots ,{N}_{Y}\}={Y}_{T}^{\text{max}}\), \({Z}_{{N}_{z}}^{\text{max}}=\text{max }\{{Z}_{j}\hspace{0.17em};j=1,\dots ,{N}_{Z}\}={Z}_{T}^{\text{max}}\), etc. Now, let us sort EH dynamic system component’s local maxima time instants \(\left[{t}_{1}^{X}<\dots <{t}_{{N}_{X}}^{X}; {t}_{1}^{Y}<\dots <{t}_{{N}_{Y}}^{Y}; {t}_{1}^{Z}<\dots <{t}_{{N}_{Z}}^{Z}\right]\) in a monotonously non-decreasing order into one single merged time vector \({t}_{1}\le \dots \le {t}_{N}\). Note that \({t}_{N}=\text{max }\{{t}_{{N}_{X}}^{X}, {t}_{{N}_{Y}}^{Y}, { t}_{{N}_{Z}}^{Z}, \dots \}\), \(N\le {N}_{X}+{N}_{Y}+{ N}_{Z}+ \dots \). In this case, \({t}_{j}\) represents occurrences times of EH component local maxima of one of MDOF system components, namely either \(X\left(t\right)\) or \(Y\left(t\right)\), or \(Z\left(t\right)\) etc. Next, we screen continuously, concurrently for the EH system component’s local maxima, within EH one-dimensional system components, recording their exceedances of MDOF limit/hazard/risk vector \(\left({\eta }_{X}, {\eta }_{Y}, {\eta }_{Z},...\right)\) by any of EH system’s components \(X, Y, Z, \dots \) Local one-dimensional EH system component maxima have been merged now into 1 temporal non-decreasing system vector \(\overrightarrow{R}=\left({R}_{1}, {R}_{2}, \dots ,{R}_{N}\right)\) in accordance with the merged temporal vector \({t}_{1}\le \dots \le {t}_{N}\). Hence, EH component’s local maxima \({R}_{j}\) is in fact actually encountered the EH system component’s local maxima, corresponding to either \(X\left(t\right)\) or \(Y\left(t\right)\), or \(Z\left(t\right)\) and so on. Finally, a unified limit/hazard system vector \(\left({\eta }_{1}, \dots ,{\eta }_{N}\right)\) is introduced, with each EH system component \({\eta }_{j}\) being either \({\eta }_{X}\), \({\eta }_{Y}\) or \({\eta }_{Z}\) and so on, depending which of \(X\left(t\right)\) or \(Y\left(t\right)\), or \(Z\left(t\right)\) etc. corresponding to the current EH component’s local maxima, having a running index \(j\). Scaling parameter \(0<\lambda \le 1\) is being introduced to simultaneously decrease limit/hazard values for all EH dynamic system components, namely new MDOF hazard/limit vector \(\left({\eta }_{X}^{\lambda },{ \eta }_{Y}^{\lambda }, {\eta }_{z}^{\lambda },...\right)\) with \({\eta }_{X}^{\lambda }\equiv \lambda {\cdot \eta }_{X}\), \(\equiv \lambda {\cdot \eta }_{Y}\), \({\eta }_{z}^{\lambda }\equiv \lambda {\cdot \eta }_{Z}\),… being now introduced. A unified limit vector \(\left({\eta }_{1}^{\lambda }, \dots ,{\eta }_{N}^{\lambda }\right)\) being introduced with each component \({\eta }_{j}^{\lambda }\) being either \({\eta }_{X}^{\lambda }\), \({\eta }_{Y}^{\lambda }\) or \({\eta }_{z}^{\lambda }\) etc. The latter identifies system’s survival probability \(P\left(\lambda \right)\) as a function of parameter \(\lambda \), note that \(P\equiv P\left(1\right)\) from Eq. (1). Non-exceedance (survival) probability/risk \(P\left(\lambda \right)\) may be now assessed
The idea behind this series of conditioning-based approximations is explained in detail in Gaspar et al. (2012), Gaidai et al. (2023g), Naess et al. (2009), Xu et al. (2018). Dependence between neighboring \({R}_{j}\) is not always negligible, hence following 1-step (conditioning number \(k=1\) memory approximation being introduced
for \(2\le j\le N\) (conditioning number \(k=2\)). Approximation, introduced by Eq. (6) may be now further expressed as
with \(3\le j\le N\) (conditioning number \(k=3\)), etc. (Balakrishna et al., 2022; Gaidai et al., 2022g, 2022h, 2022i, 2022j, 2022k). The idea is to monitor each independent damage/hazard/failure, that happened locally first in time, thus avoiding (de-clustering) cascading inter-correlated local exceedances. Since the MDOF EH system has been assumed ergodic and hence stationary, probability (system failure/damage risk) \(p_{k} \left( \lambda \right): = {\text{Prob}}\left\{ {R_{j} > \eta_{j}^{\lambda } {|} R_{j - 1} \le \eta_{j - 1}^{\lambda } , R_{j - k + 1} \le \eta_{j - k + 1}^{\lambda } } \right\}\) for \(j\ge k\) is independent of \(j\) and only dependent on the conditioning number \(k\). Hence, the non-exceedance probability may be approximated similarly to the conditional exceedance rate method
Note that Eq. (8) follows from Eq. (3) if neglecting \(\text{Prob}({R}_{1}\le {\eta }_{1}^{\lambda })\approx 1\), as design failure/damage probability being of a small order of magnitude, with \(N\gg k\). Note that Eq. (8) is similar to a well-known mean up-crossing rate equation for the hazard/failure probability/risk (probability of exceedance) (Gaidai & **ng, 2022a, b; Madsen et al., 1986; Rice, 1944). There is convergence with respect to the conditioning parameter \(k\)
Note that Eq. (9) for \(k=1\) turns into a well-known non-exceedance (survival) probability relationship with a corresponding mean up-crossing rate function
with \({\nu }^{+}(\lambda )\) denoting mean-up-crossing rate of the risk level \(\lambda \) for the above assembled non-dimensional vector \(R\left(t\right)\), assembled from scaled MDOF EH system components \(\left(\frac{X}{{\eta }_{X}}, \frac{Y}{{\eta }_{Y}}, \frac{Z}{{\eta }_{Z}}, \dots \right)\). The mean-up-crossing rate is given by Rice's formula, given in Eq. (10) with \({p}_{R\dot{R}}\) being joint PDF for \(\left(R, \dot{R}\right)\) with \(\dot{R}\) being time derivative \(R{\prime}\left(t\right)\) (Rice, 1944). Equation (10) relies on the so-called Poisson assumption, implying that upcrossing events of critical/high \(\lambda \) levels (in this study \(\lambda \ge 1\)) may be assumed to be nearly independent. For narrow band EH systems, displaying cascading/clustering hazards/failures in various system components, temporally successive components local maxima (caused by inherent inter-dependency between EH system extreme events) manifest themselves through highly correlated local maxima clusters, stored within assembled EH system vector \(\overrightarrow{R}=\left({R}_{1}, {R}_{2}, \dots ,{R}_{N}\right)\). The stationarity assumption was applied in the examples above, but the suggested method may also be used to handle nonstationary cases. Given the in situ scatter diagram having \(m=1,..,M\) environmental states, each individual short-term environmental state has individual probability \({q}_{m}\), so that \(\sum_{m=1}^{M}{q}_{m}=1\). Let one introduce a long-term statistical equation
with \({p}_{k}(\lambda ,m)\) being same function, as in Eq. (7), corresponding to a specific short-term environmental state, with number \(m\). Note that within recent years authors have successfully verified the recommended approach’s correctness for a wide range of 1-dimensional dynamic systems (Gaidai & **ng, 2022b). Next, following the extrapolation Naess–Gaidai (NG) technique is introduced, being asymptotically of Gumbel distribution type, and serving as the foundation for failure/hazard PDF-tail extrapolation. The latter strategy is predicated on the notion that a class of parametric functions required for extrapolation in general case may be described in a manner akin to that of the relationship between Gumbel distribution and Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) distribution family. Extreme values that may be detected from sampled time series do not always follow asymptotic distributions, or to say the least, it is often quite challenging to establish that they are indeed asymptotic. The latter suggests that it is important to extend focus to a range of sub-asymptotic levels. Hence, it is suggested that the NG class of sub-asymptotic distributions be appended to the asymptotic Gumbel functional class. The above introduced \({p}_{k}(\lambda )\) as functions being regular in PDF tail, specifically for values of parameter \(\lambda \) approaching, and exceeding \(1\). For \(\lambda \ge {\lambda }_{0}\), PDF tail behaves similarly to \({\text{exp}}\left\{-{\left(a\lambda +b\right)}^{c}+d\right\}\) with four parameters \(a, b, c, d\) being suitably fitted 4 constants, for suitable PDF tail cut-on \({\lambda }_{0}\) value
By plotting \({\text{ln}}\left\{{\text{ln}}\left({p}_{k}(\lambda )\right)-{d}_{k}\right\}\) versus \({\text{ln}}\left({a}_{k}\lambda +{b}_{k}\right)\), often nearly linear PDF tail behavior being observed. It is useful to do the optimization on the logarithmic level by minimizing the following error function F with respect to 4 parameters \({a}_{k}, {b}_{k}, {c}_{k},{d}_{k}\)
with \({\lambda }_{1}\) being suitable PDF tail cutoff value, namely the largest \(\lambda \)-parameter value, where the confidence interval width is still acceptable. Optimal values of four parameters \({a}_{k}, {b}_{k}, {c}_{k},{d}_{k}\) may also be determined using the sequential quadratic programming (SQP) method incorporated in the NAG Numerical Library (Numerical Algorithms Group, 2010). Weight function \(\omega \) can be defined as \(\omega \left(\lambda \right)={\left\{{\text{ln}}{\text{CI}}^{+}\left(\lambda \right)-{\text{ln}}{\text{CI}}^{-}\left(\lambda \right)\right\}}^{-2}\) with \(\left({\text{CI}}^{-}\left(\lambda \right),{ \text{CI}}^{+}\left(\lambda \right)\right)\) being 95% confidence interval (CI), empirically estimated from simulated/measured underlying dataset (Gaidai & **ng, 2022a, b; Gaidai et al., 2022b, c, d, e). For levels of \(\lambda \) approaching \(1\), the approximate limits of a p-% confidence interval (CI) of \({p}_{k}\left(\lambda \right)\) can be given as follows
with \(f(p)\) being estimated from an inverse normal distribution, for example \(f\left(90\%\right)=1.65\), \(f\left(95\%\right)=1.96\) with \(N\) being total number of EH system component’s local maxima, constituting system vector \(\overrightarrow{R}\).
The purpose of this discussion now is to address extrapolation in light of the data quality that underlies it, namely the raw PDF, CDF, and mean upcrossing rate functions tails (\(\lambda >{\lambda }_{\text{cut on}}\)) inherent anomalies. Since the mean upcrossing rate function tail has been created, by integrating the PDF tail, it is now evident that the PDF tail will be less continuous than the CDF and mean upcrossing rate function tails. In order to combat raw tail discontinuities, as seen in Fig. 2a), the authors first propose integrating mean upcrossing rate functions tail in this study.
As a transition from a convex to a concave tail shape, we secondly propose a logarithmic transformation of the integrated mean upcrossing rate functions tail to the so-called “fat tail” condition. More specifically, \(\int {\nu }^{+}\left(\lambda \right)\to \text{ln}\left(1+\int {\nu }^{+}\left(\lambda \right)\right)\) transformation has been suggested, Fig. 2b).
The recommended approach and the NG extrapolation (modified four-parameter Weibull) method are compared in Fig. 3, with a star designating the start of extrapolation. By retaining only each 100th point from the original dataset, a shorter dataset was created by 100-fold thinning the original dataset. By comparing anticipated outcomes based on the shorter dataset with findings based on the entire dataset, the recommended technique was validated in this manner. The modified Weibull extrapolation predicted a convex tail rather than a concave one, as seen in Fig. 3, but the recommended technique was performed quite accurately.
Results
When the wind speeds reach greater levels, EH efficiency will significantly fall, hence piezoelectric energy harvesters always try to scavenge energy from low-wind speeds. As a result, a stopper may be built onto the prototype, to prevent damage in high wind conditions since the stopper will dampen the considerable vibration amplitude, brought on by relatively high wind speeds. Keep in mind that the optimal wind speed range for EH operations is below 7 m/s. Using measured voltage time-series, the total horizontal aerodynamic force acting on the EH bluff body time series has been calculated, using the following equation
containing following experimental setup parameters: \({C}_{p}=30.5{\times 10}^{-9}\) F; \(M=4.2{\times 10}^{-3}\;\text{ kg}\); \(C=5.3{\times 10}^{-3}\;\text{ N}/(\text{m}/\text{s})\); \(K=9.7\;\text{ N}/\text{s}\); \(\theta ={5.0\times 10}^{-3}\; \text{N}/\text{V}\), Table 1. In this section, bivariate random process \(Z(t)=(X(t),Y(t))\) has been studied, consisting of voltage and corresponding total force processes \(X(t),Y(t)\), with 1st component (voltage \(X=V\)) being measured and 2nd component (force \(Y=F\)) being computed synchronously, over a certain representative time lapse \((0,T)\). Let one assume that samples \(({X}_{1},{Y}_{1}),\dots ,({X}_{N},{Y}_{N})\) have been taken at N equidistant discrete temporal instants \({t}_{1},\dots ,{t}_{N}\) within the measurement time lapse \(\left(0,T\right).\) This study utilizes bivariate joint cumulative distribution function (CDF) \(P\left(\xi ,\eta \right):=\text{ Prob }\left({\widehat{X}}_{N}\le \xi ,{\widehat{Y}}_{N}\le \eta \right)\) of the 2D vector \(\left({\widehat{X}}_{N},{\widehat{Y}}_{N}\right)\), with components \({\widehat{X}}_{N}=\text{max}\left\{{X}_{j} ;j=1,\dots ,N\right\}\), and \({\widehat{Y}}_{N}=\text{max}\left\{{Y}_{j} ;j=1,\dots ,N\right\}\). In this paper \(\xi \) and \(\eta \) being recorded voltage and corresponding total force values respectively at the same in-situ location with the same EH device, measured synchronously.
Wind speeds PDF frequently follows Weibull distribution. To describe how gallo** energy harvesters react to in situ wind speed data (Choi et al., 2007; Gaidai & ** energy harvesting in heat exchange systems under the influence of ash deposition. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124175 " href="/article/10.1186/s40807-023-00085-w#ref-CR78" id="ref-link-section-d93390562e9572">2022; Zhou et al., 2019), Weibull distribution is frequently used. For EH, Fig. 4a) presents the correlation between measured voltage, and the associated total horizontal EH force. Figure 4 and Eq. (1) show that due to a small order of magnitude of \(\frac{{C}_{p}}{\theta }\), horizontal force exhibits the significant linear correlation with its underlying voltage. However, nonlinear connection predominated in the tail of the bivariate extreme distribution, Fig. 4a), and Eq. (13) due to higher values of \(\dot{V}\), \(\ddot{V}\). It has been evident that the latter occurrence needs to be accounted for in non-linear statistical analysis of PDF tails. Experimentally measured voltage and corresponding horizontal force were set as 2 relevant EH system components (dimensions) \(X, Y\) thus constituting an example of two-dimensional (2D) dynamic system. Measured maxima for each system component have been used as one-dimensional extreme threshold values \({\eta }_{X}\), \({\eta }_{Y}\). In order to unify both measured time series \(X, Y\) (EH voltage and horizontal force in this case) following scaling was performed
with both system components becoming now non-dimensional, and having the same hazard/failure limit equal to 1. While maintaining temporal non-decreasing order, all EH system components’ local maxima from 2 observed time series have been combined into 1 new (synthetic) time series: \(\overrightarrow{R}=\left(\text{max}\left\{{X}_{1},{Y}_{1}\right\},\dots ,\text{max}\left\{{X}_{N},{Y}_{N}\right\}\right)\) with each local maxima set \(\text{max}\left\{{X}_{j},{Y}_{j}\right\}\) being ordered within non-decreasing times, at which these local maxima of dynamic EH system occurred. An example of a non-dimensional constructed vector \(\overrightarrow{R}\) is shown in Fig. 4b), comprised EH system components local maxima for voltage and corresponding horizontal force, that are being selected as EH system two components. Extrapolation of hazard/failure PDF tail towards 1-year return period has been done. Vector \(\overrightarrow{R}\) is composed of entirely distinct system components, with different physical dimensions, it should be noted that this vector itself has no particular physical significance (Gaidai & **ng, 2023; Gaidai et al., 2023c, d, e, f, g, h; Gaspar et al., 2012; Naess et al., 2009; Xu et al., 2018). Index \(j\) is the running index of system components local maxima that were recorded in a non-decreasing temporal sequence (Gaidai et al., 2023i, j, k, l; Liu et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2023; Yakimov et al., 2023).
Extrapolation from Eq. (9) is shown in Fig. 5 in the direction of a hazard/failure state with a 1-year return period, given interest return period, and considerably beyond, \(\lambda =0.3\) cut-on value has been used. According to Eq. (12), dotted lines represent extrapolated 95% CIs. According to Eq. (8) \(p\left(\lambda \right)\) is directly related to the target hazard/failure probability \(1-P\) from Eq. (3). Hence, in agreement with Eq. (8) system hazard/failure probability \(1-P\approx {1-P}_{k}\left(1\right)\) may be assessed. Note that in Eq. (7) \(N\) corresponds to the total number of local maxima within the unified EH system vector \(\overrightarrow{R}\). Conditioning parameter \(k=2\) was found to be sufficient due to the occurrence of convergence with respect to \(k\), see Eq. (8). Advocated methodology can treat energy system’s multidimensionality, performing accurate extrapolation based only on a limited underlying dataset, utilizing measured datasets quite effectively (Gaidai et al., 2023g, 2023h, 2023i, 2023j, 2023k; Gaspar et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2023; Naess et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2018; Gaidai et al., 2022a).
Conclusions
Traditional reliability methods dealing with system-recorded time series do not always have the advantage of efficiently handling highly dimensional systems with nonlinear cross-correlations between different system components. The main advantage of the advocated technique is its ability to examine the reliability of high dimensional non-linear dynamic systems.
This study analyzed energy harvester's dynamic system behavior, under in situ environmental settings. The novel system reliability technique has been used to assess the likelihood of device damage, given the return period of interest. The theoretical rationale of the proposed approach has been discussed in detail. The complexity and high dimensionality of dynamic systems make it necessary to develop novel, accurate, yet robust techniques that can handle available underlying datasets, making the best use of it. Despite the fact that using direct measurement or Monte Carlo simulation to analyze the reliability of dynamic systems is appealing, it is not always affordable. This study’s methodology has already been shown successful, when used with a number of simulation models, but only for 1-dimensional system responses. Overall, quite accurate forecasts have been made. The main goal of this work was to develop a general-purpose, trustworthy, yet user-friendly multi-dimensional reliability methodology.
As seen, the suggested method produced a fairly narrow confidence interval. The suggested method might therefore be helpful for a variety of nonlinear dynamic systems reliability studies. This study demonstrates how the advocated methodology may assist designers in the accurate assessment of system damage or failure risks. To summarize pros and cons of the advocated methodology:
-
Benefits of the proposed structural reliability technique compared with traditional methods lie within the ability of novel methods to tackle high-dimensional energy harvesting systems.
-
Limitations of the advocated methodology lie within the assumption of the system’s stationarity. In case when underlying trend is present, it should be identified first.
Availability of data and materials
Data will be made available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Aarnes, O., Breivik, O., & Reistad, M. (2012). Wave extremes in the northeast Atlantic. Journal of Climate, 25, 1529–1543.
Abdelkefi, A. (2016). Aeroelastic energy harvesting: A review. International Journal of Engineering Science, 100, 112–135.
Albaladejo, C., Sánchez, P., Iborra, A., Soto, F., López, J. A., & Torres, R. (2010). Wireless sensor networks for oceanographic monitoring: A systematic review. Sensors, 10, 6948.
Amin, A. A., & Hussian, A. (2014). A weighted three-parameter weibull distribution. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 9(13), 6627–6635.
Avvari, P., Yang, Y., & Soh, C. (2017). Long-term fatigue behavior of a cantilever piezoelectric energy harvester. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 28(9), 1188–1210.
Balakrishna, R., Gaidai, O., Wang, F., **ng, Y., & Wang, S. (2022). A novel design approach for estimation of extreme load responses of a 10-MW floating semi-submersible type wind turbine. Ocean Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112007
Battjes, J., & Groenendijk, H. (2000). Wave height distributions on shallow foreshores. Coastal Engineering, 40(3), 161–182.
Bidlot J., & Janssen P. (2003). Unresolved bathymetry, neutral winds and new stress tables in WAM. Tech. Rep. ECMWF Research Department Memo R60.9/JB/0400, ECMWF.
Cheng, P. W., van Bussel, G., van Kuik, G., & Vugts, J. (2003). Reliability-based design methods to determine the extreme response distribution of offshore wind turbines. Wind Energ., 6, 1–22.
Cheng, Y., Gaidai, O., Yurchenko, D., Xu, X., & Gao, S. (2022). Study on the dynamics of a payload influence in the polar ship. In: The 32nd international ocean and polar engineering conference, paper number: ISOPE-I-22-342.
Choi, S.-K., Grandhi, R. V., & Canfield, R. A. (2007). Reliability-based structural design. Springer.
Cook, N., & Harris, R. (2004). Exact and general FT1 penultimate distributions of extreme wind speeds drawn from tail-equivalent Weibull parents. Structural Safety, 26, 391–420.
Dai, H., Abdelkefi, A., & Wang, L. (2014). Theoretical modeling and nonlinear analysis of piezoelectric energy harvesting from vortex-induced vibrations. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 25(14), 1861–1874.
Daqaq, M. F. (2015). Characterising the response of gallo** energy harvesters using actual wind statistics. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 357, 365–376.
Daue, T., & Kunzmann, J. (2008). Energy harvesting systems using piezo-electric MFCs. In: 17th IEEE international symposium on the applications of ferroelectrics. IEEE; 2008. vol. 1. pp. 1–1.
Ditlevsen, O., & Madsen, H. O. (1996). Structural reliability methods. John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Ewans, K. (2014). Evaluating environmental joint extremes for the offshore industry using the conditional extremes model. Journal of Marine Systems, 130, 124–130.
Fazeres-Ferradosa, T., Taveira-Pinto, F., Romão, X., Vanem, E., Reis, M. T., & das Neves, L. (2018b). Probabilistic design and reliability analysis of scour protections for offshore windfarms. Engineering Failure Analysis, 91, 291–305.
Fazeres-Ferradosa, T., Taveira-Pinto, F., Vanem, E., Reis, M. T., & Neves, L. D. (2018a). Asymmetric copula–based distribution models for met-ocean data in offshore wind engineering applications. Wind Engineering, 42(4), 304–334.
Ferreira, J., & Guedes, S. C. (2000). Modelling distributions of significant wave height. Coastal Engineering, 40, 361–374.
Franck, M., & Luc, H. (2011). A multi-distribution approach to POT methods for determining extreme waveheights. Coastal Engineering, 58, 385–394.
Gaidai, O., Cao, Y., & Loginov, S. (2023c). Global cardiovascular diseases death rate prediction. Current Problems in Cardiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.101622
Gaidai, O., Cao, Y., **ng, Y., & Balakrishna, R. (2023d). Extreme springing response statistics of a tethered platform by deconvolution. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnaoe.2023.100515
Gaidai, O., Cao, Y., **ng, Y., & Wang, J. (2023). Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Response Statistics. Micromachines, 14(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020271.
Gaidai, O., Fu, S., & **ng, Y. (2022i). Novel reliability method for multi-dimensional nonlinear dynamic systems. Marine Structures. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marstruc.2022.103278
Gaidai, O., Hu, Q., Xu, J., Wang, F., & Cao, Y. (2023h). Carbon storage tanker lifetime assessment. Global Challenges. https://doi.org/10.1002/gch2.202300011
Gaidai, O., Wang, F., Wu, Y., **ng, Y., Rivera, M. A., & Wang, J. (2022b). Offshore renewable energy site correlated wind-wave statistics. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.probengmech.2022.103207
Gaidai, O., Wang, F., **ng, Y., & Balakrishna, R. (2023g). Novel reliability method validation for floating wind turbines. Advanced Energy and Sustainability Research. https://doi.org/10.1002/aesr.202200177
Gaidai, O., Wang, F., & Yakimov, V. (2023f). COVID-19 multi-state epidemic forecast in India. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43538-022-00147-5
Gaidai, O., Wang, K., Wang, F., **ng, Y., & Yan, P. (2022d). Cargo ship aft panel stresses prediction by deconvolution. Marine Structures. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marstruc.2022.103359
Gaidai, O., Wu, Y., Yegorov, I., Alevras, P., Wang, J., & Yurchenko, D. (2022c). Improving performance of a nonlinear absorber applied to a variable length pendulum using surrogate optimisation. Journal of Vibration and Control. https://doi.org/10.1177/10775463221142663
Gaidai, O., & **ng, Y. (2022a). A novel multi regional reliability method for COVID-19 death forecast. Engineered Science. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d799
Gaidai, O., & **ng, Y. (2022b). A novel bio-system reliability approach for multi-state COVID-19 epidemic forecast. Engineered Science. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d797
Gaidai, O., & **ng, Y. (2022c). Novel reliability method validation for offshore structural dynamic response. Ocean Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113016
Gaidai, O., & **ng, Y. (2023). Prediction of death rates for cardiovascular diseases and cancers. Cancer Innovation. https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.47
Gaidai, O., **ng, Y., & Balakrishna, R. (2022f). Improving extreme response prediction of a subsea shuttle tanker hovering in ocean current using an alternative highly correlated response signal. Results in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100593
Gaidai, O., **ng, Y., Balakrishna, R., & Xu, J. (2023e). Improving extreme offshore wind speed prediction by using deconvolution. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13533
Gaidai, O., **ng, Y., Xu, J., & Balakrishna, R. (2023j). Gaidai-**ng reliability method validation for 10-MW floating wind turbines. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-33699-7
Gaidai, O., **ng, Y., & Xu, X. (2023a). Novel methods for coupled prediction of extreme wind speeds and wave heights. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-28136-8
Gaidai, O., Xu, J., Hu, Q., **ng, Y., & Zhang, F. (2022a). Offshore tethered platform springing response statistics. Scientific Reports, 12, 21182.
Gaidai, O., Xu, J., **ng, Y., Hu, Q., Storhaug, G., Xu, X., & Sun, J. (2022e). Cargo vessel coupled deck panel stresses reliability study. Ocean Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113318
Gaidai, O., Xu, J., Yakimov, V., & Wang, F. (2023k). Analytical and computational modeling for multi-degree of freedom systems: Estimating the likelihood of an FOWT structural failure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(6), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061237
Gaidai, O., Xu, J., Yakimov, V., & Wang, F. (2023l). Liquid carbon storage tanker disaster resilience. Environment Systems and Decisions. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-023-09922-1
Gaidai, O., Xu, J., Yan, P., **ng, Y., Zhang, F., & Wu, Y. (2022h). Novel methods for wind speeds prediction across multiple locations. Scientific Reports, 12, 19614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24061-4
Gaidai, O., Xu, X., Wang, J., Ye, R., Cheng, Y., & Karpa, O. (2020). SEM-REV offshore energy site wind-wave bivariate statistics by hindcast. Renewable Energy, 156, 689–695.
Gaidai, O., Yan, P., & **ng, Y. (2022j). A novel method for prediction of extreme wind speeds across parts of Southern Norway. Frontiers in Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.997216
Gaidai, O., Yan, P., & **ng, Y. (2022k). Prediction of extreme cargo ship panel stresses by using deconvolution. Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2022.992177
Gaidai, O., Yan, P., & **ng, Y. (2023b). Future world cancer death rate prediction. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-27547-x
Gaidai, O., Yan, P., **ng, Y., Xu, J., & Wu, Y. (2022g). A novel statistical method for long-term coronavirus modelling. F1000 Research, 11, 1282.
Gaidai, O., Yan, P., **ng, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, F., & Wu, Y. (2023i). Oil tanker under ice loadings. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-34606-w
Gaspar, B., Naess, A., Leira, B., & Soares, C. (2012). System reliability analysis of a stiffened panel under combined uniaxial compression and lateral pressure loads. Structural Safety, 39(5), 30–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2012.06.002
Gong, Y., Yang, Z., Shan, X., Sun, Y., **e, T., & Zi, Y. (2019). Capturing flow energy from ocean and wind. Energies, 12, 2184.
He, L., Zhang, C., Zhang, B., et al. (2022). A dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator for wind energy harvesting and self-powered wind speed monitoring. ACS Nano. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c11658
Heffernan, J., & Tawn, J. (2004). A conditional approach for multivariate extreme values. Journal of the Royal Statistic Society: Series B, 66(3), 497–546.
Janssen, P. (2000). ECMWF wave modeling and satellite altimeter wave data. Satellites, oceanography and society (pp. 35–36). Elsevier.
Jensen, J., & Capul, J. (2006). Extreme response predictions for jack-up units in second-order stochastic waves by FORM. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 21, 330–337.
Kallos, G. (1997). The regional weather forecasting system SKIRON. In: Proceedings, symposium on regional weather prediction on parallel computer environment, Athens, Greece. p. 9.
Kim, D. H., & Lee, S. G. (2015). Reliability analysis of offshore wind turbine support structures under extreme ocean environmental loads. Renewable Energy, 79, 161–166.
Larsen, X., Kalogeri, C., Galanis, G., & Kallos, G. (2015). A statistical methodology for the estimation of extreme wave conditions for offshore renewable applications. Renewable Energy, 80, 205–218.
Li, L., Gao, Z., & Moan, T. (2013). Joint environmental data at five European offshore sites for design of combined wind and wave energy devices. In: ASME 32nd international conference on ocean, offshore and arctic engineering. vol. 8.
Liu, Z., Gaidai, O., **ng, Y., & Sun, J. (2023). Deconvolution approach for floating wind turbines. Energy Science & Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.1485
Madsen, H. O., Krenk, S., & Lind, N. C. (1986). Methods of structural safety. Prentice-Hall Inc.
Mehmood, A., Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M. R., Nayfeh, A. H., Akhtar, I., & Nuhait, A. O. (2013). Piezoelectric energy harvesting from vortex-induced vibrations of circular cylinder. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 332(19), 4656–4667.
Melchers, R. E. (1999). Structural reliability analysis and prediction. John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Mouslim, H., Babarit, A., & Jordana, A. (2008). Project development of a wave energy test site in the French Atlantic Coast. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on ocean energy, Brest, France.
Naess, A., Stansberg, C., Gaidai, O., & Baarholm, R. (2009). Statistics of extreme events in airgap measurements. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1115/OMAE2008-57754
Numerical Algorithms Group. (2010). NAG Toolbox for Matlab. Numerical Algorithms Group.
Rice, S. O. (1944). Mathematical analysis of random noise. The Bell System Technical Journal, 23, 282–332.
Rugbjerg, M., Sørensen, O., & Jacobsen, V. (2006b). Wave forecasting for offshore wind farms. In: 9th International workshop on wave hindcasting and forecasting. pp. 24–29.
Rugbjerg M, Sørensen, O. R, & Jacobsen V. (2006a). Wave forecasting for offshore wind farms. In: 9th International workshop on wave hindcasting and forecasting, Victoria, B.C. Canada.
Sherrit, S., Lee, H., Walkemeyer, P., Hasenoehrl, J., Hall, J., Colonius, T., Tosi, L., Arrazola, A., Kim, N., Sun, K., & Corbett, G. (2014). Flow energy piezoelectric bimorph nozzle harvester. Active and passive smart structures and integrated systems 2014. International society for optics and photonics. 9057: 90570D.
Soma, A., & De Pasquale, G. (2013). Design of high-efficiency vibration energy harvesters and experimental functional tests for improving bandwidth and tenability. Smart sensors, actuators, and MEMS VI. International society for optics and photonics. 8763: 87630U.
Stanton, S., Erturk, A., & Mann, B. (2012). Nonlinear nonconservative behavior and modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesters including proof mass effects. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 23(2), 183–199.
Sun, J., Gaidai, O., **ng, Y., Wang, F., & Liu, Z. (2023). On safe offshore energy exploration in the Gulf of Eilat. Quality and Reliability Engineering International. https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.3402
Teena, N. V., Sanil, K., Sudheesh, K., & Sajeev, R. (2012). Statistical analysis on extreme wave height. Natural Hazards, 64(1), 223–236.
Thoft-Christensen, P., & Murotsu, Y. (1986). Application of environmental systems reliability theory. Springer.
Wang, J., Geng, L., Zhou, S., Zhang, Z., Lai, Z., & Yurchenko, D. (2020). Design, modeling and experiments of broadband tristable gallo** piezoelectric energy harvester. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 36, 592–605.
Wang, J., Zhang, C., Hu, G., Liu, X., Liu, H., Zhang, Z., & Das, R. (2022). Wake gallo** energy harvesting in heat exchange systems under the influence of ash deposition. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124175
Wang, J., Zhou, S., Zhang, Z., & Yurchenko, D. (2019). High-performance piezoelectric wind energy harvester with Y-shaped attachments. Energy Conversion and Management, 181, 645–652.
Wilkie W., High J., Bockman J., (2002). "Reliability testing of NASA piezocomposite actuators".
Williams, R., & Grimsley, B. (2004). Inman D (2004) Manufacturing and cure kinetics modeling for macro fiber composite actuators. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 23(16), 1741–1754.
Xu, X., **ng, Y., Gaidai, O., Wang, K., Patel, K., Dou, P., & Zhang, Z. (2022). A novel multi-dimensional reliability approach for floating wind turbines under power production conditions. Frontiers in Marine Science. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.970081
Xu, Y., Øiseth, O., Moan, T., & Naess, A. (2018). Prediction of long-term extreme load effects due to wave and wind actions for cable-supported bridges with floating pylons. Engineering Structures., 172, 321–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.06.023
Yakimov, V., Gaidai, O., Wang, F., Xu, X., Niu, Y., & Wang, K. (2023). Fatigue assessment for FPSO hawsers. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnaoe.2023.100540
Yang, K., Wang, J., & Yurchenko, D. (2019). A double-beam piezo-magneto-elastic wind energy harvester for improving the gallo**-based energy harvesting. Applied Physics Letters, 115(19), 193901.
Yu, Y., Rij, J., Coe, R., & Lawson, M. (2015). Preliminary wave energy converters extreme load analysis. In: Proceedings OMAE. vol. 9.
Zhang, J., Gaidai, O., & Gao, J. (2018). Bivariate extreme value statistics of offshore jacket support stresses in Bohai bay. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 140(4), 041305.
Zhao, L., & Yang, Y. (2018). An impact-based broadband aeroelastic energy harvester for concurrent wind and base vibration energy harvesting. J. Applied Energy, 212, 233–243.
Zhao, L., Zou, H., Yan, G., Liu, F., Tan, T., Zhang, W., Peng, Z., & Meng, G. (2019). A water-proof magnetically coupled piezoelectric-electromagnetic hybrid wind energy harvester. Applied Energy, 239(C), 735–746.
Zhao, T., Xu, M., **ao, X., Ma, Y., Li, Z., & Wang, Z. (2021). Recent progress in blue energy harvesting for powering distributed sensors in ocean. Nano Energy, 88, 106199.
Zhao, Y., & Ono, T. (1999). A general procedure for first/second order reliability method (FORM/SORM). Structural Safety, 21(2), 95–112.
Zhou, C., Zou, H., Wei, K., & Liu, J. (2019). Enhanced performance of piezoelectric wind energy harvester by a curved plate. Smart Materials and Structures. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ab525a
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Synopsis
The presented model and results have environmental relevance and significance, as a new design method for green energy harvesting systems has been developed.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gaidai, O., Yakimov, V., Wang, F. et al. Safety design study for energy harvesters. Sustainable Energy res. 10, 15 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40807-023-00085-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40807-023-00085-w