Abstract
Background
Waardenburg syndrome (WS) is the most common form of syndromic deafness with phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity in the Chinese population. This study aimed to clarify the clinical characteristics and the genetic cause in eight Chinese WS families (including three familial and five sporadic cases). Further genotype–phenotype relationships were also investigated.
Methods
All probands underwent screening for the known WS-related genes including PAX3, SOX10, MITF, EDNRB, EDN3, and SNAI2 using next-generation sequencing to identify disease-causing genes. Further validation using Sanger sequencing was performed. Relevant findings for the associated genotype–phenotype from previous literature were retrospectively analyzed.
Result
Disease-causing variants were detected in all eight probands by molecular genetic analysis of the WS genes (SOX10(NM_006941.4): c.544_557del, c.553 C > T, c.762delA, c.336G > A; MITF(NM_000248.3): c.626 A > T; PAX3(NM_181459.4): c.838delG, c.452-2 A > G, c.214 A > G). Six mutations (SOX10:c.553 C > T, c.544_557del, c.762delA; PAX3: c.838delG, c.214 A > G; MITF:c.626 A > T) were first reported. Clinical evaluation revealed prominent phenotypic variability in these WS patients. Twelve WS1 cases and five WS2 cases were diagnosed in total. Two probands with SOX10 mutations developed progressive changes in iris color with age, returning from pale blue at birth to normal tan. Additionally, one proband had a renal malformation (horseshoe kidneys).All cases were first described as WS cases. Congenital inner ear malformations were more common, and semicircular malformations were exclusively observed in probands with SOX10 mutations. Unilateral hearing loss occurred more often in cases with PAX3 mutations.
Conclusion
Our findings helped illuminate the phenotypic and genotypic spectrum of WS in Chinese populations and could contribute to better genetic counseling of WS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Waardenburg syndrome (WS), also known as the auditory-pigmentary syndrome, is the most common cause of syndromic hearing loss (HL). It accounts for approximately 2–5% of all patients with congenital HL. There is no significant correlation between disease incidence and race or gender [1,2,3]. WS primarily manifests as a set of phenotypic characteristics such as sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and pigment abnormalities, including skin hypo-pigmentation (albinism), white forelock, premature graying of the hair, or heterochromia iridum. WS is characterized by a high phenotypic heterogeneity. This is related to the incomplete penetrance, but also to the different genes that have been identified. Depending on the clinical phenotypes, It is classified into four subtypes (I–IV), with type I and II being the most common [4]. Type I (WS1; OMIM 193500) is distinguished from type II (WS2; OMIM 193510) by the presentation of dystopia canthorum. Type III (WS3; OMIM 148820) shares similar symptoms to type I but is accompanied by upper limb abnormalities. Type IV (WS4; OMIM 277580) is type II but associated with Hirschsprung disease (HD).
To date, mutations in six genes, namely microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), paired box 3 (PAX3), endothelin 3 (EDN3), endothelin receptor type B (EDNRB), SRY Box 10 (SOX10), and snail homolog 2 (SNAI2), are responsible for WS. The molecular etiologies overlap between the subtypes PAX3 is exclusively associated with WS1 and WS3, MITF, SNAI2, and SOX10 are related to WS2. WS4 is mainly caused by a mutation in SOX10, EDNRB, or EDN3. Most of WS cases exhibit a dominant mode of inheritance and usually occur de novo in the probands [5]. Notably, variable phenotypes are observed within and between families, even with the same mutation making it difficult to diagnose clinically. At the molecular level, nearly 14.8% of WS1, 26.3% of WS2, and 15–35% of WS4 cases remain unexplained [6, 7].
In this study, we performed comprehensive clinical and molecular etiology analyses on eight Chinese WS families (including three familial and five sporadic cases), which led to better delineating phenotypic features and revealed several novel pathogenic mutations in PAX3, SOX10, and MITF. Further genotype–phenotype relationships were also investigated.
Methods
Patients’ description
Eight probands clinically diagnosed with WS and their family members were recruited from the Department of Otolaryngology, from the **angya Hospital Central South University, between January 2017 and December 2021. The study protocol was approved by the **angya Hospital Central South University Ethics Committee, and informed consent was obtained from each of the subject. The clinical criteria for diagnosis of WS were based on the Waardenburg Alliance, including the presence of at least two major features or one major feature plus two minor features [8].
Clinical evaluation
A comprehensive clinical history was assessed, and audiological, neurological, ophthalmologic, and dermatologic examinations were performed on all subjects. Temporal bone high-resolution computer-assisted tomography (HRCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were performed on the probands to evaluate the structure of the ear and brain. The audiological and neurological examinations consisted of otoscopy, pure-tone audiometry (PTA), immittance, distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE), and auditory brain-stem response (ABR) tests. Additional auditory steady-state response (ASSR) tests were performed for those who did not respond to the PTA test well, due to their young age. Special attention was given to the pigmentary changes of the skin, hair, iris and other developmental defects, such as dystopia canthorum and limb abnormalities. The degree of HL was defined according to the PTA based on the three frequencies (500, 1000, and 2000 Hz). Hearing loss was categorized in the following manner: normal < 26 dB HL (decibel hearing level), mild 26–40 dB HL, moderate 41–70 dB HL, severe 71–90 dB HL, and profound > 90 dB HL. The description of the relevant inspection methods above refers to the previous studies [6, 9, 10].
Mutation screening strategy
Blood samples were collected from all probands and some of their family members. Genomic DNA was extracted using a commercial blood DNA extraction kit following the manufacturer’s protocol (Tiangen, Bei**g, China) and stored at − 80 °C until use. Target region high-throughput sequencing system (Illumina® Miseq) was designed and used to screen six WS causative genes (PAX3, SOX10, MITF, EDNRB, EDN3, and SNAI2) of WS. The primer sequences for six WS-related genes were designed for the target regions as previously described [6]. Detailed methods of experiments and parameters were shown in previous studies [6]. Bidirectional sequencing validation of the target segments was performed by 2 × 250 bp sequencing with an Illumina MiSeq Sequencer by Genesky Corporation (Shanghai, China). The average effective sequencing depth for each sample was 300×, with all bases having greater than 20× sequencing depth. All pathogenic mutations detected in the cohort were validated by Sanger sequencing of patients and their family members, the primers were designed to amplify the regions flanking the variant as previously described [11].
Mutation analysis
Bioinformatics analysis and variant interpretation were both included in Mutation analyses. The Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/) was used to align the sequencing reads to the human reference genome (hg19); GATK Haplotype Caller software to identify the single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and short indels [12]. The nomenclature of Human Genome Variation Society guidelines (http://www.hgvs.org) was used to name the identified mutations. Mutations associated with known WS genes were detected and classified as pathogenic or likely pathogenic according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology (ACMG-AMP) guidelines [13]. The functional effects of the identified mutation were evaluated by computational tools including Polyphen-2 and MutationTaster. The conservation of the proteins was assessed among different species by ConSurf software. The sequences of these proteins were downloaded from the UniProt database (www.uniprot.org) and aligned in JalView (v2.11) software to calculate the conversation score.
Results
Clinical phenotypes
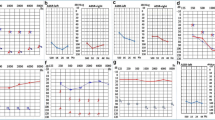
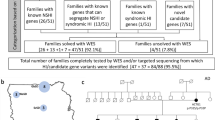
In total, 17 patients including 10 males and seven females from eight families, with some of their healthy family members, were enrolled (Fig. 1). F-2(II-5, III-9) was first described in our previous study as family 14 [6]. In this study, we expanded the collection of clinical data from other relevant patients in this extended family. The phenotypes of the related patients were recorded in detail. The study population comprised three familial and five sporadic cases ranging from one to 34 years of age. According to the diagnostic criteria of WS, five patients were diagnosed with WS2, and the others were diagnosed with WS1. The distribution of clinical features in this study population is shown in Table 1. SNHL was observed in 14 WS cases (82.4%, 14/17). The SNHL was mostly observed as bilateral non-progressive severe to profound sensorineural. However, four cases of WS1 (F2:II-5, F2:III-9, F3:II-2, S4) with unilateral SNHL were also observed, which is not common in WS cases (Figs. 2 and 3).
Pedigree of eight families with WS. The black arrow indicates the proband. Each generation is identified by a Roman numeral (I, II, III, IV) and each individual within the same generation is identified by an Arabic numeral (1, 2, 3 and so on). Squares represent males and circles represent females. The symbol with a diagonal line shows a deceased individual. Individuals’ symbols are colored black to indicate the presence of clinical characteristics of WS, unfilled symbols represent unaffected family members
Interestingly, two WS2 probands (S6 and S8) developed progressive changes in iris color with age, returning from pale blue (at birth) to normal tan gradually without any other pigmentation changes. Bilateral retinal hypopigmentation was also found in proband S-6 at one year of age (Fig. 4 A, B). Further, this proband (S-6) presented retinal hypopigmentation and renal malformation as horseshoe kidneys. Ultrasonography revealed deformity of the right kidney with an elongated shape, fusion occurring at the lower pole, and the isthmus connecting the two renal masses positioned at the midline. The renal function test indicated normal function (Fig. 4C). In addition, by comprehensive evaluation of Temporal bone computed tomography (CT), cranial MRI, and internal auditory canal MR hydrography, four WS2 patients (F1:III-3, S5, S6, S8) presented bilateral inner ear malformations to varying degrees (Fig. 5). One patient presented bilateral cochlea with hypoplastic middle and apical turns, dilated vestibule, and absent semicircular canal. The other three patients presented only with vestibular and semicircular hypoplasia. No abnormality of the auditory nerve was observed in any of these cases. Detailed information about imaging features is shown in Table 2.
Spectrum of mutations
The molecular genetic analysis of the WS-related genes for eight probands identified seven heterozygous mutations in PAX3, MITF, and SOX10 (Table 3). Three mutations occurred in the PAX3 gene(NM_181459.4): one splice mutation c.452-2 A > G, one missense mutation c.214 A > G (p.Ile72Val), and one deletion mutation c.838delG (p.Ala280fs*4). One missense mutation c.336G > A(p.Met112Ile), one nonsense mutation c.553 C > T(p.Gln185*), and two deletion mutations c.544_557del(p.Lys182Argfs*94), c.762delA(p.Asp255Thr fs*31) were detected in the SOX10 gene(NM_006941.4). One missense mutation c.626 A > T (p.His209Leu) was detected in the MITF gene(NM_000248.3). None of these eight mutations were detected in unaffected family members. The mutations detected were compared with HGMD, Exome Variant Server, and Deafness Variation databases. The results showed that six mutations have not previously been reported, excluding the c.452-2 A > G and c.336G > A variants [14,15,16,17]. Further Sanger sequencing of probands and their family members shows that all the mutations were present in the affected members. SOX10 c.544_557del was considered de novo mutations by gene tests in the proband and her parents (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). In addition, all mutations were classified according to ACMG-AMP standards and guidelines for interpreting sequence variants. The mutations and pathogenicity analysis were summarized in Table 3.
Genotype–phenotype correlation
The phenotypes of WS patients in this study with PAX3, SOX10, and MITF mutations are shown in Additional file 3: Table S1. To be interested, SNHL is present in 76.9% of all PAX3 patients (10/13) and significant phenotypic differences in hearing among different individuals were observed, even within the same family. Unilateral sensorineural hearing loss (USNHL) is present in about 40% of deaf patients with PAX3 mutations (4/10). Besides, inner ear malformations were found in 57% of the WS probands (4/7), with malformed vestibule and semicircular canals being the most common (Fig. 5). This phenotype seemed to be exclusively associated with SOX10 variants.
Discussion
Mutation spectrum
Molecular genetic analysis of the WS genes for eight families revealed eight heterozygous mutations (Fig. 6). Among the probands, 37.5% with WS1 (3/8, PAX3), 50% with WS2 (4/8, SOX10), and 22.5% with WS2 (1/8, MITF) were identified after extensive analyses of clinical phenotypes and molecular diagnosis in this cohort. No WS3 and WS4 cases or mutations in EDNRB, EDN3, or SNAI2 were identified in our study. The heterozygous mutation SOX10 c.553 C > T(p.Gln185*) in probands of F-1 introduced a stop codon and gave rise to a truncated SOX10 protein with 185 of the 466 wild-type amino acids. A heterozygous mutation (PAX3 c.452-2 A > G) in the splicing site was found in the proband, the father and sister of F-2. This mutation transformed the conservative AG sequence into AA. The mutation site would affect the normal splicing of pre-mRNA for PAX3, resulting in abnormal function or activity of the protein. This mutation site has been previously reported several times in different populations which could be a hot-spot mutation site of PAX3 in WS [6, 14, 15]. Therefore, we believed that the mutation is pathogenic, which should be the main pathogenic factor for the proband and his relatives of F-2. The mutations in PAX3 c.838delG(p.Ala280fs*4) and SOX10 c.762delA(p. Asp255Thr fs*31) were detected respectively in the probands of F-3, and S-8 caused a frameshift and stop codon into the basic domain of the corresponding protein, forming a truncated protein. These changes affected the function of the protein, resulting in the change of WS phenotype in patients. In addition, three missense heterozygote mutations PAX3 c.214 A > G(p.Ile72Val), SOX10c.336G > A(p. Met112Ile) and MITF c.626 A > T(p.His209Leu) were detected respectively in the proband of S-4, S-5, and S-7. The PAX3 c.214 A > G mutation resulted in the mutation of isoleucine 72 to valine. This mutation is located in the pair box domain (PD) conserved region of the PAX3 protein, and it is speculated that the change of amino acid might cause changes in the tertiary structure, affecting the protein’s function. The mutation site was conserved among multiple species and was predicted by Mutation Taster (disease-causing) and Polyphen-2 (score: 0.997). The SOX10 c.336G > A mutation resulted in a transition from methionine to isoleucine at 112 and is located in the high-mobility group region of SOX10 protein. Chaouid et al. [17] first found the same mutation for two WS cases with deafness, which also affected the DNA binding capacity of the region. The mutation c.626 A > T in the MITF gene is predicted to alter the highly conserved histidine at codon 209, located in the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper domain [18, 19]. Therefore, this mutation might influence DNA-binding activity and transactivation capabilities, resulting in a disease phenotype predicted by Mutation Taster (disease-causing) and Polyphen-2 (score: 0.971) (Additional file 2: Fig. S2). The deletion mutation of SOX10 c.544_557del(p.Lys182Argfs*94) in the proband of S-6 resulted in a frameshift and stop codon being inserted into the basic domain of the corresponding protein, causing a truncation. This mutation affects the function of the protein, resulting in the change of WS phenotype in patients.
Reversed changed the color of the iris in WS
The characteristic ocular abnormality of WS is abnormal pigmentation of the iris. Changes in iris pigmentation in WS included: complete heterochromia (different colors in both eyes), partial heterochromia (fragmentary blue iris in single or both eyes), and stunted bright blue iris [20]. Previous studies have described that the incidence of iris hypopigmentation ranges from 14.9 to 42% and accounts for 47% of WS2 cases [21]. Heterochromia iridum occurred in all WS patients in the present study, and five cases showed unilateral (three WS1 with PAX3 mutations and two WS2 with SOX10 mutations). The pigment content of the iris substrate and the front layer determines the color of the iris. Thus, with increasing pigment in the iris substrate, there is more light absorption and a darker color in the eyes [22]. The hypopigmentation of the iris in WS has been documented on electron microscopy to manifest as fewer melanocytes in the hypopigmented region compared with the normal brown region. This results in substantial reductions in the melanosome size in the hypopigmented region and is considered to be related to a defect in neural crest cell (NCC) migration and melanin production, a process in which WS-related genes might be involved [23, 24].
In this study, two WS2 patients presented progressive iris color changes. According to the medical history and photos, the proband (S-6) was showing bilateral pale blue irises without any other symptoms of hypopigmentation when he was born. The hearing test found bilateral severe to profound hearing loss after six months. Interestingly, the color of both eyes darkened to varying degrees with age. At the time of the visit, the whole iris color of the right eye had returned to normal brown, while the other eye had a fragmentary brown iris. The other proband (S-8) shares the same medical history and symptoms. It is also worth noting that both had identified pathogenic mutations in the SOX10 gene.
This phenomenon has not been mentioned in any other previous WS cases. Although the specific mechanism of this reversed color change in the iris is unclear, it may be related to some compensatory mechanisms of melanin. This phenomenon should attract the attention of pediatricians or otologists during clinical diagnosis and treatment. Studies have shown that variants in SOX10 and MITF were identified in some nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss (NSHL) cases [25,26,27], which implies the clinical and genetic heterogeneity of this syndrome. Whether these patients may also have this reversible change in the iris needs further investigation. Altogether, the possibility of WS for these cases initially diagnosed as NSHL based on their phenotypes cannot be ruled out. We also suggest that WS-related genes, especially SOX10 and MITF, should be included in clinical genetic testing for NSHL to avoid clinical misdiagnosis due to phenotypic variability.
Heterogeneity of hearing phenotypes and PAX3 mutations
PAX3, also known as HuP2, encodes a member of the PAX family of transcription factors, characterized by a highly conserved paired DNA binding domain first identified in Drosophila [28]. It is mainly expressed in the development of neural crest(NC) derivatives, skeletal muscle, and the central nervous system, and regulates the expression of target genes that have impact proliferation, survival, differentiation, and motility [29,30,31]. This protein is characterized by an N-terminal DNA binding and a C-terminal transactivation domains. The DNA binding domain consists of a paired box, octapeptide, and homeodomain, and the transactivation domain contains a proline-, serine- and threonine-rich region [32]. The importance of PAX3 in the neural tube, NC, and muscle development is confirmed by the molecular genetic findings in WS [33]. Mutations in the PAX3 are observed in nearly 80% of WS1 cases, whereas partial or total deletion of PAX3 and contiguous genes are often observed in WS3 cases [34]. Moreover, PAX3 mutations have also been identified in another rare disorder called craniofacial-deafness-hand syndrome (CDHS), which is considered to be an allelic variant of Waardenburg syndrome. CDHS is characterized by craniofacial anomalies, profound sensorineural deafness, dysplasia or absence of nasal bone, slit-like nostrils, blepharophimosis, and ulnar deviation of the hand with contractures of the fingers [35, 36].
Similar to our findings, previous studies have shown heterogeneity of hearing phenotypes in WS patients with PAX3 mutations [37, 38]. SNHL is found in 52.5% of the WS patients with PAX3 mutation (52.3% in WS1, 57.1% in WS3), and the degree of HL differs from mild to profound, even within one family. Importantly, USNHL is more frequently associated with mutations in PAX3 than any other WS-related genes, accounting for nearly 26% of WS1 and WS3 patients. It has also been reported that there is a strong association between the heritability of USNHL and the pigmentary abnormality[9]. Although the relevant pathogenic mechanism is still unclear, further study may be needed to focus on the effect of PAX3 during the migrating process of NCCs.
Thus far, few studies have focused on the epidemiology of USNHL. The etiology of a substantial portion of USNHL remains unknown, and genetic causes have not been elucidated. WS should be included in the differential diagnosis of children with congenital USNHL, to screen the WS-related genes, especially PAX3.
Inner ear malformation and SOX10 mutations
Several recent studies have mentioned the association between inner ear malformations and SOX10 mutations [7, 39,40,41]. Bilateral hypoplasia or dysplasia of the semicircular canals and enlarged vestibules are very frequent, while agenesis of the vestibulo-cochlear nerve and cochlear deformities have also been reported. These previous reports are somewhat consistent with our findings.
To further investigate the genotype–phenotype relationship between SOX10 mutations and inner ear malformation, an up-to-date literature overview was performed (Additional file 4: Table S2). WS patients with SOX10 mutation and inner ear malformations from the previous report were included. 60 individual WS patients were found to meet this inclusion criterion. Gender distribution was 23.8% female versus 76.2% male persons (gender was provided in 21 patients) and the mean age of the included patients was 5.6 years (standard deviation 7.9, exact age was provided in 37 patients). Fifty-six of them are WS2 and others are WS4. Temporal bone abnormalities were mostly bilateral (57/60). The morphologic abnormalities of the vestibular were shown in 96.7% (58/60) of the SOX10-related WS cases. The most frequently reported vestibular aberrations were agenesis or hypoplasia of ≥ 1 semicircular canals (SCC) (92.8%, 39/42), agenesis of posterior SCC was seen with the highest frequency (85.7%, 36/42) followed by the lateral SCC (83.3%, 35/42) and superior SCC (66.7%, 28/42). Enlarged or malformed vestibules were also observed frequently (76.2%, 32/42). Meanwhile, 76.7% (46/60) of the patients presented with the hypoplastic cochlea, which mainly showed reduced size, hypoplastic middle, and apical turns with a short modiolus. The cochlear nerves were bilaterally absent in five of the six patients who underwent MRI and were unilaterally absent in one patient. These patients have various types of mutations, including nonsense, missense, deletion, and frameshift. The copy number variations were also observed. However, within these SOX10-related WS cases, we did not find a correlation between the mutation and the type or severity of the inner ear malformations observed.
SOX10 belongs to the SOX family of transcription factors, mainly involved in developmental skeletogenesis, neurogenesis, and NC development [42, 43]. It is vital in promoting cell survival, maintaining multipotency of NC stem cells, and controlling cell fate for various NC derivatives [24].
So far, the pathogenic mechanism of inner ear malformation caused by a mutated SOX10 protein is still not fully understood. In melanocytes, SOX10 manipulates proliferation, survival, and differentiation by activating downstream target genes, like MITF. Mutations in SOX10 may result in a developmental defect in melanocyte-derived cell lineage of the inner ear, called intermediate cells of the stria vascularis, necessary for inner ear homeostasis, and eventually cause HL. Unlike the other pathogenic genes of WS, SOX10 is expressed early in the otic vesicle from four weeks of human embryonic development and then in the develo** epithelium of the cochlea and vestibule, before being restricted to supporting cells of the neurosensory epithelium. It promotes the survival of cochlear progenitors during the formation of the otocyst and the organ of Corti [44]. It is also expressed in the glial development of the cochleovestibular ganglia[45]. Breuskin et al. [46] demonstrated that loss of Sox10 function decreases the expression of Jag1, which plays an important role in the maintenance and differentiation of inner ear sensory epithelial progenitors, mediate by the Notch pathway and thus leads to the malformation of the inner ear during the development of Xenopus. Hao et al. [47] identified some key genes (WNT1, KCNQ4, STRC, and PAX6) and pathways associated with inner ear malformation in a pig model with SOX10 mutations, through RNA-seq analysis. Wen et al. [48] established WS patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells and differentiated them into NCCs. RNA-seq identified a cluster of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with inner ear development and morphogenesis, providing a rich context for investigating the molecular etiology of WS regarding inner ear malformations.
Waardenburg syndrome with renal involvement
Few studies have mentioned renal involvement in sporadic cases of WS, which includes duplicated ureteral collecting system, multicystic dysplastic kidney, and horseshoe kidney [49,50,51]. One WS family with three generations has renal agenesis which makes this finding likely to be hereditary [52]. However, no correlation between the genotype and associated phenotype can be found. A recent study has shown that Mitf-M-null mice have enlarged kidneys indicating a role for MITF-M in size control of the kidney [53]. To our knowledge, there has been no mention elsewhere in previous studies of SOX10 mutation with associated renal anomalies. The SOX10 gene is a characteristic marker for multipotent NC progenitors for various NC derivatives. During the development of the urinary system, NCC migrates to the embryologic kidney and forms nephrogenic mesenchyme, which induces differentiation and formation of the kidney [54]. Congenital kidney malformations can occur from aberrant NCC, as evidenced in previous reports. Collectively, whether the renal abnormality is a symptom of WS still needs to be further investigated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study presented a comprehensive genetic and clinical investigation of WS in a group of Chinese patients. Several unusual phenotypes were first found in WS cases, which should also be considered in the wide spectrum of WS. In addition, six novel heterozygous mutations were identified, which expanded the database of unknown mutations in WS patients. Moreover, our data revealed the clinical and genetic spectra and particular genotype–phenotype relationships in a Chinese population, which expanded our understanding of WS.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in Leiden Open Variation Database (LOVD; https://databases.lovd.nl/shared/; Individual ID: #00408235, #00408236, #00415811, #00415812, #00415813, #00415814, #00415815, #00415816). The raw sequence data reported in this study have been deposited in the SRA databases with the accession number PRJNA887200 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA887200).
Abbreviations
- WS:
-
Waardenburg syndrome
- HL:
-
Hearing loss
- SNHL:
-
Sensorineural hearing loss
- HD:
-
Hirschsprung disease
- MITF :
-
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
- PAX3 :
-
Paired box 3
- EDN3 :
-
Endothelin 3
- EDNRB :
-
Endothelin receptor type B
- SOX10 :
-
SRY Box 10
- SNAI2 :
-
Snail homolog 2
- HRCT:
-
Temporal bone high-resolution computer-assisted tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PTA:
-
Pure-tone audiometry
- DPOAE:
-
Distortion product otoacoustic emission
- ABR:
-
Auditory brain-stem response
- ASSR:
-
Auditory steady-state response
- SNVs:
-
Single nucleotide variants
- ACMG-AMP:
-
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology
- USNHL:
-
Unilateral sensorineural hearing loss
- NSHL:
-
Nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss
- NCC:
-
Neural crest cell
- CDHS:
-
Craniofacial-deafness-hand syndrome
- SCC:
-
Semicircular canals
- SSCC:
-
Superior semicircular canal
- LSCC:
-
Lateral semicircular canal
- PSCC:
-
Posterior semicircular canal
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
References
Gettelfinger JD, Dahl JP. Syndromic hearing loss: a brief review of common presentations and genetics. J Pediatr Genet. 2018;7(1):1–8.
Nayak CS, Isaacson G. Worldwide distribution of Waardenburg syndrome. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003;112(9 Pt 1):817–20.
Read AP, Newton VE. Waardenburg syndrome. J Med Genet. 1997;34(8):656–65.
**ault V, et al. Review and update of mutations causing Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2010;31(4):391–406.
Huang S, et al. Genetic insights, disease mechanisms, and biological therapeutics for Waardenburg syndrome. Gene Ther. 2021;29:479–97.
Li W, et al. New genotypes and phenotypes in patients with 3 subtypes of Waardenburg syndrome identified by diagnostic next-generation sequencing. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:7143458.
Wang G, et al. Analysis of genotype–phenotype relationships in 90 Chinese probands with Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Genet. 2022;141(3–4):839–52.
Liu XZ, Newton VE, Read AP. Waardenburg syndrome type II: phenotypic findings and diagnostic criteria. Am J Med Genet. 1995;55(1):95–100.
Kim SH, et al. Molecular etiology of hereditary single-side deafness: its association with pigmentary disorders and Waardenburg syndrome. Medicine (Baltim). 2015;94(43):e1817.
Sun L, et al. Molecular etiology and genotype–phenotype correlation of Chinese Han deaf patients with type I and type II Waardenburg syndrome. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35498.
Chen H, et al. Novel mutations of PAX3, MITF, and SOX10 genes in Chinese patients with type I or type II Waardenburg syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;397(1):70–4.
McKenna A, et al. The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20(9):1297–303.
Richards S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17(5):405–24.
Tassabehji M, et al. PAX3 gene structure and mutations: close analogies between Waardenburg syndrome and the Splotch mouse. Hum Mol Genet. 1994;3(7):1069–74.
Yang T, et al. Double heterozygous mutations of MITF and PAX3 result in Waardenburg syndrome with increased penetrance in pigmentary defects. Clin Genet. 2013;83(1):78–82.
Zhang QJ, et al. Identification of a novel mutation of SOX10 gene and analysis of the phenotype. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou **g Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;55(11):1050–6.
Chaoui A, et al. Identification and functional analysis of SOX10 missense mutations in different subtypes of Waardenburg syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2011;32(12):1436–49.
Grill C, et al. MITF mutations associated with pigment deficiency syndromes and melanoma have different effects on protein function. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(21):4357–67.
Zhang H, et al. Functional analysis of MITF gene mutations associated with Waardenburg syndrome type 2. FEBS Lett. 2012;586(23):4126–31.
Ohno N, et al. Clinical findings in Japanese patients with Waardenburg syndrome type 2. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2003;47(1):77–84.
Goldberg MF. Waardenburg’s syndrome with fundus and other anomalies. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966;76(6):797–810.
Wilkerson CL, et al. Melanocytes and iris color. Light microscopic findings. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114(4):437–42.
Mullaney PB, et al. Clinical and morphological features of Waardenburg syndrome type II. Eye (Lond). 1998;12(Pt 3a):353–7.
**ault V, et al. SOX10: 20 years of phenotypic plurality and current understanding of its developmental function. J Med Genet. 2022;59(2):105–14.
Thongpradit S, et al. MITF variants cause nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss with autosomal recessive inheritance. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12712.
Bademci G, et al. Variations in multiple syndromic deafness genes mimic non-syndromic hearing loss. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31622.
**ault V, et al. SOX10 mutations mimic isolated hearing loss. Clin Genet. 2015;88(4):352–9.
Underhill DA, Gros P. The paired-domain regulates DNA binding by the homeodomain within the intact Pax-3 protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(22):14175–82.
Blake JA, Ziman MR. Pax3 transcripts in melanoblast development. Dev Growth Differ. 2005;47(9):627–35.
Boudjadi S, et al. The expression and function of PAX3 in development and disease. Gene. 2018;666:145–57.
Monsoro-Burq AH. PAX transcription factors in neural crest development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;44:87–96.
Hart J, Miriyala K. Neural tube defects in Waardenburg syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173(9):2472–7.
Somashekar PH, et al. Phenotypic diversity and genetic complexity of PAX3-related Waardenburg syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2020;182(12):2951–8.
Wollnik B, et al. Homozygous and heterozygous inheritance of PAX3 mutations causes different types of Waardenburg syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;122A(1):42–5.
Asher JH Jr, et al. Missense mutation in the paired domain of PAX3 causes craniofacial-deafness-hand syndrome. Hum Mutat. 1996;7(1):30–5.
Wang Q, et al. Pax genes in embryogenesis and oncogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(6A):2281–94.
Minami SB, et al. A clinical and genetic study of 16 Japanese families with Waardenburg syndrome. Gene. 2019;704:86–90.
Zhang S, et al. High genetic heterogeneity in Chinese patients with Waardenburg syndrome revealed by next-generation sequencing. Front Genet. 2021;12:643546.
Elmaleh-Berges M, et al. Spectrum of temporal bone abnormalities in patients with Waardenburg syndrome and SOX10 mutations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(6):1257–63.
Niu Z, et al. A de novo mutation of the SOX10 gene associated with inner ear malformation in a Guangxi family with Waardenburg syndrome type II. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;145:110711.
Xu GY, et al. SOX10 mutation is relevant to inner ear malformation in patients with Waardenburg syndrome. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou **g Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;51(11):832–7.
Haldin CE, LaBonne C. SoxE factors as multifunctional neural crest regulatory factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(3):441–4.
Cheung M, et al. The transcriptional control of trunk neural crest induction, survival, and delamination. Dev Cell. 2005;8(2):179–92.
Bondurand N, et al. Expression of the SOX10 gene during human development. FEBS Lett. 1998;432(3):168–72.
Wakaoka T, et al. Tracing Sox10-expressing cells elucidates the dynamic development of the mouse inner ear. Hear Res. 2013;302:17–25.
Breuskin I, et al. Sox10 promotes the survival of cochlear progenitors during the establishment of the organ of Corti. Dev Biol. 2009;335(2):327–39.
Hao QQ, et al. Key genes and pathways associated with inner ear malformation in SOX10 (p.R109W) mutation pigs. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:181.
Wen J, et al. A model of waardenburg syndrome using patient-derived iPSCs with a SOX10 mutation displays compromised maturation and function of the neural crest that involves inner ear development. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:720858.
Ekinci S, et al. Waardenburg syndrome associated with bilateral renal anomaly. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40(5):879–81.
Jankauskiene A, et al. Multicystic dysplastic kidney associated with Waardenburg syndrome type 1. Pediatr Nephrol. 1997;11(6):744–5.
Garavelli L, et al. Anophthalmos with limb anomalies (Waardenburg opththalmo-acromelic syndrome): report of a new Italian case with renal anomaly and review. Genet Couns. 2006;17(4):449–55.
Webb KM, et al. Waardenburg syndrome with familial unilateral renal agenesis: A new syndrome variant? Ther Apher Dial. 2015;19(3):296–8.
Flesher JL, et al. Delineating the role of MITF isoforms in pigmentation and tissue homeostasis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020;33(2):279–92.
Sariola H, Holm-Sainio K, Henke-Fahle S. The effect of neuronal cells on kidney differentiation. Int J Dev Biol. 1989;33(1):149–55.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely appreciate these patients and their family members for their participation in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81700923), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2021M693566, 2021T140751), The science and technology innovation Program of Hunan Province China (Grant No. 2020RC2013), Hunan Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2021JJ41017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceived and designed by CF-H and JS. S-M, MY-Q, and SJ-L conducted the patient recruitment and consent, and clinical sample collection. SJ-L conducted the majority of experiments. MY-Q analyzed the related data. MY-Q and JS wrote the manuscript. The study was supervised by YF, XZ-C, and LY-M. The final version was approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of **angya Hospital Central South University. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s).
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of clinical details and clinical images was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Fig. S1.
The mutated sequence identified from the S-6 proband with his parents. The red box indicates the emplacement of the mutations and the change of the amino acids sequence.
Additional file 2: Fig. S2.
The schematic representation and protein conservativeness analysis of the localization of two new missense mutations. A. The PAX3 gene mutation detected in the S-4.The variant c.214A>G(p.Ile72Val) represented in red is a novel mutation.The mutation site was conservative among multiple species. PBD: pair box domain;HD: HMG domain. B. The MITF gene mutation detected in the S-7.The variant c.626A>T(p.His209Leu) represented in red is a novel mutation.The mutation site was conservative among multiple species. Basic: Basic domain; HLH: Helix-Loop-Helix domain; LZ: Leucine zipper domain.
Additional file 3: Table S1.
Phenotypes in WS patients with PAX3, SOX10 and MITF mutations.
Additional file 4: Table S2.
Clinical phenotypes and genotypes of the SOX10 mutated patients with inner ear malformations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Qin, M., Mao, S. et al. A comprehensive genotype–phenotype evaluation of eight Chinese probands with Waardenburg syndrome. BMC Med Genomics 15, 230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-022-01379-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-022-01379-6