Abstract
Background
The excessive use of antibiotics in the livestock feed industry caused inevitable side effects of microbial resistance. Besides this residual antibiotics in animal-derived foodstuff imposed serious health problems for humans. So this study aimed to investigate the potential use of Bacillus velezensis to substitute antibiotics for poultry production. A total of 468, 49-week-old Hy-Line Brown chickens, were randomly divided into four groups the control group (regular diet), experiment group I (0.1% B. veleznesis), experiment group II (0.2% B. veleznesis), and antibiotic group (50 mg/kg flavomycin), with three replicates per group and trial period consisted on 42 days.
Results
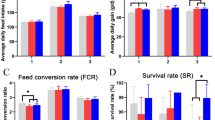
The results showed that, compared with the control group, the average egg production rate and daily feed intake of experimental groups I and II increased significantly (P < 0.05), while the average egg weight was increased in experimental group II as compared to (I) (P < 0.01). The feed conversion ratio was decreased (P > 0.05) in group (II) Egg quality parameters such as yolk weight of the experimental group II was increased, but that of the antibiotic group and experiment group I was decreased, neither significant (P > 0.05). Moreover, the eggshell strength, yolk color, albumen height, and Haugh unit were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, probiotic groups can increase the progesterone and motilin (P > 0.05) but decrease the secretin and cholecystokinin in the blood plasma (P > 0.05).
Conclusions
This study suggested that B. velezensis can substitute in-feed-antibiotics and improved most of the study parameters significantly. Which suggested that B. velezensis has potential future application value to replace the feed antibiotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Antibiotics are chemical substance produced by microorganisms which can resist pathogens to improve human and animal health as well as improve the quality of food products. Since the discovery of antibiotics in 1929, they have contributed to treat infectious diseases previously known to kill many humans and animals. Therefore, antibiotics are called guardians of human beings [1,2,3]. A class of antibiotics (Spiramycin, Tetracycline, Virginiamycin, Erythromycin) has been added to poultry feed for enhancing growth and production in large-scale intensive farming environments [4]. Adding a certain amount of feed antibiotics can not only promote the feed conversion rate, growth, development of poultry and reduce feed to egg ratio but also increases economic benefits, leading to expand the modern intensified poultry industry [5, 6].
However, with the continuous development of animal husbandry, the problem of antibiotics abuse has also emerged. Antibiotics remaining in livestock and poultry products (such as meat, eggs, and milk) may induce abnormal reactions such as disturbances in physiological and biochemical processes [7]. Some studies, for example, have shown that the abuse of antibiotics has a certain degree of correlation with the increased risk of cancer [8, 9]. The Use of antibiotics in animal production imposes a serious selection pressure on microbes which are exposed to sub-inhibitory doses of antibiotics. This has raised the problem of antibiotic resistance through mutation and gene transfer [10]. Controlling the propagation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has become a major health problem in the 21st century [11]. Besides, a high proportion of antibiotics added to animal feed is excreted in animal’s urine or manure, causing water pollution which could be great harm to water sources and human health ultimately [12, 13]. Effective intervention are required, to reform the regulatory environment and to reclassify the antibiotics, by putting some antibiotics as a treatment choice and all others strictly restricted is the suggested solution for all above problems in the countries where antibiotics are available without a prescription[14]. Similar to the successful regulation of veterinary medicine in the Republic of Korea [15]. Also, antibiotics in animal feed have been completely banned by the Chinese government from July 1, 2020. However, it is feared that banning the use of antibiotics may have adverse effects on animal health and farmers’ profits. This has led efforts from all over the world to find an animal growth promoter that can effectively replace antibiotics to prevent antibiotic residues in poultry products, such as eggs [16, 17]. Currently, probiotic preparations, Oligosaccharide preparations, enzyme preparations, and Chinese herbal medicine are effective antibiotic substitutes [18,19,20,21]. Probiotic preparations have become an emerging growth-promoting additive due to the enormous amount of research and good effect on animal growth [22, 23].
Bacillus velezensis has been widely used as a biological control agent in agricultural fields due to its excellent ability to suppress plant diseases [24, 25]. It is considered as a potential rhizobacterial organism with extraordinary biosynthetic machinery, which can trigger innate immunity in plants [26].
However, there are few experiments on the B. velezensis used as feed antibiotics replacement [24]. It was suggested that this bacteria can inhibit adherence, replication, and virulence of intestinal pathogens [27]. In addition, it can play an important role to modulate the immune system [28]. So, we prognosis that B. velezensis have the potential to be developed as a probiotic agent. In the present experiment, to prove that the B. velezensis can be a good antibiotics substitute, we investigated the effect of adding 1.0 × 1010 CFU/kg and 2.0 × 1010 CFU/kg of B. velezensis as a feed additive instead of flavomycin on the production performance, egg quality, blood physiological and biochemical indices of Hy-Line Brown laying hens. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time B. velezensis is assayed to replace antibiotics in hens feed. This study provided a practical basis for the application of B. velezensis to the laying hens feed instead of antibiotics.
Results
Production performance
As shown in Table 1, The average egg production rate in the experiment group I, and II were increased significantly as compared to the control group (P < 0.05), however, it decreased as compared to the antibiotic group. The average egg weight (AEW) was increased significantly in experimental group II as compared to the experimental group (I) The average daily feed intake of the antibiotic group, experimental group I, and experimental group II increased significantly (P < 0.01), (P < 0.01), (P = 0.045 < 0.05). There were no treatment effects on the feed conversion ratio of the control group, antibiotic group and the experimental group I, however, it reduced significantly in group (II) (P < 0.01).
Egg quality
The egg quality was determined twice in the whole period. As presented in Table 2, in the first determination on day 21 of the phase one (2–21 days), compared with the control group and antibiotic group EW, ESI and ESW in both experimental groups was slightly decreased, but not significant (P > 0.05). However, a significant decrease in ESS was observed in both experimental groups as compared to the control and antibiotics group. And the eggshell color ESC, YW, YC, AH, and HU were higher than that of the control group but lower than that of the antibiotic group.
In the second determination on day 42 of phase two (22–42 days) compared with the control group and antibiotic group the EW, ESW, and ESI had no significant difference in both experimental groups. And compared with the control group, the ESS and YC of experimental groups were not improved significantly (P > 0.05). ESC of the experimental group I was increased, The YW of the experimental group II was increased, but that of the antibiotic group and experimental group I was decreased, neither significant (P > 0.05). Moreover, the ESS, AH, and HU of the experimental groups were higher than that of the control group but lower than that of the antibiotic group. As presented in Table 2, antibiotics and B. velezensis could increase triglyceride in the first phase. However, triglyceride was reduced in the antibiotic group and experimental group I but increased in experimental group II in the second phase. Compared to the antibiotic, feed with 0.2% B. velezensis could reduce the content of cholesterol in the second phase.
The effect of B. velezensis on biochemical indices in blood plasma
As shown in Table 3, triglyceride in plasma of antibiotic group and experimental group I was increased, but reduced in experimental group II, however none was significant (P > 0.05). The level of progesterone and motilin in the blood plasma of laying hens was increased in experimental group I and II as compared to those of the control group and antibiotic group, which recommended the successful usage of B. velezensis. The results also showed that the, the level of secretin and cholecystokinin was decreased in all three test groups as compare to the control group. All the above increase and decrease in the results were not significant (P > 0.05).
Discussion
Production performance
The use of bacillus-based probiotic feed-formulation was observed to be a promising health-promoting approach. Bacillus spp. were widely used in the poultry industry [29].
At the late stage of feeding, due to the change of metabolism in the body, the absorption of nutrients in the feed was weakened, which lead to the decrease in production performance and the deterioration of egg quality, even the decrease of immunity and the deterioration of anti-stress ability, thus affecting economic benefits. Bacillus sp. such as B. coagulans has the functions of regulating or maintaining intestinal micro-ecological balance, enhancing immunity, promoting the absorption of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D, and so on [30]. Numerous studies have shown that adding Bacillus sp. to the laying hen’s feed can significantly increase egg production rate, average egg weight, reduce feed conversion ratio, and improve egg quality and immunity [63] to avoid any biasness of selection while allocating hens to the experimental groups.
Hens of the control group were fed a regular diet (59% yellow corn, 27.5% bean pulp, 8.5% limestone powder, and 5% premix, with 16% Crude protein, and 2556.0 Kcal/Kg Metabolic energy) without any active probiotic [32]. According to the results from our preliminary studies (unpublished data) [64], a new strain of B. velezensis was isolated from the manure of piglets. Hens of experimental group I and II were fed the regular diet plus 1 × 1010 CFU/kg and 2 × 1010 CFU/kg B. velezensis, respectively; and hens of the antibiotic group were fed the regular diet plus 50 mg/kg flavomycin.
Feeding management
The laying hens were kept in a 3-tier bird’s cage (28 × 48 cm x 48 cm). To avoid contamination by pathogens aviary system was used [65], in which the cages were separately housed based on the treatment, under the same conditions, including room temperature, humidity, light, and ventilation, there was no enrichment provided for any environmental condition. Similar weight hens were used, and their health condition, feeding, and drinking were recorded daily, throughout the trial period and this strategy was used to reduce the effect of confounding variables. The laying hens were fed quantitatively twice a day [32], (7 am and 2 pm) for 42 days. This study was conducted at the Dongshan Chicken Farm of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences; and the experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee, the Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the Ethics Committee of Anhui Agricultural University, Anhui, China.
Data acquisition and analysis
Eggs were collected once a day (2 pm). The data for egg production, egg weight, and feed consumption were recorded. The trial period was divided into two phases (Phase 1: day 2–21 & Phase 2: day 22–42) to examine the production parameters based on the duration of feeding. Then, the average egg production rate (AEPR), average egg weight (AEW), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and feed/egg ratio (FCR) were calculated. On day 21 of phase 1 (day 2–21) and day 42 in phase 2 (day 22–42), 39 eggs from each treatment (balanced with egg weight) were collected and the egg quality indices including egg shape index (ESI), eggshell color (ESC), eggshell strength (ESS), yolk weight (YW), yolk color (YC), eggshell weight (EW), albumen height (AH), and Haugh Unit (HU) were determined. ESI was measured with a Vernier caliper (Measuring & Cutting Tool Work Co. China). ESC was measured with the eggshell color tester (Robotmation Com., Japan). ESS was tested with the Egg Shell Force Gauge MODEL-III (EGG-0530, Robotmation Com., Japan) [66]. Yolk weight, yolk color, eggshell weight, albumen height, and Haugh Unit were determined by using the Egg Multi Tester (EMT-5200 Robotmation Com., Japan). The egg yolk was collected in an aseptic centrifuge tube and stored at -20 °C.
On the last day of the experiment, a 2.0 mL blood sample from each randomly selected hen (1hen per cage, n = 39) was collected into a micro-anticoagulant tube [65]. The blood sample was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C by high-speed freezing centrifuge to obtain the plasma then stored at -20 °C until further analysis.
Blood concentrations of cholesterol and triglyceride were determined using cholesterol and triglyceride assay kits according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Changchun Huili Biotech, China). The progesterone, motilin, secretin, and cholecystokinin of egg yolk were determined using progesterone, motilin, secretin, and cholecystokinin kits, respectively, following the manufacturer’s instructions (Shanghai Enzyme-Union Biotech, China).
Since the study conducted, was based on a feeding trial and birds were not harmed during the whole trial period. After carefully collecting the blood sample, all the birds were healthy and returned to the cage again. No animals were killed at humane endpoints.
All the data were analyzed by using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to determine whether any significant difference occurred within study groups or not. The data were presented as mean ± S.E.M, and the significance level was set up at p < 0.05 significant. The SPSS software, version 22.0 was used to analyze the data, and determine the effect of dietary treatments.
Availability of data and materials
Data used in this study will be available from corresponding author upon reasonable demand.
Abbreviations
- AEPR:
-
Average egg production rate
- AEW:
-
Average egg weight
- ADFI:
-
Average daily feed intake
- FCR:
-
Feed conversion ratio
- EW:
-
Egg weight
- ESI:
-
Egg shape index
- ESC:
-
Eggshell color
- ESS:
-
Eggshell strength
- YW:
-
Yolk weight
- ESW:
-
Eggshell weight
- YC:
-
Yolk color
- AH:
-
Albumen height
- HU:
-
Haugh Unit
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- CH:
-
Cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- CH:
-
Cholesterol
- PROG:
-
Progesterone
- MTL:
-
Motilin
- SC:
-
Secretin
- CCK:
-
Cholecystokinin
References
Barton MD. Antibiotic use in animal feed and its impact on human healt. Nutr Res Rev. 2000;13(2):279–99.
Gibson MK, Crofts TS, Dantas G. Antibiotics and the develo** infant gut microbiota and resistome. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015;27:51–6.
Yang JH, Bhargava P, McCloskey D, et al. Antibiotic-induced changes to the host metabolic environment inhibit drug efficacy and alter immune function. Cell Host Microbe. 2017;22(6):757–65. e753.
Castanon J. History of the use of antibiotic as growth promoters in European poultry feeds. Poult Sci. 2007;86(11):2466–71.
Diarra MS, Silversides FG, Diarrassouba F, et al. Impact of feed supplementation with antimicrobial agents on growth performance of broiler chickens, Clostridium perfringens and enterococcus counts, and antibiotic resistance phenotypes and distribution of antimicrobial resistance determinants in Escherichia coli isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73(20):6566–76.
Suresh G, Das RK, Kaur Brar S, et al. Alternatives to antibiotics in poultry feed: molecular perspectives. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2018;44(3):318–35.
Singh S, Shukla S, Tandia N, et al. Antibiotic residues: a global challenge. Pharma Science Monitor. 2014;5(3):184-97.
Ferri M, Ranucci E, Romagnoli P, et al. Antimicrobial resistance: a global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017;57(13):2857–76.
Boursi B, Mamtani R, Haynes K, et al. Recurrent antibiotic exposure may promote cancer formation–another step in understanding the role of the human microbiota? Eur J Cancer. 2015;51(17):2655–64.
Gillings MR, Paulsen IT, Tetu SG. Genomics and the evolution of antibiotic resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1388(1):92–107.
Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, et al. Antibiotic resistance—the need for global solutions. Lancet infect Dis. 2013;13(12):1057–98.
Kumar K, Gupta SC, Chander Y, et al. Antibiotic use in agriculture and its impact on the terrestrial environment. Advan Agron. 2005;87:1–54.
Qiao M, Ying G-G, Singer AC, et al. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ Int. 2018;110:160–72.
Organization WH. WHO Model List of Essential Medicines. 2011. WHO Medicines web. http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/EML2014.
Kang J, Park H-C, Jang H. Y, et al. National post-market surveillance assessment of veterinary medicines in Korea during the past decade. BMC Vet Res. 2017;13(1):136.
Mingmongkolchai S, Panbangred W. Bacillus probiotics: an alternative to antibiotics for livestock production. J Appl Microbiol. 2018;124(6):1334–46.
Ferber D. Livestock feed ban preserves drugs’ power.(Antibiotic Resistance). Science. 2002;295(5552):27–9.
Corrigan A, de Leeuw M, Penaud-Frézet S, et al. Phylogenetic and functional alterations in bacterial community compositions in broiler ceca as a result of mannan oligosaccharide supplementation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81(10):3460–70.
Olmos J, Ochoa L, Paniagua-Michel J, et al. Functional feed assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei using 100% fish meal replacement by soybean meal, high levels of complex carbohydrates and Bacillus probiotic strains. Mar Drugs. 2011;9(6):1119–32.
de Vries S, Pustjens AM, Kabel MA, et al. Processing technologies and cell wall degrading enzymes to improve nutritional value of dried distillers grain with solubles for animal feed: an in vitro digestion study. J Agric Food Chem. 2013;61(37):8821–8.
Tang J, Cai J, Liu R, et al. Immunostimulatory effects of artificial feed supplemented with a Chinese herbal mixture on Oreochromis niloticus against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014;39(2):401–6.
Larsen N, Thorsen L, Kpikpi EN, et al. Characterization of Bacillus spp. strains for use as probiotic additives in pig feed. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98(3):1105–18.
Gao P, Ma C, Sun Z, et al. Feed-additive probiotics accelerate yet antibiotics delay intestinal microbiota maturation in broiler chicken. Microbiome. 2017;5(1):91.
Ye M, Tang X, Yang R, et al. Characteristics and application of a novel species of Bacillus: Bacillus velezensis. ACS Chem Biol. 2018;13(3):500–5.
Shu X, Wang Y, Zhou Q, et al. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by cell-free extracts of Bacillus velezensis DY3108 with broad PH stability and excellent thermostability. Toxins (Basel). 2018;10(8):330.
Reva ON, Swanevelder DZ, Mwita LA, et al. Genetic, epigenetic and phenotypic diversity of four Bacillus velezensis strains used for plant protection or as probiotics. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:2610.
Fooks LJ, Gibson GR. In vitro investigations of the effect of probiotics and prebiotics on selected human intestinal pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2002;39(1):67–75.
Elshaghabee FM, Rokana N, Gulhane RD, et al. Bacillus as potential probiotics: status, concerns, and future perspectives. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:1490.
Jia R, Ma Q, Fan Y, et al. The toxic effects of combined aflatoxins and zearalenone in naturally contaminated diets on laying performance, egg quality and mycotoxins residues in eggs of layers and the protective effect of Bacillus subtilis biodegradation product. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016;90:142–50.
Zhen W, Shao Y, Gong X, et al. Effect of dietary Bacillus coagulans supplementation on growth performance and immune responses of broiler chickens challenged by Salmonella enteritidis. Poult Sci. 2018;97(8):2654–66.
Zhang J, **e Q, Ji J, et al. Different combinations of probiotics improve the production performance, egg quality, and immune response of layer hens. Poult Sci. 2012;91(11):2755–60.
Xu C-L, Ji C, Ma Q, et al. Effects of a dried Bacillus subtilis culture on egg quality. Poult Sci. 2006;85(2):364–8.
Wang Y, Du W, Lei K, et al. Effects of dietary Bacillus licheniformis on gut physical barrier, immunity, and reproductive hormones of laying hens. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2017;9(3):292–9.
Guo J, Dong X, Liu S, et al. Effects of long-term Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 1.921 supplementation on performance, egg quality, and fecal and cecal microbiota of laying hens. Poult Sci. 2017;96(5):1280–9.
Li H-F, Shu J-T, Du Y-F, et al. Analysis of the genetic effects of prolactin gene polymorphisms on chicken egg production. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(1):289–94.
Mazanko MS, Gorlov IF, Prazdnova EV, et al. Bacillus probiotic supplementations improve laying performance, egg quality, hatching of laying hens, and sperm quality of roosters. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2018;10(2):367–73.
Ribeiro V Jr, Albino L, Rostagno H, et al. Effects of the dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis levels on performance, egg quality and excreta moisture of layers. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 2014;195:142–6.
Chen XH, Koumoutsi A, Scholz R, et al. Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth–promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(9):1007–14.
Zhou Y, Li S, Pang Q, et al. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BLCC1-0238 can effectively improve laying performance and egg quality via enhancing immunity and regulating reproductive hormones of laying hens. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019;12(1):246–52.
Forte C, Moscati L, Acuti G, et al. Effects of dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bacillus subtilis on laying performance, egg quality, blood biochemistry and immune response of organic laying hens. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. 2016;100(5):977–87.
Yang J, Zhan K, Zhang M. Effects of the use of a combination of two Bacillus species on performance, egg quality, small intestinal mucosal morphology, and cecal microbiota profile in aging laying hens. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020;12(1):204–13.
Park N, Lee TK, Nguyen TTH, et al. The effect of fermented buckwheat on producing l-carnitine‐and γ‐aminobutyric acid (GABA)‐enriched designer eggs. J Sci Food Agric. 2017;97(9):2891–7.
Travel A, Nys Y, Bain M. Effect of hen age, moult, laying environment and egg storage on egg quality. In Improving the safety and quality of eggs and egg products. Oxford: Woodhead Publishing; 2011. p. 300–29.
Choi Y, Lee EC, Na Y, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with fermented and non-fermented brown algae by-products on laying performance, egg quality, and blood profile in laying hens. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2018;31(10):1654.
Zhao L, Zhang X, Cao F, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation with fermented Ginkgo-leaves on performance, egg quality, lipid metabolism and egg-yolk fatty acids composition in laying hens. Livest Sci. 2013;155(1):77–85.
Meng Q, Zhou W, Zhang C, et al. Serum triglyceride measurements: the commutability of reference materials and the accuracy of results. Clin Chem Lab Med (CCLM). 2017;55(9):1284–90.
Chen Y, Son K, Min B, et al. Effects of dietary probiotic on growth performance, nutrients digestibility, blood characteristics and fecal noxious gas content in growing pigs. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2005;18(10):1464–8.
Wang JP, Zhang ZF, Yan L, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of emulsifier and carbohydrase on the growth performance, serum cholesterol and breast meat fatty acids profile of broiler chickens. Anim Sci J. 2016;87(2):250–6.
Kalavathy R, Abdullah N, Jalaludin S, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus cultures on growth performance, abdominal fat deposition, serum lipids and weight of organs of broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci. 2003;44(1):139–44.
Hassaan MS, Soltan MA, Mohammady EY, et al. Growth and physiological responses of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus fed dietary fermented sunflower meal inoculated with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bacillus subtilis. Aquaculture. 2018;495:592–601.
Oka T, Schimke RT. Interaction of estrogen and progesterone in chick oviduct development: II. Effects of estrogen and progesterone on tubular gland cell function. J Cell Biol. 1969;43(1):123–37.
Hagan CR, Lange CA. Molecular determinants of context-dependent progesterone receptor action in breast cancer. BMC Med. 2014;12(1):32.
Thomas D, Noonan L, Whitehead A, et al. Invasive cervical cancer and depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate. WHO Collaborative Study of Neoplasia and Steroid Contraceptives. Bull W H O. 1985;63(3):505–11.
Kim T-I, Lim D-H, Jang S-S, et al. Effects of supplementing Barodon, Bacillus subtilis, and Ampbio on growth performance, biochemical metabolites, and hormone levels in Korean native heifers. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2018;50(7):1637–43.
Goswami C, Tanaka T, Jogahara T, et al. Motilin stimulates pepsinogen secretion in Suncus murinus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;462(3):263–8.
Tack J, Deloose E, Ang D, et al. Motilin-induced gastric contractions signal hunger in man. Gut. 2016;65(2):214–24.
Thomas H. Liver. Uncovering the secrets of secretin. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(6):315.
Johnson L, Grossman MI. Secretin: the enterogastrone released by acid in the duodenum. Am J Physiol-Legacy Cont. 1968;215(4):885–8.
You CH, Chey WY. Secretin is an enterogastrone in humans. Dig Dis Sci. 1987;32(5):466–71.
Chey W, Kim M, Lee K, et al. Secretin is an enterogastrone in the dog. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1981;240(3):G239–44.
Stollmaier W, Schwille P. Endogenous secretin in the rat-evidence for a role as an enterogastrone but failure to influence serum calcium homeostasis. Exp Clin Endocr Diab. 1992;99(03):169–74.
Houston RD, Haley CS, Archibald AL, et al. A polymorphism in the 5′-untranslated region of the porcine cholecystokinin type A receptor gene affects feed intake and growth. Genetics. 2006;174(3):1555–63.
Jayaraman S, Das PP, Saini PC, et al. Use of Bacillus Subtilis PB6 as a potential antibiotic growth promoter replacement in improving performance of broiler birds. Poult Sci. 2017;96(8):2614–22.
Khalid A, Ye M, Wei C, et al. Simultaneous production of Β-glucanase and Protease from Bacillus Velezensis strain identified in the manure of piglets. 2020.
Abrahamsson P, Tauson R. Aviary systems and conventional cages for laying hens: effects on production, egg quality, health and bird location in three hybrids. Acta Agr Scand A-An. 1995;45(3):191–203.
Tang RY, Wu ZL, Wang GZ, et al. The effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on productive performance of laying hens. Ital J Anim Sci. 2018;17(2):436–41.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge all the financial supporters of this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program of Anhui Province (201903a06020020), the Fund of College of Natural Science from Anhui Province (KJ2018A0141), Anhui Industry and Technology System of Poultry Science (AHCYTX-10), and the Fund of State Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition (2004DA125184F1725). The funding bodies were not involved in the study design, data collection, analysis and interpretation, or in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.W. and H.C designed and performed the experiments, as well as helped draft the manuscript. M.Y., C.W., A.K., and R.Y. carried out the laboratory work, participated in data analysis, participated in the design of the study and drafted the manuscript. Q.H. and B.D. collected field data. All authors gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee, Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Ethics Committee of Anhui Agricultural University, Anhui, China. The animals used in this study were derived from commercial sources, and the owners’ consent was not required.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
Authors declare that no competing interests exist between them.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, M., Wei, C., Khalid, A. et al. Effect of Bacillus velezensis to substitute in-feed antibiotics on the production, blood biochemistry and egg quality indices of laying hens. BMC Vet Res 16, 400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-020-02570-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-020-02570-6