Abstract
Background
Challenging behaviors like aggression and self-injury are dangerous for clients and staff in residential care. These behaviors are not well understood and therefore often labeled as “complex”. Yet it remains vague what this supposed complexity entails at the individual level. This case-study used a three-step mixed-methods analytical strategy, inspired by complex systems theory. First, we construed a holistic summary of relevant factors in her daily life. Second, we described her challenging behavioral trajectory by identifying stable phases. Third, instability and extraordinary events in her environment were evaluated as potential change-inducing mechanisms between different phases.
Case presentation
A woman, living at a residential facility, diagnosed with mild intellectual disability and borderline personality disorder, who shows a chronic pattern of aggressive and self-injurious incidents. She used ecological momentary assessments to self-rate challenging behaviors daily for 560 days.
Conclusions
A qualitative summary of caretaker records revealed many internal and environmental factors relevant to her daily life. Her clinician narrowed these down to 11 staff hypothesized risk- and protective factors, such as reliving trauma, experiencing pain, receiving medical care or compliments. Coercive measures increased the chance of challenging behavior the day after and psychological therapy sessions decreased the chance of self-injury the day after. The majority of contemporaneous and lagged associations between these 11 factors and self-reported challenging behaviors were non-significant, indicating that challenging behaviors are not governed by mono-causal if-then relations, speaking to its complex nature. Despite this complexity there were patterns in the temporal ordering of incidents. Aggression and self-injury occurred on respectively 13% and 50% of the 560 days. On this timeline 11 distinct stable phases were identified that alternated between four unique states: high levels of aggression and self-injury, average aggression and self-injury, low aggression and self-injury, and low aggression with high self-injury. Eight out of ten transitions between phases were triggered by extraordinary events in her environment, or preceded by increased fluctuations in her self-ratings, or a combination of these two. Desirable patterns emerged more often and were less easily malleable, indicating that when she experiences bad times, kee** in mind that better times lie ahead is hopeful and realistic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In residential care for individuals with an intellectual disability, challenging behavior is an often used umbrella term for repeatedly engaging in dangerous or threatening behaviors. These can be outer-directed, like aggression towards people or damaging property, and inner-directed, such as self-injurious behavior [1, 2]. The latter is defined as inflicting deliberate damage on- or destruction of one’s own body tissue with or without suicidal intent, for example by skin cutting, burning, scratching, or ingesting inedible objects [3]. For staff, these behaviors are hard to grasp and sometimes difficult to anticipate. Managing incidents afterwards with freedom restricting measures, such as seclusion or fixation, remains an unwanted and increasingly unaccepted common-practice that is harmful to clients and increases staff stress and turnover [4, 5]. Staff typically describe challenging behaviors as a way the individual communicates unmet “complex needs” [6]. Although group-level research reveals many biological, psychological and social correlates of challenging behavior [2, 7, 8], it remains vague what this often-used adjective “complex” means at the individual level. Research focused on the individual rather than on the group can efficiently advance our understanding of complex phenomena [9]. Therefore, this study provides a unique exploration of patterns of chronic aggressive and self-injurious behaviors in one woman with a mild intellectual disability (MID) and borderline personality disorder (BPD), day-by-day over the course of 560 days.
The overall goal is to obtain an in-depth understanding of when and why challenging behaviors occur, using an analytical strategy inspired by complex systems theory (cf [10]). This complex systems lens differs from the dominant biomedical perspective on psychopathology. That is, from a complex systems perspective psychiatric disorders are not understood as latent entities that cause symptoms through (relatively static) hard-wired biological mechanisms, but as dynamic patterns of behaviors, emotions and cognitions that are formed over time [11, 12]. Complex systems principles have guided individual-specific explorations of dynamics in high-risk young adults [13], people with depression [14,15,16] and dissociative identity disorder [17, 18]. While these studies all used quantitative timeseries analyses to describe the dynamics, qualitative methods are just as well-suited within a complex systems framework. Central to complex systems theory is a holistic approach to understand the person in their environment [12] and qualitative methods can provide a rich account thereof [19]. The current study therefore offers a holistic and dynamic exploration of a woman with MID and BPD, by employing a mixed-methods strategy with three overarching aims. In the following sections we introduce these three aims step-by-step, with more detailed theoretical background.
Summarizing daily life
The first step is to qualitatively summarize the complex nature of challenging behavior. From a complex systems perspective, any person is considered a complex system, not just individuals with challenging behavior [12]. It is complex because there is no root cause for the way a person (i.e., system as a whole) feels, thinks, or behaves at certain moments in time. Emotions, thoughts or behaviors emerge from continuous and interdependent exchanges between the system’s internal state and its environment [20]. Complex systems are everchanging, which is why an integrative understanding requires a detailed description of the interplay between the system’s and context elements over a longer period of time. It is therefore necessary to sample personal experiences and contextual influences frequently over time, for example by making use of ecological momentary assessment (EMA). EMA is a method in which someone frequently self-reports on current or very recent behaviors and experiences over time (typically via mobile-phone) [21]. The method is well-established in samples with BPD, but although feasible [22] not often used in MID research. In earlier work involving clients with BPD, momentary self-injury was associated with daily ruminations or heightened negative affect [23]. Other EMA studies found the intensity of anger associated with daily reports of aggression [24]. Such internal experiences (i.e., related to thoughts, emotions, or other behaviors) are the primary focus of most EMA research, but there are few studies that explicitly investigate contextual influences and changes [23]. This is remarkable, because theory indicates that (challenging) behaviors are not only internally driven but are to a large extend elicited by environmental factors [12]. For instance, self-injury, is known to occur more frequently when experiencing interpersonal stress [25]. However, internal factors and the environment differs between persons [26, 27]. Whereas one person’s self-injury may be triggered by an argument with parents, someone else’s work pressure may trigger it. To obtain a holistic summary of the person-environment interplay, we first explore person-specific internal states and environmental factors qualitatively.
Describing change over time
The second step is to zoom out, quantitatively exploring how these factors are ordered in time on the participant’s 560-day timeline. EMA research typically employs multiple daily self-ratings for 1–3 weeks, but individual accounts of challenging behaviors over longer timeframes are scarce. Some studies used not daily but weekly caretaker-reports of challenging behavioral incidents. These showed that, during a period of 41 weeks, staff of 33 inpatients with MID reported in total 210 aggressive- and 104 self-injurious incidents [28, 29]. Interestingly, 4 of those 33 inpatients were responsible for over half of the 210 aggressive incidents, while a staggering 85% of the 104 self-injurious incidents were from only 2 clients. Few individuals thus account for many incidents, but little is known about the day-to-day temporal patterns of such chronic challenging behaviors over the course of weeks or months.
When a person is tracked over longer periods of time, one can detected phases in which certain behaviors are relatively stable. A single-case study using EMA of a person with a major depressive disorder over almost eight months (239 days) [15] found two distinct phases. The first four months were characterized by consistent low self-reported depressive symptoms. On the 127th day this abruptly changed, marking the start of a four-month period characterized by consistently high depressive symptoms. From a complex systems perspective, these two stable phases (before and after day 127) are called attractors [30]. That is, the dynamics of the person (i.e., person-environment system) are attracted towards a specific behavioral pattern that remains relatively stable over time (e.g., a depressive phase in this example). Importantly, stability does not speak to the desirableness of the patterns, but only to the consistency of change over time. For example, consistently never self-harming, consistently being aggressive once-per-week on Tuesdays, or consistently self-harming on weekends are all examples of stable patterns. Following complex systems theory, stable patterns of challenging behaviors can thus be understood as attractors [11, 12]. Our second research question is how challenging behaviors are ordered on the participant’s 560-day timeline? This is done by identifying if there are different attractor states (e.g. time-periods with relatively few vs. many challenging behaviors) and explicate ways in which these time-periods are (dis)similar from one another in terms of internal states (e.g., experienced emotions) and environmental influences (e.g., social interactions).
Change-mechanisms
In the third and last step we zoom in again by exploring transition-points: moments that ‘kickstart’ abrupt change towards a new attractor (cf. day 127 in [15]). Complex systems theory posits two general mechanisms for the change from one attractor to another that are relevant in the context of this study.
First, instability-induced change (also called bifurcation-induced change [17, 18, 33]). We ultimately described, per identified transition, whether it was preceded or accompanied by significant instability and/or an extraordinary event. These extraordinary events were codes categorized into subthemes during the thematic analysis procedure. That is, after the coders had familiarized themselves with the data, generated and discussed initial codes they reached consensus about which events reflected everyday events and which events were extraordinary across the 560 day period. In the absence of instability, an extraordinary event occurring the week prior to a transition was considered an potential indicator of an event-induced mechanism (cf. Figure 1). Change was potentially instability induced when the dynamic complexity of aggression and/or self-injury was significantly high the week before or during change, without an extraordinary event the week prior. In the presence of both instability and an extraordinary event, we conclude change was potentially event- and instability-induced.
Results
Summarizing daily life
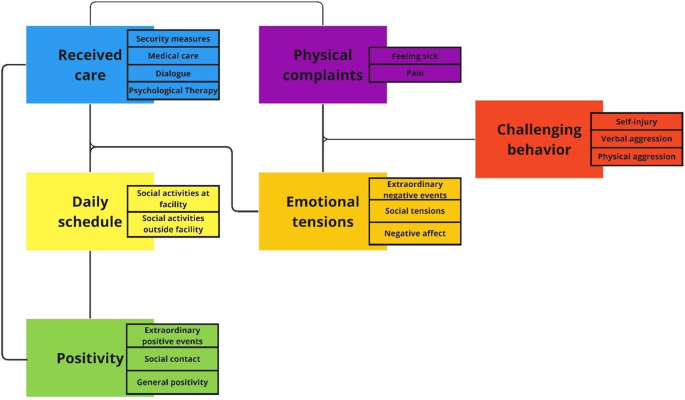
To first obtain a comprehensive summary of her daily life we conducted a thematic analysis of the care taker’s records. The analysis resulted in a thematic map consisting of six themes and sixteen subthemes. The six themes were the received care, daily activities not related to care, positivity, physical complaints, emotional tensions, and challenging behavior. These themes reflect categorizations that are interrelated. We visualized (sub)themes and their interrelations in Fig. 3.
Anything positive reported in the daily records was coded under the theme positivity. This pertained to events that were extraordinary positive for her on the 560 days. Positive social contact was a subtheme that reflected more casual positive interactions with care professionals, family or friends. The subtheme general positivity included any mention of positive affect. This could be sense of humor, making a relaxed impression, having a good day, or positive dialogue with care professional. For example the mention “client played boardgames after the barbecue and visibly enjoyed herself” indicates that positivity occurred during descriptions of the issue of the day, which are subdivided under two themes: received care and daily schedule. The latter involved her daily schedule unrelated to medical or psychological treatment, which could be either at the facility (e.g., doing the household or taking a walk) or social activities away from the facility (e.g., board games at activity center). Received care related to any actions from care professionals, which could be either in the form of security measures (e.g., checking her room for potential objects used for self-injury or secluding the participant), dialogue with care professionals (e.g., talking about what is on her mind, complimenting the participant), medical care (e.g., treatment of wounds at care facility or hospitalization), or psychological therapy sessions (dialectical behavior therapy and psychomotor therapy).
Challenging behavior was a theme with three subthemes: verbal aggression, physical aggression, and self-injury. The latter two were also self-reported on a daily basis by the participant. Daily record accounts of challenging behavior related to emotional and/or physical discomfort, for example “client cut herself with a broken piece of plate, she says she wanted to experience different pain than the pain in her stomach”. The theme physical complaints related to either feeling sick (e.g., nauseated) or mentions of the participant communicating experiencing physical pain. Both could be a cause and consequence of challenging behavior. For example, self-injury caused wounds, which lead to inflammation, which naturally come with pain or sickness such as fever. Self-injury through re-opening existing wounds was the most frequently reported self-injurious form, which exacerbated physical complaints. That required her receiving (extra) care. Related to both challenging behaviors and physical complaints were emotional tensions – a broad theme that comprised of three subthemes. Records describing extraordinary negative events (e.g., losing her pet), social tensions (e.g., quarrels with staff or family) and general descriptions of negative affect (e.g., feeling irritated, fearful, frustrated, or insecure). Emotional tensions could be triggered during any daily activity and could be both cause and consequence of physical complaints. For example “client is working on a painting. When we adjust schedule to playing a boardgame she becomes angry”. Moreover, it could result in receiving extra care (e.g., support from staff when in distress) or was the consequence of dissatisfaction with received care (e.g., anger after imposed security measure). Challenging behavior always came with some form of emotional tension.
To better interpret the thematic map, the researcher then asked the participant’s clinician whether the participant knows better and worse times and what typically indicates to staff whether her overall well-being is high or low. Before having seen the results, she confirmed that the frequency of self-injurious and physically aggressive incidents is most telling about her overall well-being. This indicates challenging behaviors summarize her overall state. From the (sub)themes generated in the thematic analysis, the clinician then identified 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors for her challenging behaviors. These factors were either specific codes or broader (sub)themes: reliving past trauma, hallucinating, negative affect, receiving medical care, receiving compliments, the imposing of freedom restricting measures, experiences of physical pain and sickness, receiving psychological therapy, tensions with her family, and positive social interactions. These variables were used for subsequent analyses.
Describing change trajectory
The participant completed the daily survey 494 times during the 560 days (88%). Physical aggressive incidents were self-reported on 65 days (13%), while self-injury was self-reported on 247 days (50%). Staff reported aggressive and self-injurious incidents on respectively 75 days (16%) and 164 days (33%). A χ2 test indicated agreement between self- and informant ratings. That is, counts of observed matches between self- and informant ratings of these challenging behaviors (i.e., both reporting daily presence or absence of behavior) was significantly higher than the expected count for self-injury, χ2 (1, N = 494) = 91.56, p < 0.001, and for aggression, χ2 (1, N = 494) = 12.76, p < 0.001. As both challenging behaviors can occur without being noticed by staff (e.g., when on leave), we analyze self-reported challenging behavioral dynamics.
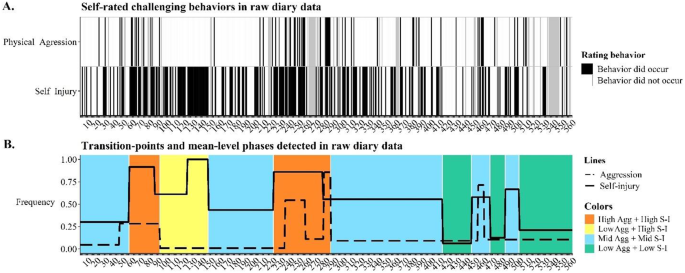
Binary timeseries of self-reported physical aggression and self-injurious behavior during 560 days and changes in its mean frequency. X-axes show number of days. Panel A shows raw challenging behavioral timelines. Gray cells are days that the participant did not complete her diary. In panel B, the lines reflect mean-level changes in raw diary timelines, detected by recursive partitioning algorithm. Colors reflect identified challenging behavioral attractor states (see text for details). The same color means a qualitatively similar attractor. Identified transition-points between attractors are thus the days (on x-axis) when the color changes
Figure 4A illustrates the raw binary timeseries of self-reported physical aggression and self-injury for 560 days. The recursive partitioning algorithm [42] first detected mean-frequency changes in raw diary timelines (4A) – the outcome of which is visualized with dashed and solid lines in Fig. 4B. After visual inspection of the binary timeseries (4A) and their mean-levels (lines in 4B), we found 10 transitions that mark that end of an old- and start of a new attractor (colors in 4B). When the mean-level changes detected by recursive partitioning (up or downward trend in lines 4B) of the two challenging behaviors occurred in the same direction within close proximity to one another (i.e., within 14 days), we marked it as transition that starts or ends a challenging behavioral phase. For example, on day 86 for self-injury a 30% drop was detected by recursive partitioning and on day 91 aggression dropped by 28%. Here we marked day 91 as the transition, as it marked the end of a phase with frequent challenging behavior. Similarly, when self-injury and aggression increased on respectively day 446 and 452, we marked 446 as the transition for a start with frequent challenging behaviors. One exception was made, based on a clear difference in absolute change: on day 46 the proportion of aggressive incidents increased with 25%, while 11 days later the proportion in self-injurious incidents increased by 60%. Hence, only day 57 was marked as a transition. Two detected mean-changes were not marked as transitions: the increase of self-injury on day 122 and the decrease in aggressive incidents on day 257. The latter (day 257) was not marked as an attractor change, because of the large number of missing values that followed this transition (see gray band in Fig. 4A). Day 122 was not marked after visual inspection of the self-injurious incidents timeseries (Fig. 4A) we noted that (1) the upward trend may have started sooner (possibly day 110) and (2) this upward trend did not seem significant as the frequency of self-injuries– relative to the entire timeline – was already high between day 57 and day 146.
Table 1 summarizes, for each phase, the mean frequency (i.e., percentage of days) that both challenging behaviors were self-reported in the diaries. Furthermore, we calculated the mean frequency per phase for each of the 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors (see Supplementary Material 1). To obtain insight into what makes phases (dis)similar from each other in terms of these risk- and protective factors, we compared the mean frequency of them within each phase to the 560-day mean of that factor. We considered a phase-mean salient if it was above or below 1 SD relative to that factor’s 560-day mean. For example, salient about phase 1 (day 1 to 56) was that familial tensions occurred on 18% of days, which was relatively often, given that it is > 1 SD relative to the 560-day mean of 5%. Although Table 1 shows that the 11 frequencies of staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors differ between phases, we find no unequivocal bivariate if-then explanation (e.g., if a phase has familial tensions, then high aggression) for either of the challenging behavioral frequencies.
In addition to describing average frequencies across phases, we also analyzed bivariate associations at the within-day level (contemporaneous) and across days (lag-1). That is, whether challenging behaviors and reports of staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors co-occurred on the same day and from day-to-day. Fisher’s exact test revealed that, across the entire 560-day timeline, freedom restricting measures were more often applied on days with aggression (OR = 5.27, 95%CI [2.82, 9.78]) or self-injury (OR = 2.72, 95%CI [1.56, 4.89]). Across the 560-day period, there were no bivariate contemporaneous associations between challenging behaviors and reliving trauma, hallucinating, receiving medical care, compliments or psychological therapy, having pain, sickness, experiencing negative affect or familial tensions, or positive interactions. On days after an implemented freedom restricting measure, our participant was more likely to engage in aggressive (OR = 4.80, 95%CI [2.58, 8.86]) and/or self-injurious behavior (OR = 1.97, 95%CI [1.67, 3.39]). On days after a psychological therapy session (DBT or psychomotor therapy) she was less likely to engage in self-injurious behavior (OR = 0.36, 95%CI [0.15, 0.79]). To explore these associations within phases (and possible differences between phases), we repeated the same Fisher’s tests per phase, on both the contemporaneously and lagged timescale (484 tests; 11 themes × 2 behaviors × 11 phases × 2 timescales). The only significant associations that hold within certain phases evolve around freedom restricting measures, indicating that these measures were more likely to occur on the same day as aggression in phase 5, before days with self-injury in phase 7 and before days with aggression in phase 11. All other contemporaneous and lag-1 associations between challenging behaviors and the 11 variables that the clinician hypothesized to be explanatory, were non-significant (evaluated at p < 0.01 due to multiple testing).
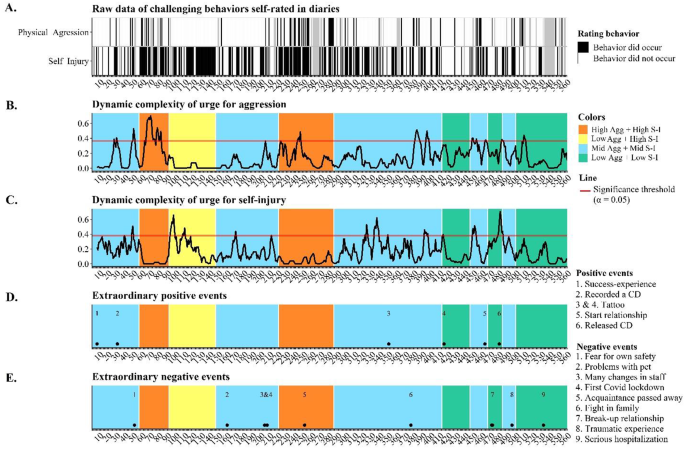
Combined graph of the participant’s self-reported challenging behavioral patterns, transition-points, dynamic complexity, and extraordinary events. Panel A shows the raw data of self-reported physical aggression and self-injury. Gray cells are missing data. Panel B and C reflect the dynamic complexity of both challenging behaviors. High values reflect unstable patterns, whereas low dynamic complexity reflects stability during the 7 prior days. The horizontal red lines mark the significance threshold for each variable; dynamic complexity values above the lines indicate statistical significance (α = 0.05). Orange, yellow, blue, and green background colors are attractor states. Panel D and E reflect pinpointed positive and negative extraordinary events that were identified as such in the daily records
Change-mechanisms
Figure 5 shows the occurrence of challenging behaviors (panel A), the (in)stability of self-reported patterns in urges for challenging behaviors (panel B and C), and extraordinary events (panel D and E) on the 560-day timelineFootnote 1. Each point on the graphs in panel B and C reflects how unstable (i.e., irregular and erratic) the fluctuations of self-rated urges for challenging behaviors were in the previous 7 days. Low values indicate stable patterns, whereas high dynamic complexity values are indicative of temporal instability. Everyday events are extremely plentiful, making them impractical to pinpoint on a timeline. Extraordinary events, however, were derived from thematic analysis results. We considered two subthemes: positive events and negative events (see themes positivity and emotional tensions in Fig. 3), as they reflected impactful events that were extraordinary across the 560-day timeline.
Table 2 summarizes what happens one week before each of the 10 transition-points. There were four transitions towards an attractor with more frequent challenging behavior than before. These undesirable transitions were all either instability-induced, environment-induced or a combination of both (Table 2). Day 221, for example, was likely an event-induced change, given that there was no instability, but the first Covid-19 lockdown likely led to this undesirable change. Social contact with friends and family – as well as support from staff – were drastically reduced while in lockdown, disrupting her everyday routine increasing her need for aggression and self-injury as an outlet. There were also six desirable changes. One such example was that the week before she finished her tattoo (extraordinary event on day 413) was instable, possibly due to prospect of this exhilarating moment, marked the start of a new phase with few challenging behaviors. However, the relation between transitions, instability and extraordinary events was not entirely clear-cut, as two desirable transition-points (day 147 and 286) occurred during stable periods and without any notable events. Figure 5 further shows that extraordinary events occurred during stability, but without a transition (e.g., starting her tattoo on day 350). Even an extraordinary event in combination with instability was no guarantee for a transition (e.g., on day 367 a fight in the family occurred during a highly unstable week without a transition). In summary, although instability seemed to increase the chance of transitions – especially in combination with an extraordinary event – our findings do not imply that instability and extraordinary events are incontrovertible warning signals that always explain meaningful change on the participant’s 560-day timeline.
Discussion and conclusions
The current study provides a unique exploration of day-by-day aggressive and self-injurious patterns in one woman with a MID and BPD. Applying a three-step-approach inspired by complex systems theory, we aimed for an in-depth understanding of her challenging behaviors over the course of 560 days. Summarizing her daily life was the first step, revealing that a large set of internal and environmental factors relevant to her daily life. The clinician narrowed this large set down to 11 staff hypothesized risk- and protective factors: freedom restrictive measures, reliving trauma, hallucinating, experiencing pain, sickness, negative affect, familial tensions, positive interactions, receiving medical care, compliments or psychological therapy. Overall, freedom restricting measures were more likely to occur on the same day as challenging behaviors, which is not surprising. It is striking, however, that self-injury and/or aggression were more likely to occur the day after a coercive measure by staff, indicating that although these measures may be effective to suppress certain behaviors in the moment, they have detrimental effects on the longer run [4, 5]. Furthermore, we found that on the day after a psychological therapy session (DBT or psychomotor therapy) she was less likely to self-injure. These results imply that downscaling of freedom restricting measures and upscaling of psychological therapy (where possible) is warranted. All other bivariate associations between hypothesized risk- and protective factors with both challenging behaviors – explored phase-by-phase and day-by-day – were non-significant, indicating that challenging behaviors are not governed by mono-causal if-then explanations (e.g., if phase has many familial tensions, then high aggression or if day with hallucination, then self-injury). The multitude of bivariate null-results speaks to the complex nature of these behaviors at the case-level [2, 6,7,8].
In the second step, we described the trajectory of challenging behaviors over time. We identified 11 distinct, relatively stable phases within the 560-days timeline. These 11 phases could be narrowed down to four qualitatively different attractor states: high levels of self-injury and aggression (2 phases), average levels of self-injury and aggression (5 phases), low levels of self-injury and aggression (3 phases), or high levels self-injury with low levels of aggression (1 phase). The mean frequency of the 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors varied by phase: no two phases were similar (Table 1).
In the third step we focused on (the week before) transitions between attractors, exploring potential change-inducing mechanisms (Fig. 1). Our findings suggest that the mechanism of two transitions remained unknown, two were event-induced, two were instability-induced and four could be environment- and/or instability-induced (Table 2). Six transitions were thus potentially instability-induced, which is in line with empirical evidence for instability as an early warning signal for upcoming transitions [17, 33, 34]. Nevertheless, extraordinary events and/or instability did not unequivocally imply a transition, as both instability and extraordinary events occurred without transitions afterwards (Fig. 5). The two unknown mechanisms were both for desirable transitions, which could mean that relatively minor events in daily life apparently were enough to elicit positive change. One possible explanation would be that her desirable attractor is stronger than the undesirable one. That is, we could perceive her undesirable basin (Fig. 1) to be shallower, making this state easier malleable relatively minor everyday events. Future research could explore this further with recently developed analytical methods that quantify the stability of an attractor state [48].
There were three notable limitations to this study. First, results from a case-study are obviously not generalizable. Repeating (and finetuning) our three-step-approach on different cases, will reveal the extent to which of our findings are person-specific or generalizable across cases. This will ultimately increase our understanding of challenging behaviors and consequently enable optimized care. Second, our thematic analysis was based on care professionals’ daily records. Registering relevant events in the electronic health records is a routine practice in the residential care setting – done with the intention to document the client’s case file and keep colleagues up to date. Hence, care professionals received no instructions as to how extensive or comprehensive their reports should be. This meant that when a specific code was not identified from the records on a specific day, it may either have not been observed by care professional(s) or simply not been registered. Seemingly trivial happenings, such as giving complements will likely have occurred more often than that the coders coded in the records. Third, despite a-priori anonymization of the records, it was evident that the records included reports of many different (approximately > 30 different) care professionals. The richness of the described daily events likely partially depended on who reported and how much time that person had. Fourth, our three-step procedure was subject to many researcher’s degrees of freedom. The 11 staff-hypothesized (sub)themes that the participant’s clinician selected out of the thematic map, for example, remained a personal choice. Furthermore, the criterion we used to evaluate a threshold for instability (one tailed z-test at p < 0.05) is based on convention (cf [16, 18, 33]), but ultimately still a choice. On the other hand, there are no established guidelines available for a complex systems guided case study.
This study also had strengths. First, by shedding light on events in the environmental that may ‘push’ the system into another state, our study adds to the (complex systems) psychological literature that has so far predominantly focused on instability preceding transitions [24, 33, 34, 45]. Qualitative analyses of case records allowed us to distinguish everyday- from extraordinary events. Because this distinction was informant-based and not self-reported, it is possible that meaningful events were missed (here or in any step of our analysis). Future qualitative or mixed-methods research should further explore the nature of events that the individual perceives to ‘kickstart’ transitions. A second strength is that our research gives a helicopter view of day-by-day processes across several months. The majority of EMA research in BPD studies within-day fluctuations. For our participant behavior did not only fluctuate within-days, also across time-periods of multiple weeks or months. This may inspire EMA research in BPD to consider further exploring fluctuations on slower timescales. Nevertheless, within-day processes remain relevant. Complex systems, after all, are characterized by interacting processes across many timescales [12, 49]. In our case, unobserved instability at shorter timescales (e.g., hour-to-hour) could have induced our (un)observed transitions. After all, within-day affective instability is a well-documented correlate of challenging behaviors in BPD [23, 24]. The case records did provide within-day detail, but because we eventually quantified these into dichotomous codes per day (present vs. absent), the richness of within-day information was lost. Future research should zoom further into what happens within the day of (or days before) a transition. Statistical process control charts [50] could then be used to detect whether significant rises in tensions predict challenging during the day.
The participant selection in this study was solely based on convenience sampling, that is, she was the only one in DBT who adhered to the diaries this consistently for this long. The uniqueness of the already collected diary data, both in terms of the chronicity of her challenging behavior [28, 29] and her devoted compliance to the diaries, was the reason she and her legal guardians were asked for this study. Whether or not these study procedures can be replicated in different cases depends on how well the implemented diary procedure elicits an intrinsic motivation to stay compliant. There were certain participant- and study characteristics that contributed to her uniquely long-term compliance, which are lessons for scientists or practitioners who wish to collect similar data. First, the diaries were an integral part of her DBT program – for which she was already highly motivated. Second, the diaries items were constructed in collaboration with the participant, and thus tailored to her experience world. A personalized approach to EMA in practice, by integrating it in therapy and individualizing item-selection, is an opportunity for increasing participant involvement and compliance [22, 51]. Third, for compliance it may have been helpful that the participant has lived in residential care since childhood. This institutionalization – at least with our participant – contributed to the responsibility she felt to follow through on prescribed activities in her care plan. Completing the diaries became part of her daily routine structure. It is likely that this played a part in her continued compliance to the diaries, even when the Covid pandemic made DBT impossible. Nevertheless, further research into factors that enhance or hamper EMA compliance is necessary.
Importantly, personalized daily diary monitoring – and therefore this study’s three-step analytical procedure – is already certainly feasible for other individuals [22]. Replicating this design is therefore encouraged. Complex systems theoretical principles have already guided mainly quantitative timeseries analytical inquiries in different clinical case studies with less measurements (e.g., 91 [17] or 138 [18]) and more measurements (e.g., 1.476 [15]). Based on these studies [15, 17, 18] we would we expect that altering between different phases over time is a finding that is likely to replicate. However, other clients without such chronic challenging behavior and without such an institutionalized background would likely show very different patterns. That is, dynamic patterns with qualitatively different – and potentially less strong – attractor states. At this point, it remains speculation how this case study’s findings relate to other clients. The surge of EMA applications in clinical settings during the past years suggests that large n = 1 datasets may become more commonly available. Replicating our three-step method would allow for between-person comparisons, shedding light on how (a)typical the nature of our participant’s attractor states and number of change-points was, compared to others (e.g., people with BPD and/or in residential MID care).
The study altogether illustrates the added value of in-depth case-study research [9] and the utility of complex systems principles to guide such an inquiry. Our three-step approach adheres to recent calls for holistic and dynamic accounts of challenging behaviors in BPD [52]. Over time, few (if any) if-then relationships could be said to possibly explain the participant’s challenging behavior, substantiating it as a complex phenomenon that is difficult to grasp. Our results thus make explicit why care professionals describe to these behaviors as “complex” [6]. Nevertheless, in-depth idiographic science can help disentangle this complexity, generating new insights relevant for practice. Zooming out revealed different phases of challenging behaviors. For staff it is good to recognize available attractors and adjust care accordingly. With our participant it illustrated that she – just as anyone – has both ups and downs. Her desirable attractors actually emerged more often than desirable ones (three periods of low aggression and self-injury vs. two periods with high aggression and self-injury). Moreover, her desirable patterns were less easily malleable than undesirable ones. For the participant, this means that when things are down, kee** in mind better times are ahead is as hopeful as it is realistic. Repeating this idiographic design on other persons with chronic challenging behavioral patterns may therefore nuance the bad reputation they may have at the care facility.
Data availability
R scripts are publicly available from https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/XRMHU. Preprocessed data are available upon reasonable request via https://doi.org/10.17026/SS/VOXYE9. Requests can be made for research purposes only.
Notes
In Fig. 5 we present the dynamic complexity of the most relevant two variables for these challenging behaviors. For completeness sake, we present raw data of all seven self-rated variables and their (average) dynamic complexity in Supplementary Material 2. Visualizations of the 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors, in combination with challenging behaviors and instability are accessible through https://hulsmans.shinyapps.io/themes/.
References
Emerson E, Kiernan C, Alborz A, Reeves D, Mason H, Swarbrick R, et al. The prevalence of challenging behaviors: a total population study. Res Dev Disabil. 2001;22(1):77–93.
Ali A, Blickwedel J, Hassiotis A. Interventions for challenging behaviour in intellectual disability. Adv Psychiatr Treat. 2014;20(3):184–92.
Nock MK. Self-injury. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2010;6(1):339–63.
van Dorp M, Nijhof KS, Mulder EA, Popma A. Defining seclusion: a qualitative multiphase study based on the perspectives of youth and professionals in secure residential youth care in the Netherlands. Resid Treat Child Youth. 2021;38(4):404–23.
Deveau R, McGill P. Impact of practice leadership management style on staff experience in services for people with intellectual disability and challenging behaviour: a further examination and partial replication. Res Dev Disabil. 2016;56:160–4.
Griffith GM, Hastings RP. He’s hard work, but he’s worth it. The experience of caregivers of individuals with intellectual disabilities and challenging behaviour: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27(5):401–19.
Crowell SE, Beauchaine TP, Linehan MM. A biosocial developmental model of borderline personality: elaborating and extending Linehan’s theory. Psychol Bull. 2009;135(3):495–510.
Tevis C, Matson JL. Challenging behaviour in children with developmental disabilities: an overview of behavioural assessment and treatment methods. BJPsych Adv. 2022;28(6):401–9.
Hekler EB, Klasnja P, Chevance G, Golaszewski NM, Lewis D, Sim I. Why we need a small data paradigm. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):133.
Thelen E, Ulrich BD. Hidden skills: a dynamic systems analysis of treadmill step** during the first year. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 1991;56(1):1–98.
Hayes AM, Andrews LA. A complex systems approach to the study of change in psychotherapy. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):197.
Olthof M, Hasselman F, Oude Maatman F, Bosman AMT, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Complexity theory of psychopathology. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. 2023;132(3):314–23.
Schreuder MJ, Hartman CA, Groen RN, Smit A, Wichers M, Wigman JTW. Anticipating transitions in mental health in at-risk youths: a 6-month daily diary study into early-warning signals. Clin Psychol Sci. 2022;11(6):1026–43.
Schreuder MJ, Wigman JTW, Groen RN, Weinans E, Wichers M, Hartman CA. Anticipating the direction of symptom progression using critical slowing down: a proof-of-concept study. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1).
Wichers M, Groot PC, Psychosystems ESM, Group EWS, Group. Critical slowing down as a personalized early warning signal for depression. Psychother Psychosom. 2016;85(2):114–6.
Wichers M, Schreuder MJ, Goekoop R, Groen RN. Can we predict the direction of sudden shifts in symptoms? Transdiagnostic implications from a complex systems perspective on psychopathology. Psychol Med. 2018;49(3):380–7.
Fartacek C, Schiepek G, Kunrath S, Fartacek R, Plöderl M. Real-time monitoring of non-linear suicidal dynamics: methodology and a demonstrative case report. Front Psychol. 2016;7:130.
Schiepek G, Stöger-Schmidinger B, Aichhorn W, Schöller H, Aas B. Systemic case formulation, individualized process monitoring, and state dynamics in a case of dissociative identity disorder. Front Psychol. 2016;7.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
van Geert PLC. Dynamic systems, process and development. Hum Dev. 2020;63(3–4):153–79.
Shiffman S, Stone AA, Hufford MR. Ecological momentary assessment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2008;4(1):1–32.
Hulsmans DHG, Poelen EAP, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A, Otten R. The feasibility of daily monitoring in adolescents and young adults with mild intellectual disability or borderline intellectual functioning. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2023;36(4):847–58.
Gee BL, Han J, Benassi H, Batterham PJ. Suicidal thoughts, suicidal behaviours and self-harm in daily life: a systematic review of ecological momentary assessment studies. Digit Health. 2020;6:2055207620963958.
Scott LN, Wright AGC, Beeney JE, Lazarus SA, Pilkonis PA, Stepp SD. Borderline personality disorder symptoms and aggression: a within-person process model. J Abnorm Psychol. 2017;126(4):429–40.
Coifman KG, Berenson KR, Rafaeli E, Downey G. From negative to positive and back again: polarized affective and relational experience in borderline personality disorder. J Abnorm Psychol. 2012;121(3):668–79.
Wright AGC, Hallquist MN, Stepp SD, Scott LN, Beeney JE, Lazarus SA, et al. Modeling heterogeneity in momentary interpersonal and affective dynamic processes in borderline personality disorder. Assessment. 2016;23(4):484–95.
Woods WC, Arizmendi C, Gates KM, Stepp SD, Pilkonis PA, Wright AGC. Personalized models of psychopathology as contextualized dynamic processes: an example from individuals with borderline personality disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2020;88(3):240–54.
van den Bogaard KJHM, Nijman HLI, Palmstierna T, Embregts PJCM. Characteristics of aggressive behavior in people with mild to borderline intellectual disability and co-occurring psychopathology. J Ment Health Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;11(2):124–42.
van den Bogaard KJHM, Nijman HLI, Palmstierna T, Embregts PJCM. Self-injurious behavior in people with intellectual disabilities and co-occurring psychopathology using the self-harm scale: a pilot study. J Dev Phys Disabil. 2018;30(5):707–22.
Olthof M, Hasselman F, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Complexity in psychological self-ratings: implications for research and practice. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):317.
Cui J, Hasselman F, Olthof M, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Common practices in detecting psychological early warning signals may lead to incorrect results [Internet]. (2022). PsyAr**v Preprints. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/59fu4.
Kelso JAS, Scholz JP, Schöner G. Nonequilibrium phase transitions in coordinated biological motion: critical fluctuations. Phys Lett A. 1986;118(6):279–84.
Olthof M, Hasselman F, Strunk G, van Rooij M, Aas B, Helmich MA, et al. Critical fluctuations as an early-warning signal for sudden gains and losses in patients receiving psychotherapy for mood disorders. Clin Psychol Sci. 2020;8(1):25–35.
Schreuder MJ, Hartman CA, George SV, Menne-Lothmann C, Decoster J, van Winkel R, et al. Early warning signals in psychopathology: what do they tell? BMC Med. 2020;18(1):269.
Heard HL, Linehan MM. Dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder. In: Norcross JC, Goldfried MR, editors. Handbook of psychotherapy integration. Oxford University Press; 2019. pp. 257–83.
Creswell JW, Plano Clark VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. London, England: SAGE; 2006.
MAXQDA. Software for qualitative analysis [Internet]. VERBI Software Consult Sozialforschung GmbH. http://www.maxqda.com.
RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated development environment for R [Internet], Boston MA. 2022. http://www.rstudio.com/.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Found Stat Comput Vienna, Austria. 2020; https://www.r-project.org/.
Kazdin AE. Single-case experimental research designs. Methodological issues and strategies in clinical research. 4th ed. Washington: American Psychological Association; 2015. pp. 459–83.
Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis [Internet]. Springer-Verlag New York; 2016. https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org.
Hasselman F, An. R toolbox for studying complex adaptive systems and networks [Internet]. 2023. https://fredhasselman.github.io/casnet/.
Therneau TM, Atkinson EJ. (2022). An introduction to recursive partitioning using the RPART routines [Internet]. 2022. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rpart/vignettes/longintro.pdf.
Tang TZ, DeRubeis RJ. Sudden gains and critical sessions in cognitive-behavioral therapy for depression. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1999;67(6):894–904.
Lutz W, Ehrlich T, Rubel J, Hallwachs N, Röttger M-A, Jorasz C, et al. The ups and downs of psychotherapy: sudden gains and sudden losses identified with session reports. Psychother Res. 2013;23(1):14–24.
Schiepek G, Strunk G. The identification of critical fluctuations and phase transitions in short term and coarse-grained time series-a method for the real-time monitoring of human change processes. Biol Cybern. 2010;102(3):197–207.
Moritz S, Bartz-Beielstein T, ImputeTS. Time series missing value imputation in R. R J. 2017;9(1):207.
Cui J, Hasselman F, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Unlocking nonlinear dynamics and multistability from intensive longitudinal data: a novel method. Psychol Methods. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000623.
Wallot S, Kelty-Stephen DG. Interaction-dominant causation in mind and brain, and its implication for questions of generalization and replication. Minds Mach (Dordr). 2018;28(2):353–74.
Snippe E, Smit AC, Kuppens P, Burger H, Ceulemans E. Recurrence of depression can be foreseen by monitoring mental states with statistical process control. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. 2023;132(2):145–55.
Riese H, Von Klipstein L, Schoevers RA, van der Veen DC, Servaas MN. Personalized ESM monitoring and feedback to support psychological treatment for depression: a pragmatic randomized controlled trial (Therap-i). BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1).
Selby EA, Harnedy LE, Hiner M, Kim J. Developmental and momentary dynamics in the onset and maintenance of nonsuicidal self-injurious behavior and borderline personality disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022;24(12):897–909.
Acknowledgements
We are most thankful to the participant for her long adherence to the daily diaries, and for allowing us to use the data to make this research report. Another big thanks goes out to her clinician for the discussing the thematic analysis results with us. We also thank her legal guardian for proofreading this manuscript. Lastly, we wish to thank Masters students Sophia Politis, Jynthe van Dongen, Fenne van Mil and Maud Wouters for their help with the thematic analysis.
Funding
DH, RO and EP were supported by funding from the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw); Grant Number 555002014. ALA and MO were supported by a NWO VIDI grant, Grant No. VI.Vidi.191.178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DH: formulated the research plans and questions, designed and performed qualitative and quantitative analyses, interpreted the results, wrote the initial manuscript draft, and revised the manuscript. RO: formulated the research plans and questions, project supervision, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. EP: formulated the research plans and questions, project supervision, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. AvV: formulated the research plans and questions, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. SD: helped design and perform qualitative data analysis, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. MO: helped design quantitative analyses, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. FH: helped design and perform quantitative analyses, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. A-LA: formulated the research plans and questions, helped design quantitative analyses, project supervision, interpreted the results, and was a major contributor in revising the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from the participant and her legal guardian to analyze the daily diaries and daily records and write this case-report. Her clinical team (clinician and closest care professionals) were consulted and approved study procedures. The Ethics Committee Social Sciences of Radboud University and the Ethics committee of the care organization were consulted prior to conducting this study. Due to the use of already existing data, the need for formal approval was waived. Both committees judged that our procedures were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
The participant’s legal guardian read the final version of this manuscript and provided written informed consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Hulsmans, D.H.G., Otten, R., Poelen, E.A.P. et al. A complex systems perspective on chronic aggression and self-injury: case study of a woman with mild intellectual disability and borderline personality disorder. BMC Psychiatry 24, 378 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05836-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05836-7