Abstract
Genes containing the SET domain can catalyse histone lysine methylation, which in turn has the potential to cause changes to chromatin structure and regulation of the transcription of genes involved in diverse physiological and developmental processes. However, the functions of SET domain-containing (StSET) genes in potato still need to be studied. The objectives of our study can be summarized as in silico analysis to (i) identify StSET genes in the potato genome, (ii) systematically analyse gene structure, chromosomal distribution, gene duplication events, promoter sequences, and protein domains, (iii) perform phylogenetic analyses, (iv) compare the SET domain-containing genes of potato with other plant species with respect to protein domains and orthologous relationships, (v) analyse tissue-specific expression, and (vi) study the expression of StSET genes in response to drought and heat stresses. In this study, we identified 57 StSET genes in the potato genome, and the genes were physically mapped onto eleven chromosomes. The phylogenetic analysis grouped these StSET genes into six clades. We found that tandem duplication through sub-functionalisation has contributed only marginally to the expansion of the StSET gene family. The protein domain TDBD (PFAM ID: PF16135) was detected in StSET genes of potato while it was absent in all other previously studied species. This study described three pollen-specific StSET genes in the potato genome. Expression analysis of four StSET genes under heat and drought in three potato clones revealed that these genes might have non-overlap** roles under different abiotic stress conditions and durations. The present study provides a comprehensive analysis of StSET genes in potatoes, and it serves as a basis for further functional characterisation of StSET genes towards understanding their underpinning biological mechanisms in conferring stress tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The nucleosome, the fundamental unit of eukaryotic chromatin material, consists of two DNA strands wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins, which comprises two copies of each H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 protein [1]. Post-translational modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and SUMOylation, covalently modify the N-terminal region of core histones [2, 3]. These modifications impact chromatin structure and accessibility and thereby can regulate gene expression [4, 5]. In plants, histone methylation is among the most well-understood histone modifications. This modification plays a crucial regulatory role in plant growth and development, reproductive processes, and response to environmental factors [5,33]
The length of StSET gene sequences ranged from 430 to 28,651 nucleotides. Three genes, namely StSET21, StSET29, and StSET49, contained a single exon, while the remaining genes contained up to 24 exons (Fig. 2B; Table S1). The length of protein sequences of StSET genes ranged from 112 to 2421 amino acids. The proteins of StSET genes had an average and median molecular weight of 87.7 and 78.2 kilodaltons (kDa), respectively. The protein of StSET43 had the highest molecular weight of 276.5 kDa, while the protein of the StSET17 gene had the lowest molecular weight of 13 kDa. The StSET proteins had a theoretical pI spectrum of 4.51 to 9.47. We predicted that about 84% of the StSET proteins (48 StSETs) are unstable. Amino acid composition analysis showed that Serine (Ser), Glycine (Gly), Leucine (Leu), and Lysine (Lys) are the predominant amino acid residues of StSET proteins. The grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) values indicated that StSET proteins are hydrophilic (Table S2).
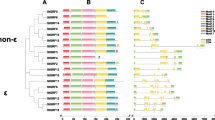
Gene structure and protein domain organisation of StSET genes with respect to their phylogenetic order. A). The estimated phylogenetic tree for StSET genes, B). Gene structure of StSET genes, and C). Protein domain organisation of StSET proteins. We visualised the phylogenetic tree, the gene structure and the protein domain organisations using TBTools v1.098696 [34]
We found 23 unique protein domains in the protein sequences of StSET genes, including the SET domain (Fig. 2C; Table 1). About 38% of protein sequences of StSET genes (22 genes) contained only the SET domain, while the remaining genes contained diverse combinations of multiple protein domains along with the SET domain. For example, about 17% of protein sequences of StSET genes contained the combination of the SET, Pre_SET, and SAD_SRA protein domains, while one contained a combination of eight protein domains, such as SET, PWWP, FYRN, FYRC, PHD, PHD_2, zf-HC5HC2H_2, and zf-HC5HC2H (Table 2).
The gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis identified significantly enriched GO terms (p < 0.05) involved in various biological processes (56 GO terms), molecular functions (57 GO terms), and cellular components (55 GO terms). For example, 100% and about 82.5% of StSET genes were predicted to be involved in catalytic activity and response to stimulus, respectively (Figure S2; Table S3).
We predicted for approximately 93% of StSET genes a localisation in the nucleus, while for the others a localisation in the mitochondria (StSET1) or the chloroplast (StSET8 and StSET41) (Table S1) was predicted. Three genes (StSET28, StSET45, and StSET53) were predicted to have transmembrane helices (Table S1).
Identification of duplicated StSET genes
We found four tandemly duplicated gene (TDG) clusters in StSET genes with cluster sizes from 2—5 genes. The TDG clusters contained about 23% of StSET genes. We found two TDG clusters with StSET genes on chromosome 3, while one was on chromosomes 7 and 8 (Fig. 1). We estimated the non-synonymous (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitution ratios (Ka/Ks) for each pair of tandemly duplicated StSET genes, and the ratios ranged from 0.39—0.99.
Phylogenetic analysis of StSET genes
We estimated a phylogenetic tree that clustered all StSET genes into six clades denoted as C1—C6 (Fig. 2A). The largest clades, C1 and C2, contained an equal number of StSET genes (14 genes in each clade), while the smallest clade (C6) contained four StSET genes. Further, we estimated a phylogenetic tree for SET domain-containing genes from Solanum tuberosum, Solanum lycopersicum, Oryza sativa, and Arabidopsis thaliana, and this phylogenetic tree also clustered all the genes into six clades denoted as C1—C6 (Fig. 3).
Phylogeny of SET domain-containing genes of potato and Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum, and Oryza sativa. We visualised the computed phylogenetic trees using iTol [35]
Identification of cis-elements and conserved motifs
We identified 41 unique cis-elements in the non-overlap** 1 Kb region upstream (potential promoter sequence) to the transcription start site of StSET genes (Table 3; Table S4). Among these, we identified several cis-elements described previously in the context of various environmental factors. For example, the promoter sequences of 53 StSET genes contained cis-elements described previously in the context of light-responsiveness. In addition, we found several drought-responsive, abscisic acid-, salicylic acid-, methyl jasmone acid- and auxin-responsive elements (Fig. 4). In addition, we identified 20 conserved motifs with a length range of 28—100 nucleotides within the potential promoter sequences of StSET genes (Table S5). Motifs 7 and 2 were conserved in 44 and 32 StSET genes, respectively, while motifs 1, 8, and 15 were conserved in two StSET genes (Table S5).
The cis-elements (CAREs) with a frequency > = 3, detected within a 1 kb region upstream of the transcription start site. The yellow color bars indicate the number of genes in which respective cis-element is identified. The magenta color bars indicate the sum of respective cis-elements. We identified cis-elements within the promoter sequences using the PlantCARE database with a frequency cut-off of three for each cis-element [36]
Tissue-specific expression of StSET genes
We investigated the expression patterns of all the identified StSET genes in 15 tissues, namely pollen, style, flower, fruit, leaf, petiole, stem, shoot, root, stolon, tuber, tuber meristem, tuber periderm, tuber flesh, and tuber sprout using the expression data retrieved from the StCoExpNet database [37]. A detectable expression, i.e., an average transcript per million (TPM) > 1 across samples of respective tissues, was observed in at least one tissue for 47 out of 57 StSET genes (Fig. 5). In addition, we found that about 84% of the StSET genes were assigned to 27 different co-expression clusters. We observed variation in expression between members of a phylogenetic clade and across phylogenetic clades (Figure S3). We found that seven of 13 tandemly duplicated StSET genes were expressed at least in one tissue. Moreover, three StSET genes belonging to TDG3, StSET37, StSET38, and StSET40, showed tissue-specific expression in pollen with an average Tau index of 0.9928 (Fig. 5; Table S6). In contrast, the remaining two genes, StSET36 and StSET39, revealed a low expression across tissues but showed slightly increased expression in flower and pollen, respectively. Two genes of TDG4, StSET44 and StSET45, were expressed in all tissues except pollen (Fig. 5; Table S6).
Global expression patterns of StSET genes in fifteen different tissues. Three genes, such as StSET37, StSET38, and StSET40, showed tissue-specific expression in pollen with an average Tau index of 0.9928. The expression values are log-transformed transcripts per million (TPM). The TPM values are retrieved from StCoExpNet [37]. Clades indicate the phylogenetic clades present in Fig. 2A. Tandemly duplicated StSET genes are labelled with corresponding cluster names (TDG3 & TDG4)
Expression profiling of StSET genes in response to abiotic stress conditions
We investigated the relative expression of four StSET genes (StSET13, StSET30, StSET48 and StSET52) in three different potato genotypes: Karlena (drought-tolerant), Kolibri (drought-tolerant), and Laura (drought-sensitive and heat-tolerant), under drought and heat stress. We examined two-time points—9 days (T3) and 18 days (T6) in stress—plus four days after recovery (T7) for expression analysis.
The RT-qPCR results showed a change in expression for all four genes under heat and drought stress in a genotype dependent manner. Compared to the control conditions the relative expression of all four genes increased 9 days after heat stress. Under prolonged exposure to heat stress (18 days), the relative expression of the investigated genes went down in Laura (heat tolerant) while the reverse was true for Karlena and Kolibri (heat sensitive) (Fig. 6). Compared to the control conditions, the relative expression of all StSET genes decreased under extreme drought stress (18 days after stress, 2.8% VMC). The relative expression of either gene increased (StSET13, StSET52) or remained at similar levels (StSET30 and StSET48) compared to control conditions in drought tolerant cultivars. The relative expression all four genes was comparable with those in control conditions after stress release in all cultivars (Fig. 6).
Expression profiling of StSET genes in response to abiotic stress treatments. Relative gene expression of four StSET genes analysed by RT-qPCR in response to drought and heat stress conditions in three potato clones. Karlena and Kolibri are drought-tolerant genotypes. Laura is drought-sensitive and heat-tolerant. The bar represents mean ± standard error (n = 3). T3 and T6 indicate that the RNA was sampled on the 9th and 18th day of respective stress conditions, while T7 indicates that the RNA was sampled on the fourth day after the recovery phase. The control T3 indicates that the RNA was sampled on the ninth day from the control plants
Comparative analysis of SET domain-containing genes
To derive orthologous relationships of StSET genes, a comparative map** approach was followed wherein we compared the physically mapped SET domain-containing genes of potato with those of nine other species, namely Arabidopsis thaliana, Camellia sinensis, Gossypium raimondii, Malus domestica, Oryza sativa, Populus trichocarpa, Setaria italica, Solanum lycopersicum, and Triticum aestivum. In this study, we defined the orthologous SET domain-containing genes between potato and the species mentioned earlier based on the following criteria: If the SET domain-containing genes of the other nine species showed at least 50% of sequence identity and query coverage against StSET in BLASTP search, they were considered orthologs to StSETs. Based on these criteria, we observed a considerable variation in the number of orthologous SET domain-containing genes between potato and the species mentioned earlier (Table S7). For example, Solanum lycopersicum contained the highest number (about 79%) of orthologous SET domain-containing genes with potatoes. In contrast, Oryza sativa contained the lowest number (about 37%) of orthologous SET domain-containing genes with potatoes (Table S7; Fig. 7).
A comparative physical map of orthologous SET-domain containing genes among potato and other plant species visualised using CIRCOS v0.69–8 [38]. The comparative physical map between A) Potato and Solanum lycopersicum, and B) Potato and Oryza sativa
We observed the presence and absence of protein domains in SET domain-containing genes between potato and three other species (Table 1). For example, the protein domain, TDBD (PFAM ID: PF16135), was identified only in potato. In contrast, the protein domain, GYF_2 (PFAM ID: PF14237), was not detected in potato. Further, we observed the presence and absence of a unique combination of protein domains in SET domain-containing genes between potatoes and three other species (Table 2). For example, the protein domain combination, SET, Pre-SET, SAD_SRA, and Iso_dh, was only identified in potato, while the protein domain combination, SET, SAD_SRA, was absent in potato.