Abstract
Background
Although mitochondrial (mt) gene order is highly conserved among vertebrates, widespread gene rearrangements occur in anurans, especially in neobatrachians. Protein coding genes in the mitogenome experience adaptive or purifying selection, yet the role that selection plays on genomic reorganization remains unclear. We sequence the mitogenomes of three species of Glandirana and hot spots of gene rearrangements of 20 frog species to investigate the diversity of mitogenomic reorganization in the Neobatrachia. By combing these data with other mitogenomes in GenBank, we evaluate if selective pressures or functional constraints act on mitogenomic reorganization in the Neobatrachia. We also look for correlations between tRNA positions and codon usage.
Results
Gene organization in Glandirana was typical of neobatrachian mitogenomes except for the presence of pseudogene trnS (AGY). Surveyed ranids largely exhibited gene arrangements typical of neobatrachian mtDNA although some gene rearrangements occurred. The correlation between codon usage and tRNA positions in neobatrachians was weak, and did not increase after identifying recurrent rearrangements as revealed by basal neobatrachians. Codon usage and tRNA positions were not significantly correlated when considering tRNA gene duplications or losses. Change in number of tRNA gene copies, which was driven by genomic reorganization, did not influence codon usage bias. Nucleotide substitution rates and dN/dS ratios were higher in neobatrachian mitogenomes than in archaeobatrachians, but the rates of mitogenomic reorganization and mt nucleotide diversity were not significantly correlated.
Conclusions
No evidence suggests that adaptive selection drove the reorganization of neobatrachian mitogenomes. In contrast, protein-coding genes that function in metabolism showed evidence for purifying selection, and some functional constraints appear to act on the organization of rRNA and tRNA genes. As important nonadaptive forces, genetic drift and mutation pressure may drive the fixation and evolution of mitogenomic reorganizations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Organization of metazoan mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) is usually conserved [1]. Notwithstanding, many cases of genome reorganization (e.g., rearrangement, duplication and loss) occur in closely related animals [2–4]. Typically, the mitogenome of metazoans encodes 13 protein-coding genes along with 2 rRNAs and 22 tRNAs. The 13 protein-coding genes, all of which play vital roles in the respiration chain, producing 95% of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) required for cellular energy through oxidative phosphorylation [5]. The function of these proteins results in the distribution of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) diversity being far from random [6]. Evidence for adaptive evolution of mtDNA genes exists in some vertebrate lineages, such as mammals and reptiles [7–9].
Many studies have indicated that protein-coding genes of the mitogenome experienced adaptive or purifying selection, yet the role that selective pressure plays on reorganization of the mitogenome is subject to debate. On the one hand, mitogenomic organization may evolve neutrally [10]. Dowton et al. [2] characterized 67 gene arrangements in the Hymenoptera and suggested that tRNAs occupy selectively neutral positions. Furthermore, Boussau et al. [11] proposed that mitogenomic structural evolution (i.e., gene duplication) was influenced by population size. The genomic duplication is more likely to occur in lineages where the efficiency of selection had been reduced and the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous substitution (dN/dS) increased. These findings indicate that mitogenomic reorganization accompanies lower or relaxed selection, and that fixation of the structural alteration is nonadaptive [11, 12]. On the other hand, positive selection could also act on gene order in the mitogenome. The location of highly transcribed RNAs (such as 12S and 16S rRNA) is adjacent to transcriptional regulatory elements in the control region (CR) [13]. Significant correlations between codon usage and tRNA positions in vertebrate mt genomes (e.g., [14]), suggest that frequently transcribed tRNA genes, such as hydrophobic residues, also occur close to the CR due to functional efficiency. Loss of a duplicated gene may not occur randomly, but rather retention may depend on the distribution of the copies [15]. Thus, changes in tRNA gene positions could owe to adaptive selection [14].
Variation in number of tRNA genes may influence codon usage bias in mitogenomes. Genome reorganization of mtDNA has been linked to variation in the number of tRNA genes [16]. Translational selection may drive the coevolution of tRNA genes and codon usage [17]. Positive correlations between tRNA abundance and codon usage bias have been observed in some unicellular (e.g., Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and multicellular (e.g., Caenorhabditis elegans) eukaryotic genomes [18, 19]. In mitochondria, oxidative phosphorylation often requires a few cytosolic tRNAs encoded by nuclear DNA [20], and these imported tRNAs could compensate for changes in the number of mt tRNA genes. Consequently, the influence asserted by changes in the number of tRNA genes and the role played by selection on mitogenome rearrangements remains elusive [21]. An understanding of selective constraints on mitogenomic reorganization might provide some clarity on the mechanisms that underlie mitogenome evolution. Unfortunately, little is known about how gene duplications, losses, and rearrangements of tRNA genes influence codon usage of mt genes due to the paucity of examples of mitogenomic reorganization within closely related species. Among vertebrates, anurans (especially neobatrachians) facilitate revealing the relationship between tRNA genes positions and codon usage due to the high levels of gene rearrangements [22–24]. The variation also allows for explorations into how variation in tRNA gene copy number influences codon usage bias.
Most mitogenomes of non-neobatrachians (e.g., Archaeobatrachia) have the vertebrate ancestral gene order (AGO) [25, 26]; Leiopelma archeyi and Leptolalax pelodytoides are exceptions [24, 27]. In contrast, rearranged gene orders (RGO) characterize neobatrachians [28, 29], which share LTPF clusters (trnL-trnT-trnP-trnF) resulted from rearrangements of four typical vertebrate tRNA genes [29–31]. Further, recurrent gene rearrangements involve duplications and/or losses of CR and tRNA genes [3, 32–35]. These findings contrast with the proposition that vertebrates possess highly conserved mitogenomic organizations [1, 36].
Accelerated mt substitution rates in protein-coding genes occur in neobatrachians. Such could be a consequence of relaxed purifying selection in the ancestor of neobatrachians [23, 37]. However, highly rearranged mt genomes and high rates of nucleotide substitution are not significantly correlated [23, 37]. Studies on the correlation between tRNA gene rearrangements and codon usage could provide new insights into the role played by selection on mitogenomic reorganization.
Herein, we sequence the mt genome of three congeneric species of Glandirana and three hotspots of gene rearrangements across 20 species in the Ranoides. We supplement these data with sequences from GenBank to examine the relationship between tRNA gene arrangements and codon usage in anurans. Our results suggest selection does not favor any specific rearrangement of gene position. Further, tRNA gene duplications or losses do not appear to influence codon usage bias. Our findings shed light on the non-adaptive evolution of mitogenomic reorganization, at least in neobatrachians.
Results and discussion
trnS (AGY) pseudogene of Glandiranaand gene rearrangement in Ranidae
We failed to sequence the complete mt genome of Glandirana rugosa, G. emeljanovi, and G. tientaiensis (Table 1, [GenBank: KF771341–KF771343]) due to long, highly repetitive nucleotides in the CRs. All three mtDNA genomes contained 13 protein-coding genes, two rRNA genes, 21 tRNA genes [Ψ trnS (AGY)], and non-coding regions (Additional file 1). The mt genomes of Glandirana were arranged identically to those typical of other neobatrachians, except for the presence of trnS (AGY) pseudogenes (Additional files 1, 2). Coding genes were similar in length to their counterparts in other anurans. Differences in mtDNA genome size and organization of Glandirana owed to the size of repeat-sequences in the CR (Additional file 1).
We re-designed a pair of PCR primers that were conserved in Glandirana (data not shown) to amplify this region [GenBank: KF771278–KF771280] for confirming the presence of trnS (AGY) pseudogenes. All three mitogenomes in Glandirana included 62–63 bp of a non-coding sequence downstream of trnH in the typical location of trnS (AGY). The primary sequence of trnS (AGY) in Glandirana was very similar to those in the other frogs (Figure 1), though anticodons differed from the typical canonical sequence GCT and among the three species (CCC in G. rugosa; CTA in G. emeljanovi; and TCA in G. tientaiensis). With the exception of the original position of trnS (AGY), homologous fragments were not found. As previously reported in G. rugosa [22], pseudogene trnS (AGY) occurred in all of our Glandirana. This occurrence constituted a synapomorphy for the three species.
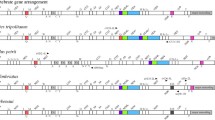
Our study identified gene rearrangements in three ranid hotspot fragments (Table 1). The typical gene order of the trnW–trnY block was trnW, trnA, trnN, origin of light strand replication (OL), trnC, and trnY (WANCY). In some species of Amolops and Odorrana, three gene rearrangements differed from the consensus order across vertebrates. The tandem duplication–random loss (TDRL) model provided a plausible mechanism for these rearrangements [38, 39]. The hypothesized duplicated region in the mitogenome of Amolops chunganensis, A. granulosus, A. kangtingensis, A. loloensis, and A. mantzorum included a partial fragment of trnA, all of trnN and OL, and a partial fragment of trnC (Figure 2a). The inferred duplications in the mitogenome of Odorrana schmackeri included all of trnN, OL, trnC, trnY, and partial cox1 (~264 bp) (Figure 2b). The hypothesized duplicated region in the mtDNA of O. versabilis included a partial fragment of trnA, and all of trnN (Figure 2c). In the WANCY fragments, gene rearrangements were detected for O. schmackeri, O. versabilis and the five species of Amolops, but differences in the duplicated fragments and the position of the pseudogenes or superfluous gene copies suggested these features originated separately (Figure 2). The WANCY region was reported to be a hotspot for gene order rearrangement in amphibians [39, 40], and our discovery was consistent with these findings.
Putative mechanism of gene rearrangement of the mitochondrial sequences according to a model of tandem duplication of gene regions and subsequent gene deletions. WANCY gene rearrangement in (a) Amolops chunganensis, A. granulosus, A. kangtingensis, A. loloensis, and A. mantzorum, (b) Odorrana schmackeri, and (c) O. versabilis.
All analyzed species of Odorrana shared a translocation of trnH, which moved to CR from between nad4 and trnS (AGY). This result was consistent with the previous observations [22, 32]. The original trnH in Babina pleuraden also become a pseudogenes. Owing to shared patterns, Kakehashi et al. [41] proposed that the trnH–trnE block was duplicated in the ancestral lineage of Babina and Odorrana. However, Babina okinavana, B. holsti, and B. subaspera have functional trnH genes in the ancestral position [41]. These results suggest that random losses the duplications may drive the differences in gene order in closely-related species.
An inter-genic spacer occurs between nad5 and nad6 in Babina adenopleura and Odorrana schmackeri at lengths of 457 bp and 306 bp, respectively. We cannot identify the noncoding sequences and no evidence suggests they were homologous fragments. This evidence indicates independent origins.
Genomic features and phylogenetic relationship
The final concatenated alignment of our mtDNA dataset for 50 species contained 10836 nucleotide positions, including 7361 variable sites of which 6746 were potentially parsimony-informative. Maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) methods of phylogenetic reconstruction obtained in the same tree topologies for 13 mt protein-coding genes. The trees differed only in branch lengths (Figure 3). Monophyly of the Neobatrachia was supported by our work and previous studies [42, 43], while the Archaeobatrachia was paraphyletic [44, 45]. The major clades of frogs (Figure 3) were consistent in recent morphological and molecular analyses [46–48].
A maximum likelihood phylogeny of the derived from 13 coding protein of mtDNA sequences for Anura. Bayesian inference obtained the same topology. Numbers above the lines or beside the nodes were rapid bootstrap proportions calculated with 1000 replicates and Bayesian posterior probabilities, respectively. The branch lengths are to scale. Mt genomic features that are useful markers for inferring relationships, and genomic features of each species are labeled on tree as follows: (A) LTPF cluster; (B) trnS (AGY) pseudogene; (C) translocation of trnH; (D) translocation of nad5; (E) LTPF changed into TLPF cluster; (F) duplication of CR and trnM; (G) duplication of trnM; (H) translocation of trnE and loss one copy of trnM; (I) trnA, trnN, trnC and trnE gene loss; (J) trnQ, trnA, trnN, trnC, trnY, and trnP gene loss; (K) translocation of nad5; (L) translocation of trnP; (M) translocation of trnL(CUN); (N) WANCY changed into WACYN; (O) translocation of nad5, trnE, and trnP.
The aligned ranid data contained 1322 nucleotide positions. Of these sites, 677 were variable and 535 were potentially parsimony-informative. Figure 4 depicted the phylogeny of ranids based on 12S and 16S rRNA. ML and BI analyses produced identical trees. All neobatrachian families (Ranidae, Dicroglossidae, Rhacophoridae, Mantellidae, and Microhylidae) formed a clade and monophyly of each ranid genus was well supported. Within the Ranidae, our analyses recovered a sister taxa relationship between Rana + Lithobates and Odorrana + Babina (Figure 4), which was consistent previous studies [48]. However, the phylogenetic relationships among Amolops, Glandirana, Pelophylax, and Hylarana conflicted with other hypotheses [42, 49, 50]. Our results located Glandirana as the sister taxon of Amolops, but with weak Bayesian support (BPP = 80). Analyses of the mt protein-coding genes and the 12S and 16S rRNA (Figures 3, 4) did not support monophyly of section Pelophylax (including the subgenera Pelophylax and Rugosa [Glandirana]) as proposed by Dubois [51]. This corresponded to the previous view that Pelophylax was polyphyletic [50].
A strict consensus tree from the Bayesian inference analyses derived from the sequences of the genes 12S and 16S rRNA for Ranidae. Numbers above the lines or beside the nodes were Bayesian posterior probabilities. The mt genomic features of each species on the tree are as follows: (A) translocation of trnH; (B) trnE transposition and CR-psH-S1-nad5; (C) WANCY rearrangement; (D) transposition of trnG-nad3 block and duplication of CR; (E) trnS (AGY) pseudogene; (F) translocation of trnC.
We mapped genomic features of neobatrachian mtDNA on the phylogeny (Figures 3, 4) to provide additional data for inferring history. Generally, gene rearrangements have been considered to be relatively rare, random events and, thus, they constituted useful synapomorphies [52–54]. Four tRNA genes, trnL (CUN), trnT, trnP, and trnF, were rearranged to form the LTPF cluster (labeled “A” in Figure 3), which was a synapomorphy for the Neobatrachia. Descendants shared unique gene rearrangements in ancestral lineages and/or additional rearrangements. For example, all the descendants of Dicroglossidae shared the trnM duplication [28, 33, 47, 55] (Figure 3). The Rhacophoridae and Mantellinae shared the translocation of nad5 [56, 57] (Figure 3). Finally, the five species of Amolops formed a clade and all species shared the same WANCY gene rearrangement (Figure 4).
Gene rearrangements comprised distinct genomic characters for some genera (Figures 3, 4). For example, Glandirana was associated with genomic features derived from the pseudogene trnS (AGY), Odorrana was associated with structural trnH translocations, and Pelophylax retained the ancestral condition of typical LTPF. The derived features of the mitogenomes could serve as useful indicators of phylogenetic relationships, especially in lineages gene sequence data often lead to ambiguous results [42, 48]. Duplication of the trnH–trnE block supports the sister relationship of Babina and Odorrana [41] (Figure 4). Duplication of trnM also supports the rooting of Occidozyga martensii as the sister group of Dicroglossidae (Figure 3).
In highly rearranged lineages, convergent and parallel gene rearrangements happened frequently in non-sister lineages. Thus, genomic features require careful consideration when being employed for phylogenetic inference. Gene rearrangements vary in their phylogenetic distributions and rates among lineages [4]. In neobatrachians, convergent gene rearrangements occur. For example, a single origin cannot be invoked to explain the distribution of trnM in both Mantellinae and Dicroglossidae; the duplications arose independently (Figure 3) and the positions and residues of duplicated fragments differ [3, 28, 35]. A similar pattern involving the translocation of nad5 was observed in the Rhacophoridae and Fejervarya [33, 56]. Parallel rearrangements also occur in gene rearrangement hotspots (e.g., WANCY and CR) [3].
Correlation between codon usage and tRNA gene position
There are no significant correlations between codon usage and the location of tRNA in most of the AGOs, and no increased correlations in recurrent rearranged neobatrachians compared to basal neobatrachians (Additional file 3). Among the analyzed species, 14 have the AGOs of other vertebrates and 30 RGOs occur in Leiopelma archeyi and the neobatrachians (Additional file 2). Codon usage and tRNA position in the AGOs are very weakly correlated (Figure 5a; Pearson’s correlation coefficient r = -0.005, two-tailed p = 0.93, n = 308; Spearman’s rho correlation coefficient r = -0.118, two-tailed p = 0.039, n = 308). In contrast, the two variables show a significant correlation in neobatrachian RGOs (Figure 5b; Pearson’s correlation r = -0.551, two-tailed p < 0.001, n = 625; Spearman’s rho coefficient nonparametric correlation coefficient r = -0.607, two-tailed p < 0.001, n = 625). However, codon usage and tRNA positions are not significantly correlated in L. archeyi, which is an archaeobatrachian with an independent RGO (Figure 5c; Pearson’s correlation coefficient r = 0.001, two-tailed p = 0.998, n = 22; Spearman’s rho correlation coefficient r = -0.06, two-tailed p = 0.789, n = 22). Correlations between codon usage and tRNA do not increase in neobatrachians upon adding rearrangements relative to basal neobatrachians (Additional file 3). As seen in Glandirana and Limnonectes bannaensis, the loss of tRNA genes does not effect this correlation.
A linear regression plot between position of tRNA genes and usage of the corresponding codon. (a) 15 species with evolutionarily stable gene order; (b) 28 slightly rearranged gene orders in neobatrachians; (c) Leiopelma archeyi. Data points for the tRNA genes that specify hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids are colored magenta and green, respectively. The regression lines were derived from the all data points in each plot.
Codon usages and tRNA positions were thought to be significantly correlated in typical vertebrates [14]. The tRNA genes of these amino acids occur near the CR where transcription efficiency is high [13]. In mitogenomes, the 13 protein-coding genes associate with transmembrane proteins that are rich in hydrophobic amino acid residues. The tRNA genes that specify hydrophobic amino acid locate much closer to the CR than do hydrophilic amino acids. Consequently, some form(s) of adaptive selection might maintain novel mt gene orders and the rearrangement of genes with higher codon usage to regions near the CR to enhance transcription efficiency [14]. However, our analyses fail to detect a significant correlation in many archaeobatrachians possessing AGOs as well as in Leiopelma archeyi (Additional file 3). In comparison, significant correlations occur between codon usage and position of tRNAs in all neobatrachians sharing rearrangement LTPF. However, this does not infer a recent adaptation in the lineages with RGOs. Although rearrangement LTPF dramatically improves correlations, all other recurrent rearrangements do not do so. These recurrent rearrangements marginally or insignificantly improve correlations in neobatrachians (Additional file 3). Thus, highly-used tRNA genes in recent, re-appearing RGOs do not appear to be located closer to the CR than typical RGOs.
Codon usage bias and tRNA gene number
Analyses of the relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) in 14 anurans mitochondrial genomes yield insights into the relationship between changes in the number of tRNA genes (e.g., duplication/loss) and codon usage bias. The results did not indicate a difference in codon usage bias in duplicated or lost tRNA genes (Additional file 4). Gene trnM was duplicated in Dicroglossidae and Mantella madagascariensis yet their codon usage does not differ from those of other anurans (Chi-square test, p >0.05). Three species of Glandirana that lost trnS (AGY) did not differ in codon usage from closely related species (p >0.05). The same situation occurs in Limnonectes bannaensis in which tRNAs trnA, trnN, trnC, and trnE are absent [34].
The change in tRNA copy numbers could have accompanied gene rearrangement, as explained by the tandem duplication-random loss (TDRS) model [39, 58]. Directional mutation pressure on each strand of DNA and translational selection are major factors in codon usage bias [59]. Codon usage and tRNA abundance are tightly correlated in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae [19]. This implies that tRNA gene copy numbers can evolve to match codon usage. Under translational selection, codon usage and tRNA gene content may have evolved to alternative stable states, where selection favors codons that are most rapidly translated by the current tRNAs [17]. However, tRNA gene duplications and losses do not show significant changes in codon bias among closely related anurans. The long period of accumulating mutations and the compactness of mtDNA might preclude such changes. The importation of nuclear tRNAs may also explain the absence of a correlation. Protein synthesis requires the replacement of tRNAs. In most organisms, mitochondrial biogenesis requires the importation of both large number of proteins and at least a few cytosolic tRNAs [20, 60]. Cytosolic tRNAs replace lost mt tRNA as well as reduce the influence of mt tRNA gene duplications or rearrangements. This alone may explain the absence of correlation between tRNA position and codon usage. Even though the importation of cytosolic tRNAs may compensate for missing mt tRNA genes, most vertebrates have a complete set of mt tRNA genes [20, 61]. The tRNA genes absent in Glandirana also occur rarely in other vertebrates, though they have been found in the wallaroo (Macropus robustus) [62], Chinese big-headed turtle Platysternon megacephalum [63] and large-headed frog Limnonectes bannaensis [34].
Nucleotide substitution and mitogenomic reorganization
Neobatrachian mt genomes have higher nucleotide substitution rates than archaeobatrachians [23, 37, 64]. To check the differences in the rates of nucleotide divergence in neobatrachians, we calculated average synonymous (dS) and nonsynonymous (dN) substitutions using a maximum likelihood tree for each of the 13 mitochondrial protein-coding genes as well as six congeneric pairwise comparisons among our anurans. Congeneric comparisons comprised two AGOs (Bombina maxima and B. bombina; and Xenopus laevis, and X. tropicalis) and four RGOs (Glandirana emeljanovi and G. rugosa; Limnonectes fujianensis and L. bannaensis; Pelophylax nigromaculata and P. chosenica; and Bufo japonicas, and B. gargarizans) (Figure 6). All neobatrachian mitochondrial genes have a significantly elevated dN (p < 0.01) and dS (p < 0.01).
Six pairwise comparison of sequence divergence for each mitochondrial gene. Species-pairs are as follows: Bombina maxima and B. bombina; Xenopus laevis and X. tropicalis; Glandirana emeljanovi and G. rugosa; Limnonectes fujianensis and L. bannaensis; Pelophylax nigromaculata and P. chosenica; and Bufo japonicas and B. gargarizans.
Nonsynonymous/synonymous substitution rates (dN/dS = ω) for each gene can test whether or not mitogenomic reorganization associates with an overall relaxation of selective pressures on mt function. In all comparisons, dN/dS differs significantly from a null ratio of 1 (Figure 6; range 0.000–0.245). The mean dN/dS does not differ significantly between the AGOs and RGOs (p >0.05). ML estimates of ω indicate that purifying selection acts on each protein-coding gene; no significant difference (p >0.05) occurs in the fitting of models M1a (nearly neutral) and M2a (positive selection) (Additional file 5). Estimates of ω under the two-ratio model for the Anura are not higher than its null model and only cob differs significantly by LRT (Table 2, Additional file 5). Values of ω are significantly less than 1 for all 13 protein-coding genes in the AGO and RGOs (Figure 6, Table 2). This result supports the presence of strong purifying selection in anurans [23, 37], which strongly preserves mt gene function [65, 66]. However, ratios of ω for all genes, except cob, nad3, nad4L, and nad6, are significantly higher in neobatrachians when compared to non-neobatrachians (Table 2). Similarly, independent values of ω inferred for the stem branch of Natatanura are generally higher than the respective null model and evaluations of most individual genes obtain significant results (Table 2, Additional file 5). Corresponding to previous studies [37], the elevated ω in the branch leading to the Neobatrachia indicates the possible relaxation of purifying selection on protein-coding genes (Table 2).
A positive correlation occurs between the rates of mt gene rearrangement and mt nucleotide diversity in some lineages of invertebrates [21, 67, 68]. Accordingly, Shao et al. [67] hypothesized that an increase in substitution rates can drive elevated rates of gene rearrangement. A high substitution rate leads to an increase in mutation at the sites of initiation and termination of the mt genome replication. These mutations may cause errors during replication of mt genomes and then cause gene rearrangements through gene duplications and deletions [15, 38]. Considering the TDRL model, a high rate of nucleotide substitution leads to an increase in the rate of mt gene rearrangement. High rates of nucleotide substitution also tend to occur in modified genomes of salamanders [69]. However, fast nucleotide substitution rates are not required to increase the propensity of mitogenomic rearrangements [23, 37]. Our results show that neobatrachian mt genes have a significantly elevated dN (p < 0.01) and dS (p < 0.01). Irisarri et al. [23] proposed that an accelerated rate of mt substitution rate was a result of the relaxation of purifying selection on protein-coding genes. In neobatrachians, some clades, such as Rhacophoridae, Mantellinae, and Dicroglossidae (Figure 3), have an increase in the rate of mt gene rearrangement. However, no significant difference in substitution rate occurs between non-rearranged and rearranged ranoids [37]. Thus, the high diversity of recurrent rearrangements in neobatrachians appears to be driven by variables beyond a high rate of nucleotide substitution, for example, life histories and genetic drift—both of which may increase the chance that rearranged mt genomes survive and drive fixation [67]. Considering rearrangements in the archaeobatrachians Leiopelma archeyi and Leptolalax pelodytoides [24, 27], accelerated substitution rates may be lineage-specific features, rather than accompanying gene rearrangement. No differences in rate of change occur between lineages with gene duplications and their non-duplicated counterparts [37]. Our results also failed to detect significant differences in rates when tRNA genes are lost (e.g., Glandirana branch, LRT p >0.05). Overall, these results indicate that high substitution rates and the relaxation of purifying selection can increase the chance of mitogenomic reorganization in neobatrachians, but they are not required.
Selective pressure on mitogenomic reorganization
Selection on reorganized mitogenomes is less well studied compared to selection on mt protein-coding genes [2, 14]. Although a positive correlation might occur between codon usage and tRNA gene positions [14], genomic reorganization does not improve this relationship. Adaptive selection does not appear to act on tRNA gene positions after genomic rearrangement. Further, the widespread importation of cytosolic tRNA into mitochondria [20] may preclude a codon usage bias owing to tRNA gene duplications or losses. The nonadaptive evolution of gene order suggests that random loss follows gene duplication. Hotspots of gene rearrangement (eg. WANCY) in Amolops and Odorrana (Figure 3) have similar portions of duplicated genes yet the positions of silenced genes vary. These findings support the TDRL model of rearrangement in many neobatrachians [22, 29, 56].
Nucleotide substitution rates and ω are higher in neobatrachian mt genomes than in archaeobatrachians and yet no significant correlation exists between the rates of mitogenomic reorganization and mt nucleotide diversity [23, 37]. Values of ω strongly indicate that purifying selection likely contributes to the maintenance of metabolic function in anurans and trans-membrane protein functions likely constrain nonsynonymous mutations [23]. Some functional constraints on the mitogenomic organization of rRNA and tRNA genes exist (e.g., 12S and 16S rRNAs generally locate near the CR due to requiring high transcriptional rates [13]; secondary structures of tRNA genes involve punctuation models or termination signals [70]). Functional constraints do not necessarily favor one gene rearrangement over another. The fixation of large-scale mitogenomic reorganization largely involves two nonadaptive fores: random genetic drift and mutation pressure [11, 71]. Further studies on the molecular and demographic mechanisms of this hypothesis may yield new insights into the evolution of mitogenomic reorganization.
Methods
We sequenced the mt genome of Glandirana rugosa, G. emeljanovi, and G. tientaiensis (Table 1). We also sequenced four mtDNA fragments including one conserved sequence [12S–16S rRNA] and three hotspots of rearrangements in 20 ranid species across the genera Amolops, Babina, Hylarana, Odorrana and Rana (Table 1). Specimens were stored in 95% ethanol at -20°C in the Chengdu Institute of Biology. All work with animals was conducted according to relevant national and international guidelines. All animal care and experimental procedures were approved by the Chengdu Institute of Biology Animal Care and Use Committee.
Total genomic DNA was extracted from muscle tissue through SDS-proteinase K/phenol-chloroform protocols [72]. Using complete mtDNA information available for Ranidae, we designed 13 pairs of primers (Additional file 6) that amplified overlap** fragments spanning the entire mt genome. From our 20 species, we determined three hotspot fragments (nad2–cox1, nad3–nad5, and nad5–cob) and partial fragments of 12S and 16S rRNA genes using primers described in Kurabayashi [73]. We amplified these fragments using a combination of normal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and long-and-accurate (LA) PCR methods; normal PCR was carried out in a 25 μL mixture containing 0.5–1.0 μL of template DNA, 2.5 μL 10 × PCR buffer, 0.5 μL of each primer (10 pm/μL), 2 μL MgCl2, 2 μL dNTPs and 0.3 μL of Extaq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa Bio, Dalian, China) with reaction conditions as follows: 4 min at 95°C, followed by 33 cycles of 40 s at 94°C, 45 s at 48–58°C, 1.5 min at 72°C and a final extension of 8 min at 72°C. LA-PCR was carried out in a 25 μL mixture containing 0.5–1.0 μL of template DNA, 12.5 μL 2 × PCR buffer, 0.5 μL of each primer (10 pm/μL), 4 μL dNTPs and 0.5 μL of KOD FX DNA polymerase (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). PCR conditions consisted of 3 min at 98°C, followed by 33 cycles of 50 s at 94°C, 60 s at 50–58°C, 4 min at 72°C and a final extension for 10 min at 72°C. We sub-cloned PCR fragments of the CR containing long tandem repeats using a pMD™ 18-T Vector (TaKaRa Bio, Dalian, China) and sequenced this fragment by additional walking primers (Additional file 6). DNA sequencing was performed on an ABI 3730 automatic DNA sequencer.
Genome annotation
We extracted protein-coding sequences from each mt genome and identified mt tRNA genes using tRNAscan-SE v.1.21 (http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE) [74]. We excluded incorrect annotations by comparing original annotations from GenBank with the vertebrate mt genetic code. We identified trnS (AGY) by visually inspecting unassigned regions for sequences with similarity and assigning them to previously identified mt tRNA isotypes. We determined the locations of the 13 protein-coding and 2 rRNA genes through comparisons with homologous sequences in other anurans [22, 29, 30].
We downloaded 40 complete and 3 partial anuran mt genomes from GenBank (Additional file 2). We used taxonomic names prior to Frost [75] to test their hypothesis and referred to NCBI Organelle Genome Resource and MitoZoa (http://www.caspur.it/mitozoa) [76] to determine genome organizations for each species (Additional file 2).
Measuring codon usage and the position of each tRNA gene
We chose 15 archaeobatrachian species plus 29 neobatrachian species to examine variation in codon usage and gene arrangement. We determined correlations between physical (base pair [bp]) distances of each tRNA gene from the CR (from the 5’ end of the tRNA gene to the 3’ end of the CR) and codon usage of the 13 protein-coding genes (where overlap** codons were considered once for each gene) following Satoh et al. [14]. For mt genomes with two CR or tRNA copies, we analyzed the first copy.
To evaluate the codon usage bias in a single codon family, we calculated relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values of every codon in each sample. RSCU values were obtained by using DAMBE [77] and MEGA5 [78]. We evaluated trnL and trnS codons, which had two groups of codons (CUN and UUR, and AGY and UCN, respectively), as two synonymous codon families [79].
Genetic divergence, molecular evolution and phylogenetics
We aligned sequences of the 13 mt protein-coding genes using ClustalW in MEGA5 [78]. To avoid artificial alignment errors, we used Gblocks v.0.19b [80] with the following settings to remove ambiguous alignments: 26 minimum conserved positions, 42 minimum flanking positions, 8 maximum non-conserved positions, and a minimum length of a block of 5 while allowing gap positions in half.
We used DnaSP 5.10 [81] to determine DNA polymorphism and divergence, including the number of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site (dS) and nonsynonymous substitutions per nonsynonymous site (dN). Maximum likelihood (ML) estimates of nonsynonymous/synonymous substitution rates (ω) were obtained with CODEML in the PAML4.4 package [82]. The nearly neutral (M1a) and positive selection (M2a) models were compared using a likelihood ratio test (LRT). To detect if the 13 protein-coding genes of neobatrachian species experienced divergent patterns of selection compared to non-neobatrachian species and other amphibians, we applied a two-ratio model test to the each-gene and all-gene datasets. Two separate two-ratio models were fitted: one ratio was assigned to the interested branch (Anura, Neobatrachia, Natatanura) and the other was assigned to the remaining lineages. These two-ratio models were also compared against the null model (one ratio model) by LRT.
To further confirm the phylogenetic relationships among anurans, 46 Anura and four outgroup taxa (two Caudata [GenBank: NC_008085, NC_004926] and two Gymnophiona [GenBank: NC_006301, NC_006302]) were included in this analyses. We constructed the phylogenies using the concatenated 13 mt protein-coding genes and partitioned these genes by codon position. The best fitted substitution model for each partition was estimated using Akaike information criterion (AIC) implemented in jModeltest [83]. The model of GTR + I + G was chosen for ML and Bayesian inference (BI) analyses, which were performed with RAxML BlackBox web-servers (http://phylobench.vital-it.ch/raxml-bb/index.php) [84] and MrBayes 3.1 [85], respectively. BI analyses used the following settings: 10 million Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) generations, a sampling frequency of 1000, and calculating a majority rule consensus tree after omitting the first 25% trees as burn-in.
To provide further insight into the phylogenetic relationships of species with gene rearrangments, we conducted additional ML and BI analyses using 12S and 16S rRNA sequence data from 65 taxa (58 ranids from nine genera, three dicroglossids, one rhacophorid, one mantellid, and two microhylids; Figure 4). Alignment of these sequences was verified using secondary structure [86]. We used the same procedures for tree reconstruction as described above for the 13 mt protein-coding genes.
Availability of supporting data
Organization and features of mitochondrial genome in three species of Glandirana are available in Additional file 1. Detailed information of 46 anurans mitochondrial genomes used in this study is given in Additional file 2. The correlations between the codon usage and tRNA positions of each 44 anuran species are available in Additional file 3. Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values in 13 protein-coding genes of anurans mitochondrial genomes are given in Additional file 4. Positive selection detection of the mt protein genes among different branches are presented in Additional file 5. Primers designed for amplifying the complete mitochondrial genome of Glandirana are listed in Additional file 6.
Abbreviations
- atp6:
-
ATP synthase subunit 6
- atp8:
-
ATP synthase subunit 8
- cob:
-
Cytochrome b
- cox1:
-
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I
- cox2:
-
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II
- cox3:
-
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III
- CSB:
-
Conserved sequence blocks
- CR:
-
Control regions
- ESGO:
-
Evolutionarily stable gene orders
- LTPF:
-
trnL (CUN), trnT, trnP, and trnF
- LRT:
-
Likelihood ratio test
- mt:
-
Mitochondrial
- nad1:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1
- nad2:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2
- nad3:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3
- nad4:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4
- nad4L:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 L
- nad5:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5
- nad6:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6
- OL:
-
The origin of light strand replication
- OH:
-
The origin of heavy strand replication
- RGO:
-
Rearranged gene orders
- TAS:
-
Termination associated sequence
- TDRL:
-
Tandem duplication and random loss
- WANCY:
-
trnW, trnA, trnN, OL, trnC, and trnY.
References
Boore JL: Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucl Acids Res. 1999, 27 (8): 1767-1780.
Dowton M, Cameron SL, Dowavic JI, Austin AD, Whiting MF: Characterization of 67 mitochondrial tRNA gene rearrangements in the hymenoptera suggests that mitochondrial tRNA gene position is selectively neutral. Mol Biol Evol. 2009, 26 (7): 1607-1617.
Kurabayashi A, Sumida M, Yonekawa H, Glaw F, Vences M, Hasegawa M: Phylogeny, recombination, and mechanisms of stepwise mitochondrial genome reorganization in mantellid frogs from Madagascar. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25 (5): 874-891.
Bernt M, Braband A, Schierwater B, Stadler PF: Genetic aspects of mitochondrial genome evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013, 69 (2): 328-338.
Das J: The role of mitochondrial respiration in physiological and evolutionary adaptation. Bioessays. 2006, 28 (9): 890-901.
Galtier N, Nabholz B, Glemin S, Hurst G: Mitochondrial DNA as a marker of molecular diversity: a reappraisal. Mol Ecol. 2009, 18 (22): 4541-4550.
Shen YY, Liang L, Zhu ZH, Zhou WP, Irwin DM, Zhang YP: Adaptive evolution of energy metabolism genes and the origin of flight in bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010, 107 (19): 8666-8671.
Castoe T, De Koning A, Kim H, Gu W, Noonan B, Naylor G, Jiang Z, Parkinson C, Pollock D: Evidence for an ancient adaptive episode of convergent molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009, 106 (22): 8986-8991.
Da Fonseca RR, Johnson WE, O'Brien SJ, Ramos MJ, Antunes A: The adaptive evolution of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. BMC Genomics. 2008, 9: 22-
Brown WM: The mitochondrial genome of animals. Molecular evolutionary genetics. Edited by: MacIntyre RJ. 1985, New York: Plenum Press, 95-130.
Boussau B, Brown JM, Fujita MK: Nonadaptive evolution of mitochondrial genome size. Evolution. 2011, 65 (9): 2706-2711.
Lynch M: The frailty of adaptive hypotheses for the origins of organismal complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007, 104 (Suppl 1): 8597-8604.
Christianson T, Clayton D: A tridecamer DNA sequence supports human mitochondrial RNA 3'-end formation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988, 8 (10): 4502-4509.
Satoh T, Sato Y, Masuyama N, Miya M, Nishida M: Transfer RNA gene arrangement and codon usage in vertebrate mitochondrial genomes: a new insight into gene order conservation. BMC Genomics. 2010, 11 (1): 479-
Lavrov DV, Boore JL, Brown WM: Complete mtDNA sequences of two millipedes suggest a new model for mitochondrial gene rearrangements: duplication and nonrandom loss. Mol Biol Evol. 2002, 19 (2): 163-169.
Gissi C, Iannelli F, Pesole G: Evolution of the mitochondrial genome of Metazoa as exemplified by comparison of congeneric species. Heredity. 2008, 101 (4): 301-320.
Higgs PG, Ran WQ: Coevolution of codon usage and tRNA genes leads to alternative stable states of biased codon usage. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25 (11): 2279-2291.
Duret L: tRNA gene number and codon usage in the C. elegans genome are co-adapted for optimal translation of highly expressed genes. Trends Genet. 2000, 16 (7): 287-289.
Rocha EPC: Codon usage bias from tRNA's point of view: redundancy, specialization, and efficient decoding for translation optimization. Genome Res. 2004, 14 (11): 2279-2286.
Schneider A: Mitochondrial tRNA import and its consequences for mitochondrial translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011, 80 (1): 1033-1053.
Xu W, Jameson D, Tang B, Higgs PG: The relationship between the rate of molecular evolution and the rate of genome rearrangement in animal mitochondrial genomes. J Mol Evol. 2006, 63 (3): 375-392.
Kurabayashi A, Yoshikawa N, Sato N, Hayashi Y, Oumi S, Fujii T, Sumida M: Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the endangered frog Odorrana ishikawae (family Ranidae) and unexpected diversity of mt gene arrangements in ranids. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2010, 56 (2): 543-553.
Irisarri I, Mauro DS, Abascal F, Ohler A, Vences M, Zardoya R: The origin of modern frogs (Neobatrachia) was accompanied by acceleration in mitochondrial and nuclear substitution rates. BMC Genomics. 2012, 13 (1): 626-
Zhang P, Liang D, Mao R-L, Hillis DM, Wake DB, Cannatella DC: Efficient sequencing of Anuran mtDNAs and a mitogenomic exploration of the phylogeny and evolution of frogs. Mol Biol Evol. 2013, 30 (8): 1899-1915.
Roe BA, Ma DP, Wilson RK, Wong JFH: The complete nucleotide sequence of the Xenopus laevis mitochondrial genome. J Biol Chem. 1985, 260 (17): 9759-9774.
Pabijan M, Spolsky C, Uzzell T, Szymura JM: Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in Bombina (Anura; Bombinatoridae). J Mol Evol. 2008, 67 (3): 246-256.
Irisarri I, San Mauro D, Green D, Zardoya R: The complete mitochondrial genome of the relict frog Leiopelma archeyi: insights into the root of the frog Tree of Life. Mitochondrial DNA. 2010, 21 (5): 173-182.
Alam M, Kurabayashi A, Hayashi Y, Sano N, Khan M, Fujii T, Sumida M: Complete mitochondrial genomes and novel gene rearrangements in two dicroglossid frogs, Hoplobatrachus tigerinus and Euphlyctis hexadactylus, from Bangladesh. Genes Genet Syst. 2010, 85 (3): 219-232.
Sumida M, Kanamori Y, Kaneda H, Kato Y, Nishioka M, Hasegawa M, Yonekawa H: Complete nucleotide sequence and gene rearrangement of the mitochondria genome of the Japanese pond frog Rana nigromaculata. Genes Genet Syst. 2001, 76 (5): 311-325.
Cao SY, Wu XB, Yan P, Hu YL, Su X, Jiang ZG: Complete nucleotide sequences and gene organization of mitochondrial genome of Bufo gargarizans. Mitochondrion. 2006, 6 (4): 186-193.
Igawa T, Kurabayashi A, Usuki C, Fujii T, Sumida M: Complete mitochondrial genomes of three neobatrachian anurans: a case study of divergence time estimation using different data and calibration settings. Gene. 2008, 407 (1–2): 116-129.
Su X, Wu XB, Yan P, Cao SY, Hu YL: Rearrangement of a mitochondrial tRNA gene of the concave-eared torrent frog, Amolops tormotus. Gene. 2007, 394 (1–2): 25-34.
Ren ZM, Zhu B, Ma EB, Wen J, Tu TY, Cao Y, Hasegawa M, Zhong Y: Complete nucleotide sequence and gene arrangement of the mitochondrial genome of the crab-eating frog Fejervarya cancrivora and evolutionary implications. Gene. 2009, 441 (1–2): 148-155.
Zhang JF, Nie LW, Wang Y, Hu LL: The complete mitochondrial genome of the large-headed frog, Limnonectes bannaensis (Amphibia: Anura), and a novel gene organization in the vertebrate mtDNA. Gene. 2009, 442 (1–2): 119-127.
Zhou Y, Zhang JY, Zheng RQ, Yu BG, Yang G: Complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization of the mitochondrial genome of Paa spinosa (Anura: Ranoidae). Gene. 2009, 447 (2): 86-96.
Shadel G, Clayton D: Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in vertebrates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997, 66 (1): 409-435.
Kurabayashi A, Sumida M: Afrobatrachian mitochondrial genomes: genome reorganization, gene rearrangement mechanisms, and evolutionary trends of duplicated and rearranged genes. BMC Genomics. 2013, 14 (1): 633-
Boore JL: The duplication/random loss model for gene rearrangement exemplified by mitochondrial genomes of deuterostome animals. Comparative Genomics. Edited by: Sankoff D, Nadeau J. 2000, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, Springer, 133-147.
San Mauro D, Gower DJ, Zardoya R, Wilkinson M: A hotspot of gene order rearrangement by tandem duplication and random loss in the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol Biol Evol. 2006, 23 (1): 227-234.
Mueller RL, Boore JL: Molecular mechanisms of extensive mitochondrial gene rearrangement in plethodontid salamanders. Mol Biol Evol. 2005, 22 (10): 2104-2112.
Kakehashi R, Kurabayashi A, Oumi S, Katsuren S, Hoso M, Sumida M: Mitochondrial genomes of Japanese Babina frogs (Ranidae, Anura): unique gene arrangements and the phylogenetic position of genus Babina. Genes Genet Syst. 2013, 88 (1): 59-67.
Frost DR, Grant T, Faivovich J, Bain RH, Haas A, Haddad CFB, De Sa RO, Channing A, Wilkinson M, Donnellan SC, Raxworthy CJ, Campbell JA, Blotto BL, Moler P, Drewes RC, Nussbaum RA, Lynch JD, Green DM, Wheeler WC: The amphibian tree of life. Bull Amer Mus Nat Hist. 2006, 297: 1-370.
Roelants K, Gower DJ, Wilkinson M, Loader SP, Biju SD, Guillaume K, Moriau L, Bossuyt F: Global patterns of diversification in the history of modern amphibians. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007, 104 (3): 887-892.
Roelants K, Bossuyt F: Archaeobatrachian paraphyly and pangaean diversification of crown-group frogs. Syst Biol. 2005, 54 (1): 111-126.
Gissi C, San Mauro D, Pesole G, Zardoya R: Mitochondrial phylogeny of Anura (Amphibia): a case study of congruent phylogenetic reconstruction using amino acid and nucleotide characters. Gene. 2006, 366 (2): 228-237.
Irisarri I, Vences M, San Mauro D, Glaw F, Zardoya R: Reversal to air-driven sound production revealed by a molecular phylogeny of tongueless frogs, family Pipidae. BMC Evol Biol. 2011, 11 (1): 114-
Chen G, Wang B, Liu J, **e F, Jiang J: Complete mitochondrial genome of Nanorana pleskei (Amphibia: Anura: Dicroglossidae) and evolutionary characteristics of the amphibian mitochondrial genomes. Curr Zool. 2011, 57 (6): 785-805.
Alexander Pyron R, Wiens JJ: A large-scale phylogeny of Amphibia including over 2800 species, and a revised classification of extant frogs, salamanders, and caecilians. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2011, 61 (2): 543-583.
Stuart BL: The phylogenetic problem of Huia (Amphibia: Ranidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2008, 46 (1): 49-60.
Che J, Pang JF, Zhao H, Wu GF, Zhao EM, Zhang YP: Phylogeny of Raninae (Anura : Ranidae) inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2007, 43 (1): 1-13.
Dubois A: Notes on the classification of Ranidae (Amphibia, Anura). Bull Mensuel Soc Linn Lyon. 1992, 61 (10): 305-352.
Boore JL, Brown WM: Big trees from little genomes: mitochondrial gene order as a phylogenetic tool. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998, 8 (6): 668-674.
Boore JL: The use of genome-level characters for phylogenetic reconstruction. Trends Ecol Evol. 2006, 21 (8): 439-446.
Boore JL, Fuerstenberg SI: Beyond linear sequence comparisons: the use of genome-level characters for phylogenetic reconstruction. Phil Trans R Soc B. 2008, 363 (1496): 1445-1451.
Shan X, **a Y, Zheng Y-C, Zou F-D, Zeng X-M: The complete mitochondrial genome of Quasipaa boulengeri (Anura: Dicroglossidae). Mitochondrial DNA. 2014, 25 (2): 83-84.
Sano N, Kurabayashi A, Fujii T, Yonekawa H, Sumida M: Complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Schlegel's tree frog Rhacophorus schlegelii (family Rhacophoridae): duplicated control regions and gene rearrangements. Genes Genet Syst. 2005, 80 (3): 213-224.
Kurabayashi A, Usuki C, Mikami N, Fujii T, Yonekawa H, Sumida M, Hasegawa M: Complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of a Malagasy poison frog Mantella madagascariensis: evolutionary implications on mitochondrial genomes of higher anuran groups. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2006, 39 (1): 223-236.
Macey JR, Schulte JA, Larson A, Papenfuss TJ: Tandem duplication via light-strand synthesis may provide a precursor for mitochondrial genomic rearrangement. Mol Biol Evol. 1998, 15 (1): 71-75.
Jia WL, Higgs PG: Codon usage in mitochondrial genomes: distinguishing context-dependent mutation from translational selection. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25 (2): 339-351.
Duchene AM, Pujol C, Marechal-Drouard L: Import of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases into mitochondria. Curr Genet. 2009, 55 (1): 1-18.
Schneider A, Marechal-Drouard L: Mitochondrial tRNA import: are there distinct mechanisms?. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10 (12): 509-513.
Janke A, Xu XF, Arnason U: The complete mitochondrial genome of the wallaroo (Macropus robustus) and the phylogenetic relationship among Monotremata, Marsupialia, and Eutheria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997, 94 (4): 1276-1281.
Peng QL, Nie LW, Pu YG: Complete mitochondrial genome of Chinese big-headed turtle, Platysternon megacephalum, with a novel gene organization in vertebrate mtDNA. Gene. 2006, 380 (1): 14-20.
Hoegg S, Vences M, Brinkmann H, Meyer A: Phylogeny and comparative substitution rates of frogs inferred from sequences of three nuclear genes. Mol Biol Evol. 2004, 21 (7): 1188-1200.
Meiklejohn CD, Montooth KL, Rand DM: Positive and negative selection on the mitochondrial genome. Trends Genet. 2007, 23 (6): 259-263.
Castellana S, Vicario S, Saccone C: Evolutionary patterns of the mitochondrial genome in Metazoa: exploring the role of mutation and selection in mitochondrial protein–coding Genes. Genome Biol Evol. 2011, 3: 1067-1079.
Shao R, Dowton M, Murrell A, Barker SC: Rates of gene rearrangement and nucleotide substitution are correlated in the mitochondrial genomes of insects. Mol Biol Evol. 2003, 20 (10): 1612-1619.
Oliveira D, Raychoudhury R, Lavrov DV, Werren JH: Rapidly evolving mitochondrial genome and directional selection in mitochondrial genes in the parasitic wasp Nasonia (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25 (10): 2167-2180.
Chong RA, Mueller RL: Evolution along the mutation gradient in the dynamic mitochondrial genome of salamanders. Genome Biol Evol. 2013, 5 (9): 1652-1660.
Ojala D, Montoya J, Attardi G: tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature. 1981, 290 (5806): 470-474.
Lynch M, Koskella B, Schaack S: Mutation pressure and the evolution of organelle genomic architecture. Science. 2006, 311 (5768): 1727-1730.
Sambrook J, Russell DW: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2001, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Press
Kurabayashi A, Sumida M: PCR primers for the neobatrachian mitochondrial genome. Curr Herpetol. 2009, 28 (1): 1-11.
Lowe T, Eddy S: tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucl Acids Res. 1997, 25 (5): 955-964.
Frost DR: Amphibian Species of the World: an online reference. Version 5.5 (31 January, 2011). 2011, [http://research.amnh.org/vz/herpetology/amphibia/]
Lupi R, Meo PDO, Picardi E, D’Antonio M, Paoletti D, Castrignanò T, Pesole G, Gissi C: MitoZoa: a curated mitochondrial genome database of metazoans for comparative genomics studies. Mitochondrion. 2010, 10 (2): 192-199.
**a X, **e Z: DAMBE: Software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J Hered. 2001, 92 (4): 371-373.
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S: MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011, 28 (10): 2731-2739.
Kamatani T, Yamamoto T: Comparison of codon usage and tRNAs in mitochondrial genomes of Candida species. Biosystems. 2007, 90: 362-370.
Castresana J: Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol. 2000, 17 (4): 540-552.
Librado P, Rozas J: DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009, 25 (11): 1451-1452.
Yang Z: PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007, 24 (8): 1586-1591.
Posada D: jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25 (7): 1253-1256.
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J: A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst Biol. 2008, 57 (5): 758-771.
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F: MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics. 2001, 17 (8): 754-755.
Cannone JJ, Subramanian S, Schnare MN, Collett JR, D'Souza LM, Du Y, Feng B, Lin N, Madabusi LV, Müller KM: The comparative RNA web (CRW) site: an online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs. BMC Bioinformatics. 2002, 3 (1): 2-
Acknowledgments
We thank Liyan Qing, Jianli **ong, Mian Hou, Cheng Li, Shujun Zhang, Dingqi Rao and Hui Zhao for the collection of samples, and we are grateful to Rui Peng, **zhong Fu and three anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. This research was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (NSFC–31272282, 31372181), by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014 M552386) and West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y4C3021100), and in part by Discovery Grant 3148 from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
YX carried out molecular lab work. YX and YZ conceived the project and analyzed the data. YX, RWM, PW, IM, and XZ wrote the paper. IM collected the specimens. XZ and RWM finalized the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12864_2013_6391_MOESM2_ESM.xls
Additional file 2: Gene organization of 46 anurans mitochondrial genomes. GenBank accession numbers and classification of anuran mitochondrial genomes used in this study. Organizations for each species were checked with NCBI Organelle Genome Resource and MitoZoa (http://www.caspur.it/mitozoa). Gene nomenclature from MitoZoa. (XLS 66 KB)
12864_2013_6391_MOESM4_ESM.xls
Additional file 4: Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values in 13 protein-coding genes of anurans mitochondrial genomes.(XLS 46 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
**a, Y., Zheng, Y., Miura, I. et al. The evolution of mitochondrial genomes in modern frogs (Neobatrachia): nonadaptive evolution of mitochondrial genome reorganization. BMC Genomics 15, 691 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-691
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-691