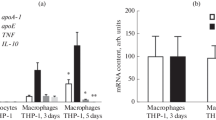
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is characterized by excessive uptake of cholesterol-rich low-density lipoprotein (LDL) by vascular wall macrophages. The macrophages are transformed into foam cells, lipids accumulate in the intima of arteries, atherosclerotic plaques arise, and cardiovascular diseases develop. Adiponectin is an adipose tissue adipokine and possess anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory activities, which are mediated by adiponectin binding to its receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2. To exert its anti-atherogenic effect, adiponectin may regulate the reverse cholesterol transport and prevent foam cells formation. The small-molecule adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon was assumed to modulate expression of reverse cholesterol transport and inflammation genes in human macrophages. Several AdipoRon concentrations (0, 5, 10, and 20 µM) were tested for effect on expression of the lipid metabolism genes ABCA1, ABCG1, APOA1, NR1H3 (LXRα), NR1H2 (LXRβ), PPARG, and ACAT1 and the inflammation genes IL6, TNFA, and TLR4 in cultured human primary macrophages and the THP-1 macrophage cell line. Cell viability was measured using the MTS assay. ABCA1, ABCG1, APOA1, NR1H3, NR1H2, PPARG, ACAT1, IL6, TNFA, and TLR4 mRNA levels in human primary macrophages were assessed by real-time PCR. The PPARG and ABCA1 relative mRNA levels were found to increase in human primary macrophages treated with 5 or 10 μM AdipoRon for 24 h. A higher AdipoR-on concentration (20 μM) was cytotoxic to macrophages, especially THP-1 cells. The effect of Adipo-Ron on human macrophages and potential adiponectin receptor agonists are of interest to study in view of the need to develop new approaches to atherosclerosis prevention and treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ghantous C.M., Kamareddine L., Farhat R., Zouein F.A., Mondello S., Kobeissy F., Zeidan A. 2020. Advances in cardiovascular biomarker discovery. Biomedicines. 8, 552.
Libby P., Buring J.E., Badimon L., Hansson G.K., Deanfield J., Bittencourt M.S., Tokgözoğlu L., Lewis E.F. 2019. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 5, 56.
Kryukov N.N., Nikolaevsky E.N., Polyakov V.P. 2010. Ishemicheskaya bolezn’ serdtsa (sovremennye aspekty kliniki, diagnostiki, lecheniya, profilaktiki, meditsinskoi reabilitatsii, ekspertizy): Monografiya. (Coronary Heart Disease (Current Aspects of Clinic, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Medical Rehabilitation, Examination): A Monograph). Samara: FGOU VPO Samarsk. Gos. Med. Univ. Roszdrava.
Severino P., D’Amato A., Pucci M., Infusino F., Adamo F., Birtolo L.I., Netti L., Montefusco G., Chimenti C., Lavalle C., Maestrini V., Mancone M., Chilian W.M., Fedele F. 2020. Ischemic heart disease pathophysiology paradigms overview: from plaque activation to microvascular dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 8118.
Ryzhkova A.I., Karagodin V.P., Sukhorukov V.N., Sazonova M.A., Orekhov A.N. 2017. Desialylated low-density lipoproteins in human blood. Clin. Med. Russ. J. 95 (3), 216–221.
Miller Y.I., Choi S., Fang L., Harkewicz R. 2009. Toll-like receptor-4 and lipoprotein accumulation in macrophages. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 19, 227–232.
Demina E.P., Smutova V., Pan X., Fougerat A., Guo T., Zou C., Chakraberty R., Snarr B.D., Shiao T.C., Roy R., Orekhov A.N., Miyagi T., Laffargue M., Sheppard D.C., Cairo C.W., Pshezhetsky A.V. 2021. Neuraminidases 1 and 3 trigger atherosclerosis by desialylating low-density lipoproteins and increasing their uptake by macrophages. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 10, e018756.
Mischenko E.L., Mischenko A.M., Ivanisenko V.A. 2021. Mechanosensitive molecular interactions in atherogenic regions of arteries: development of atherosclerosis. Vavilov. Zh. Genet. Sel. 25, 552–561.
Yu X., Fu C., Zhang D., Yin K., Tang C. 2013. Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 424, 245–252.
Chistiakov D.A., Bobryshev Y.V., Orekhov A.N. 2016. Macrophage-mediated cholesterol handling in atherosclerosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 20, 17–28.
Shemiakova T., Ivanova E., Grechko A.V., Gerasimova E.V., Sobenin I.A., Orekhov A.N. 2020. Mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage in the context of pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Biomedicines. 8, 166.
Shemiakova T., Ivanova E., Wu W.K., Kirichenko T.V., Starodubova A.V., Orekhov A.N. 2021. Atherosclerosis as mitochondriopathy: repositioning the disease to help finding new therapies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 660473.
Nikiforov N.G., Grachev A.N., Sobenin I.A., Orekhov A.N., Kzhyshkovskaya Yu.G. 2012. Macrophages and lipoprotein metabolism in atherosclerotic lesions. Patol. Fiziol. 13, 900–922. www.medline.ru.
Bezsonov E.E., Sobenin I.A., Orekhov A.N. 2021. Immunopathology of atherosclerosis and related diseases: focus on molecular biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4080.
Smirnova L.A., Khasanova Z.B., Ezhov M.V., Polevaya T.Yu., Matchin Yu.G., Balakhonova Yu.G., Sobenin I.A., Postnov A.Yu. 2014. Relation of mitochondrial genome mutations to atherosclerotic lesions of coronary and carotid arteries. Klinitsist. 1, 34–41.
Remmeriea A., Scott C.L. 2018. Macrophages and lipid metabolism. Cell. Immunol. 330, 27–42.
Miroshnikova V.V., Panteleeva A.A., Pobozheva I.A., Razgildina N.D., Polyakova E.A., Markov A.V., B-elyaeva O.D., Berkovich O.A., Baranova E.I., Nazarenko M.S., Puzyrev V.P., Pchelina S.N. 2021. ABCA1 and ABCG1 DNA methylation in epicardial adipose tissue of patients with coronary artery disease. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 21, 566.
Liberale L., Bonaventura A., Vecchiè A., Matteo C., Dallegri F., Montecucco F., Carbone F. 2017. The role of adipocytokines in coronary atherosclerosis. Curr. Atherosclerosis Rep. 19, 10.
Villarreal-Molina M.T., Antuna-Puente B. 2012. Adiponectin: anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects. Biochimie. 94, 2143–2149.
Choi H.M., Doss H.M., Kim K.S. 2020. Multifaceted physiological roles of adiponectin in inflammation and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1219.
van Stijn C.M.W., Kim J., Lusis A.J., Barish G.D., Tangirala R.K. 2015. Macrophage polarization phenotype regulates adiponectin receptor expression and adiponectin anti-inflammatory response. FASEB J. 29, 636–649.
Shabalala S.C., Dludla P.V., Mabasa L., Kappo A.P., Basson A.K., Pheiffer C., Johnson R. 2020. The effect of adiponectin in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the potential role of polyphenols in the modulation of adiponectin signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 131, 110785
Lia H., Yub X.H., Ouc X., Ouyangd X.P., Tang C.K. 2021. Hepatic cholesterol transport and its role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerosis. Prog. Lipid Res. 83, 101109.
Christen T., Trompet S., Noordam R., van Klinken J.B., van Dijk K.W., Lamb H.J., Cobbaert C.M., den Heije M., Jazet I.M., Jukema J.W., Rosendaal F.R., de Mutsert R. 2018. Sex differences in body fat distribution are related to sex differences in serum leptin and adiponectin. Peptides. 107, 25–31
Pobozheva I.A., Razgilьdina N.D., Polyakova E.A., Panteleeva A.A., Belyaeva O.D., Nifontov S.E., G-alkina O.V., Kolodina D.A., Berkovich O.A., Baranova E.I., Pchelina S.N., Miroshnikova V.V. 2020. Adiponectin gene expression in epicardial and subcutaneous adipose tissue in coronary heart disease. Kardiologiya. 60, 62–69.
Jonas M.I., Kurylowicz A., Bartoszewicz Z., Lisik W., Jonas M., Domienik-Karlowicz J., Puzianowska-Kuznicka M. 2017. Adiponectin/resistin interplay in serum and in adipose tissue of obese and normal-weight individuals. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 9, 95.
Sadashiv, Tiwari S., Paul B.N., Kumar S., Chandra A., Dhananjai S., Pal M., Negi S. 2013. Adiponectin mRNA in adipose tissue and its association with metabolic risk factors in postmenopausal obese women. Hormones. 12, 119–127.
Razgil’dina N.D., Brovin D.L., Pobozheva I.A., Panteleeva A.A., Miroshnikova V.V., Belyaeva O.D., Nifontov S.E., Galkina O.V., Kolodina D.A., Berkovich O.A., Baranova E.I., Pchelina S.N., Miroshnikova V.V. 2018. ADIPOQ gene expression in subcutaneous and intraabdominal adipose tissue in women with different degrees of obesity. Tsitologiya. 60, 531–535.
Liang B., Wang X., Guo X., Yang Z., Bai R., Liu M., **ao C., Bian Y. 2015. Adiponectin upregulates ABCA1 expression through liver X receptor alpha signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8, 450–457.
Furukawa K., Hori M., Ouchi N., Kihara S., Funahashi T., Matsuzawa Y., Miyazaki A., Nakayama H., Horiuchi S. 2004. Adiponectin down-regulates acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase-1 in cultured human monocyte-derived macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 317, 831–836.
Yuan B., Huang L., Yan M., Zhang S., Zhang Y., ** B., Ma Y., Luo Z. 2018. Adiponectin downregulates TNF-α expression in degenerated intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 43, E381–E389.
Choi H.M., Doss H.M., Kim K.S. 2020. Multifaceted physiological roles of adiponectin in inflammation and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1219.
Ohashi K., Parker J.L., Ouchi N., Higuchi A., Vita J.A., Gokce N., Pedersen A.A., Kalthoff C., Tullin S., Sams A., Summer R., Walsh K. 2010. Adiponectin promotes macrophage polarization toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 6153–6160.
Zhang Y., Zhao J., Li R., Lau W.B., Yuan Y., Liang B., Li R., Gao E., Koch W.J., Ma X., Wang Y. 2015. Adipo-Ron, the first orally active adiponectin receptor activator, attenuates postischemic myocardial apoptosis through both AMPK-mediated and AMPK-independent signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 309, E275–E282.
Okada-Iwabu M., Iwabu M., Ueki K., Yamauchi T., Kadowaki T. 2015. Perspective of small-molecule Adipo-R agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Diabetes Metab. J. 39, 363–372.
Natvig D.B., Perlmann P., Vizgel Kh. 1980. Limfotsity: vydelenie, fraktsionirovanie i kharakteristika. (Lymphocytes: Isolation, Fractionation, and Characterization). Moscow: Meditsina, pp. 185–201.
Miroshnikova V.V., Panteleeva A.A., Bazhenova E.A., Demina E.P., Usenko T.S., Nikolaev M.A., Semenova I.A., Neimark A.E., Khe Chzh., Belyaeva O.D., Berkovich O.A., Baranova E.I., Pchelina S.N. 2016. Regulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 transporter gene expression in intraabdominal adipose tissue. Biomed. Khim. 62, 283–289.
Okada-Iwabu M., Yamauchi T., Iwabu M., Honma T., Hamagami K., Matsuda K., Yamaguchi M., Tanabe H., Kimura-Someya T., Shirouzu M., Ogata H., Tokuyama K., Ueki K., Nagano T., Tanaka A., Yokoyama S., Kadowaki T. 2013. A small-molecule A-dipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature. 503, 493–499.
Tian L., Luo N., Zhu X., Chung B.H., Garvey W.T., Fu Y. 2012. Adiponectin-adipoR1/2-APPL1 signaling axis suppresses human foam cell formation; differential ability of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 to regulate inflammatory cytokine responses. Atherosclerosis. 221, 66–75.
Tsubakio-Yamamoto K., Matsuura F., Koseki M., Oku H., Sandoval J.C., Inagaki M., Nakatani K., Nakaoka H., Kawase R., Yuasa-Kawase M., Masuda D., Ohama T., Maeda N., Nakagawa-Toyama Y., Ishigami M., Nishida M., Kihara S., Shimomura I., Yamashita S. 2008. Adiponectin prevents atherosclerosis by increasing cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 375, 390–394.
Lee T.H., Christie B.R., van Praag H., Lin K., Ming-Fai Siu P., Xu A., So K., Yau S. 2021. AdipoRon treatment induces a dose-dependent response in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 2068.
Duan Z., Tu C., Liu Q., Li S., Li Y., **e P., Li Z. 2020. Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon attenuates calcification of osteoarthritis chondrocytes by promoting autophagy. J. Cell. Biochem. 121, 3333–3344.
Salvator H., Grassin-Delyle S., Brollo M., Couderc L., Abrial C., Victoni T., Naline E., Devillier P. 2021. Adiponectin inhibits the production of TNF-α, IL-6 and chemokines by human lung macrophages. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 718929.
Mallardo M., Costagliola C., Nigro E., Daniele A. 2021. AdipoRon negatively regulates proliferation and migration of ARPE-19 human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Peptides. 146, 170676.
Messaggio F., Mendonsa A.M., Castellanos J., Nagathihalli N.S., Gorden L., Merchant N.B., VanSaun M.N. 2017. Adiponectin receptor agonists inhibit leptin induced pSTAT3 and in vivo pancreatic tumor growth. Oncotarget. 8, 85378–85391.
Ramzan A.A., Bitler B.G., Hicks D., Barner K., Qamar L., Behbakht K., Powell T., Jansson T., Wilson H. 2019. Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon induces apoptotic cell death and suppresses proliferation in human ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 461, 37–46.
Wang S., Wang C., Wang W., Hao Q., Liu Y. 2020. Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon inhibits the proliferation of myeloma cells via the AMPK/autophagy pathway. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 28, 171–176.
Akimoto M., Maruyama R., Kawabata Y., Tajima Y., Takenaga K. 2018. Antidiabetic adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon suppresses tumour growth of pancreatic cancer by inducing RIPK1/ERK-dependent necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 9, 804.
Parida S., Siddharth S., Sharma D. 2019. Adiponectin, obesity, and cancer: clash of the bigwigs in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 2519.
Nigro E., Daniele A., Salzillo A., Ragone A., Naviglio S., Sapio L. 2021. AdipoRon and other adiponectin receptor agonists as potential candidates in cancer treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 5569.
Mauro L., Pellegrino M., De Amicis F., Ricchio E., Giordano F., Rizza P., Catalano S., Bonofiglio D., Sisci D., Panno M.L., Andò S. 2014. Evidences that estrogen receptor α interferes with adiponectin effects on breast cancer cell growth. Cell Cycle. 13, 553–564.
Illiano M., Nigro E., Sapio L., Caiafa I., Spina A., Scudiero O., Bianco A., Esposito S., Mazzeo F., Pedone P.V., Daniele A., Naviglio S. 2017. Adiponectin down-regulates CREB and inhibits proliferation of A549 lung cancer cells. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 45, 114–120.
Nigro E., Scudiero O., Sarnataro D., Mazzarella G., Sofia M., Bianco A., Daniele A. 2013. Adiponectin affects lung epithelial A549 cell viability counteracting TNF-α and IL-1ß toxicity through AdipoR1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 45, 1145–1153.
Kim A.Y., Lee Y.S., Kim K.H., Lee J.H., Lee H.K., Jang S., Kim S., Lee G.Y., Lee J., Jung S., Chung H.Y., Jeong S., Kim J.B. 2010. Adiponectin represses colon cancer cell proliferation via AdipoR1- and -R2-mediated AMPK activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 24, 1441–1452.
Nigro E., Orlandella F.M., Polito R., Mariniello R.M., Monaco M.L., Mallardo M., De Stefano A.E., Iervolino P.L.C., Salvatore G., Daniele A. 2021. Adiponectin and leptin exert antagonizing effects on proliferation and motility of papillary thyroid cancer cell lines. J. Physiol. Biochem. 77, 237–248.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to S.V. Orlov, E.E. Larionova, and D.A. Tanyanskii (Institute of Experimental Medicine) for help in experiments with THP-1 cells and discussion of the results.
Funding
This work was supported by the state programs “Study of the Molecular and Cell Components of the Pathogenesis of Socially Important Disorders to Develop Methods for Their Early Diagnosis and Treatment” (project no. 121060200125-2, experiments on gene expression in primary macrophage cultures) and “Molecular Mechanisms Activating Lipoprotein Transport across the Endothelium at Various Stages of Atherogenesis” (project no. FGWG-2022-0003, experiments on THP-1 cell viability).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study. The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee at Pavlov First St. Petersburg State Medical University.
Additional information
Translated by T. Tkacheva
Abbreviations: CCD, cardiovascular disorder; CHD, coronary heart disease; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LXRα and LXRβ, liver X receptors α and β; RXR, retinoid X receptor; PPARα and PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and γ; ABCA1 and ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; RCT, reverse cholesterol transport; AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, adiponectin receptors 1 and 2; APOA1, apolipoprotein A1; ACAT-1, acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 1; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6, interleukin 6; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; FBS, fetal bovine serum.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pobozheva, I.A., Dracheva, K.V., Pchelina, S.N. et al. AdipoRon Effect on Expression of Lipid Metabolism Genes in Cultured Human Primary Macrophages. Mol Biol 57, 616–623 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893323040143
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893323040143