Abstract
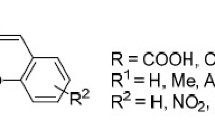
Brewster angle reflectometry has been developed as a tool for determining the absorbance and refractive index changes in molecular monolayers containing spiropyran. The method is sensitive to changes in both the real and imaginary parts of the refractive index in the monolayers. It was used to monitor the conversion of spiropyran to merocyanine and the reversal of this reaction when the molecules were immobilised on quartz using silane coupling. An analytical solution of Fresnel formula allowed the transient reflectometry data to be converted into transient absorption information. Absorbances of transients as low as ~10−6 were possible using the current apparatus with a single laser pulse transient measurement. It was found that spiropyran photoconverted to merocyanine with an efficiency of ~0.1. The photochemical reversion of converted merocyanine to spiropyran occurred with efficiencies of 0.03-0.2 and this was probably site dependent. It was found that the thermal conversion from merocyanine to spiropyran was slow and even after 10 min there was no significant thermal reversion. This measurement was possible because the real part of the refractive index of the monolayer could be monitored with time using an off-resonance probe at a wavelength where the merocyanine did not absorb light meaning that the probe did not photobleach the sample. Thus our method also provides a non-intrusive method for probing changes in molecules in thin films.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Wang, Y. Song and L. Jiang, Photoresponsive surfaces with controllable wettability, J. Photochem. Photobiol., C, 2007, 8, 18.
R. Rosario, D. Gust, M. Hayes, F. Jahnke, J. Springer and A. A. Garcia, Photon-modulated wettability changes on spiropyran-coated surfaces, Langmuir, 2002, 18, 8062.
A. Athanassiou, M. Varda, E. Mele, M. I. Lygeraka, D. Pisignano, M. Farsari, C. Fotakis, R. Cingolani and S. H. Anastasiadis, Combination of microstructuring and laser irradiation for the reversible wettabiltiy of photosensitised polymer surfaces, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 2006, 83, 351.
H. Tachibana, Y. Yamanaka, H. Sakai, M. Abe and M. Matsumoto, J-aggregate formation of amphiphilic merocyanine in Langmuir-Blodgett films, J. Lumin., 2000, 87-89, 800.
M. Matsumoto, Photoreactions and lateral patterning in Langmuir and Langmuir-Blodgett films, Chem. Rec., 2007, 7, 69.
K. Balashev, I. Panaitov and J. E. Proust, Propagation of photoinduced surface pressure perturbation along a mixed benzospiropyran-octadecanol monolayer, Langmuir, 1997, 13, 5373.
J. Hobley, T. Oori, S. Gorelik, S. Kajimoto, H. Fukumura and D. Hönig, Time-resolved Brewster angle microscopy for photochemical and photothermal studies on thin-films and monolayers, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2008, 8, 1.
J. Hobley, T. Oori, S. Kajimoto, S. Gorelik, K. Hatanaka, D. Hönig and H. Fukumura, Laser-induced phase change in Langmuir films observed using nanosecond pump-probe Brewster angl microscopy, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 2008, 93, 947.
M. J. Lear and J. Hobley, You make it, I break it, COSMOS, 2008, 4, 99.
E. Katz, B. Willner and I. Willner, Light-controlled electron transfer reactions at photoisomeririzable monolayer electrodes by means of electrostatic interactions: active interfaces for amperometric transduction of recorded optical signals, Biosens. Bioelectron., 1997, 12(8), 703.
B. Mecheri, P. Baglioni, O. Pieroni and G. Caminati, Molecular switching in nano-structured photochromic films of biopolymers, Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2003, 23, 893.
E. Aznar, R. Casasus, B. Garcia-Acosta, M. D. Marcos, R. Martinez-Manez, F. Sancenon, J. Soto and P. Amoros, Photochemical and chemical two-channel control of functional hybrid architectures, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 2228.
T. Seki, Dynamic photoresponsive functions in organized layer systems comprised of azobenzene-containing polymers, Polym. J., 2004, 36(6), 435.
Y.-G. Mo, R. O. Dillon, P. G. Snyder and T. E. Tiwald, Optical properties of photochromic organic-inorganic composites, Thin Solid Films, 1999, 355, 1.
Y.-G. Mo, R. O. Dillon and P. G. Snyder, Spectroscopic analysis of photochromic films, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A, 1999, 17(1), 170.
S.-H. Kim, H.-J. Suh, K.-N. Koh, S.-A. Suck, H.-J. Choi and H.-S. Kim, Surface plasmon resonance study on the interaction between photochromic spironaphthoxazine with L-phenylalanine in self assembled monolayers on gold, Dyes Pigm., 2004, 62, 93.
K. Sasaki and T. Nagamura, Ultrafast all-optical switch using complex refractive index changes of thin films containing photochromic dyes, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1997, 71(4), 434.
P. Kubelka and F. Munk, Ein Beitrag zur optik der farbanstriche, Z. Tech. Phys., 1931, 12, 593.
F. Wilkinson and C. J. Willsher, The use of diffuse reflectance laser flash photolysis to study primary photoprocesses in anisotropic media, Tetrahedron, 1987, 43(7), 1197.
G. P. Kelly, P. A. Leicester, F. Wilkinson, D. R. Worrall, L. F. Vieira Ferreira, R. Chittock and W. toner, Picosecond diffuse reflectance and transmission laser photolysis study of various triaryl-2-pyrazolines, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 1990, 46(6), 975.
M. Ichikawa, H. Fukumura and H. Masuhara, Picosecond regular reflection spectroscopic study on ultrafast heat generation in copper phthalocyanine solid, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, 12211.
H. Kawai, K. Nakano and T. Nagamura, White light optical waveguide detection of transient absorption spectra in ultrathin organic films upon pulsed laser excitation, Chem. Lett., 2001, 1300.
D. Kleine, J. Lauterbach, K. Kleinermans and P. Hering, Cavity ring-down spectroscopy of molecularly thin iodine films, Appl. Phys. B: Lasers Optics, 2001, 72, 249.
J. A. Piest, M. Anni, R. Cingolani and G. Gigli, Singlet to triplet excitation spectrum of thin film tris-(8-hydroxyquinolate)-aluminium in direct absorption, Synth. Met., 2008, 158, 1062.
I. M. P. Aarts, B. Hoex, A. H. M. Smets, R. Engeln, W. M. M. Kessels and M. C. M. van de Sanden, Direct and highly sensitive measurement of defect-related absorption in amorphous silicon thin films by cavity ring-down spectroscopy, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84(16), 3079.
R. N. Muir and A. J. Alexander, Structure of monolayer dye films studied by Brewster angle cavity ring-down spectroscopy, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2003, 5, 1279.
C. Zhu, B. **ang, L. Zhu and R. Cole, Determination of absorption cross sections of surface adsorbed HNO3 in the 290-330nm region by Brewster angle cavity ring-down spectroscopy, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2008, 458, 373.
X. Wang, M. Hinz, M. Vogelsang, T. Welsch, D. Kaufmann and H. Jones, A new approach to detecting biologically active substances with evanescent wave cavity ring-down spectroscopy, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2008, 467, 9.
R. Katoh, A. Furube, A. V. Barzykin, H. Arakawa and M. Tachya, Kinetics and mechanism of electron injection and charge recombination in dye-sensitized nanocrystalline semiconductors, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2004, 248, 1195.
T. Yoshihara, M. Murai, Y. Tamaki, A. Furube and R. Katoh, Trace analysis by transient absorption spectroscopy: estimation of the solubility of C60 in polar solvents, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2004, 394, 161.
R. Teppner, S. Bae, K. Haage and H. Motschmann, On the Analysis of Ellipsometric Measurements of Adsorption Layers at Fluid Interfaces, Langmuir, 1999, 15, 7002–7009.
B. L. Frey, R. M. Corn and S. C. Weibel, Polarization-Modulation Approaches to Reflection-Absorption Spectroscopy, in Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy, ed. J. Chalmers and P. R. Griffiths, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK, 2001, vol. 2. pp. 1042–1056.
S. Henon and J. Meunier, Microscope at the Brewster-angle - Direct observation of 1st-order phase transitions in monolayers, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1991, 62(4), 936.
D. Hönig, D. Möbius, Direct visualisation of monolayers at the air-water interface by Brewster-angle microscopy, J. Phys. Chem., 1991, 95(12), 4590.
au]2_H. Fujiwara, Spectroscopic Ellipsometry, Principles and applications, Wiley, West Sussex, England, 2007, p. 33; (b) p. 46.; (c) p. 26.; (d) p. 176.; (e) p. 178.
D. A. Reeves and F. Wilkinson, Photochromism of Spiropyrans: Part 1. Mechanism of photocolouration, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 2, 1973, 69, 1381.
CRC Handbook, Refractive index and transmittance of representative glasses, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 79th edn, 1998-1999, pp. 10–217.
J. Hobley, V. Malatesta, R. Millini, L. Montanari and W. O. N. Parker Jr, Proton exchange and isomerization reactions of photochromic and reverse photochromic spiro-pyrans and their merocyanine forms, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 1999, 1, 3259.
J. M. Galvin and G. B. Schuster, Preparation and characterization of mixed thin films containing spiropyrans and long chain alkyl silanes: towards a command of surfaces for liquid crystal realignment, Supramol. Sci., 1998, 5, 89.
J. Hobley and F. Wilkinson, Photochromism of naphthoxazine-spiro-indolines by direct excitation and following sensitisation by triplet-energy donors, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1996, 92(8), 1323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is part of a themed issue on synthetic and natural photoswitches.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorelik, S., Hongyan, S., Lear, M.J. et al. Transient Brewster angle reflectometry of spiropyran monolayers. Photochem Photobiol Sci 9, 141–151 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/b9pp00105k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b9pp00105k