Abstract.
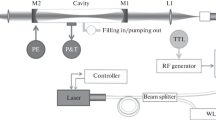
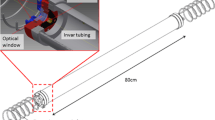
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) has so far mostly been used for measurements in the gas phase. Only in 1999 was a first spectrum of condensed phase published. This spectrum was measured by using a coated plate between the cavity mirrors. Rather than using this method, our measurements were made using the cavity mirrors as a substrate. This way, the scattering losses could be reduced by approximately a factor of 100. In our measurements we investigated molecularly thin layers of iodine. The iodine spectra were taken in the frequency range from 16200 to 17200 cm-1 using pulsed CRDS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 April 2000 / Revised version: 26 July 2000 / Published online: 22 November 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleine, D., Lauterbach, J., Kleinermanns, K. et al. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy of molecularly thin iodine layers . Appl Phys B 72, 249–252 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400000453
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400000453