Abstract
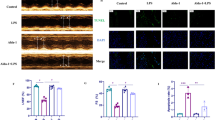
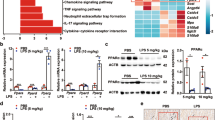
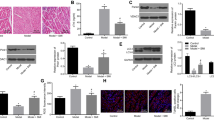
Previous studies have demonstrated that cardiomyocyte apoptosis, ferroptosis, and inflammation participate in the progress of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (SIC). Although Islet cell autoantigen 69 (ICA69) is an imperative molecule that could regulate inflammation and immune response in numerous illnesses, its function in cardiovascular disease, particularly in SIC, is still elusive. We confirmed that LPS significantly enhanced the expression of ICA69 in wild-type (WT) mice, macrophages, and cardiomyocytes. The knockout of ICA69 in lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced mice markedly elevated survival ratio and heart function, while inhibiting cardiac muscle and serum inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen (ROS), and ferroptosis biomarkers. Mechanistically, increased expression of ICA69 triggered the production of STING, which further resulted in the production of intracellular lipid peroxidation, eventually triggering ferroptosis and heart injury. Intriguingly, ICA69 deficiency only reversed the ferroptotic marker levels, such as prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2), malonaldehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxynonenal (4HNE), glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), superoxide dismutase (SOD), iron and lipid ROS, but had no effects on the xCT-dependent manner. Additionally, greater ICA69 level was identified in septic patients peripheralblood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) than in normal control groups. Generally, we unveil that ICA69 deficiency can relieve inflammation and ferroptosis in LPS-induced murine hearts and macrophages, making targeting ICA69 in heart a potentially promising treatment method for SIC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response that is accompanied by multiple organ dysfunction, oxidative stress, and overmuch inflammatory cytokines [1] sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (SIC) is one of the common and well-elucidated complications in sepsis and sepsis-induced shock, while Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin (Lipopolysaccharide, LPS) serves as a key sepsis mediator for septicemia-associated multiple organ dysfunction or mortality [2].
Encoded by the ICA1 gene, ICA69 has a limited cellular distribution and tissue distribution. Past study primarily highlighted the physiopathological function of ICA69 in organ-specific autoimmune illnesses including Type 1 diabetes (T1D) [3]. Thymic deletion of ICA69 expression, for instance, is adequate to give rise to inflammatory events in various organs [4]. Nevertheless, our research revealed that ICA69 was notably regulated upward in lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac tissue. According to previous research findings, ICA69 enrichment occurs in the proximity of the Golgi complex and its N-terminal half involves a BAR domain, a component that could bend or bind membranes and has mutual effect with phosphatide [5]. And the BAR-domain family encompasses numerous constituents, the majority of which function in transport and endocytosis [6].
STING, composed of multiple assumed transmembrane regions, is primarily anchored as a homodimer in the ER membrane in resting conditions [7]. Recent work suggests that, after STING binds cGAMP, it transfers to the ER-Golgi intermedium compartment (ERGIC) and the Golgi via the process depending on the COPI (coat protein complex I), COPII complex and ARF GTPases [8, 9], which is essential for the phosphorylation of STING and subsequent IRF3 stimulation [10, 11]. As STING marks an imperative molecule that can modulate inflammation and defense response in SIC, and participates in septic heart damage via inducing cardiac muscle cell pyroptosis [12], these results hint that ICA69 may participate in STING-dependent innate immune response.
Ferroptosis is a ROS-related and iron-related cell death, which is crucial for organ damage and target treatment of tumors [13, 14]. Recent studies show that the ferroptosis induction via high-iron diet or Gpx4 consumption stimulates the STING-related DNA sensor pathway, which finally causes the infiltration of macrophagus and pancreatic tumorigenesis [Assessment of oxidative stress our team carried out the specimen preparation as per the assay kit specification. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) [53], superoxide dismutase (SOD) [54], GSH/GSSG [55], total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) [56] in serum and heart samples were measured via colorimetric determination by assay kits according to previous studies mentioned above. The results of MDA, SOD were expressed as a unit per mg protein (U/mg prot). The tissue weight was accurately weighed, while the homogenate was mechanically prepared in an ice bath at 2500 rpm for 10 min to produce a 10% supernatant. After the sample is prepared, the protein level can be detected by the BCA Protein Concentration Assay Kit to facilitate the subsequent calculation of Fe content in tissues or cells per unit protein weight. Afterwards, iron standard test sample and iron test base liquid were added in sequence. Eventually, we mix the well, while detecting the standard well at 562 nm with the enzyme plate analyzer, measuring the well absorbance, and finish the colorimetry within 1 h. The quantity of cardiac tissue creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB) was determined by a biochemical analyzing machine automatically (ADVIA® 2400, Siemens Ltd., China). The enzyme activities of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in serum were identified by rapid and sensitive assay kits according to the instruction. Briefly, we produced the specimens for the standard curve by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide mother liquor and LDH buffer. A 50 μL Reaction Mix with 48 μL LDH Assay Buffer in it and 2 μL LDH Substrate Mix was supplemented into the specimens or standard specimens for a whole hour at 37 °C free of light, producing a 450 nm absorbance. The extra mice in all groups (n = 10) were raised to study the survival status. The mortality was daily documented at the identical time node, while the survival rate was computed within seven days posterior to LPS injection at 10 mg/kg or PBS. Echocardiography was implemented by a Vevo 3100 ultrasonic equipment with a 10-MHz linear array ultrasound transducer (Fujifilm, VisualSonics, USA) after mice were anesthetized by 1.5% isoflurane. As the medial echocardiographic readings were collected from 3–5 heart cycles, the heart function indexes, such as fractional shortening (FS), heart rate (bpm), ejection fraction (EF), etc., were documented. The entire measured data here were depicted by average ± SEM or characteristic images of 1 representative from 3 separate assays. As GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 software for Windows was adopted for statistic observation, the comparison between the two groups was performed by Student’s t-test, and the diversities between the groups were compared by two-way ANOVA and corrected by Bonferroni, with survival condition assessed by Kaplan–Meier analysis. Human data were studied by Wilcoxon (Exact) rank-sum test, while association among the expression of ICA1 in PBMCs and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II value of septic cases was evaluated by the Pearson correlation analysis. A P < 0.05 was deemed as significant on statistics.Iron in serum and cardiac tissue
LDH and CK MB in cardiac tissue
Survival condition
Echocardiography
Statistical analysis
Data availability
The datasets adopted in our research are accessible from the relevant author on reasonable request.
References
Deutschman CS, Tracey KJ. Sepsis: current dogma and new perspectives. Immunity 2014;40:463–75.
Jia L, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ma Y, Shen J, Fu Z, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 in macrophages drives septic cardiac dysfunction via suppressing lysosomal degradation of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Circ Res. 2018;122:1532–44.
Bonifacio E, Achenbach P. Birth and coming of age of islet autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019;198:294–305.
Fan Y, Gualtierotti G, Tajima A, Grupillo M, Coppola A, He J, et al. Compromised central tolerance of ICA69 induces multiple organ autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2014;53:10–25.
Buffa L, Fuchs E, Pietropaolo M, Barr F, Solimena M. ICA69 is a novel Rab2 effector regulating ER-Golgi trafficking in insulinoma cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008;87:197–209.
Habermann B. The BAR-domain family of proteins: a case of bending and binding? EMBO Rep. 2004;5:250–5.
Shu C, Yi G, Watts T, Kao CC, Li P. Structure of STING bound to cyclic di-GMP reveals the mechanism of cyclic dinucleotide recognition by the immune system. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:722–4.
Gui X, Yang H, Li T, Tan X, Shi P, Li M, et al. Autophagy induction via STING trafficking is a primordial function of the cGAS pathway. Nature 2019;567:262–6.
Brandizzi F, Barlowe C. Organization of the ER-Golgi interface for membrane traffic control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:382–92.
Zhang BC, Nandakumar R, Reinert LS, Huang J, Laustsen A, Gao ZL, et al. STEEP mediates STING ER exit and activation of signaling. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:868–79.
Jia M, Qin D, Zhao C, Chai L, Yu Z, Wang W, et al. Redox homeostasis maintained by GPX4 facilitates STING activation. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:727–35.
Li N, Zhou H, Wu H, Wu Q, Duan M, Deng W, et al. STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3. Redox Biol. 2019;24:101215.
Li N, Wang W, Zhou H, Wu Q, Duan M, Liu C, et al. Ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis is involved in sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:303–18.
Lee H, Zandkarimi F, Zhang Y, Meena JK, Kim J, Zhuang L, et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:225–34.
Dai E, Han L, Liu J, **e Y, Zeh HJ, Kang R, et al. Ferroptotic damage promotes pancreatic tumorigenesis through a TMEM173/STING-dependent DNA sensor pathway. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6339.
Kuang F, Liu J, Li C, Kang R, Tang D. Cathepsin B is a mediator of organelle-specific initiation of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;533:1464–9.
Ning L, Wei W, Wenyang J, Rui X, Qing G. Cytosolic DNA-STING-NLRP3 axis is involved in murine acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Clin Transl Med. 2020;10:e228.
Saitoh T, Fujita N, Hayashi T, Takahara K, Satoh T, Lee H, et al. Atg9a controls dsDNA-driven dynamic translocation of STING and the innate immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:20842–6.
Zhao Q, Yin L, Zhang L, Jiang D, Liu L, Ji H. Chitoheptaose promotes heart rehabilitation in a rat myocarditis model by improving antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:2394704.
Su CH, Ho YC, Lee MW, Tseng CC, Lee SS, Hsieh MK, et al. 1-nitropyrene induced reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in macrophages through AIF nuclear translocation and AMPK/Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:9314342.
Li D, Weng Y, Wang G, Zhen G. Anti-septic potential of 7-alpha-obacunyl acetate isolated from the toona sinensis on cecal ligation/puncture mice via suppression of JAK-STAT/NF-kappaB signal pathway. Infect Drug Resist. 2021;14:1813–21.
Cowan DB, Noria S, Stamm C, Garcia LM, Poutias DN, Del NP, et al. Lipopolysaccharide internalization activates endotoxin-dependent signal transduction in cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2001;88:491–8.
Barber GN. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:760–70.
Yang WS, Sriramaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS. et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31.
Shen E, Fan J, Chen R, Yee SP, Peng T. Phospholipase Cgamma1 signalling regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;43:308–18.
Alim I, Caulfield JT, Chen Y, Swarup V, Geschwind DH, Ivanova E, et al. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell 2019;177:1262–79.
Yang WS, Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26:165–76.
Van der Paal J, Neyts EC, Verlackt C, Bogaerts A. Effect of lipid peroxidation on membrane permeability of cancer and normal cells subjected to oxidative stress. Chem Sci. 2016;7:489–98.
Baechler BL, Bloemberg D, Quadrilatero J. Mitophagy regulates mitochondrial network signaling, oxidative stress, and apoptosis during myoblast differentiation. Autophagy 2019;15:1606–19.
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, **e E, Yang X, Wei J, et al. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:2672–80.
Stockwell BR, Friedmann AJ, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ. et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171:273–85.
Ji X, Qian J, Rahman S, Siska PJ, Zou Y, Harris BK, et al. xCT (SLC7A11)-mediated metabolic reprogramming promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression. Oncogene 2018;37:5007–19.
Gorrini C, Harris IS, Mak TW. Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:931–47.
Sato H, Tamba M, Kuriyama-Matsumura K, Okuno S, Bannai S. Molecular cloning and expression of human xCT, the light chain of amino acid transport system xc-. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2000;2:665–71.
Cao S, Zhang Q, Wang C, Wu H, Jiao L, Hong Q, et al. LPS challenge increased intestinal permeability, disrupted mitochondrial function and triggered mitophagy of piglets. Innate Immun. 2018;24:221–30.
Mallik B, Dwivedi MK, Mushtaq Z, Kumari M, Verma PK, Kumar V. Regulation of neuromuscular junction organization by Rab2 and its effector ICA69 in Drosophila. Development. 2017;144:2032–44.
Hannemann M, Sasidharan N, Hegermann J, Kutscher LM, Koenig S, Eimer S. TBC-8, a putative RAB-2 GAP, regulates dense core vesicle maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002722.
Hopfner KP, Hornung V. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:501–21.
Luo WW, Li S, Li C, Lian H, Yang Q, Zhong B, et al. iRhom2 is essential for innate immunity to DNA viruses by mediating trafficking and stability of the adaptor STING. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:1057–66.
Ishikawa H, Ma Z, Barber GN. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature. 2009;461:788–92.
Lu Y, Qiu Y, Chen P, Chang H, Guo L, Zhang F, et al. ER-localized Hrd1 ubiquitinates and inactivates Usp15 to promote TLR4-induced inflammation during bacterial infection. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4:2331–46.
Dobbs N, Burnaevskiy N, Chen D, Gonugunta VK, Alto NM, Yan N. STING activation by translocation from the ER is associated with infection and autoinflammatory disease. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;18:157–68.
Agmon E, Stockwell BR. Lipid homeostasis and regulated cell death. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017;39:83–9.
Liu J, Wu X, Wang H, Wei J, Wu Q, Wang X. et al. HFE inhibits type I IFNs signaling by targeting the SQSTM1-mediated MAVS autophagic degradation. Autophagy. 2021;17:1962–77.
Zhang H, Zeng L, **e M, Liu J, Zhou B, Wu R, et al. TMEM173 drives lethal coagulation in sepsis. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27:556–70.
Marinho FV, Benmerzoug S, Oliveira SC, Ryffel B, Quesniaux V. The emerging roles of STING in bacterial infections. Trends Microbiol. 2017;25:906–18.
Reinert LS, Lopusna K, Winther H, Sun C, Thomsen MK, Nandakumar R, et al. Sensing of HSV-1 by the cGAS-STING pathway in microglia orchestrates antiviral defence in the CNS. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13348.
Paludan SR. Activation and regulation of DNA-driven immune responses. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2015;79:225–41.
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315:801–10.
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. CHEST 1992;101:1644–55.
Riedhammer C, Halbritter D, Weissert R. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells: isolation, freezing, thawing, and culture. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1304:53–61.
Huang SH, Xu M, Wu HM, Wan CX, Wang HB, Wu QQ, et al. Isoquercitrin attenuated cardiac dysfunction via AMPKalpha-dependent pathways in LPS-treated mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62:e1800955.
Gong K, Li W. Shikonin, a Chinese plant-derived naphthoquinone, induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through reactive oxygen species: a potential new treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51:2259–71.
Zhou Q, Wang X, Shao X, Wang H, Liu X, Ke X, et al. tert-butylhydroquinone treatment alleviates contrast-induced nephropathy in rats by activating the Nrf2/Sirt3/SOD2 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4657651.
Deng C, Zhang B, Zhang S, Duan C, Cao Y, Kang W, et al. Low nanomolar concentrations of Cucurbitacin-I induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis by perturbing redox homeostasis in gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2106.
Zhang DY, Wan Y, Xu JY, Wu GH, Li L, Yao XH. Ultrasound extraction of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves and their effect on enhancing antioxidant activity. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;137:473–9.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81704180 and 81774109). This work was also supported in part by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. LY19H290008) and Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau Foundation (No. 2018ZY003, Y20190108, and No. Y20190202). The authors also thank the Laboratory Animal Research Center and the Institute of Translational Medicine in Wenzhou Medical University for technical assistance. Our research was backed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 81704180 and 81774109); the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. LY19H290008) and Wenzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (No. 2018ZY003, Y20190108, and No. Y20190202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.W., C.K., and X.N. designed the whole research, analyzed all results, and wrote the manuscript. J.W. provided technical and material support. A.Z. and Y.Z. participated in most of the experiments. Q.D., Y.M., and S.L. performed the development of methodology and writing, review, and revision of the paper. F.L., Y.L., J.Z., and X.Y. helped in performing experiments. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
On the ethics review, human study (ChiCTR-INR-2100051426) was accepted by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University and was conformed to the protocols in the Declaration of Helsinki and in the Federal Policy for the Protection of Human Subjects, with informed consent provided by each participated patient. Each animal assay, aiming to bring the mouse killing to the minimum, was accepted by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee (Approval Ethical Inspection ID: wydw2019-0559).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, C., Ni, X., Wang, Y. et al. ICA69 aggravates ferroptosis causing septic cardiac dysfunction via STING trafficking. Cell Death Discov. 8, 187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-00957-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-00957-y
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
STING upregulation mediates ferroptosis and inflammatory response in lupus nephritis by upregulating TBK1 and activating NF-κB signal pathway
Journal of Biosciences (2024)
-
Ferroptosis mechanisms and regulations in cardiovascular diseases in the past, present, and future
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2024)
-
The mechanism of ferroptosis and its related diseases
Molecular Biomedicine (2023)
-
Targeting epigenetic and posttranslational modifications regulating ferroptosis for the treatment of diseases
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways
Cell Death & Disease (2023)