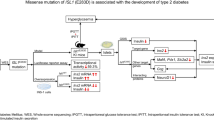
Abstract
Islet β cell dysfunction and insulin resistance are the main pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the mechanism remains unclear. Here we identify a rs3819316 C > T mutation in lncRNA Reg1cp mainly expressed in islets associated with an increased risk of T2D. Analyses in 16,113 Chinese adults reveal that Mut-Reg1cp individuals had higher incidence of T2D and presented impaired insulin secretion as well as increased insulin resistance. Mice with islet β cell specific Mut-Reg1cp knock-in have more severe β cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Mass spectrometry assay of proteins after RNA pulldown demonstrate that Mut-Reg1cp directly binds to polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1), further immunofluorescence staining, western blot analysis, qPCR analysis and glucose stimulated insulin secretion test reveal that Mut-Reg1cp disrupts the stabilization of insulin mRNA by inhibiting the phosphorylation of PTBP1 in β cells. Furthermore, islet derived exosomes transfer Mut-Reg1cp into peripheral tissue, which then promote insulin resistance by inhibiting AdipoR1 translation and adiponectin signaling. Our findings identify a novel mutation in lncRNA involved in the pathogenesis of T2D, and reveal a new mechanism for the development of T2D.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Diabetes and its complications are widespread in the world and have become one of the major threats to human health. According to data released by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) in 2021 [1], about 537 million people worldwide are living with diabetes. Without sufficient action to address the pandemic, the number of people suffered from diabetes would raise to 783 million by 2045 [1, 2]. More than 90% of all diabetics have T2D, which is characterized by a decrease in the number of β cells or a decline of β cells function, resulting in an inability to compensate for the high insulin requirement in insulin resistant states [3, 4]. Islet β cell dysfunction and insulin resistance are the main pathogenesis of T2D, while the mechanism of which still remains complex and unclear.
Over the years, multiple genome-wide association studies have linked single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at more than 250 loci to T2D risk in the human genome, and the majority of diabetes susceptibility loci are mapped to non-coding regions [5,6,7,8]. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are classified as non-protein coding transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides [9, 10], which regulate a wide range of biological processes such as cellular differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, gene regulation, and cancer development via binding to DNA, RNA, or protein complexes [11,12,13,14]. lncRNAs have been shown to be involved in controlling β-cell proliferation, compensation, apoptosis and function [15, 16]. Understanding the functions of lncRNAs in β-cell biology might provide crucial insights into the pathogenesis of diabetes.
In our previous study, we identified a novel rs3819316 C > T mutation in lncRNA -Reg1cp, which is associated with high bone mass (HBM) by directly binding to Krüppel-like factor 3 to regulate angiogenesis [17]. It’s worth noting that Reg1cp belongs to Reg family and is a pseudogene which is conservedly expressed in human and is mainly expressed in pancreas, especially in islet [18, 19]. So, we further investigate the role of Reg1cp in glucose homeostasis. In the present study, we demonstrate this mutation in Reg1cp promotes T2D development both by impaired islet β cell function and increased insulin resistance.
Results
rs3819316 C > T mutation in Reg1cp gene is a risk factor of type 2 diabetes
In our previous study we identified a rs3819316 C > T mutation in Reg1cp gene which is associated with HBM [17]. As Reg1cp is mainly expressed in pancreas, especially in islet [18, 19], we further analyzed glucose metabolism related indexes in Chinese population (n = 16,113, including 6,744 males and 9,369 females). Among them, 1554 heterozygous Reg1cp individuals (Reg1cp+/mut) and 90 homozygote Reg1cp individuals (Reg1cpmut/mut) were identified. These Reg1cp+/mut and Reg1cpmut/mut individuals had higher incidence of diabetes and prediabetic states compared with those with the WT gene (Table 1). Significant correlations of rs3819316 C > T mutation with diabetes and prediabetic states were observed after adjusting for gender, age and body mass index (BMI) (OR 1.44 [95% CI 1.29–1.61], p = 9.52e−11; OR 1.39 [95% CI 1.24–1.57], p = 6.57e–08, respectively).
To find more clues beneath the connection between rs3819316 C > T mutation and diabetes, further analyses for glucose metabolism related indexes were performed in 12,885 non-diabetic individuals, as shown in Fig. 1, the rs3819316 C > T mutation was significantly associated with fasting plasma glucose (FPG), 2 h plasma glucose (2hPG), glucose area under curve (GAUC), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (HOMA-β), Stumvoll first phase insulin secretion (STU1), and Stumvoll second phase insulin secretion (STU2). These results suggested that Reg1cp might be a new diabetes associated gene.
Associations of rs3819316 C > T mutation with glucose metabolism related indexes were analyzed after adjustment for gender, age and body mass index (BMI). A Analysis of glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c); B Analysis of fasting plasma glucose (FPG); C Analysis of 2 h plasma glucose (2hPG) based on oral glucose tolerance test; D Analysis of the area under the curve of the glucose (GAUC) from 0 to 120 min based on oral glucose tolerance test; E Analysis of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR); F Analysis of homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (HOMA-β); G Analysis of Stumvoll first-phase insulin secretion (STU1); H Analysis of Stumvoll second-phase insulin secretion (STU2). I Analysis of GUTT index based on oral glucose tolerance test. Data shown as median (interquartile range), N. Kruskal Wallis test for continuous variables and χ2 test for categorical variables were applied to assess the differences among three groups.
Mutant Reg1cp impaired the glucose metabolism in mice
To investigate the impact of wild-type Reg1cp (WT-Reg1cp) and mutant Reg1cp (Mut-Reg1cp) on glucose metabolism in vivo, we constructed transgenic mice expressing WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp in insulin positive pancreatic islet β cells (Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice or Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice) by intercrossing mice carrying Rosa26-loxP-flanked-stop cassette controlling WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp alleles expression (Rosa-Reg1cp-wt mice or Rosa-Reg1cp-mut mice) with RIP-Cre transgenic mice that express Cre recombinase under the control of the rat insulin 2 promoter [20]. As expected, the expression of Reg1cp was detected in the islet of transgenic mice by qPCR and Reg1cp FISH with insulin immunofluorescent staining. Sanger sequencing further confirmed the successful knock-in of WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp (Supplementary Fig. 1A–D). Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice and Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice had normal pancreatic exocrine elements including ducts and acini, and scattered endocrine islets with normal distribution (Supplementary Fig. 1E).
When maintained on regular diet, Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice showed no differences in body weight, fasting blood glucose and fasting serum insulin levels as compared with Rosa-Reg1cp-wt control mice (Fig. 2A–C). The fed blood glucose and fed serum insulin levels of Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice also remained indistinguishable as compared with Rosa-Reg1cp-wt control mice when maintained on regular diet (Fig. 2D, E). Consistently, the glucose tolerance and clearance of Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice also had no obvious changes compared with Rosa-Reg1cp-wt control mice, as shown by the results of glucose tolerance tests (GTTs) (Fig. 2F, G) and insulin tolerance tests (ITTs) (Fig. 2H, I). These results indicated that WT-Reg1cp knock-in did not affect the glucose metabolism in mice under regular diet. However, the fasting and fed blood glucose and serum insulin levels were increased in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice as compared with Rosa-Reg1cp-mut littermate controls (Fig. 2B–E). The results of GTTs and ITTs indicated the glucose tolerance and clearance of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice were worse than Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls (Fig. 2F–I). In general, these results demonstrated that Mut-Reg1cp affected glucose homeostasis in mice.
A–E The body weight (A), fasting blood glucose level (B), fasting serum insulin level (C), fed blood glucose level (D) and fed serum insulin level (E) of Rosa-Reg1cp-wt, Rosa-Reg1cp-mut, Reg1cp-wtRIP+ and Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice under regular diet. F–I The GTTs (F) and ITTs (H) in Reg1cp-wtRIP+, Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and related Rosa-Reg1cp-wt and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls under regular diet. Bar graphs showing the calculated values for area under curve (AUC) during the 120-min test course of the GTTs (G) and ITTs (I) (mg dl−1 × 120 min × 103). J–M The GTTs (J) and ITTs (L) in Reg1cp-wtRIP+, Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and related Rosa-Reg1cp-wt and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls under HFD. Bar graphs showing the calculated values for area under curve (AUC) during the 120-min test course of the GTTs (K) and ITTs (M) (mg dl−1 × 120 min × 103). n = 6 in each group from three independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS no significance; One-way ANOVA.
Metabolic stressors, such as high-fat diet (HFD) could accelerate the disruption of glucose homeostasis. We next examined animals maintained on HFD. After 12-week HFD started at 12 weeks of age, we found that the impaired glucose tolerance as judged by GTTs and deteriorated insulin resistance as detected by ITTs induced by HFD were aggravated in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice compared with their littermate controls (Fig. 2J–M). The fasting blood glucose levels and fasting serum insulin levels were increased in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice compared with Rosa-Reg1cp-mut littermate controls when maintained on HFD (Supplementary Fig. 1G, H). However, the body weight, fasting blood glucose levels, fasting serum insulin levels, glucose tolerance and clearance showed no significant differences between Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-wt control mice (Fig. 2J–M, Supplementary Fig. 1F–H). Those results indicated that WT-Reg1cp did not affect glycometabolism and Mut-Reg1cp disrupted glucose homeostasis with or without metabolic stress.
Mut-Reg1cp aggravated hyperglycemia by impaired β cell function
To further investigate the underlying mechanism of Mut-Reg1cp regulating glycometabolism, we evaluated the β cell mass, proliferation and senescence by immunofluorescent staining and analyzed the function of β cell by glucose stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) test between these transgenic mice. The β cell mass of Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice and Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice remained indistinguishable as compared with their littermate controls whether maintained on regular diet (Fig. 3A, B) or HFD (Supplementary Fig. 2A, B). The Ki-67 positive or P21 positive β cells showed no significant differences between the transgenic mice and their littermate controls whether maintained on regular diet or HFD, indicating that neither WT- nor Mut-Reg1cp affected the proliferation and senescence of β cells (Supplementary Fig. 2C–H). SA-β Gal staining of MIN6 cells also showed no difference in senescence after transfection with Mut-Reg1cp or WT-Reg1cp plasmids (Supplementary Fig. 2I–J).
A, B Representative immunostaining images of insulin (green), glucagon (red) and DAPI, nucleus (blue) (A) and quantification of β cell mass (B) in Reg1cp-wtRIP+, Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and related Rosa-Reg1cp-wt and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls under regular diet. Scale bar: 100 μm. C In vivo GSIS test analysis of glucose stimulated insulin level (left panel) and the increased rate of insulin after glucose stimulation (right panel) of Rosa-Reg1cp-wt, Rosa-Reg1cp-mut, Reg1cp-wtRIP+ and Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (0’ and 15’ means 0 and 15 min after an intraperitoneal injection of glucose). D In vitro GSIS test analysis of glucose stimulated insulin level in MIN6 cells transfected with Control, Mut-Reg1cp or WT-Reg1cp plasmids. E Top 10 changed cellular functions which differentially expressed genes enriched in indicated by KEGG-enrichment analysis of MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp or Control plasmids. F Top 10 changed cellular functions which differentially expressed genes enriched in indicated by KEGG-enrichment analysis of MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp or WT-Reg1cp plasmids. In A–D, n = 6 in each group from three independent experiments. In E, F, n = 3. Data shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; NS no significance; One-way ANOVA.
However, the β cell function was impaired in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice, as indicated by in vivo GSIS test (Fig. 3C). The impaired β cell function was also confirmed by in vitro GSIS test of MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp or WT-Reg1cp plasmids (Fig. 3D). To further evaluate the effects of Mut-Reg1cp on β cells, we assessed the RNA level of MIN6 cells, which were transfected with Mut-Reg1cp or WT-Reg1cp plasmids. We then performed KEGG-enrichment analysis of the RNA-seq data and found that multiple β cell function related systems, including insulin secretion and cAMP signaling pathway were changed in Mut-Reg1cp plasmid transfected MIN6 cells compared with blank control or WT-Reg1cp plasmid transfected groups (Fig. 3E, F, Supplementary Fig. 3A, B). These results indicated that Mut-Reg1cp impaired the function of β cells.
Mut-Reg1cp impaired the insulin secretion by inhibiting phosphorylation of PTBP1
Reg1cp belongs to Reg family and has been reported to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation through activation of REG3A in colon cells [21]. However, we didn’t detect the changes in expression levels of Reg1, Reg2, Reg3α and Reg3γ in MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp or WT-Reg1cp plasmids (Supplementary Fig. 4).
Our previous study demonstrated that this mutation in Reg1cp led to a large change in its structure so that mutated Reg1cp could directly bind to KLF3 in endothelial cells to abolish the function of KLF3 [17]. To further elucidate the mechanisms whereby mutated Reg1cp may accelerate the development of T2D, we conducted mass spectrometry (MS) of proteins after RNA pulldown using WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp in MIN6 cells. 16 polypeptides of 12 proteins could only be combined by Mut-Reg1cp instead of WT-Reg1cp (Supplementary Table 1). Among these identified peptides, 3 peptides from PTBP1 protein which could only be retrieved by Mut-Reg1cp caught our attentions (Supplementary Fig. 5A–D). cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PTBP1 has been reported to be a common downstream target of glucose in the posttranscriptional upregulation of β cell’s secretory granule (SG) biogenesis [22]. So, we chose PTBP1 for further analysis.
Biotinylated RNA pull-down confirmed that Mut-Reg1cp, but not WT-Reg1cp, specifically retrieved PTBP1 (Fig. 4A). We then conducted RNA immunoprecipitation of MIN6 transfected with the Mut-Reg1cp plasmids. The anti-PTBP1 antibody also could pull down Mut-Reg1cp (Fig. 4B). MIN6 cells transfected with WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp plasmid had similar protein and mRNA level of PTBP1 compared with control groups (Fig. 4C, D). However, the phosphorylation PTBP1 level of MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp after IBMX treatment was significant lower when compared with the controls (Fig. 4E), and there was no difference between Mut-Reg1cp plasmid transfection group and co-expression of Mut-Reg1cp and WT-Reg1cp group (Supplementary Fig. 5E and F). The decreased phosphorylation level of PTBP1 was further confirmed in islet isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (Fig. 4F). These results indicated that Mut-Reg1cp could directly bind to PTBP1 and inhibit its phosphorylation.
A Mut-Reg1cp retrieved PTBP1, as detected by immunoblotting. B Semi-quantitative PCR showed PTBP1 retrieved Mut-Reg1cp. C, D Western blot analysis of the expression of PTBP1 (C) and qRT-PCR analysis of Ptbp1 (D) in MIN6 cells transfected with Control, WT- Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp plasmids. E, F Western blot analysis of the expression of phosphorylation and total PTBP1 (p-PTBP1 and t-PTBP1) in MIN6 cells transfected with Control, WT- Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp plasmids (E) or in islets isolated from WT, Reg1cp-wtRIP+or Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (F) with or without IBMX treatment. G, H Representative immunostaining images of PTBP1 (green) and DAPI, nucleus (blue) (G) and quantification of PTBP1 positive nucleus (H) in MIN6 cells transfected with Control or Mut-Reg1cp plasmids before or after IBMX treatment. Scale bar: 20 μm. I Western blot analysis of the expression of p-PTBP1 in cytoplasm of MIN6 cells transfected with Control or Mut-Reg1cp plasmids with or without IBMX treatment. J RT-PCR analysis of Insulin, ICA512 and Chga in MIN6 cells transfected with Control, WT- Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp plasmids. K RT-PCR analysis of Insulin, ICA512 and Chga in islets isolated from Rosa-Reg1cp-mut or Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice. A, B was representative of two independent experiments. In C–K, n = 6 in each group from two independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS no significance; One-way ANOVA.
cAMP-dependent phosphorylation induced the nucleocytoplasmic translocation of PTBP1 to stabilize mRNAs encoding various SG proteins in β cells [22]. IBMX treatment significantly reduced the number of PTBP1 positive nuclei in MIN6 cells. However, this phenomenon was attenuated after Mut-Reg1cp plasmid transfection (Fig. 4G, H). The lower phosphorylation of PTBP1 was further confirmed in cytoplasm of Mut-Reg1cp plasmid transfected MIN6 cells (Fig. 4I). The levels of mRNAs encoding components of SG proteins including Insulin 1, pro-ICA512 and Chga in Mut-Reg1cp transfected MIN6 cells were lower after IBMX-stimulation (Fig. 4J). The lower level of insulin 1, pro-ICA512 and Chga mRNAs were further confirmed in islet isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (Fig. 4K).
Taken together, these results indicated that Mut-Reg1cp attenuated the stabilization and translation of mRNAs encoding insulin via directly binding to and inhibiting the phosphorylation of PTBP1, which further impaired β cell function.
Major metabolic tissues of Reg1cp-mut RIP + mice obtained islets-derived exosomal Reg1cp and showed insulin resistance
Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice showed significant increasing insulin resistance indicated by ITTs (Fig. 2H, I, L, M). Furthermore, the activation of insulin signaling in liver, muscle and epididymal white adipose tissue (ewat) of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice induced by insulin stimulations was also restrained when compared with the littermate controls as evidenced by the immunostaining of phospho (p)-IR, p-AKT, and p-GSK3β in these tissues (Fig. 5A–F). These results suggested that Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice had significant impaired insulin sensitivity which couldn’t be explained by modulating phosphorylation of PTBP1 in β cells.
A–F Representative pictures (A, C, E) and quantitative measurements (B, D, F) of western blot analysis of insulin stimulated IR, AKT, and GSK3β phosphorylation in liver (A, B), muscle (C, D) and epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT, E, F) of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and related Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. G Semi-quantitative PCR showed the expression level of Mut-Reg1cp in different tissues of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice. H Protein levels of Calnexin, CD9 and TSG101 in MIN6 cells or exosomes released by MIN6 cells. I Protein levels of TSG101, CD9 and CD63 in exosomes isolated from mice serum. J Semi-quantitative PCR showed the expression level of Mut-Reg1cp in exosomes isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice serum, cultured medium of primary islets isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice or cultured medium of MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp plasmids. K MIN6 cells derived exosomes were marked with red fluorescence dye PKH26 and then cocultured with 3T3-L1 adipocytes, C2C12 myocytes, and Hepa1-6 hepatocytes; Representative immunostaining images of PKH26 (red) and DAPI, nucleus (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. In A–F, n = 6 in each group from three independent experiments. G–K were representative of two independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; Student’s t test.
To further investigate the potential reasons for the significant increased insulin resistance in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice, we analyzed circulating proteins in serum from Reg1cp-wtRIP+ mice, Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and wild type mice after 12-week HFD through mass spectrometry. Thirteen identified proteins showed significant changes in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice compared with Reg1cp-wtRIP+ group and wild type control group (Supplementary Fig. 6A–E). None of those circulating proteins had been reported as an inducer of insulin resistance, except for CHGA, a secretory protein that occurs in endocrine, neuroendocrine, and neuronal cells and is also a major cargo in insulin secretory vesicles in β cells [23,24,25], whose expression level was affected by the cytoplasmic localization of PTBP1 [22]. We also confirmed the lower level of Chga mRNA in β cells isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice or MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp plasmids (Fig. 4J, K). Thus, the higher circulation level of CHGA in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (Supplementary Fig. 6C–E) might be cause by the hormone imbalance induced by insulin resistance. Those results indicated that the significant increased insulin resistance of metabolic tissues of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice might not due to the variation of circulating proteins in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice.
The RIP-Cre system which was supposedly specifically expressed Cre recombinase in 80% or more of β cells, has been reported with leaky expression in the brain and other neuroendocrine cell types such as the pituitary gland, not in other metabolic tissues [20]. It’s worth noting that, although the amount was very small, we detected the presence of Reg1cp in peripheral tissue such as muscle, liver and adipose tissue in transgenic mice (Fig. 5G, Supplementary Fig. 1A, B). Given that pancreatic islet could secret endocrine factors via exosomes to communicate with peripheral organs [26, 27], we investigated whether pancreatic islet-secreted exosomes would transfer Mut-Reg1cp into peripheral tissue. We isolated exosomes from cultured primary islets and serum of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (Fig. 5H, I) and detected the presence of Mut-Reg1cp in those isolated exosomes (Fig. 5J). We also detected the presence of Mut-Reg1cp in exosomes isolated from culture medium of MIN6 cells transfected with Mut-Reg1cp plasmids (Fig. 5J). MIN6 cells derived exosomes were marked with red fluorescent dye PKH26 and then cocultured with 3T3-L1 adipocytes, C2C12 myocytes, or Hepa1-6 hepatocytes. Twelve hours later, these cells exhibited efficient uptake of MIN6 cells exosomes, as evidenced by the existence of red fluorescence inside these cells (Fig. 5K). All of those results indicated that islet in Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice transferred the mutated Reg1cp into peripheral tissues via exosomes.
Exosomal Mut-Reg1cp impaired insulin sensitivity in vivo
To further confirm the influences of islets-derived exosomes on insulin sensitivity in vivo, insulin-sensitive young wild-type C57/BL6J mice (2-month old) were administered with the exosomes isolated from serum of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice or Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls via tail vein injection (two times per week for two weeks, 50 μg each time). Administration of circulating exosomes from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice increased the fasting blood glucose levels, fasting serum insulin, and HOMA-IR index of young wild-type C57/BL6J mice when compared with administration of circulating exosomes from Rosa-Reg1cp-mut control mice (Fig. 6A−C). Consistently, the glucose tolerance and clearance of young wild-type C57/BL6J mice were also significantly abrogated by the treatment of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice circulating exosomes, as shown by the results of GTTs and ITTs (Fig. 6D–G). Furthermore, the activation of insulin signaling in muscle and liver of young wild-type C57/BL6J mice induced by insulin stimulations was also inhibited by the treatment of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice circulating exosomes, as evidenced by the immunostaining of p-IR, p-AKT, and p-GSK3β in these tissues (Fig. 6H–K). Taken together, these results suggested that exosomes contained Mut-Reg1cp impaired insulin sensitivity in vivo.
A–C Fasting blood glucose level (A), fasting serum insulin level (B) and HOMA-IR index (C) of mice treated with exosomes isolated from serum of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. D–G The GTTs (D) and ITTs (F) in mice treated with serum exosomes isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. Bar graphs showing the calculated values for area under curve (AUC) during the 120-min test course of the GTTs (E) and ITTs (G) (mg dl−1 × 120 min × 103). H–I Representative pictures (H) and quantitative measurements (I) of Western blot analysis of insulin stimulated IR, AKT, and GSK3β phosphorylation in liver of mice treated with serum exosomes isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. J, K Representative pictures (J) and quantitative measurements (K) of Western blot analysis of insulin stimulated IR, AKT, and GSK3β phosphorylation in muscle of mice treated with serum exosomes isolated from Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. n = 6 in each group from three independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; Student’s t test.
Mut-Reg1cp promoted insulin resistance by inhibiting AdipoR1 translation
Our previous study showed that Mut-Reg1cp, but not WT-Reg1cp, specifically bound to PTBP1 (Fig. 4A), which has been reported to play an important role in regulating ADIPOR1 protein expression and adiponectin signaling by associating with 3′UTR of AdipoR1 mRNA [28]. Downregulation of the AdipoR1 was involved in the development of insulin resistance and diabetes [29].
To further investigate whether Mut-Reg1cp impaired insulin sensitivity through PTBP1-AdipoR1 pathway. We transfected C2C12 myocytes with Mut-Reg1cp plasmid and confirmed the binding of Mut-Reg1cp and PTBP1 in C2C12 myocytes (Fig. 7A). We observed the lower expression level of ADIPOR1 (Fig. 7B, C) in C2C12 myocytes transfected with Mut-Reg1cp plasmid. However, the influence of Mut-Reg1cp on the expression of ADIPOR1 was disappeared after Ptbp1 siRNA treatment (Fig. 7B, C), which indicated that the Mut-Reg1cp impaired insulin sensitivity through PTBP1 dependent suppression on ADIPOR1 expression. The lower expression level of ADIPOR1 was also observed in C2C12 myocytes and Hepa1-6 hepatocytes treated with exosomes contained Mut-Reg1cp (Fig. 7D-G) or muscle and liver of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice (Fig. 7H–K). We also detected the presence of Mut-Reg1cp in exosomes isolated from serum of Reg1cpmut/mut individuals (Fig. 7L). Furthermore, the treatment of exosomes isolated from serum of Reg1cpmut/mut individuals decreased the level of ADIPOR1 and its downstream AMPK phosphorylation in human HepG2 hepatocytes (Fig. 7M, N). All of these results suggested that exosomes contained Mut-Reg1cp impaired insulin sensitivity through adiponectin signaling by inhibiting the expression of ADIPOR1 both in animal models and in human cells.
A Mut-Reg1cp retrieved PTBP1, as detected by immunoblotting. B, C Representative pictures (B) and quantitative measurements (C) of western blot analysis of PTBP1 and ADIPOR1 level in C2C12 myocytes transfected with Mut-Reg1cp or control plasmids with or without si-Ptbp1 treatment. D, E Representative pictures (D) and quantitative measurements (E) of western blot analysis of ADIPOR1 level in C2C12 myocytes treated with exosomes contained Mut-Reg1cp or not. F, G Representative pictures (F) and quantitative measurements (G) of western blot analysis of ADIPOR1 level in Hepa1-6 hepatocytes treated with exosomes contained Mut-Reg1cp or not. H, I Representative pictures (H) and quantitative measurements (I) of western blot analysis of ADIPOR1 level in muscle of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. J, K Representative pictures (J) and quantitative measurements (K) of western blot analysis of ADIPOR1 level in liver of Reg1cp-mutRIP+ mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut controls. L Semi-quantitative PCR showed the expression level of Reg1cp in exosomes isolated from human serum. M, N Representative pictures (M) and quantitative measurements (N) of western blot analysis of ADIPOR1, p-AMPK and t-AMPK level in HepG2 hepatocytes treated with exosomes isolated from human serum. A and L were representative of two independent experiments. In B–K, M, N, n = 6 in each group from two independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS no significance; Student’s t test for E, G, I, K, N. One-way ANOVA for C.
Discussion
LncRNAs have been shown to be involved in controlling β-cell proliferation, apoptosis or function during T2D development [15, 16]. In the current study, we identified a mutation in Reg1cp and presented genetic, clinical, in vivo and in vitro experimental evidences to demonstrate that Reg1cp promotes the development of T2D both by impairing islet β cell function and increasing insulin resistance.
Regenerating genes (Reg) are the members of the calcium-dependent lectin gene superfamily [19, 30], which are involved in cell proliferation and differentiation [31, 32]. LncRNA Reg1cp is encoded as a pseudogene that is mainly expressed in the pancreas, especially in islet [18]. Our previous study identified this rs3819316 C > T mutation in Reg1cp through a HBM pedigree investigation [ Human participants were enrolled from Shanghai Nicheng community, China and Endocrinology Department of **angya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China. Individuals with missing glucose metabolism related indexes, severe disability, hepatic dysfunction and cancer were excluded. Subjects without a self-reported history of diabetes were administrated to an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) after a 75 g oral glucose load. Diabetes was diagnosed according to the 2010 criteria of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) [43]. Medical history, details of the anthropometric indices and biochemical traits related to diabetes were recorded. Height (m), weight (kg), waist circumference (cm) and hip circumference (cm) were measured, and body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight/height2. Blood samples were collected for the measurements of metabolic indexes including glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). Plasma glucose and insulin levels at 0, 30, 120 min timepoints of all participants were also tested. Based on these collected indexes, area under the curve of the glucose from 0 to 120 min (GAUC) and area under the curve of the insulin from 0 to 120 min (IAUC) were calculated. Insulin resistance and β cell function were assessed by HOMA for insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) and beta cell function (HOMA-β) [44]. Stumvoll first- and second-phase insulin secretion indices (STU1, STU2) and GUTT index were generated by computations proposed by Stumvoll et al. [45] and Gutt et al. [46]. The human study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, Shanghai, China and Ethics Committee of **angya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China. It was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Second Revision of the Declaration of Helsinki, and written informed consent was signed by every participant. To generate islet β cell specific WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp knock-in mice, mice carrying a loxP-flanked-Stop cassette controlling WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp alleles expression (Rosa-Reg1cp-wt mice or Rosa-Reg1cp-mut mice) and RIP-Cre transgenics were interbred. The Rosa-Reg1cp-wt mice or Rosa-Reg1cp-mut littermates were used as controls. The RIP-Cre transgenic mice (Stock No. C001002) were purchased from Cyagen Biosciences Inc (China). Rosa-Reg1cp-wt mice and Rosa-Reg1cp-mut mice were constructed by Bioray Laboratories Inc (China). For mice experiments, six male mice were used for each group for each independent experiment. Animal care protocols and experiments were reviewed and approved by Medical Ethics Committee of **angya Hospital of Central South University. All mice were maintained in the specific pathogen-free facility of the Department of Laboratory Animals, Central South University. Pancreatic islets were isolated from whole pancreas of mice through the injection of 0.8 mg/mL collagenase V (Sigma–Aldrich) into the pancreatic duct, followed by digestion at 37 °C for 25 min with mild shaking, and isolated islets were picked by hand selection under a dissecting microscope. Pancreatic islets were treated with 0.05% trypsin in PBS for 5 min at 37 °C to isolate primary pancreatic islet β-cells. Pancreatic islets and MIN6 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FBS, 1mM L-glutamine, 1 mM HEPES, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 50 μM 2-mercaptoethanol, and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. 3T3-L1, C2C12, or HepG2, Hepa1-6 cells were cultured in DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. All cells were cultured in a humidified incubator with 95% air and 5% CO2 at 37 °C. MIN6 cell line was bought from MeisenCTCC company and has been authenticated by STR profiling. Serum exosomes were isolated using ExoQuickTM Exosome Precipitation Solution (SBI, EXOQ5A-1) according to the manufactor’s instructions. Culture medium exosomes were isolated using Total Exosome Isolation (from cell culture media) Kit (Invitrogen, 4478359) according to the manufactor’s instructions. To identify the isolated exosomes, Western blotting analysis was conducted to detect the expression of TSG101 (Proteintech, 28283-1-AP, 1:1000), Calnexin (Proteintech, 10427-2-AP, 1:1000), CD63 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-5275, 1:1000), and CD9 (Proteintech, 20597-1-AP, 1:1000). For the administration of exosomes to mice, exosomes were injected to recipient mice via tail vein injection (two times a week, 50 μg/time for 2 weeks). For the cell treatment, exosomes were added to the culture medium on the basis of 2 μg of exosomes per 1 × 105 recipient cells. To monitor the exosome trafficking, exosomes were marked by a PKH26 fluorescent cell linker kit (Sigma), according to the manufactor’s instructions. The measurement of blood glucose levels and serum insulin were performed as reported previously [39]. Blood glucose concentrations were measured by glucometer. Serum Insulin levels were tested by Mouse Insulin (INS) Elisa Kit (Nan**g Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, H203-1-2) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The glucose tolerance tests (GTTs) and insulin tolerance tests (ITTs) were performed as reported previously [12]. For GTTs, mice were intraperitoneally treated with glucose at dosage of 1 g/kg after overnight fast. For ITTs, mice were intraperitoneally treated with insulin at dosage of 0.75 U/kg after 6 h fast. Blood was collected by venous bleeding from the tail vein at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min after glucose or insulin injection, and glucose concentrations were measured by glucometer. For MIN6 cell, cells were seeded onto 12-well plates at a density of 1 × 106 cells. For primary islets, 30–40 islets were handpicked for each assay replicate per well. Medium was collected after a 1-h incubation at each glucose concentration. For in vivo GSIS, the insulin was measured from serum collected at the 0 and 15 min after an intraperitoneal injection of glucose (2 g/kg body weight). Secreted insulin levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) insulin kit (Nan**g Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, H203). Results were normalized to the total insulin content. Immunofluorescence staining was performed as reported previously [47]. For tissue Immunohistochemistry staining, samples were embedded in paraffin. Four-micrometer-thick sections were stained with individual primary antibodies to mouse insulin (Servicebio, gb13121, 1:300), Glucagon (Servicebio, gb11097, 1:1000), Ki67 (Abcam, ab15580, 1:100), P21(Abcam, ab188224, 1:100) overnight at 4 °C. For Immunocytochemistry staining, cells were stained with individual primary antibodies to PTBP1 (Thermo Fisher/Invitrogen, 32-4800, 1:100) overnight at 4 °C. We counted the numbers of positively stained cells in four random visual fields in five sequential sections per sample in each group. MIN6 senescence was induced by treating with 450 μM H2O2 for 24 h and then cellular senescence was evaluated by senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA beta-gal) staining using a Senescence β-Galactosidase Staining Kit (Solarbio, G1580) according to manufacturer’s instructions. After RNA quality examination, a total amount of 2 μg RNA per sample was used as input material for the RNA sample preparations. Sequencing libraries were generated using NEBNext® Ultra™ RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (#E7530L, NEB, USA) following the manufacturer’s recommendations and index codes were added to attribute sequences to each sample. Briefly, mRNA was purified from total RNA using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads. Fragmentation was carried out using divalent cations under elevated temperature in NEBNext First Strand Synthesis Reaction Buffer (5X). First strand cDNA was synthesized using random hexamer primer and RNase H. Second strand cDNA synthesis was subsequently performed using buffer, dNTPs, DNA polymerase I and RNase H. The library fragments were purified with QiaQuick PCR kits and elution with EB buffer, then terminal repair, A-tailing and adapter added were implemented. The aimed products were retrieved and PCR was performed, then the library was completed. The clustering of the index-coded samples was performed on a cBot cluster generation system using HiSeq PE Cluster Kit v4-cBot-HS (Illumina) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After cluster generation, the libraries were sequenced on an Illumina platform and 150 bp paired-end reads were generated. KEGG Enrichment (fisher.test and p.adjust) was performed to show the biological processes affected among different groups. The RNA sequencing data was deposited on the Sequence Read Archive website with the BioProject accession number PRJNA874533. The 3’-end biotin-labeled RNA probes used in RNA pull-down were generated using RNA 30 End Biotinylation Kit (20160, Pierce) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Five picomoles of 30-biotinylated RNA was used in each pulldown assay. Briefly, biotin-labeled full-length WT-Reg1cp or Mut-Reg1cp were incubated with nuclear lysate of MIN6 or C2C12 cells for 60 min. Then, streptavidin agarose beads (Invitrogen) were added and incubated at room temperature (RT) for another 60 min. The retrieved proteins were subjected to western blot analysis or mass spectrometry. The mass spectrometry assay was performed by Shanghai Applied Protein Technology Co. Ltd. RNA immunoprecipitation was performed using Magna RIP RNA-Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation Kit (17-700, Millipore) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The RNA samples precipitate was extracted, reverse transcribed using T7 High YieldRNA Synthesis Kit (E2040S, NEB) according to manufacturer’s instructions and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. Protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) and blotted on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore). The membranes were blocked with 5% milk (170-6404, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) and incubated with specific primary antibodies: PTBP1 (Thermo Fisher/Invitrogen, 32-4800, 1:1000), AdipoR1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-518030,1:500), P-IR (Cell Signaling Technology, 3024S, 1:1000), t-IR (Cell Signaling Technology, 3025S, 1:1000), P-AKT (Cell Signaling Technology, 9271S, 1:1000), t-AKT (Cell Signaling Technology, 4691S, 1:1000), P-GSK3β (Cell Signaling Technology, 9336S, 1:1000), t-GSK3β (Cell Signaling Technology, 9315S, 1:1000), GAPDH (OriGene, TA802519, 1:3000), β-ACTIN (OriGene, TA811000, 1:3000), then reprobed with appropriate horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary antibodies. Blots were visualized using SuperSignal West Pico PLUS Chemiluminescent Substrate (SD251210, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) Phosphorylation PTBP1 antibody was constructed by ProMab Biotechnologies (Hunan China) used the antigen as a synthetic peptide GTKRGSDELF (PTB1 amino acids 11-20) with Ser-16 phosphorylated. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range). For comparisons of two groups, two-tailed Student’s t-test was used. For comparisons of multiple groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used followed by Bonferroni’s posttest in GraphPad Prism 7.0. Differences were considered significant at P < 0.05. The clinical characteristics of the patients were summarized with SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). For continuous variables, normality testing was performed, quantitative traits with skewed distribution were logarithmically transformed, mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range) was used for a general description, differences between groups were determined via the Wilcoxon test. For categorical variables, the number of subjects were used for a general description, and differences between groups were determined via the χ2 test. Associations between phenotypes and genotypes were determined in PLINK (v1.07;http://pngu.mgh.harvard. edu/~purcell/plink/) using an additive genetic model. The associations of rs3819316 C > T mutation with diabetes and prediabetic states were tested by a logistic regression model. Linear regression analysis was used to test the associations of rs3819316 C > T mutation with glucose metabolism related indexes. No randomization or blinding was used, and no animals were excluded from analysis. Sample sizes were selected on the basis of previous experiments.Methods
Human participants for genoty** and glucose metabolism related indexes analysis
Mice
Primary cell isolation and cell culture
Exosomes isolation, identification and treatment
Blood glucose, serum insulin and HOMA-IR index
Glucose and insulin tolerance tests
GSIS
Immunofluorescence staining
SA-β-gal assay
RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
RNA pull-down assay
RNA immunoprecipitation
Western blot
Statistical analyses
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and Supplementary Files or available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Microarray data that support the findings of this study have been deposited in Sequence Read Archive website (Home - SRA - NCBI (nih.gov)) with the BioProject accession number PRJNA874533.
Change history
30 November 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05467-4
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edn. 2021. http://www.diabetesatlas.org/ (2021).
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pr. 2022;183:109119.
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:88–98.
Holman N, Young B, Gadsby R. Current prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults and children in the UK. Diabet Med. 2015;32:1119–20.
Khetan S, Kales S, Kursawe R, Jillette A, Ulirsch JC, Reilly SK, et al. Functional characterization of T2D-associated SNP effects on baseline and ER stress-responsive beta cell transcriptional activation. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5242.
de Goede OM, Nachun DC, Ferraro NM, Gloudemans MJ, Rao AS, Smail C, et al. Population-scale tissue transcriptomics maps long non-coding RNAs to complex disease. Cell. 2021;184:2633–2648.e19.
Cho YS, Chen CH, Hu C, Long J, Ong RT, Sim X, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies eight new loci for type 2 diabetes in east Asians. Nat Genet. 2011;44:67–72.
Yan J, Jiang F, Zhang R, Xu T, Zhou Z, Ren W, et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies a novel INS mutation causative of maturity-onset diabetes of the young 10. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017;9:376–83.
Knoll M, Lodish HF, Sun L. Long non-coding RNAs as regulators of the endocrine system. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11:151–60.
Akerman I, Tu Z, Beucher A, Rolando DMY, Sauty-Colace C, Benazra M, et al. Human pancreatic beta cell lncRNAs control cell-specific regulatory networks. Cell Metab. 2017;25:400–11.
Li CJ, **ao Y, Yang M, Su T, Sun X, Guo Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA Bmncr regulates mesenchymal stem cell fate during skeletal aging. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:5251–66.
**ao YZ, Yang M, **ao Y, Guo Q, Huang Y, Li CJ, et al. Reducing hypothalamic stem cell senescence protects against aging-associated physiological decline. Cell Metab. 2020;31:534–48. e5.
Wong CM, Tsang FH, Ng IO. Non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular functions and pathological implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:137–51.
Ransohoff JD, Wei Y, Khavari PA. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:143–57.
Lopez-Noriega L, Rutter GA. Long non-coding RNAs as key modulators of pancreatic beta-cell mass and function. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:610213.
Mirza AH, Kaur S, Pociot F. Long non-coding RNAs as novel players in beta cell function and type 1 diabetes. Hum Genomics. 2017;11:17.
Yang M, Guo Q, Peng H, **ao YZ, **ao Y, Huang Y, et al. Kruppel-like factor 3 inhibition by mutated lncRNA Reg1cp results in human high bone mass syndrome. J Exp Med. 2019;216:1944–64.
Gharib B, Fox MF, Bartoli C, Giorgi D, Sansonetti A, Swallow DM, et al. Human regeneration protein/lithostathine genes map to chromosome 2p12. Ann Hum Genet. 1993;57:9–16.
Miyashita H, Nakagawara K, Mori M, Narushima Y, Noguchi N, Moriizumi S, et al. Human REG family genes are tandemly ordered in a 95-kilobase region of chromosome 2p12. FEBS Lett. 1995;377:429–33.
Magnuson MA, Osipovich AB. Pancreas-specific Cre driver lines and considerations for their prudent use. Cell Metab. 2013;18:9–20.
Yari H, ** L, Teng L, Wang Y, Wu Y, Liu GZ, et al. LncRNA REG1CP promotes tumorigenesis through an enhancer complex to recruit FANCJ helicase for REG3A transcription. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5334.
Knoch KP, Meisterfeld R, Kersting S, Bergert H, Altkruger A, Wegbrod C, et al. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PTB1 promotes the expression of insulin secretory granule proteins in beta cells. Cell Metab. 2006;3:123–34.
Bandyopadhyay GK, Mahata SK. Chromogranin A regulation of obesity and peripheral insulin sensitivity. Front Endocrinol. 2017;8:20.
Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y, Birmingham A, Seo JB, et al. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miRNAs can modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell. 2017;171:372–84.e12.
Taupenot L, Harper KL, O’Connor DT. The chromogranin-secretogranin family. N. Engl J Med. 2003;348:1134–49.
Krishnan P, Syed F, Jiyun Kang N, Mirmira RG, Evans-Molina C. Profiling of RNAs from human islet-derived exosomes in a model of type 1 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:23.
**ong L, Chen L, Wu L, He W, Chen D, Peng Z, et al. Lipotoxicity-induced circGlis3 impairs beta cell function and is transmitted by exosomes to promote islet endothelial cell dysfunction. Diabetologia. 2022;65:188–205.
Lustig Y, Barhod E, Ashwal-Fluss R, Gordin R, Shomron N, Baruch-Umansky K, et al. RNA-binding protein PTB and microRNA-221 coregulate AdipoR1 translation and adiponectin signaling. Diabetes. 2014;63:433–45.
Yamauchi T, Nio Y, Maki T, Kobayashi M, Takazawa T, Iwabu M, et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat Med. 2007;13:332–9.
Zhang YW, Ding LS, Lai MD. Reg gene family and human diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2635–41.
Kiji T, Dohi Y, Nishizaki K, Takasawa S, Okamoto H, Nagasaka S, et al. Enhancement of cell viability in cryopreserved rat vascular grafts by administration of regenerating gene (REG) inducers. J Vasc Res. 2003;40:132–9.
Tohma Y, Dohi Y, Shobatake R, Uchiyama T, Takeda M, Takasawa S, et al. Reg gene expression in periosteum after fracture and its in vitro induction triggered by IL-6. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2257
So WY, Liu WN, Teo AKK, Rutter GA, Han W. Paired box 6 programs essential exocytotic genes in the regulation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13:eabb1038.
Bell GI, Polonsky KS. Diabetes mellitus and genetically programmed defects in beta-cell function. Nature. 2001;414:788–91.
Sawicka K, Bushell M, Spriggs KA, Willis AE. Polypyrimidine-tract-binding protein: a multifunctional RNA-binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:641–7.
Knoch KP, Nath-Sain S, Petzold A, Schneider H, Beck M, Wegbrod C, et al. PTBP1 is required for glucose-stimulated cap-independent translation of insulin granule proteins and Coxsackieviruses in beta cells. Mol Metab. 2014;3:518–30.
**e J, Lee JA, Kress TL, Mowry KL, Black DL. Protein kinase A phosphorylation modulates transport of the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:8776–81.
Ehehalt F, Knoch K, Erdmann K, Krautz C, Jager M, Steffen A, et al. Impaired insulin turnover in islets from type 2 diabetic patients. Islets. 2010;2:30–6.
Su T, **ao Y, **ao Y, Guo Q, Li C, Huang Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal MiR-29b-3p regulates aging-associated insulin resistance. ACS Nano. 2019;13:2450–62.
Ribeiro D, Horvath I, Heath N, Hicks R, Forslow A, Wittung-Stafshede P. Extracellular vesicles from human pancreatic islets suppress human islet amyloid polypeptide amyloid formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:11127–32.
Xu H, Du X, Xu J, Zhang Y, Tian Y, Liu G, et al. Pancreatic beta cell microRNA-26a alleviates type 2 diabetes by improving peripheral insulin sensitivity and preserving beta cell function. PLoS Biol. 2020;18:e3000603.
Li J, Zhang Y, Ye Y, Li D, Liu Y, Lee E, et al. Pancreatic beta cells control glucose homeostasis via the secretion of exosomal miR-29 family. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12055.
American Diabetes A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:S62–9.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Stumvoll M, Van Haeften T, Fritsche A, Gerich J. Oral glucose tolerance test indexes for insulin sensitivity and secretion based on various availabilities of sampling times. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:796–7.
Gutt M, Davis CL, Spitzer SB, Llabre MM, Kumar M, Czarnecki EM, et al. Validation of the insulin sensitivity index (ISI0,120): comparison with other measures. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000;47:177–84.
Yang M, Li CJ, Sun X, Guo Q, **ao Y, Su T, et al. MiR-497 approximately 195 cluster regulates angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis by maintaining endothelial Notch and HIF-1alpha activity. Nat Commun. 2017;8:16003.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 92149306, 82120108009, 81930022, 82170903), the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No: BX20200390), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No: 2021M703642) and The Youth Science Foundation of **angya Hospital (Grant No: 2020Q01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MY, XHL, and JY designed the experiments and generated data; MY, WHG, and QG carried out majority of the experiments; QG, DDY, LJ, and RZ contributed to acquiring data; MY and YLL wrote the manuscript; XHL co-advised the study; MY, XHL, and JY is the guarantor of this work and has full access to all the data in this study and takes the responsibility for data accuracy.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, WH., Guo, Q., Liu, YL. et al. Mutated lncRNA increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by promoting β cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Cell Death Dis 13, 904 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05348-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05348-w
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Changes of LncRNAs during the Process of Antioxidants Antagonize Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Damage in Islet β Cells
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2024)
-
PTBP1 as a potential regulator of disease
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)