Abstract
Autophagy is an important catabolic process, which sustains intracellular homeostasis and lengthens cell survival under stress. Here we identify the ankyrin-repeat-containing, SH3-domain-containing, and proline-rich region-containing protein 2 (ASPP2), a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor, as a molecular regulator of starvation-induced autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). ASPP2 expression is associated with an autophagic response upon nutrient deprivation and downregulation of ASPP2 facilitates autophagic flux, whereas overexpression of ASPP2 blocks this starvation-induced autophagy in HCC cells. Mechanistically, ASPP2 inhibits autophagy through regulating BECN1 transcription and formation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3 (PIK3C3) complex. Firstly, ASPP2 inhibits p65/RelA-induced transcription of BECN1, directly by an ASPP2-p65/RelA-IκBα complex which inhibits phosphorylation of IκBα and the translocation of p65/RelA into the nucleus. Secondly, ASPP2 binds to BECN1, leading to decreased binding of PIK3C3 and UV radiation resistance-associated gene (UVRAG), and increased binding of Rubicon in PIK3C3 complex. Downregulation of ASPP2 enhances the pro-survival and chemoresistant property via autophagy in HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Decreased ASPP2 expression was associated with increased BECN1 and poor survival in HCC patients. Therefore, ASPP2 is a key regulator of BECN1-dependent autophagy, and decreased ASPP2 may contribute to tumor progression and chemoresistance via promoting autophagy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Autophagy is a lysosomal-dependent cellular degradation process, in which the cell self-digests its proteins and organelles and thus generates nutrients and energy to maintain essential cellular activities following nutrient starvation.1 Autophagy plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of diverse diseases, such as neuronal degeneration, aging, and cancer.2, 3, 4, 5, 6 There is increasing evidence demonstrating that autophagy is activated in cancer cells including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) under different stress conditions, such as starvation, growth factor deprivation, hypoxia, damaging stimuli, and therapeutic agents and such inducible autophagy constitutes an important pro-survival mechanism in response to cellular stresses.7, 8
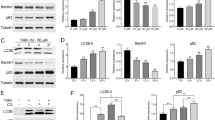
BECN1, an important autophagy-related gene, is the first identified mammalian gene to induce autophagy.9, 10 It is a 60 kD protein containing a Bcl-2 homology domain (BH3), a coiled–coiled domain (CCD) and an evolutionarily conserved domain (ECD).11, 12 It is commonly expressed at very low levels in breast, prostate, and ovarian cancers;9 however, the expression of BECN1 mRNA is significantly increased in liver tumor tissues and HCC cell lines despite that it is undetectable in normal liver tissues, indicating its important role in liver cancer survival.13 Mounting evidence indicates that one efficacious mechanism by which BECN1 promotes HCC cells survival is through autophagy induction.23 We found that overexpression of ASPP2 inhibited the expression of p65/RelA in the nucleus, whereas inhibition of ASPP2 expression enhanced p65/RelA entry into the nucleus (Figure 3e, right and Supplementary Figure 4C).
As ASPP2 is a known binding protein of p65/RelA,22 we tested its ability to repress the entry of p65/RelA into the nucleus by binding and inactivating p65/RelA. Double IF staining showed that endogenous p65/RelA co-localized with ASPP2 in the cytoplasm of HCC-LM3 cells (Supplementary Figure 4D). Exogenously expressed cytoplasmic ASPP2 also co-localized with p65/RelA, retaining more p65/RelA in the cytoplasm (Figure 3f, left). ASPP2 co-immunoprecipitated with p65/RelA, IκBα, and IκBβ in HCC-LM3 cells. The amount of p65/RelA and IkBα bound with ASPP2 was increased in ASPP2-overexpressed cells, and decreased in ASPP2-silenced cells (Figure 3f, right and Supplementary Figure 4E). These results indicate that ASPP2 binds to p65 and IκBα. Furthermore, the interaction between ASPP2 and IκBα inhibited phosphorylation of IκBα, inducing cytoplasmic accumulation of IκBα (Figure 3g). In contrast, downregulation of ASPP2 promotes phosphorylation of IκBα in HCC-LM3 cells under starvation environment (Supplementary Figure 4E). The amount of the IκBα bound with p65/RelA was visibly higher after overexpression of ASPP2 in HCC-LM3 cells (Figure 3h).
To confirm the intracellular effect of p65/RelA binding to BECN1 promoter, chromatin-immunoprecipitation was performed in HepG2 and Huh7 cells to monitor the recruitment of p65/RelA to the BECN1 promoter. Chromatin-immunoprecipitation analysis revealed that overexpression of ASPP2 in Huh7 cells resulted in less DNA of the BECN1 promoter co-immunoprecipated with p65/RelA. In contrast, downregulation of ASPP2 in HepG2 cells resulted in the recruitment of more p65/RelA on the BECN1 promoter (Figure 3i). These results indicate that ASPP2 negatively regulates the expression of BECN1 by abrogating p65/RelA-dependent transcription in HCC cells. We also detected the effect of p65/RelA in autophagy regulated by ASPP2. We found that overexpression of BECN1 or p65/RelA with ASPP2 in HCC-LM3 cells increased the conversion of LC3I to LC3II and the degradation of p62/SQSTEM1 compared with only overexpression ASPP2 (Supplementary Figure 4G). These results suggested that p65/RelA reversed ASPP2-impaired autophagy.
ASPP2 inhibits autophagy via interaction with BECN1
A proteomic analysis predicted that TP53BP2 (ASPP2) interacted with BECN1.24 As BECN1 is a key component of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3 (PIK3C3) complex, we asked whether the interaction between ASPP2 and BECN1 was involved in the regulation of this autophagy initiation complex.
In immunofluorescent staining, BECN1 co-localized with endogenous ASPP2 in part of the cells during starvation-induced autophagy (Figure 3a, upper). Endogenous ASPP2 was found to co-immunoprecipitate with endogenous BECN1 in HCC-LM3 during growth in EBSS medium, and the interaction was reduced when ASPP2 was downregulated (Figure 4a, lower). This interaction was further confirmed by ectopic expression of V5-tagged ASPP2 and flag-tagged BECN1 in HEK293T cells (Figure 4b).
ASPP2 colocalizes with BECN1 and co-immunoprecipitates with BECN1. (a) HCC-LM3 were treated with EBSS for 6 h. Location of endogenous ASPP2 and BECN1 was analyzed by double IF. Scale bars: 30 μm (upper). The ASPP2-BENC1 complex was immunoprecipitated with anti-ASPP2 and analyzed by western blotting (lower). (b) Flag-tagged BECN1 was co-transfected with ASPP2-V5 into HEK293T cells, which were analyzed by western blotting following IP with anti-Flag antibody (upper). V5-tagged ASPP2 was co-transfected with Flag-BECN1 into HEK293T cells, which were analyzed by western blotting following IP with anti-V5 antibody (lower). (c) Schematic representation of truncated ASPP2 mutants (upper). V5-tagged full-length and deletion mutants of ASPP2 were co-transfected with Flag-BECN1 into HEK293T. V5 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate full-length and fragments of ASPP2 (*, V5-tagged protein). (d) Flag-BECN1 and V5-tagged ASPP2 fragments were co-transfected into HCC-LM3 cells for 48 h, followed by 6 h EBSS treatment. Anti-V5 (red) and anti-flag (green) antibodies were used to analyze location of proteins by double IF staining. Scale bars: 30 μm. (e) Schematic representation of truncated BECN1 mutants (upper). Flag-tagged full-length and deletion mutants of BECN1 were co-transfected with ASPP2-V5(1-360) into HEK293T. Flag antibody was used to immunoprecipitate full-length and fragments of BECN1 (*, Flag-tagged protein). (f) ASPP2 fragments were transfected into HCC-LM3 cells for 48 h, followed by 6 h EBSS treatment. Endogenous the PIK3C3 complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-BECN1 antibody and analyzed for co-immunoprecipitation of BECN1-PIK3C3 conjugates (IP). Twenty-four hours after transfection, HEK293T cells were treated with EBSS for 6 h in (b), (c), and (e). In all IP analyses, host species-matched nonspecific IgG served as negative controls, and whole-cell lysates (input) are included for comparison
To identify the interaction domains between ASPP2 and BECN1, three ASPP2 mutants were used: ASPP2(1-360), ASPP2(360-925), and ASPP2(925-1128). Each V5-tagged ASPP2 mutants was tested for binding with flag-tagged BECN1 in HEK293T cells. ASPP2(1-360), but not ASPP2(360-925) and ASPP2(925-1128) was able to co-immunoprecipitate with BECN1 (Figure 4c). Similar result was observed in HCC-LM3 cells by immunofluorescent staining using transfected flag-tagged BECN1 and V5-tagged ASPP2 fragments (Figure 4d). These data suggested that N-terminal ASPP2 binds BECN1. We also used a series of flag-tagged BECN1 deletion mutants (BECN1[1–150], BECN1[150–241], and BECN1[243–450]) and examined their interaction with V5-tagged ASPP2(1-360). The middle domain of BECN1 (aa, 150–241, CCD domain), not the N terminus and C terminus, was required for interaction with ASPP2 (Figure 4e). These results suggested that the interaction between ASPP2 and BECN1 might influence the function of BECN1 CCD domain.
Formation of the PIK3C3 complex plays an essential role in autophagy.11 We next examined the role of ASPP2 in forming the PIK3C3 complex and the ability of ASPP2 to regulate PIK3C3 kinase activity. We observed that the BECN1–PIK3C3 interaction was increased in HCC-LM3 and HepG2 cells with downregulated ASPP2 during starvation-induced autophagy (Figure 5a). Moreover, only ASPP2(1-360), the domain of ASPP2 binding to BECN1, could inhibit interaction between BECN1 and PIK3C3 (Figure 4f). We also examined the effects of downregulated ASPP2 on the interaction between BECN1 and its binding partners, BCL2, Rubicon, PIK3C3, UV radiation resistance-associated gene (UVRAG), and ATG14 in HCC-LM3 and HepG2 cells. Rubicon, which are negative regulator of PIK3C3 kinase activity, were decreased by co-immunoprecipitation in ASPP2-silencing cells, but not BCL2. As the promoters of PIK3C3 kinase activity, only UVRAG bound with BECN1 was increased in ASPP2-silenced cells. ATG14 did not change obviously (Figure 5a). UVRAG and ATG14 could bind to the BECN1 CCD domain, which also binds to ASPP2 from our above results (Figure 4e). Thus, we tested whether ASPP2 could disrupt BECN1 interaction with UVRAG rather than ATG14 by co-immunoprecipiation with BECN1. As expected, overexpression of ASPP2 induced less level of UVRAG, but not ATG14, bound to BECN1 (Figure 5b). These results were confirmed in HCC-LM3 and Huh7 cells with overexpression of ASPP2 (Figure 5c). All of these indicated that binding of ASPP2 to BECN1 suppresses formation of the PIK3C3 complex by disrupting the interaction between BECN1 and UVRAG.
Downregulation of ASPP2 increases the BECN1 interactome and BECN1-associated PIK3C3 kinase activity in HCC cells. (a) HCC-LM3 and HepG2 infected with LV-shNon or LV-shASPP2, followed by 6 h EBSS treatment, were lysed for immunoprecipitation with BECN1-specific antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies as indicated. (b) HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-BECN1, HA-UVRAG, HA-ATG14, and ASPP2-V5 or Flag-BECN1, HA-UVRAG, HA-ATG14, and V5-vector for 24 h, and then treated with EBSS for 6 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibody (BECN1) and analyzed by western blotting. (c) HCC-LM3 and Huh7 transfected with pcDNA3.1 or pASPP2, followed by 6 h EBSS treatment, were lysed for immunoprecipitation with BECN1-specific antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies as indicated. (d) HCC-LM3 cells infected with LV-shNon or LV-shASPP2 for 72 h, or transfected with vector or pASPP2 for 48 h, were treated with EBSS for 6 h. Then cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-BECN1 antibody. The PI3-Kinase activity ELISA kit was used to measure the kinase activity of the PIK3C3 protein immunoprecipitated. (e) At 24 h posttransfection with p40(phox)PX-EGFP fusion, HCC-LM3 with LV-shNon or LV-shASPP2 were detected using an inverted fluorescence microscope. Huh7 were detected after co-transfection with p40(phox)PX-EGFP fusion and pASPP2 vectors for 48 h. p40(phox)PX-EGFP-positive vesicles were quantified and analyzed. The scale bars represent 10 μm. Data are shown as the means±S.D. from triplicate experiments. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01)
The BECN1–PIK3C3 interaction is associated with increased PIK3C3 kinase activity. Overexpression of ASPP2 decreased PIK3C3 kinase activity, and silencing of ASPP2 increased it (Figure 5d). The analysis of foci formation of p40(phox)PX-EGFP fusion protein demonstrated that downregulation of ASPP2 significantly increased PIK3C3 lipid kinase activity in HCC-LM3 cells (Figure 5e). Conversely, overexpression of ASPP2 in Huh7 decreased the levels of BECN1–PIK3C3 interaction and inhibited the lipid kinase activity of PIK3C3 during autophagy (Figure 5e). All these results suggest that binding of ASPP2 to BECN1 can suppress or destabilize the interaction of the BECN1, PIK3C3, and UVRAG core complex, contributing to the decreased PIK3C3 kinase activity.
Autophagy enhanced by downregulation of ASPP2 contributes to survival and chemoresistance of HCC
To further investigate the role of ASPP2 in tumor development through regulating autophagy, we analyzed cell proliferation and survival during nutrition deprivation. The anchorage-independent cell growth of HepG2 and HCC-LM3 were significantly enhanced by ASPP2 silencing, and the colony foci greater than 200 μm were found in ASPP2 silencing groups (Figure 6a). These changes by knockdown of ASPP2 can be compromised by 3-MA, indicating that the ASPP2 downregulation increases the development of HCC by facilitating starvation-induced autophagy. The results of plate-colony assay showed the same tendency (Figure 6b). It has been reported that autophagy activation elicited by starvation serves as a pro-survival mechanism. Then, apoptosis was investigated in ASPP2-silenced cells. Knockdown of ASPP2 attenuated starvation-induced apoptosis in HepG2 and HCC-LM3, and 3-MA can compromise these effects (Figure 6c).
Autophagy enhanced by downregulation of ASPP2 contributes to survival and chemoresistance of HCC cells. (a) HCC-LM3 and HepG2 cells infected with LV-shNon or LV-shASPP2 were treated with EBSS for 6 h with or without 3-MA pretreated 1 h, and then plated in semisolid soft agar medium to monitor anchorage-independent growth. (b) The cells handled as above were plated in dishes for colony assay. (c) HCC-LM3 and HepG2 cells infected with LV-shNon or LV-shASPP2 were pretreated with 10 mM 3-MA or not for 1 h followed by culture in EBSS for 24 h. The percentage of apoptotic cells was measured by Annexin V-FITC/PI (propidium iodide) double staining. The early apoptotic cells (Annexin V+/PI-) were quantified. (d) The infected HCC cells pretreated with 3-MA for 1 h were seeded in 96-well plates with 5-FU (7.5 μg/ml) or VP16 (30 μg/ml) for MTS assay at 48 and 72 h. Values were given as the means±S.D. of six wells. (e) The cells handled as (d) for 24 h were analyzed by Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining for apoptosis. The early apoptotic cells (Annexin V+/PI-) were quantified. (f) The cells handled as (e) were analyzed by western blotting for conversion of LC3I to LC3II. Data are shown as the means±S.D. from triplicate experiments. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01)
Current evidence supports the idea that tumor resistance to anticancer therapies including chemotherapy can be enhanced through upregulation of autophagy in various tumor cell lines.25 MTS (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt) assay showed that knockdown of ASPP2 increased tumor cell viability under the treatment of fluorouracil (5-FU) or etoposide (VP16), whereas inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA could block the autophagy-induced chemoresistance (Figure 6d). Meanwhile, increased percentage of apoptotic cells in ASPP2-silenced cell with 5-FU or VP16 with 3-MA treatment, compared with only 5-FU or VP16-treated cells (Figure 6e). After downregulation of ASPP2, the conversion of LC3I to LC3II induced by chemotherapeutic agent were increased in HCC-LM3 cells (Figure 6f).
To further confirm the autophagy-dependent promotion of tumor growth and chemoresistant effect of ASPP2 downregulation, luciferase-expressing HCC-LM3-luc cells infected with LV-shASPP2 or LV-shNon were injected into the flank of nude mice, which were treated with or without CQ and 5-FU. Thirty days after xenografting, downregulation of ASPP2 significantly enhanced the growth of HCC-LM3 cells in nude mice, though 5-FU decreased the rate of tumor growth partly. However, CQ can delay tumor growth in the ASPP2 silenced and control group, especially combined with 5-FU (Figure 7a and b). Consistent with the in vitro experimental results, fewer apoptotic cells were found in HCC-LM3 xenografts with ASPP2 silencing, and CQ overcame this chemoresistance, resulting in activation of apoptosis (Figure 7c and d). All these data demonstrate that silencing of ASPP2 can enhance the ability of resistance to chemotherapeutic agent through autophagy activation in HCC.
(a–e) Inhibition of autophagy blocked chemoresistance of HCC xenografts induced by downregulation of ASPP2 in nude mice. (a) Whole-body bioluminescent images of HCC-LM3-luc tumor xenograft mice were determined by the Xenogen IVIS 100 imaging System. (b) Quantitate fluorescence intensities of tumors from in vivo images at at indicated time points. The fluorescence intensity of the mice was measured by recording CCD photon counts. (c) TUNEL analysis was performed in tumor sections derived from the mice as in (a) at day 30 after cell inoculation. The apoptotic nuclei are seen as dark brown color under a microscope. Cell nuclei were counter stained with methyl green. Representative images of ASPP2 immunostaining in xenograft tumors (left). Scale bars represent 40 μm. (d) The percentage of apoptotic cells was calculated by counting brown-stained nuclei versus green-stained nuclei from five randomly chosen fields in each section. Data are present as means±S.D. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01) (e–f) ASPP2 and BECN1 expression in human HCC tissues. (e) Representative images of ASPP2 and BECN1 expression in HCC tissues examined by immunohistochemistry. Scale bars represent 100 μm. The statistical correlation between ASPP2 and BECN1 expression are shown on lower panel. (f) Kaplan–Meier analysis of survival in patients with HCC. Kaplan–Meier survival curves for patients with HCC according to levels of ASPP2 and BECN1 expression were shown in upper (RFS) and lower (OS). (g) Diagram summarizing the role of ASPP2 in regulating BECN1-dependant autophagic activity. CQ, chloroquine
Expression of ASPP2 correlates negatively with BECN1 in surgical specimens of HCC
To assess the clinical relevance of ASPP2 and BECN1, we further examined ASPP2 and BECN1 protein expression in 186 HCC tissues by immunohistochemistry (Figure 7e). There was no significant correlation between ASPP2 expression and age, gender, alpha-fetoprotein level, and tumor size. A total of 59.8% (73/122) of the tumor samples in which ASPP2 had high expression, showed low expression of BECN1, whereas high expression of BECN1 was found in about 67.2% (43/64) of tumor samples in which ASPP2 was low expression. The correlation between ASPP2 and BECN1 expression was inversely associated (P<0.001; Figure 7e). The results further supported our conclusion that ASPP2 negatively regulated BECN1 expression in HCC.
The correlation in clinic pathologic parameters in all HCC patients was statistically analyzed (Supplementary Table S1). A significant correlation between the BECN1 expression and tumor volume was observed (P=0.002). Importantly, in the ASPP2 low group, a significant correlation between the presence of BECN1 and advanced tumor volume was observed (P=0.008). In contrast, this correlation was not statistically significant in the ASPP2 high group (P=0.166; Supplementary Table S2). No significant correlation was found between BECN1 expression and other variables, including age, sex, tumor stage, or recurrence time. The potential association between ASPP2 or BECN1 expression level and recurrence-free survival (RFS) or overall survival (OS) was retrospectively evaluated. Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that RFS and OS (Figure 7f) were significantly worse among patients in ASPP2low/BECN1high group.
In univariate analysis, ASPP2 and BECN1 expression status were prognositic factors for RFS and OS (Supplementary Table S3). The tumor number was significantly associated with OS and AJCC stage with RFS. ASPP2 and BECN1 were prognostic for RFS (P<0.001) and OS (P<0.001, Supplementary Table S3). In multivariate analysis, tumor number, ASPP2, and BECN1 expression status remained the significant independent predictors of RFS and OS. Patients with high expression of BECN1 were about 1.669 times more likely to suffer from relapse than ones with low expression of BECN1 (hazard ratio: 1.669; 95% confidence interval: 1.090–2.555). Patients with high expression of ASPP2 were about 0.623 times less to suffer from relapse than ones with low expression of ASPP2 (hazard ratio: 0.623; 95% confidence interval: 0.405–0.960). AJCC stage was the independent predictor only for RFS (Supplementary Table S4). Thus, increased expression of BECN1 with decreased ASPP2 may serve as a prognostic indicator for patients with HCC.
Discussion
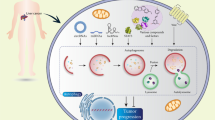
Autophagy plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of diverse disease, such as neuronal degeneration, aging, and cancer.26 Here we demonstrate that downregulation of ASPP2 promotes the development of HCC by enhancing starvation-induced autophagy via regulating regulating BECN1 transcription and formation of PIK3C3 complex (Figure 7g).
In our study, the trends of BECN1 change are the most consistent in ASPP2-silencing and ASPP2-overexpression HCC cells. Although ATG5/7 are almost influenced by ASPP2 in HepG2 and Huh7, the change levels of ATG5/7 are not significant in HCC-LM3 cells with ASPP2 overexpression (Supplementary Figure 3). Meanwhile, there is no report about the correlation between ASPP2 and BECN1 in autophagy. Therefore, we focused on the regulation of ASPP2 on BECN1 in this study.
In mechanism, we found that ASPP2 can bind p65/RelA, preventing p65/RelA activating BECN1 transcription. Recently, ASPP2 was found to inhibit ΔNp63 expression through its ability to bind IκBβ and enhance nuclear p65/RelA, which mediates the repression of p63 in squamous cell carcinoma cells.27 In this study, however, we showed that overexpression of ASPP2 did not increase IκBβ bound with ASPP2 in HCC cells during starvation-induced autophagy (Figure 3f), suggesting the level of IκBβ expression might be limited and not the key regulator of p65/RelA in HCC cells or under nutrient-deprived environment. Instead of IκBβ, we found that ASPP2 interacted with p65/RelA and IκBα, maintaining the p65/RelA-IκBα complex and suppressing phosphorylation of IκBα, which can trigger itself degradation and release p65/RelA.23
Second, two stable PIK3C3 complexes have been described in both yeast and mammals are implicated in autophagosome formation.11 Complex II (containing UVRAG) follows the stage of complex I (containing ATG14) regulation. In complex II, UVRAG bridges BECN1 and PIK3C3 complex.28 Our data show that ASPP2 disrupts the association of complex II rather than the formation of complex I. Interestingly, downregulation of ASPP2 inhibits combination of BECN1 and rubicon, which is a suppressor of the PIK3C3 complex. Rubicon binds only to a subpopulation of UVRAG complexes.29 These data further proved that ASPP2 specifically regulates the function of complex II during autophagosome formation. Recently, ASPP2 was reported to induce autophagic apoptosis by decreasing BCL2 expression and maintaining nuclear ASPP2-BCL2 complexes.30 It focused on the role of nuclear ASPP2 on autophagy. However, our study focuses on the function of ASPP2 in cytoplasm on autophagy. Moreover, ASPP2 binds BECN1 at its CCD domain, which is not associated with BCL2. Therefore, the function of cytoplasmic ASPP2 on autophagy might be different from the one of nuclear ASPP2.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
HepG2 and HEK293T cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). HCC-LM3 was obtained from the Liver Cancer Institute, Zhong Shan Hospital, Fudan University (Shanghai, People's Republic of China). Huh7 was obtained from Cell Bank of Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, People's Republic of China). A polyclonal population of HCC-LM3 stably expressing the Luc reporter gene was generated by transfection with pcDNA-Luc plasmid and a Geneticin (G418) selection. All these cell lines were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% (vol/vol) FBS (Gibco), 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) at 37 °C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2. For serum and amino acid starvation, cells were cultured in serum-free EBSS (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany, E2888), which we refer to as nutrient-free medium. 3-methyladenine (3-MA; 10 mM; Sigma-Aldrich, M9281), chloroquine (CQ; 30 μM; Sigma-Aldrich, C6628).
Plasmids, small interfering RNA, and lentivirus
pcDNA3.1-ASPP2 (full, (1–360), (360–925), (925–1128))-V5 was obtained from Dr **n Lu’s Lab at Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, Oxford, UK. pcDNA3.0-flag-BECN1 was obtained from Prof. Mujun Zhao’s Lab at Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai, People's Republic of China. pCMV-p65/RelA-flag was constructed by PCR and inserted into pCMV-C-Flag vector (Beyotime Biotech. D2632, Shanghai, People's Republic of China). Various truncated BECN1 promoters were generated by PCR and inserted into reporter vector pGL3.0-enhancer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). p40(phox)PX-EGFP, pFlag-BECN1 ((1–150), (150–241), (242–450)), pCI-neo-HA-hUVRAG and pCI-neo-HA-hATG14 were purchased from Addgene (Cambridge, MA, USA).
Small interfering RNAs targeting BECN1 (siBECN1) were generated by GenePharma (Shanghai, People's Republic of China) and were transfected with DharmaFECT4 (ThermoScientific, T-2004-02). Lentiviral plasmid vectors encoding short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) targeting ASPP2 or scramble shRNA were generated and designated as LV-shASPP2 and LV-shNon, respectively. Further details are available in the Supplementary Material.
Real-time PCR and western blotting
Isolation of total cellular RNA was carried out by using the NucleoSpin RNAII (MACHEREY-NAGEL, 740955), and first-strand cDNA was generated using the PrimeScript RT reagent kit (Takara, DRR037A). The cDNA sample was then measured by real-time PCR with an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System as recommended by the manufacturer.
Total cell lysate was prepared as described before.19 The primers and antibodies used in this study are listed in the Supplementary Table S5 and Supplementary Table S6. The nuclear extracts from cells were prepared using NE-PER Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Extraction Reagents Kit (Pierce, 78833).
Luciferase reporter assays
HCC (3 × 104) cells were plated in 48-well plates and transfected with pGL3.0-enhancer (Promega) and full or various truncated BECN1 promoter-luciferase constructs together with the pRL-TK in triplicate by X-tremeGENE HP DNA Transfection Reagent (Roche, 06366236001). We treated cells as indicated at 24 h after transfection, and then collected cells for performing the luciferase assays with the Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega). Luciferase activities were calculated as fold induction compared with that in pGL3.0-enhancer. All bar diagrams are shown as the means±S.D.
Animal studies
Six-week-old male athymic BALB/c nude mice were purchased from the Shanghai Experimental Animal Center of Chinese Academic of Sciences (Shanghai, People's Republic of China) and were maintained in specific pathogen-free conditions. Animal care and experimental protocols were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of Shanghai Medical Experimental Animal Care Commission. For in vivo treatment, HCC-LM3 cells (5 × 106) infected with LV-shNon and LV-shASPP2 (at a MOI of 50) were implanted subcutaneously into the flank of nude mice (six in each group, male BALB/c nu/nu). By day 7, tumors were well established in the mice with an average size of ~300 mm3. Mice were intraperitoneally given 5-FU (10 mg/kg body weight) daily for 5 days or chloroquine (45 mg/kg body weight) every 3 days for a total of six times. The mice were killed 30 days later, and the tumors and surrounding tissues were isolated for histopathology examination.
Patient samples and immunohistochemical staining
One hundred and eighty-six primary HCC samples were obtained from patients who had undergone curative hepatic resection at Guangxi Cancer Hospital (Nanning, Guangxi, People's Republic of China). The expression of ASPP2 and BECN1 were analyzed with immunohistochemistry assay. Evaluation of immunostaining was independently performed by two experienced pathologists. Details can be found in the Supplementary Material.
Statistic analysis
All statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS 16.0 for Windows software. The χ2 test was used to compare qualitative variables; quantitative variables were analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t-test and Wilcoxon rank sum test. Kaplan–Meier analysis was used to determine the survival data. Data were presented as the mean±S.E.M. All statistical tests were two-sided, and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Other Material and Methods are available in the Supplementary Material and Methods.
References
Mizushima N, Komatsu M . Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 2011; 147: 728–741.
Chen N, Karantza V . Autophagy as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2011; 11: 157–168.
Hensley K, Harris-White ME . Redox regulation of autophagy in healthy brain and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 2015; 84: 50–59.
Lapierre LR, Kumsta C, Sandri M, Ballabio A, Hansen M . Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of autophagy in aging. Autophagy 2015; 11: 867–880.
Kenific CM, Debnath J . Cellular and metabolic functions for autophagy in cancer cells. Trends Cell Biol 2015; 25: 37–45.
Jiang X, Overholtzer M, Thompson CB . Autophagy in cellular metabolism and cancer. J Clin Invest 2015; 125: 47–54.
Cui J, Gong Z, Shen HM . The role of autophagy in liver cancer: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1836: 15–26.
Dash S, Chava S, Chandra PK, Aydin Y, Balart LA, Wu T . Autophagy in hepatocellular carcinomas: from pathophysiology to therapeutic response. Hepat Med 2016; 8: 9–20.
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K, Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H et al. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 1999; 402: 672–676.
Yue Z, ** S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N . Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 15077–15082.
Wirawan E, Lippens S, Vanden Berghe T, Romagnoli A, Fimia GM, Piacentini M et al. Beclin1: a role in membrane dynamics and beyond. Autophagy 2012; 8: 6–17.
Toton E, Lisiak N, Sawicka P, Rybczynska M . Beclin-1 and its role as a target for anticancer therapy. J Physiol Pharmacol 2014; 65: 459–467.
Tang H, Da L, Mao Y, Li Y, Li D, Xu Z et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes cells to starvation-induced autophagy via up-regulation of beclin 1 expression. Hepatology 2009; 49: 60–71.
Song H, **a SL, Liao C, Li YL, Wang YF, Li TP et al. Genes encoding Pir51, Beclin 1, RbAp48 and aldolase b are up or down-regulated in human primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10: 509–513.
Kiyono K, Suzuki HI, Matsuyama H, Morishita Y, Komuro A, Kano MR et al. Autophagy is activated by TGF-beta and potentiates TGF-beta-mediated growth inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8844–8852.
Song J, Guo X, **e X, Zhao X, Li D, Deng W et al. Autophagy in hypoxia protects cancer cells against apoptosis induced by nutrient deprivation through a Beclin1-dependent way in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 2011; 112: 3406–3420.
Al-Shenawy HA . Expression of Beclin-1, an autophagy-related marker, in chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma and its relation with apoptotic markers. APMIS 2016; 124: 229–237.
Trigiante G, Lu X . ASPP [corrected] and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 217–226.
Zhao J, Wu G, Bu F, Lu B, Liang A, Cao L et al. Epigenetic silence of ankyrin-repeat-containing, SH3-domain-containing, and proline-rich-region- containing protein 1 (ASPP1) and ASPP2 genes promotes tumor growth in hepatitis B virus-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010; 51: 142–153.
Wang Y, Wang XD, Lapi E, Sullivan A, Jia W, He YW et al. Autophagic activity dictates the cellular response to oncogenic RAS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 13325–13330.
Copetti T, Bertoli C, Dalla E, Demarchi F, Schneider C . p65/RelA modulates BECN1 transcription and autophagy. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 2594–2608.
Yang JP, Hori M, Takahashi N, Kawabe T, Kato H, Okamoto T . NF-kappaB subunit p65 binds to 53BP2 and inhibits cell death induced by 53BP2. Oncogene 1999; 18: 5177–5186.
Chen LF, Greene WC . Sha** the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 392–401.
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP, Harper JW . Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature 2010; 466: 68–76.
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N, Zhang M et al. Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis 2013; 4: e838.
Chen N, Karantza V . Autophagy as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2014; 11: 157–168.
Tordella L, Koch S, Salter V, Pagotto A, Doondeea JB, Feller SM et al. ASPP2 suppresses squamous cell carcinoma via RelA/p65-mediated repression of p63. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 17969–17974.
Itakura E, Kishi C, Inoue K, Mizushima N . Beclin 1 forms two distinct phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes with mammalian Atg14 and UVRAG. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 5360–5372.
Matsunaga K, Saitoh T, Tabata K, Omori H, Satoh T, Kurotori N et al. Two Beclin 1-binding proteins, Atg14L and Rubicon, reciprocally regulate autophagy at different stages. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 385–396.
Liu K, Shi Y, Guo X, Wang S, Ouyang Y, Hao M et al. CHOP mediates ASPP2-induced autophagic apoptosis in hepatoma cells by releasing Beclin-1 from Bcl-2 and inducing nuclear translocation of Bcl-2. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1323.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by grants from Ministry of Science and Technology of China ‘973’ and ‘863’ programs (2010CB945603, 2011CB966202, 2014AA020704, 2014AA020704 and 2014AA021103), National Nature Science Foundation of China (81402424, 81030042, 81472719, 81402030, 81670573, 81472281), State Key Project for Infection Disease and New Drug Development, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering (14DZ2272300), Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (B905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by GM Fimia
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Disease website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Cell Death and Disease is an open-access journal published by Nature Publishing Group. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Wang, H., Liang, B. et al. Downregulation of ASPP2 improves hepatocellular carcinoma cells survival via promoting BECN1-dependent autophagy initiation. Cell Death Dis 7, e2512 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.407
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.407
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Targeting and regulation of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma: revisiting the molecular interactions and mechanisms for new therapy approaches
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
mRNA sequencing and CyTOF analysis revealed ASPP2 altered the response patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells to usnic acid
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2023)
-
Effects of Cadmium and/or Lead on Autophagy and Liver Injury in Rats
Biological Trace Element Research (2020)
-
ASPP2 inhibits tumor growth by repressing the mevalonate pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Downregulation of ASPP2 promotes gallbladder cancer metastasis and macrophage recruitment via aPKC-ι/GLI1 pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2018)