Abstract
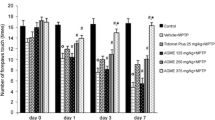
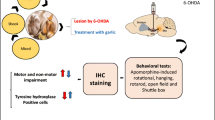
Parkinson’s disease (PD) results mostly from the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. It is characterized by the manifestations of anxiety, tremor, muscle rigidity, bradykinesia and cognitive impairments. Oxidative stress is attributed to the neurodegeneration of PD. Curcuma longa is a commonly used spice and has high levels of anti-oxidative phyto-constituents. Here, we evaluated whether the chronic oral administration of C. longa extract affects the degree of anxiety, neuromotor and cognitive deficits of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-infused PD model rats. Following the surgery, animals were orally administered with C. longa extract for twelve weeks. The degree of anxiety/depression, motor and cognitive performances were determined with a variety of neurobehavioral experimental paradigms, including elevated plus, Morris water maze task, rotarod, open field, forced swim, sucrose preference and tail suspension tests. Brain levels of lipid peroxide (LPO) were measured by standard method. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), α-synuclein, synaptosome-associated protein-25 (SNAP25) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) of the brain tissues were measured by ELISA. Oral administration of C. longa significantly (P < 0.05) protected the deterioration of the motor activity, learning-related memory cognitions and the degree of anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in PD model rats. The preventive effects were accompanied with decreased brain levels of LPO, TNFα, α-synuclein and increased levels of cognition-related proteins SNAP-25 and BDNF. The experimental results suggest that C. longa ameliorates PD-like symptoms by suppressing the oxidative/pro-inflammatory stress and levels of α-synuclein and increasing the levels of SNAP-25 and BDNF.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The experimental data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
References
Aarsland D, Marsh L, Schrag A (2009) Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24:2175–2186. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22589
Agid Y, Cervera P, Hirsch E et al (1989) Biochemistry of Parkinson’s disease 28 years later: a critical review. Mov Disord 4(Suppl 1):S126–S144. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870040514
Agrawal SS, Gullaiya S, Dubey V et al (2012) Neurodegenerative shielding by curcumin and its derivatives on brain lesions induced by 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease in albino Wistar Rats. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol 2012:942981. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/942981
Akter F, Haque M, Islam J et al (2015) Chronic administration of Curcuma longa extract improves spatial memory-related learning ability in aged rats by inhibiting brain Cortico-Hippocampal oxidative stress and TNFα. Adv Alzheimer’s Dis. https://doi.org/10.4236/aad.2015.43008
Annett LE, Torres EM, Ridley RM et al (1995) A comparison of the behavioural effects of embryonic nigral grafts in the caudate nucleus and in the putamen of marmosets with unilateral 6-OHDA lesions. Exp Brain Res 103:355–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241495
Barata-Antunes S, Teixeira FG, Mendes-Pinheiro B et al (2020) Impact of aging on the 6-OHDA-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103459
Barnett SA (1976) The rat: a study in behavior. Aggress Behav 2:164–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-2337(1976)2:2%3c164::AID-AB2480020210%3e3.0.CO;2-M
Benzie IFF, Wachtel-Galor S (2011) Herbal medicine: biomolecular and clinical aspects, 2nd edn. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Blum D, Torch S, Lambeng N et al (2001) Molecular pathways involved in the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP: contribution to the apoptotic theory in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 65:135–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00003-x
Buchanan T, Preston S (2014) Stress leads to prosocial action in immediate need situations. Front Behav Neurosci 8:5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00005
Buddhala C, Loftin SK, Kuley BM, et al (2015) Dopaminergic, serotonergic, and noradrenergic deficits in Parkinson disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2:949–959. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.246
Buttner-Ennever J (1997) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd edn. By George Paxinos and Charles Watson. (Pp. xxxiii+80; illustrated; f$69.95 paperback; ISBN 0 12 547623; comes with CD-ROM.) San Diego: Academic Press. 1996. J Anat 191:315–317. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-7580.1997.191203153.x
Campos FL, Carvalho MM, Cristovão AC et al (2013) Rodent models of Parkinson’s disease: beyond the motor symptomatology. Front Behav Neurosci 7:175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00175
Carvalho MM, Campos FL, Coimbra B et al (2013) Behavioral characterization of the 6-hydroxidopamine model of Parkinson’s disease and pharmacological rescuing of non-motor deficits. Mol Neurodegener. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-8-14
Castagné V, Moser P, Roux S, Porsolt RD (2011) Rodent models of depression: forced swim and tail suspension behavioral despair tests in rats and mice. Curr Protoc Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0810as55
Cerqueira JJ, Mailliet F, Almeida OFX et al (2007) The prefrontal cortex as a key target of the maladaptive response to stress. J Neurosci 27:2781–2787. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4372-06.2007
Chandra S, Chen X, Rizo J et al (2003) A broken alpha -helix in folded alpha -Synuclein. J Biol Chem 278:15313–15318. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M213128200
Chandra S, Khan S, Avula B et al (2014) Assessment of total phenolic and flavonoid content, antioxidant properties, and yield of aeroponically and conventionally grown leafy vegetables and fruit crops: a comparative study. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med 2014:253875. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/253875
Chen M, Du Z-Y, Zheng X et al (2018) Use of curcumin in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res 13:742–752. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.230303
Chung KK, Zhang Y, Lim KL et al (2001) Parkin ubiquitinates the alpha-synuclein-interacting protein, synphilin-1: implications for Lewy-body formation in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 7:1144–1150. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1001-1144
Cohen-Cory S, Kidane AH, Shirkey NJ, Marshak S (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the development of structural neuronal connectivity. Dev Neurobiol 70(5):271–288
Crofts HS, Dalley JW, Collins P et al (2001) Differential effects of 6-OHDA lesions of the frontal cortex and caudate nucleus on the ability to acquire an attentional set. Cereb Cortex 11:1015–1026. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/11.11.1015
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00568-3
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
Del Rey NL-G, Quiroga-Varela A, Garbayo E et al (2018) Advances in Parkinson’s disease: 200 years later. Front Neuroanat 12:113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00113
Deumens R, Blokland A, Prickaerts J (2002) Modeling Parkinson’s disease in rats: an evaluation of 6-OHDA lesions of the nigrostriatal pathway. Exp Neurol 175:303–317
Du X-X, Xu H-M, Jiang H et al (2012) Curcumin protects nigral dopaminergic neurons by iron-chelation in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Bull 28:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-012-1238-2
Dunnett SB, Björklund A (1999) Prospects for new restorative and neuroprotective treatments in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 399:A32–A39
Emamzadeh FN, Surguchov A (2018) Parkinson’s disease: biomarkers, treatment, and risk factors. Front Neurosci 12:612. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00612
Fischer R, Maier O (2015) Interrelation of oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease: role of TNF. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:610813. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/610813
Giri RK, Rajagopal V, Kalra VK (2004) Curcumin, the active constituent of turmeric, inhibits amyloid peptide-induced cytochemokine gene expression and CCR5-mediated chemotaxis of THP-1 monocytes by modulating early growth response-1 transcription factor. J Neurochem 91:1199–1210. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02800.x
Gradowski RW, Santiago RM, Zaminelli T, Bassani TB (2013) Antidepressant-like effect of curcumin in 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Trends Neurol 7:69–80
Gupta SC, Kismali G, Aggarwal BB (2013) Curcumin, a component of turmeric: from farm to pharmacy. BioFactors 39:2–13
Hall C, Ballachey EL (1932) A study of the rat’s behavior in a field. A contribution to method in comparative psychology. Univ Calif Publ Psychol 6:1–12
Halliday GM, Blumbergs PC, Cotton RG et al (1990) Loss of brainstem serotonin- and substance P-containing neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 510:104–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(90)90733-r
Halliday G, Lees A, Stern M (2011) Milestones in Parkinson’s disease–clinical and pathologic features. Mov Disord 26:1015–1021. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23669
Handley SL, Mithani S (1984) Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists in a maze-exploration model of ’fear’-motivated behaviour. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00504983
Hauser DN, Hastings TG (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease and monogenic parkinsonism. Neurobiol Dis 51:35–42
Henderson JM, Watson S, Halliday GM et al (2003) Relationships between various behavioural abnormalities and nigrostriatal dopamine depletion in the unilateral 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. Behav Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00087-6
Hong SL, Lee GS, Syed Abdul Rahman SN et al (2014) Essential oil content of the rhizome of curcuma purpurascens Bl. (Temu Tis) and its antiproliferative effect on selected human carcinoma cell lines. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/397430
Hornykiewicz O, Kish SJ (1987) Biochemical pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 45:19–34
Hornykiewicz O, Kish SJ (1987). Biochemical pathophysiol of Parkinson’s disease. In Parkinson’s Disease, Yahr M, KJ Bergmann, eds. (New York: Raven Press), pp. 19–34.
Hossain S, Rahaman A, Nahar T et al (2012) Syzygium cumini (L.) skeels seed extract ameliorates in vitro and in vivo oxidative potentials of the brain cerebral cortex of alcohol-treated rats: Syzygium cumini (L.) skeels seed extract inhibits oxidative potentials of brain. Orient Pharm Exp Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0044-0
Hossain S, Bhowmick S, Islam S et al (2015) Oral administration of ganoderma lucidum to lead-exposed rats protects erythrocytes against hemolysis: implicates to anti-anemia. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/463703
Hossain S, Bhowmick S, Jahan S et al (2016) Maternal lead exposure decreases the levels of brain development and cognition-related proteins with concomitant upsurges of oxidative stress, inflammatory response and apoptosis in the offspring rats. Neurotoxicology 56:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2016.07.013
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181
Hwang O (2013) Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 22:11–17. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2013.22.1.11
Jellinger KA (2012) Neuropathology of sporadic Parkinson’s disease: evaluation and changes of concepts. Mov Disord 27:8–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23795
Jonsson G (1980) Chemical neurotoxins as denervation tools in neurobiology. Annu Rev Neurosci 3:169–187. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001125
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Haass C (2000) Physiology and pathophysiology of alpha-synuclein. Cell culture and transgenic animal models based on a Parkinson’s disease-associated protein. Ann NY Acad Sci 920:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06902.x
Kaur G, Behl T, Bungau S et al (2021) Dysregulation of the gut-brain axis, dysbiosis and influence of numerous factors on gut microbiota associated Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 19:233–247. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200606233050
Lanska DJ (2009) The history of movement disorders. In: Finger S, Boller F, Tyler KL (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 501–546
Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ (2006) Mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease linked to pathological α-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron 52:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.026
Lee S-Y, Cho S-S, Li Y et al (2020) Anti-inflammatory effect of curcuma longa and Allium Hookeri co-treatment via NF-κB and COX-2 pathways. Sci Rep 10:5718. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62749-7
Leite-Almeida H, Almeida-Torres L, Mesquita AR et al (2009) The impact of age on emotional and cognitive behaviours triggered by experimental neuropathy in rats. Pain 144:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2009.02.024
Lim GP, Chu T, Yang F et al (2001) The curry spice curcumin reduces oxidative damage and amyloid pathology in an alzheimer transgenic mouse. J Neurosci 21:8370–8377. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08370.2001
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05292
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(96)89160-4
Lu B (2003) BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn Memory 10(2):86–98
Luthman J, Fredriksson A, Sundström E et al (1989) Selective lesion of central dopamine or noradrenaline neuron systems in the neonatal rat: motor behavior and monoamine alterations at adult stage. Behav Brain Res 33:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-4328(89)80121-4
Ma KH, Huang WS, Chen CH, Lin SZ, Wey SP, Ting G, Liu JC (2002) Dual SPECT of dopamine system using [99mTc] TRODAT-1 and [123I] IBZM in normal and 6-OHDA-lesioned formosan rock monkeys. Nucl Med Biol 29:561–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8051(02)00303-7
Mahul-Mellier A-L, Burtscher J, Maharjan N et al (2020) The process of Lewy body formation, rather than simply α-synuclein fibrillization, is one of the major drivers of neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117:4971–4982. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913904117
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I et al (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287:1265–1269. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5456.1265
Mishra A, Krishnamurthy S (2019) Rebamipide mitigates impairments in mitochondrial function and bioenergetics with α-Synuclein pathology in 6-OHDA-induced Hemiparkinson’s model in rats. Neurotox Res 35:542–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9983-2
Mishra S, Palanivelu K (2008) The effect of curcumin (turmeric) on Alzheimer’s disease: an overview. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 11:13–19. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-2327.40220
Mogi M, Togari A, Tanaka K et al (1999) Increase in level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned striatum in rats without influence of systemic L-DOPA on the TNF-alpha induction. Neurosci Lett 268:101–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00388-2
Monville C, Torres EM, Dunnett SB (2006) Comparison of incremental and accelerating protocols of the rotarod test for the assessment of motor deficits in the 6-OHDA model. J Neurosci Methods 158:219–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.06.001
Nass R, Przedborski S (2008) Parkinson’s disease: molecular and therapeutic insights from model systems. Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam; Boston
Nelson KM, Dahlin JL, Bisson J et al (2017) The essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin. J Med Chem 60:1620–1637. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Patt S, Gerhard L (1993) A Golgi study of human locus coeruleus in normal brains and in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 19:519–523. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00480.x
Pêgo JM, Morgado P, Pinto LG et al (2008) Dissociation of the morphological correlates of stress-induced anxiety and fear. Eur J Neurosci 27:1503–1516. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06112.x
Perez RG, Waymire JC, Lin E et al (2002) A role for α-synuclein in the regulation of dopamine biosynthesis. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-08-03090.2002
Perlbarg V, Lambert J, Butler B et al (2018) Alterations of the nigrostriatal pathway in a 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease evaluated with multimodal MRI. PLoS ONE 13:e0202597. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202597
Phuyal N, Jha PK, Raturi PP, Rajbhandary S (2020) Total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activities of fruit, seed, and bark extracts of Zanthoxylum armatum DC. Sci World J 2020:8780704. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8780704
Pohl F, Lin PKT (2018) The potential use of plant natural products and plant extracts with antioxidant properties for the prevention/treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: in vitro, in vivo and clinical trials. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123283
Potashkin JA, Blume SR, Runkle NK (2011) Limitations of animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s Disease, 2011(Special), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/658083
Potter PE (2013) Curcumin: a natural substance with potential efficacy in Alzheimer’s disease. J Exp Pharmacol 5:23–31. https://doi.org/10.2147/JEP.S26803
Prasad S, Gupta SC, Tyagi AK, Aggarwal BB (2014) Curcumin, a component of golden spice: from bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol Adv 32(6):1053–1064
Przedborski S, Levivier M, Jiang H et al (1995) Dose-dependent lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway induced by intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Neuroscience 67:631–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(95)00066-r
Roeling TA, Docter GJ, Voorn P et al (1995) Effects of unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions on neuropeptide immunoreactivity in the basal ganglia of the common marmoset, Callithrix jacchus, a quantitative immunohistochemical analysis. J Chem Neuroanat 9:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-0618(95)00072-0
Saidi NE, Nsibi A, Mani S et al (2020) Unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat as relevant model to study the pain related to Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.31487/j.NNB.2019.04.03
Sánchez-Iglesias S, Rey P, Méndez-Alvarez E et al (2007) Time-course of brain oxidative damage caused by intrastriatal administration of 6-hydroxydopamine in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 32:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9232-6
Santiago RM, Barbiero J, Gradowski RW et al (2014) Induction of depressive-like behavior by intranigral 6-OHDA is directly correlated with deficits in striatal dopamine and hippocampal serotonin. Behav Brain Res 259:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.10.035
Simola N, Morelli M, Carta AR (2007) The 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. N Eurotox Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033565
Slinkard K, Singleton VL (1977) Total phenol analysis: automation and comparison with manual methods. Am J Enol Vitic 28(1):49–55
Sørensen JB, Matti U, Wei SH et al (2002) The SNARE protein SNAP-25 is linked to fast calcium triggering of exocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.251673298
Stefanis L (2012) α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009399
Sturman O, Germain P-L, Bohacek J (2018) Exploratory rearing: a context- and stress-sensitive behavior recorded in the open-field test. Stress 21:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1080/10253890.2018.1438405
Sumiyoshi E, Hashimoto M, Hossain S et al (2021) Anredera cordifolia extract enhances learning and memory in senescence-accelerated mouse-prone 8 (SAMP8) mice. Food Funct 12:3992–4004. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO03272G
Sveinbjornsdottir S (2016) The clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 139(Suppl):318–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13691
Teegarden S (2012) Behavioral phenoty** in rats and mice. Mather Methods 2:122
Thiele SL, Warre R, Nash JE (2012) Development of a unilaterally-lesioned 6-OHDA mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/3234
Thompson RD, Grant CV (1971) Automated preference testing apparatus for rating palatability of foods 1. J Exp Anal Behav 15:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1971.15-215
Totterdell S, Hanger D, Meredith GE (2004) The ultrastructural distribution of alpha-synuclein-like protein in normal mouse brain. Brain Res 1004:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2003.10.072
Vieira JCF, Bassani TB, Santiago RM et al (2019) Anxiety-like behavior induced by 6-OHDA animal model of Parkinson’s disease may be related to a dysregulation of neurotransmitter systems in brain areas related to anxiety. Behav Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111981
Wakabayashi K, Tanji K, Mori F, Takahashi H (2007) The Lewy body in Parkinson’s disease: molecules implicated in the formation and degradation of α-synuclein aggregates. Neuropathology 27(5):494–506
Wanneveich M, Moisan F, Jacqmin-Gadda H et al (2018) Projections of prevalence, lifetime risk, and life expectancy of Parkinson’s disease (2010–2030) in France. Mov Disord 33:1449–1455. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27447
Wolters EC (2009) Non-motor extranigral signs and symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15 Suppl 3: S6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70770-9
Ying M, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2008) Genetic models of Familial Parkinson’s disease. In: Nass R, Przedborski S (eds) Parkinson’s disease molecular and Therapeutic insights from model systems. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 225–236
Zeng XS, Geng WS, Jia JJ (2018) Neurotoxin-induced animal models of parkinson disease: pathogenic mechanism and assessment. ASN Neuro. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091418777438
Funding
This project was partially supported by Bangladesh Medical Research Council (BMRC) and Higher Education Quality Enhancement Program (HEQEP, CP-358) by World Bank.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All the rats in this study were cared for and sacrificed in accordance with procedures outlined by the Ethical Committee of Jahangirnagar University in its Guidelines for Animal Experimentation at Jahangirnagar University. Reference no. BBEC, JU/M 2021/8(3).
Conflict of interest
Sujan Bhowmick has no conflict of interest. Marzan Sarkar has no conflict of interest. Jakir Hussain has no conflict of interest. Mehedi Hassan has no conflict of interest. Mafroz Basunia has no conflict of interest. Taslima Nahar has no conflict of interest. Azizur Rahman has no conflict of interest. Borhan Uddin has no conflict of interest. Shahdat Hossain has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhowmick, S., Sarkar, M., Hussain, J. et al. Curcuma longa extract ameliorates motor and cognitive deficits of 6-hydroxydopamine-infused Parkinson’s disease model rats. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 22, 773–787 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-021-00606-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-021-00606-2