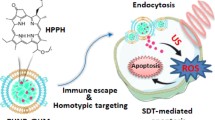
Abstract
The therapeutic efficiency of sonodynamic therapy (SDT) mainly depends on the presence of oxygen (O2) to generate harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS); thus, the hypoxic tumor microenvironment significantly limits the efficacy of SDT. Therefore, the development of oxygen-independent free radical generators and associated combination therapy tactics can be a promising field to facilitate the anticancer capability of SDT. In this study, a biomimetic drug delivery system (C-TiO2/AIPH@PM) composed of an alkyl-radical generator (2,2′-azobis[2-(2-imidazolin-2-yl)propane] dihydrochloride, AIPH)-loaded C-TiO2 hollow nanoshells (HNSs) as the inner cores, and a platelet membrane (PM) as the outer shells is successfully prepared for synergistic SDT and oxygen-independent alkyl-radical therapy. The PM encapsulation can significantly prolong the blood circulation time of C-TiO2/AIPH@PM compared with C-TiO2/AIPH while enabling C-TiO2/AIPH@PM to achieve tumor targeting. C-TiO2/AIPH@PM can efficiently produce ROS and alkyl radicals, which can achieve a more thorough tumor eradication regardless of the normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Furthermore, the generation of these radicals improves the efficiency of SDT. In addition, nitrogen (N2) produced due to the decomposition of AIPH enhances the acoustic cavitation effect and lowers the cavitation threshold, thereby enhancing the penetration of C-TiO2/AIPH@PM at the tumor sites. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrate that C-TiO2/AIPH@PM possesses good biosafety, ultrasound imaging performance, and excellent anticancer efficacy. This study provides a new strategy to achieve oxygen-independent free radical production and enhance therapeutic efficacy by combining SDT and free radical therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meng, X. Q.; Li, D. D.; Chen, L.; He, H.; Wang, Q.; Hong, C. Y.; He, J. Y.; Gao, X. F.; Yang, Y. L.; Jiang, B. et al. High-performance self-cascade pyrite nanozymes for apoptosis-ferroptosis synergistic tumor therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5735–5751.
Yan, J. Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y. D.; Zhu, W. W.; Li, L.; He, B. Mitochondria-targeted tetrahedral DNA nanostructures for doxorubicin delivery and enhancement of apoptosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 492–503.
Yan, J. Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Zhu, W. W.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Pu, Y. J.; He, B. Redox-responsive polyethyleneimine/tetrahedron DNA/doxorubicin nanocomplexes for deep cell/tissue penetration to overcome multidrug resistance. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 36–49.
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Q.; Yang, H. C.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y. J.; Sharma, A.; Yin, P.; Li, X. Y.; Kim, J. S.; Sun, Y. Advanced biotechnology-assisted precise sonodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11227–11248.
Wang, H.; Guo, J. X.; Lin, W.; Fu, Z.; Ji, X. R.; Yu, B.; Lu, M.; Cui, W. G.; Deng, L. F.; Engle, J. W. et al. Open-shell nanosensitizers for glutathione responsive cancer sonodynamic therapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110283.
Zhu, D. M.; Chen, H.; Huang, C. Y.; Li, G. X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Fan, K. L. H2O2 self-producing single-atom nanozyme hydrogels as light-controlled oxidative stress amplifier for enhanced synergistic therapy by transforming “cold” tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2110268.
Fan, Q.; He, Z. M.; **ong, J. X.; Chao, J. Smart drug delivery systems based on DNA nanotechnology. ChemPlusChem 2022, 87, e202100548.
Wang, X. W.; Zhong, X. Y.; Li, J. X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Inorganic nanomaterials with rapid clearance for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8669–8742.
Zhang, R. F.; Chen, L.; Liang, Q.; **, J. Q.; Zhao, H. Q.; **, Y. L.; Gao, X. F.; Yan, X. Y.; Gao, L. Z.; Fan, K. L. Unveiling the active sites on ferrihydrite with apparent catalase-like activity for potentiating radiotherapy. Nano Today 2021, 41, 101317.
Tang, G. H.; He, J. Y.; Liu, J. W.; Yan, X. Y.; Fan, K. L. Nanozyme for tumor therapy: Surface modification matters. Exploration 2021, 1, 75–89.
Yang, N. L.; Gong, F.; Cheng, L.; Lei, H. L.; Li, W.; Sun, Z. B.; Ni, C. F.; Wang, Z. H.; Liu, Z. Biodegradable magnesium alloy with eddy thermal effect for effective and accurate magnetic hyperthermia ablation of tumors. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa122.
Xu, S. Y.; Shi, X. X.; Ren, E.; Zhang, J. Z.; Gao, X.; Mu, D.; Liu, C.; Liu, G. Genetically engineered nanohyaluronidase vesicles: A smart sonotheranostic platform for enhancing cargo penetration of solid tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112989.
Ju, Y. Y.; Shi, X. X.; Xu, S. Y.; Ma, X. H.; Wei, R. J.; Hou, H.; Chu, C. C.; Sun, D.; Liu, G.; Tan, Y. Z. Atomically precise water-soluble graphene quantum dot for cancer sonodynamic therapy. Adv. Sci., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202105034.
Wang, M. F.; Hou, Z. Y.; Liu, S. N.; Liang, S.; Ding, B. B.; Zhao, Y. J.; Chang, M. Y.; Han, G.; Al Kheraif, A. A.; Lin, J. A multifunctional nanovaccine based on l-arginine-loaded black mesoporous titania: Ultrasound-triggered synergistic cancer sonodynamic therapy/gas therapy/immunotherapy with remarkably enhanced efficacy. Small 2021, 17, 2005728.
Zhu, D. M.; Ling, R. Y.; Chen, H.; Lyu, M.; Qian, H. S.; Wu, K. L.; Li, G. X.; Wang, X. W. Biomimetic copper single-atom nanozyme system for self-enhanced nanocatalytic tumor therapy. Nano Res., in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4359-6.
Zhu, D. M.; Zhang, T. F.; Li, Y.; Huang, C. Y.; Suo, M.; **a, L. G.; Xu, Y. H.; Li, G. X.; Tang, B. Z. Tumor-derived exosomes codelivering aggregation-induced emission luminogens and proton pump inhibitors for tumor glutamine starvation therapy and enhanced type-I photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121462.
Fan, K. L.; **, J. Q.; Fan, L.; Wang, P. X.; Zhu, C. H.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X. D.; Liang, M. M.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X. Y. et al. In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1440.
Pan, X. T.; Wang, W. W.; Huang, Z. J.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, F. R.; Yuan, H. J.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Y.; Liu, H. Y. MOF-derived double-layer hollow nanoparticles with oxygen generation ability for multimodal imaging-guided sonodynamic therapy. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 13659–13663.
Pan, X. T.; Bai, L. X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, B. L.; Shi, X. H.; Liu, H. Y. Metal-organic-framework-derived carbon nanostructure augmented sonodynamic cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800180.
Wang, W. W.; Pan, X. T.; Yang, H. L.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q. Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Xu, B. L.; Wang, J. H.; Shi, X. H.; Bai, F. et al. Bioactive metal-organic frameworks with specific metal-nitrogen (M-N) active sites for efficient sonodynamic tumor therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20003–20012.
Zhu, J. Y.; Ouyang, A.; Shen, Z. L.; Pan, Z. H.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, Q. L.; Chen, Y. T.; Zhang, P. Y. Sonodynamic cancer therapy by novel iridium-gold nanoassemblies. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 1907–1912.
Zhang, H. Y.; Pan, X. T.; Wu, Q. Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. H.; Liu, H. Y. Manganese carbonate nanoparticles-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction for enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Exploration 2021, 1, 20210010.
Yue, W. W.; Chen, L.; Yu, L. D.; Zhou, B. G.; Yin, H. H.; Ren, W. W.; Liu, C.; Guo, L. H.; Zhang, Y. F.; Sun, L. P. et al. Checkpoint blockade and nanosonosensitizer-augmented noninvasive sonodynamic therapy combination reduces tumour growth and metastases in mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2025.
Guan, X.; Yin, H. H.; Xu, X. H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B. G.; Yue, W. W.; Liu, C.; Sun, L. P.; Xu, H. X. et al. Tumor metabolism-engineered composite nanoplatforms potentiate sonodynamic therapy via resha** tumor microenvironment and facilitating electron-hole pairs’ separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000326.
Yin, Y. F.; Jiang, X. W.; Sun, L. P.; Li, H. Y.; Su, C. X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, X. L.; Zhao, C. K.; Chen, Y. et al. Continuous inertial cavitation evokes massive ROS for reinforcing sonodynamic therapy and immunogenic cell death against breast carcinoma. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101009.
Wang, X. W.; Wang, X. Y.; Yue, Q. F.; Xu, H. Z.; Zhong, X. Y.; Sun, L. N.; Li, G. Q.; Gong, Y. H.; Yang, N. L.; Wang, Z. H. et al. Liquid exfoliation of TiN nanodots as novel sonosensitizers for photothermal-enhanced sonodynamic therapy against cancer. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101170.
Sun, L. N.; Cao, Y.; Lu, Z. Z.; Ding, P.; Wang, Z. L.; Ma, F. S.; Wang, Z.; Pei, R. J. A hypoxia-irrelevant Fe-doped multivalent manganese oxide sonosensitizer via a vacancy engineering strategy for enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Nano Today 2022, 43, 101434.
Wu, T. T.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z. H. Engineering macrophage exosome disguised biodegradable nanoplatform for enhanced sonodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110364.
Gong, C. C.; Zhao, J. M.; Meng, X. D.; Yang, Z.; Dong, H. F. Engineering Cu-CuFe2O4 nanoenzyme for hypoxia-relief and GSH-depletion enhanced chemodynamic/sonodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135083.
Yang, K. K.; Yue, L. D.; Yu, G. C.; Rao, L.; Tian, R.; Wei, J. W.; Yang, Z. Q.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X. J.; Xu, M. Z. et al. A hypoxia responsive nanoassembly for tumor specific oxygenation and enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 120822.
Zhu, P.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. L. Nanoenzyme-augmented cancer sonodynamic therapy by catalytic tumor oxygenation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3780–3795.
Guo, Q. L.; Dai, X. L.; Yin, M. Y.; Cheng, H. W.; Qian, H. S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, D. M.; Wang, X. W. Nanosensitizers for sonodynamic therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: Current progress and future perspectives. Military Med. Res. 2022, 9, 26.
Huang, D. Q.; Zhao, C.; Wen, B. J.; Fu, X.; Shang, L. R.; Kong, W. T.; Zhao, Y. J. Oxygen-carrying microfluidic microcapsules for enhancing chemo-sonodynamic therapy on patient-derived tumor organoid models. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134871.
Lin, X. H.; Qiu, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, X. F.; Huang, G. M.; Song, J. B.; Chen, X. Y.; Yang, H. H. Ultrasound activation of liposomes for enhanced ultrasound imaging and synergistic gas and sonodynamic cancer therapy. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 747–756.
Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J. L.; Zeng, Y. Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W. et al. Hypoxia-adapted sono-chemodynamic treatment of orthotopic pancreatic carcinoma using copper metal-organic frameworks loaded with an ultrasound-induced free radical initiator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 38114–38126.
Ye, J. M.; Fu, Q. R.; Liu, L. T.; Chen, L. L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. Q.; Li, Z.; Su, L. C.; Zhu, R.; Song, J. B. et al. Ultrasound-propelled Janus Au NR-mSiO2 nanomotor for NIR-II photoacoustic imaging guided sonodynamic-gas therapy of large tumors. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 2218–2229.
Zhang, C.; **n, L.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, J. L.; Zeng, Y. Q.; Li, Q. Y.; Zhang, Y. et al. Metal-organic framework (MOF)-based ultrasound-responsive dual-sonosensitizer nanoplatform for hypoxic cancer therapy. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2022, 11, 2101946.
Shen, S.; Zhu, C. L.; Huo, D.; Yang, M. X.; Xue, J. J.; **a, Y. N. A hybrid nanomaterial for the controlled generation of free radicals and oxidative destruction of hypoxic cancer cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8801–8804.
Huang, G. M.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, F. F.; **e, J. G.; Chen, X.; Wang, L. L.; Yang, H. H. Magnetothermally triggered free-radical generation for deep-seated tumor treatment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2926–2931.
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ji, Y. S.; Fan, L. Y.; Ding, B. B.; Lin, J.; Wang, L. L. Mitochondrial targeted melanin@mSiO2 yolk-shell nanostructures for NIR- II -driven photo-thermal-dynamic/immunotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134869.
Li, Y. C.; Yu, H. L.; Ren, J. J.; Lu, G. J.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z. G.; Kang, Y. J.; Xue, P. Acidic TME-responsive nano-Bi2Se3@MnCaP as a NIR-II-triggered free radical generator for hypoxia-irrelevant phototherapy with high specificity and immunogenicity. Small 2022, 18, 2104302.
Cao, Y.; Wu, T. T.; Dai, W. H.; Dong, H. F.; Zhang, X. J. TiO2 nanosheets with the Au nanocrystal-decorated edge for mitochondria-targeting enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 9105–9114.
Liang, S.; Deng, X. R.; Xu, G. Y.; **ao, X.; Wang, M. F.; Guo, X. S.; Ma, P. A.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J. A novel Pt-TiO2 heterostructure with oxygen-deficient layer as bilaterally enhanced sonosensitizer for synergistic chemo-sonodynamic cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908598.
Wang, X. W.; Wang, X. Y.; Zhong, X. Y.; Li, G. Q.; Yang, Z. J.; Gong, Y. H.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. V-TiO2 nanospindles with regulating tumor microenvironment performance for enhanced sonodynamic cancer therapy. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 041411.
Wang, X. W.; Zhong, X. Y.; Cheng, L. Titanium-based nanomaterials for cancer theranostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 430, 213662.
Geng, B. J.; Xu, S.; Li, P.; Li, X. K.; Fang, F. L.; Pan, D. Y.; Shen, L. X. Platinum crosslinked carbon dot@TiO2−x p–n junctions for relapse-free sonodynamic tumor eradication via high-yield ROS and GSH depletion. Small 2022, 18, 2103528.
Han, X. X.; Huang, J.; **g, X. X.; Yang, D. Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z. G.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. Oxygen-deficient black titania for synergistic/enhanced sonodynamic and photoinduced cancer therapy at near infrared-II biowindow. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4545–4555.
Wang, X. W.; Zhong, X. Y.; Bai, L. X.; Xu, J.; Gong, F.; Dong, Z. L.; Yang, Z. J.; Zeng, Z. J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Ultrafine titanium monoxide (TiO1+x) nanorods for enhanced sonodynamic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6527–6537.
Jiang, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X. Y.; Ouyang, B. S.; Liu, H. X.; Pang, Z. Q.; Yang, W. L. Platelet membrane-camouflaged magnetic nanoparticles for ferroptosis-enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Small 2020, 16, 2001704.
Li, B. Z.; Chu, T. J.; Wei, J. Y.; Zhang, Y. L.; Qi, F. L.; Lu, Z. F.; Gao, C.; Zhang, T. J.; Jiang, E. S.; Xu, J. C. et al. Platelet-membrane-coated nanoparticles enable vascular disrupting agent combining anti-angiogenic drug for improved tumor vessel impairment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2588–2595.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research fund of Anhui Institute of Translation Medicine (No. 2021zhyx-C49), the Foundation of Anhui Medical University (No. 2021xkj030), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 2208085QC81), the Basic and Clinical Cooperative Research and Promotion Program of Anhui Medical University (No. 2021xkjT028), and Grants for Scientific Research of BSKY from Anhui Medical University (No. 1406012201). The authors would like to thank the shiyanjia lab (https://www.shiyanjia.com) for the XPS test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Wang, T., Huang, C. et al. Platelet membrane-coated C-TiO2 hollow nanospheres for combined sonodynamic and alkyl-radical cancer therapy. Nano Res. 16, 782–791 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4646-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4646-2