Abstract
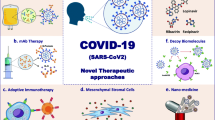
Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has attracted much attention around the world due to its rapid transmission among humans and relatively high mortality rate. Studies are increasing to find the best therapeutic approach for the disease and its management. Regenerative medicine offers various cell-tissue therapeutics and related products, such as stem cell therapy, natural killer (NK) cell therapy, Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, exosomes, and tissue products. Interestingly, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can reduce inflammatory symptoms and protect against cytokine storm, which critically contributes to the COVID-19 progression. Notably, having the potentials to exert cytotoxic effects on infected cells and induce interferon production probably make NK cells a candidate for COVID-19 cell therapy. Besides, exosomes are one of the crucial products of cells that can exert therapeutic effects through the induction of immune responses and neutralizing antibody titers. The paper aims to briefly consider current options for COVID-19 therapy to show that there is no specific cure for COVID-19, and then assess the real opportunities and range of promises regenerative medicine can provide for specific treatment of COVID-19.

Therapeutic Potential of Regenerative Medicine against COVID19.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Coronaviruses are enveloped non-segmented positive-sense RNA viruses belonging to the family Coronaviridae that can infect many hosts like humans and other mammals [
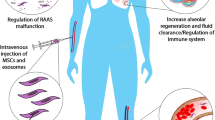
Regenerative medicine offers various cell-tissue therapeutics and related products. It deals with the use of cells themselves either as therapeutic agents or as a vehicle for other therapeutic agents such as cytokines. Of particular interest to the subject are mesenchymal stem cells that not only possess the potential for regenerative medicine but also have shown promising results in the modulation of inflammatory responses [7]. Besides, MSCs can secrete exosomes, extracellular membrane vesicles with size at the nanoscale [8]. Cell-derived exosomes serve as vectors of cell therapy acted on intercellular interactions by a range of macromolecules they can carry. Notably, exosomes have been of high importance to immune regulation and for this may become of use for cancer therapy [9, 10]. Natural killer (NK) cell therapy has also shown to produce a marked anti-tumor effect, and this effect is mostly attributed to the direct action of NK cells on the immune system [11]. In this manner, regenerative medicine and its immunoregulatory effects can be applied to the COVID-19, a viral infection associated with immune dysregulation [12].
The present study aims to briefly consider current options for COVID-19 therapy to show that there is no specific cure for COVID-19, and then assess the real opportunities and range of promises regenerative medicine can provide for specific treatment of COVID-19.
Current Evidence-Based Recommendations for COVID-19 Treatment
Plasma Therapy
The plasma of patients recovered from viral infections can be considered as an appropriate treatment option without serious adverse effects [13]. As mentioned earlier, the present century has witnessed two other pandemics caused by coronaviruses: SARS in 2002–2003 and the MERS in 2012. For both cases, convalescent plasma was a therapeutic option [14]. Although convalescent plasma therapy has not been used in the United States in decades due to the availability of better therapeutic solutions such as vaccines, it is than 100 years old. Researchers claimed that during the 1918 influenza epidemic in Spain, the transfer of survivors’ blood products, resulted in a 50% reduction in the mortality rate of critically ill patients [15]. An equivalent policy was also utilized to treat measles and polio decades ago. However, vaccine science and anti-viral drugs were developed, and plasma therapy was banned for these conditions in the 1950s [16]. The use of plasma therapy has been recommended during recent infectious outbreaks caused by Ebola [17] and H1N1 [18]. Notably, studies demonstrate that convalescent plasma is a successful therapy in reducing the mortality rate and shortening the period of hospitalization in patients with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV [19, 20].
FDA has already announced plasma therapy as a therapeutic option for patients with COVID-19 [21]. However, this method requires gathering plasma or serum from a sufficient number of people recovered from COVID-19. Therefore, plasma therapy can be considered as an option in the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19 until a superior treatment is found [14]. Plasma therapy by passive transfer of antibodies acts on the neutralization of the virus.
In the case of inaccessibility of preparing the plasma from recovered people, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and genetically engineered animal hosts producing human antibodies can be considered as alternative sources of antibody preparation for SARS-CoV-2 [22]. Monoclonal antibodies have exhibited their efficacy for the treatment of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV [23]. They, therefore, might possess the potential for the treatment of COVID-19. Noteworthy is the fact that the primary concept of passive antibody therapy is prevention and prophylaxis, while its therapeutic aspect stands on the second seat. The antibody transfer has the highest efficacy if will be administered at the early stage of the disease.
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy can be used to treat many diseases, especially viral infections such as Ebola, influenza A, and HIV-1. The elderly patients are more likely to develop severe COVID-19, and their ICU admission ratio is substantially higher than that for the younger patients. Patients admitted to the ICU have higher amounts of cytokines such as IL-6, G-CSF, IP10, MCP-1, MIP1A, and TNF-α [13] and such a cytokine storm can lead to severe organ damage and death. Corticosteroids are commonly used among critically ill patients. These drugs cannot specifically target the aforementioned inflammatory cytokines, but result in a general inhibitory effect over the immune system. The use of corticosteroids may, therefore, be associated with unwanted side effects in COVID-19 [24]. Current evidence highlights the role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 pneumonia. Consistently, patients with COVID-19, especially those who have high IL-6 levels, have shown clinical improvement following treatment with Tocilizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-6 pathway [25].
Small Molecule Drug-Based Therapies
Although the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV2, has recently been identified, the similarity of this virus with SARS-CoV in the genetic content might help the development of therapies of the novel coronavirus using previous treatments. Also, both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2 utilize the same host cell surface receptor. Therefore, blocking strategies used to prevent SARS-CoV cell entry might be useful against SARS-CoV2 [23]. Drugs designated based on the viral genome offer another potential therapeutic approach [26]. A salient example of these types of drugs is siRNA, small molecule drugs that can inhibit the viral replication cycle, host cell enzyme, or viral entry mechanism. Although these drugs have shown anti-viral activity in vitro and in vivo, most of them have the challenge of suppressing the immune system, and therefore, they should be used with caution.
Immune Regulation Therapy and Interferon Utilizing
Immunotherapeutic approaches have been extensively used in the treatment of cancer [27, 28], autoimmune diseases [29, 30], and other immune system-related diseases [31, 32]. They can be adopted to ameliorate immune responses in COVID-19. By considering the success of interferons in viral infections, there are ongoing studies that investigate the efficacy ofinterferon-alpha-1b and alpha-2b for COVID-19 treatment [33, 34]. Also, studies demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 profoundly affects T cell function [33]. Patients with a severe form of the disease are most likely to possess a low number of lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils and a high number of leukocytes along with a high neutrophil-lymphocyte-ratio (NLR). Both helper T (Th) cell counts and suppressor T cell counts are decreased in COVID-19 patients, and Th cell counts are much lower in the severe group of patients. Also, we witness rising the number of naïve Th cells besides falling the number of memory Th cells in severe cases. This evidence remarks on the potential of T cell-based immunotherapies for COVID-19.
The Real Opportunities for Regenerative Medicine in COVID-19 Treatment
The primary regenerative cells in the lung are stem cells and progenitor cells that maintain the stable state and repair damage to the epithelial cells of the lung [35]. Stem cells offer a potential method to treat extremely virulent coronavirus. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown the capacity to suppress lung inflammatory responses in the animal model of the influenza virus [79]. Moreover, MucilAir™ is a low passage human airway epithelial cell model, which shows maximum similarity with physiological conditions [80]. Also, SCR-1 cells that express GFP have been utilized to study graded doses of drugs for anti-SARS drug screening [81]. These cell-based models have been valuable to drug discovery for coronaviruses. However, it seems that 3D models of the infected lung that previously described could better mimic the natural structure and function of lung structures, mainly when they are obtained from iPSCs. Overall, these models would pave the way into the drug screening process of coronaviruses.
Conclusion
The virus responsible for the ongoing pandemic of COVID-19 has shown to be a professional pathogen that can easily spread person-to-person no matter who and where [82]. While the number of deaths attributed to COVID-19 is approaching 400.000, no specific treatment exists for the disease, and the current treatment methods for COVID-19 are confined to the previous therapeutic techniques for similar viruses or last generations of coronaviruses, including SARS- and MERS-CoVs. Such a situation calls attention from various medical specialties and subspecialties [83,84,85].
COVID-19 can involve multiple systems, including the central nervous system, the gastrointestinal system, and the respiratory system, and this will depend on its profound effects on the immune system [86,87,88]. Regenerative medicine offers various cell-tissue therapeutics and related products that might help the reversal of COVID-19-related immune dysregulation. In particular, the promising features of MSCs, including their regenerative properties and ability to differentiate into diverse cell lineages, have generated considerable interest among researchers whose work has offered intriguing perspectives on cell-based therapies for various diseases. The immunomodulatory effects of MSCs, which may assist in inhibiting cytokine storm and lung inflammation, are of particular interest for COVID-19 therapy [89]. Besides, the potentials of NK cells to exert cytotoxic effects on infected cells and induce interferon production probably make NK cells a candidate for COVID-19 cell therapy. Cell-derived exosomes can be used as vectors for macromolecules, which can influence immune cells and signaling pathways, and therefore, become interesting for COVID-19 therapy. Finally, iPSCs can help the development of a personalized approach to COVID-19 therapy.