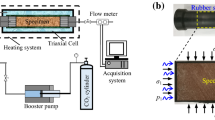
Abstract
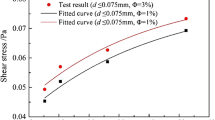
To investigate the influence of confining pressures and temperatures on the seepage characteristics of fractured rocks, seepage tests were conducted on a fractured silty mudstone using a self-developed experimental system, and the effects of different factors on coefficient of permeability were discussed. The results showed that the increasing confining pressure will gradually decrease the coefficient of permeability, and this process is divided into two stages: 1) the fast decrease stage, which corresponds to a confining pressure less than 30 kPa, and 2) the slow decrease stage, which corresponds to a confining pressure larger than 30 kPa. Unlike confining pressure, an increase in temperature will increase the coefficient of permeability. It is noted that fracture surface roughness will also affect the variation of coefficient of permeability to a certain extent. Among the three examined factors, the effect of confining pressure increases is dominant on fracture permeability coefficient. The relationship between the confining pressure and coefficient of permeability can be quantified by an exponential function.
摘要
为研究围压和温度对粉砂质泥岩裂隙渗流特性的影响,采用自行研发的裂隙渗流实验系统对裂 隙粉质泥岩进行渗流试验,探讨了不同因素对渗透系数的影响。结果表明:围压的增大会导致渗透系 数逐渐减小,该过程分为快速减小和缓慢减小两个阶段。其中,快速减小阶段对应的围压小于30 kPa; 缓慢降低阶段对应的稳压则大于30 kPa。温度对裂隙渗透系数的影响与围压不同,温度升高将导致渗 透系数增加。此外,裂隙面粗糙度也在一定程度上影响渗透系数的变化,但这种变化受到围压的影响 较大,当围压大于50 kPa 时,这种影响逐渐消失。可以看出,在以上三种因素中,围压的变化是影响 裂缝渗透系数改变的主要因素,且围压和裂隙渗透系数之间的关系可以通过指数函数来量化
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HUENGES E, KOHL T, KOLDITZ O, BREMER J, SCHECK-WENDEROTH M, VIENKEN T. Geothermal energy systems: research perspective for domestic energy provision [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 70(8): 3927–3933. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2881-2.
ZHANG J H, LI F, ZENG L, PENG J H, LI J. Numerical simulation of the moisture migration of unsaturated clay embankments in southern China considering stress state [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01916-6.
GAO Q F, JRAD M, HATTAB M, FLEUREAU J M. Pore morphology, porosity and pore size distribution in kaolinitic remoulded clays under triaxial loading [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 20(6): 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001682.
JAVADI M, SHARIFZADEH M, SHAHRIAR K, MITANI Y. Critical Reynolds number for nonlinear flow through rough-walled fractures: The role of shear processes [J]. Water Resources Research, 2014, 50(2): 1789–1804. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR014610.
ZHANG J, PENG J, ZENG L, LI J, LI F. Rapid estimation of resilient modulus of subgrade soils using performance-related soil properties [J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2019, 22(3): 1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2019.1643022.
ZENG L, XIAO L, ZHANG J, FU H Y. The role of nanotechnology in subgrade and pavement engineering: A review [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2020, 20(8): 4607–4618. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.18491.
REN D, SUN W, HUANG H, NAN J X, CHEN B. Determination of microscopic waterflooding characteristics and influence factors in ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoir [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(9): 2134–2144. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3622-6.
TSANG Y W, TSANG C F. Channel model of flow through fractured media [J]. Water Resources Research, 1987, 23(3): 467–479. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/WR023i003p00467.
NICHOLL M J, RAJARAM H, GLASS R J, DETWILER R L. Saturated flow in a single fracture: Evaluation of the Reynolds equation in measured aperture fields [J]. Water Resources Research, 1999, 35(11): 3361–3373. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/1999WR900241.
WANG L, CARDENAS M B, SLOTTKE D T, KETCHAM R A, SHARP J M. Modification of the local cubic law of fracture flow for weak, inertia, tortuosity and roughness [J]. Water Resources Research, 2015, 51(4): 2064–2080. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014WR015815.
GAO Q F, DONG H, HUANG R, LI Z F. Structural characteristics and hydraulic conductivity of an eluvial-colluvial gravelly soil [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(7): 5011–5028. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-01455-1.
ZHANG J, PENG J, LIU W, LU W H. Predicting resilient modulus of fine-grained subgrade soils considering relative compaction and matric suction [J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2019, 8: 1–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2019.1651756.
HUANG X, ZHANG R. Catastrophe stability analysis for shallow tunnels considering settlement [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(4): 949–960. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3796-6.
TZELEPIS V, MOUTSOPOULOS K N, PAPASPYROS J N E, ABDTSIHRINTZIS V A. Experimental investigation of flow behavior in smooth and rough artificial fractures [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 521: 108–118. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.054.
RAU G C, ANDERSEN M S, ACWORTH R I. Experimental investigation of the thermal dispersivity term and its significance in the heat transport equation for flow in sediments [J]. Water Resources Research, 2012, 48(3): 3454–3467. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011038.
SHARMEEN R, ILLMAN W A, BERG S J, YEH T J, PARK Y J, SUDICK E A, ANDO K. Transient hydraulic tomography in a fractured dolostone: Laboratory rock block experiments [J]. Water Resources Research, 2012, 48(10): 1075–1086. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2012WR012216.
QIAN J, ZHAN H, ZHAO W, SUN F G. Experimental study of turbulent unconfined groundwater flow in a single fracture [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 311(1–4): 134–142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.01.013.
LIU R, LI B, JIANG Y. Critical hydraulic gradient for nonlinear flow through rock fracture networks: The roles of aperture, surface roughness, and number of intersections [J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2016, 88: 53–65. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.12.002.
LIN H, DENG J G, LIU W, XU J, LIU H L. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation in weakly consolidated sandstone reservoirs [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(12): 2944–2952. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3964-8.
VITEL M, ROUABHI A, TIJANI M, GUERIN F. Modeling heat and mass transfer during ground freezing subjected to high seepage velocities [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2016, 73: 1–15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.11.014.
GUO Ai-guo, ZHAI **-yi. Correction of the influence of rubber film restraint in triaxial compression test [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2002(4): 442–445. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2002.04.012. (in Chinese)
XIONG Feng, SUN Wei, JIANG Qing-hui, YE Zu-yang, XUE Dao-rui, LIU Ru-yan. A low-speed nonlinear seepage model for rough rock fissures and its experimental verification [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(9): 3294–3302, 3312. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2623. (in Chinese)
CHENG W, LIU Z, YANG H, WANG W Y. Non-linear seepage characteristics and influential factors of water injection in gassy seams [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 91(2): 41–53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2017.10.002.
XIAO Y, DESAI C S, DAOUADJI A, STUEDLEIN A W, LIU H, ABUELNAGA, H. Grain crushing in geoscience materials-Key issues on crushing measure, testing and modelling: Review and preface[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(2): 363–374. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.11.006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51838001, 51878070, 51908073, 51908069) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019SK2171) supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Hunan Province, China; Project(kq1905043) supported by the Training Program for Excellent Young Innovators of Changsha, China; Project(2019IC04) supported by Double First-class Scientific Research International Cooperation Expansion Project of Changsha University of Science & Technology, China; Project(CX20200811) supported by Postgraduate Research and Innovation Key Project of Hunan Province, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Hy., Jiang, Hb., Qiu, X. et al. Seepage characteristics of a fractured silty mudstone under different confining pressures and temperatures. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 1907–1916 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4419-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4419-6