Abstract
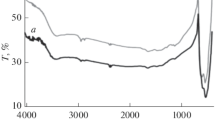
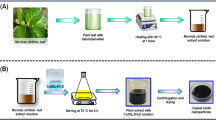
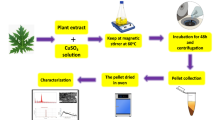
The current study was planned to synthesize copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) using aqueous Fumaria indica (F. indica) plant extract and was calcined at 100, 300, 600 and 900 °C using Muffle furnace. The X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that crystallinity and crystallite size increase (from 14.9 to 79.29 nm) with increasing calcination temperature. The microstructure was analyzed through scanning electron microscopy, while the constituent elements were identified through energy-dispersive X-ray. The diffuse reflectance spectroscopy analysis was carried out and the optical band gap was determined through Tauc plot, which was found to decrease (from 1.82 to 1.46 eV) with increasing calcination temperature. The surface functional moieties were identified by performing Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Agar well diffusion process was followed to screen CuO NPs against Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria, where higher activity was found against Gram-negative bacteria. The antioxidant activity of CuO NPs was evaluated during the neutralization ABTs free radical, thus it can be used to reduce the damaging effects of antioxidants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminuzzaman M, Kei LM, Liang WH (2017) Green synthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their photocatalytic activities. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol 1828. pp 020016. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4979387
Arts K, Nadu T (2018) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biological applications. Microbiol Curr Res 2:2–3
Choi H, Park SH (2004) seedless growth of free-standing copper nanowires by chemical vapor deposition. J Am Chem Soc 126(20):6248–6249
Dhas NA, Raj CP, Gedanken A (1998) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of metallic. Chem Mater 4756:1446–1452. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm9708269
Hafeez M, Arshad R, Khan J et al (2019) Populus ciliata mediated synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for potential biological applications. Mater Res Express 6:055043. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab0601
Hamadanian M, Reisi-Vanani A, Majedi A (2010) Synthesis, characterization and effect of calcination temperature on phase transformation and photocatalytic activity of Cu, S-codoped TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 256:1837–1844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.10.016
Haq S, Rehman W, Waseem M et al (2018a) Effect of heating on the structural and optical properties of TiO2 nanoparticles: antibacterial activity. Appl Nanosci 8:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0647-6
Haq S, Rehman W, Waseem M et al (2018b) Fabrication of pure and moxi fl oxacin functionalized silver oxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. J Photochem Photobiol B 186:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.07.011
Haq S, Ansar K, Wajid Y et al (2020a) Green synthesis of silver oxide nanostructures and investigation of their synergistic effect with moxifloxacin against selected microorganisms. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01763-8
Haq S, Rehman W, Waseem M et al (2020b) Green synthesis and characterization of tin dioxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic and antimicrobial studies. Mater Res Express 7:1–9
Haq S, Rehman W, Waseem M et al (2020c) Effect of annealing temperature on structural phase transformations and band gap reduction for photocatalytic activity of mesopores TiO2 nanocatalysts. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 31:1312–1322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01810-4
Hashemipour H, Zadeh ME, Pourakbari R, Rahimi P (2011) Investigation on synthesis and size control of copper nanoparticle via chemical reduction method. Int J Phys Sci 6:4331–4336. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJPS10.204
Imran Din M, Rani A (2016) Recent advances in the synthesis and stabilization of nickel and nickel oxide nanoparticles: a green adeptness. Int J Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3512145
Jain S, Mehata MS (2017) Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Sci Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15724-8
Johnson P, Krishnan V, Loganathan C et al (2018) Rapid biosynthesis of Bauhinia variegata flower extract-mediated silver nanoparticles: an effective antioxidant scavenger and α-amylase inhibitor. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:1488–1494. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1374283
Jushi SS, Mahumuni S (1999) Radiation induced synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles. Nanostruct Mater 10(7):1135-1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(98)00153-6
Khalifa ZS (2017) Grain size reduction on nanostructured TiO 2 thin fi lms due to annealing. RSC Adv 7:30295–30302. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00706j
Khoshnamvand M, Ashtiani S, Huo C et al (2019) Use of Alcea rosea leaf extract for biomimetic synthesis of gold nanoparticles with innate free radical scavenging and catalytic activities Use of Alcea rosea leaf extract for biomimetic synthesis of gold nanoparticles with innate free radical scavenging. J Mol Struct 1179:749–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.11.079
Naika HR, Lingaraju K, Manjunath K et al (2018) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. extract and their antibacterial activity Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. extract and their antibacterial activity. Integr Med Res 9:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2014.04.006
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Rostami-vartooni A, Hussin SM (2015) L . leaves and their catalytic performance for N -arylation of indoles and amines. JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.12.018
Nethravathi PC, Kumar MAP, Suresh D, Lingaraju K (2015) Materials science in semiconductor processing tinospora cordifolia mediated facile green synthesis of cupric oxide nanoparticles and their photocatalytic, antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Semicond Process 33:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.01.034
Ramasamy S, Selvam M (2015) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles from Hibicus rosasinensis and their antimicrobial, antioxidant activities. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 6:1183–1190
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS, Rahiman AK (2017a) Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.101
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS, Rahiman AK (2017b) Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.101
Sankar R, Manikandan P, Malarvizhi V, Fathima T (2014) Spectrochimica acta part A: molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy green synthesis of colloidal copper oxide nanoparticles using carica papaya and its application in photocatalytic dye degradation. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 121:746–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.12.020
Shakya A, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2012) Holistic psychopharmacology of fumaria indica (Fumitory) 2012:182–199
Shakya A, Chatterjee SS, Kumar V (2015) Role of fumarates in adaptogenics like efficacies of traditionally used Fumaria indica extracts. CELLMED. https://doi.org/10.5667/tang.2014.0028
Singh J, Dutta T, Kim KH et al (2018) “Green” synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J Nanobiotechnol 16:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0408-4
Sorbiun M, Shayegan E, Ali M (2018) Green synthesis of zinc oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of oak fruit hull (jaft) and comparing their photocatalytic degradation of basic violet 3. Int J Environ Res 12:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-018-0064-4
Surmawar NV, Thakare SR, Khaty NT (2011) One-pot, single step green synthesis of copper nanoparticles : SPR nanoparticles. Phys Chem 3(4):302–308. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/19430892.2011.633478
Taylor CJ, Gilmer DC, Colombo DG et al (1999) Does Chemistry really matter in the chemical vapor deposition of titanium dioxide ? precursor and kinetic effects on the microstructure of polycrystalline films. J Am Chem Soc 121:5220–5229
Zaidi A, Bukhari SM, Khan FA et al (2015) Ethnobotanical, phytochemical and pharmacological aspects of daphne mucronata (Thymeleaceae). Trop J Pharm Res 14:1517–1523. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v14i8.27
Zarei Z, Razmjoue D, Karimi J (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from caralluma tuberculata extract and its antibacterial activity. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01586-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamid, A., Haq, S., Ur Rehman, S. et al. Calcination temperature-driven antibacterial and antioxidant activities of fumaria indica mediated copper oxide nanoparticles: characterization. Chem. Pap. 75, 4189–4198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01650-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01650-7